Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (17): 4498-4507.doi: 10.12307/2026.136
Previous Articles Next Articles
Revealing the regulatory targets of plasma proteins in rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of genomics
Cheng Yuebin1, Wang Baojian2, Dai Wenkang2, Yin Yueshan2, Sun Zhiqiang1, Peng Zhiyun1, Shang Yuhang1, Ma Yufeng2
- 1Orthopedics of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100000, China; 2Department of Muscle Injury (Pain), The Third Affiliated Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100000, China
-
Received:2025-04-08Accepted:2025-07-30Online:2026-06-18Published:2025-12-03 -
Contact:马玉峰,博士,副主任医师,北京中医药大学第三附属医院筋伤(疼痛)科,北京市 100000 -
About author:程悦斌,男,1998年生,北京中医药大学在读硕士,主要从事中医骨伤科方向研究。 -
Supported by:Capital Health Development Research Special Project, No. 2020-2-7036 (to MYF); Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Key Research Project, No. 2020-JYB-ZDGG-142-3 (to MYF); “New Drug R&D Cultivation Project” of The Third Affiliated Hospital of Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. BZYSY-2022-XYYF-02 (to MYF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cheng Yuebin, Wang Baojian, Dai Wenkang, Yin Yueshan, Sun Zhiqiang, Peng Zhiyun, Shang Yuhang, Ma Yufeng. Revealing the regulatory targets of plasma proteins in rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of genomics[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4498-4507.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
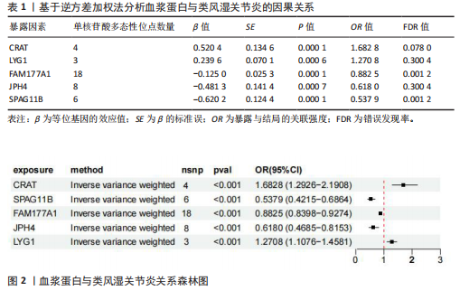
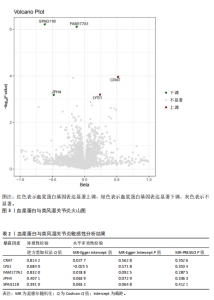
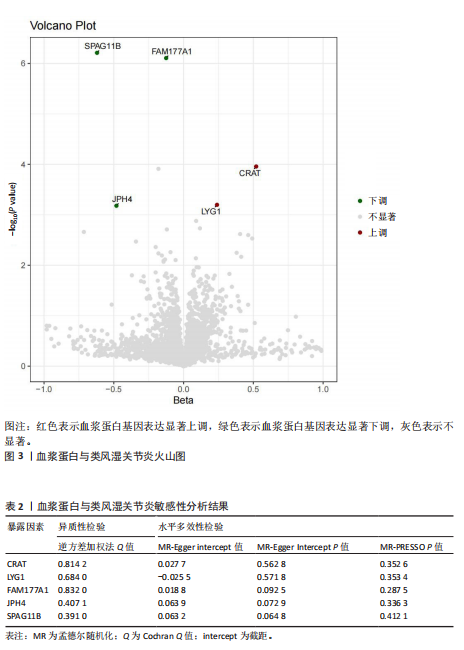
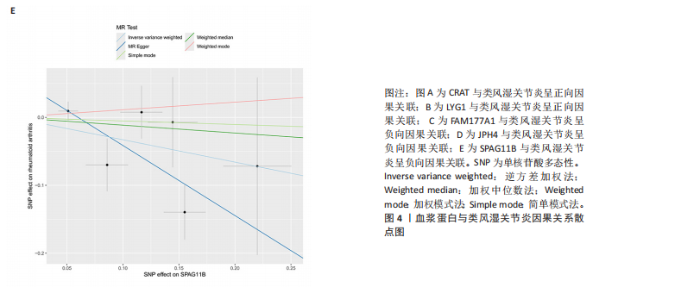
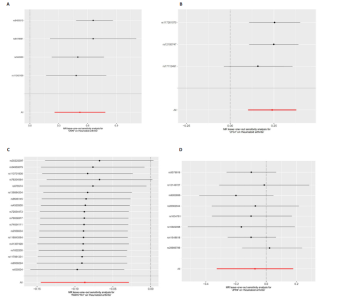
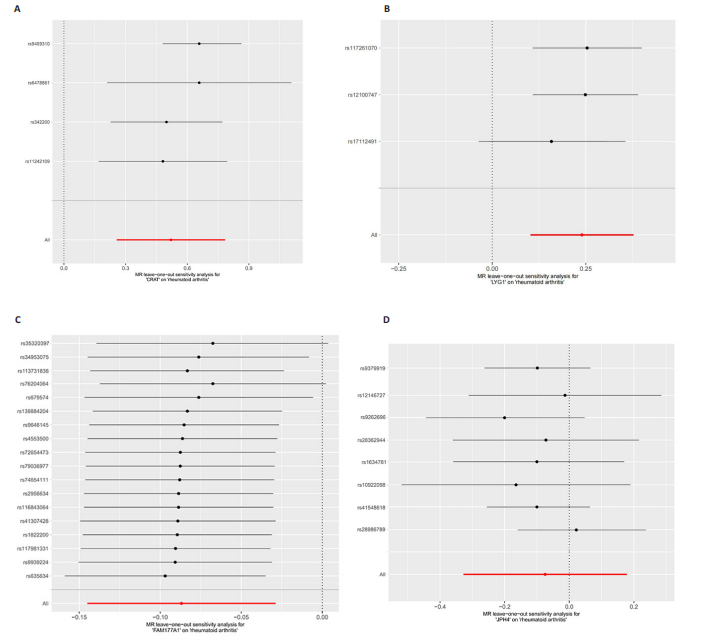
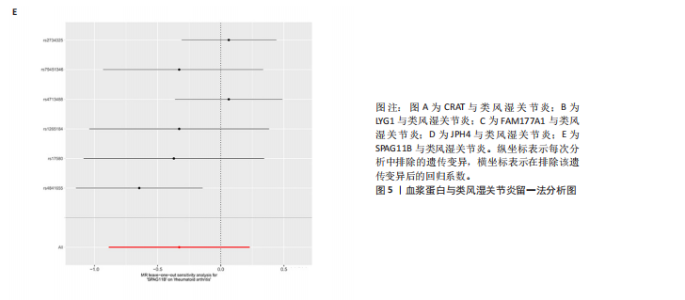
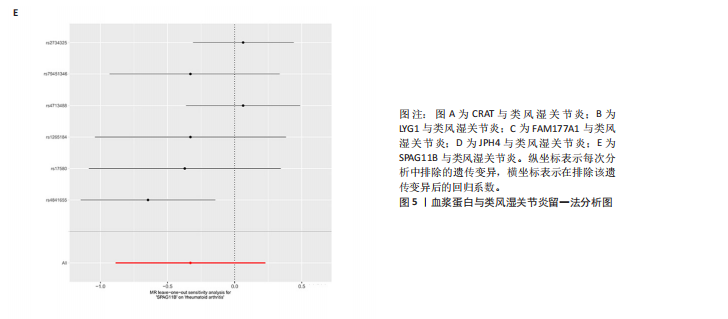
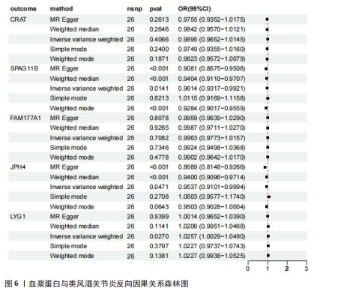
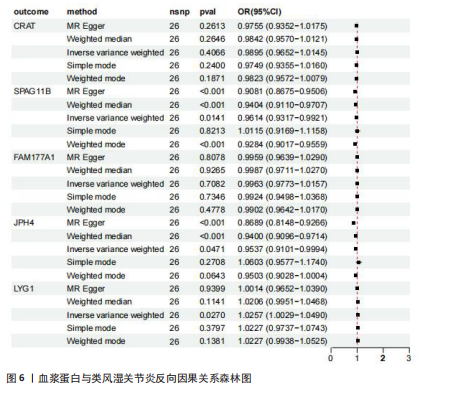
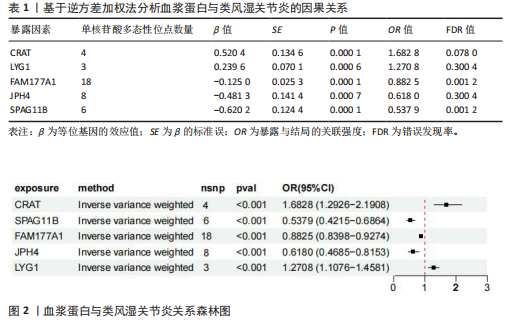
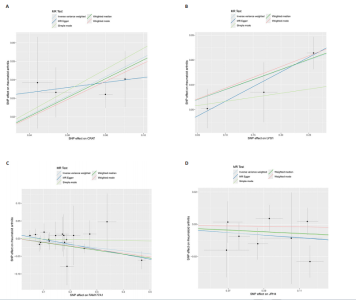
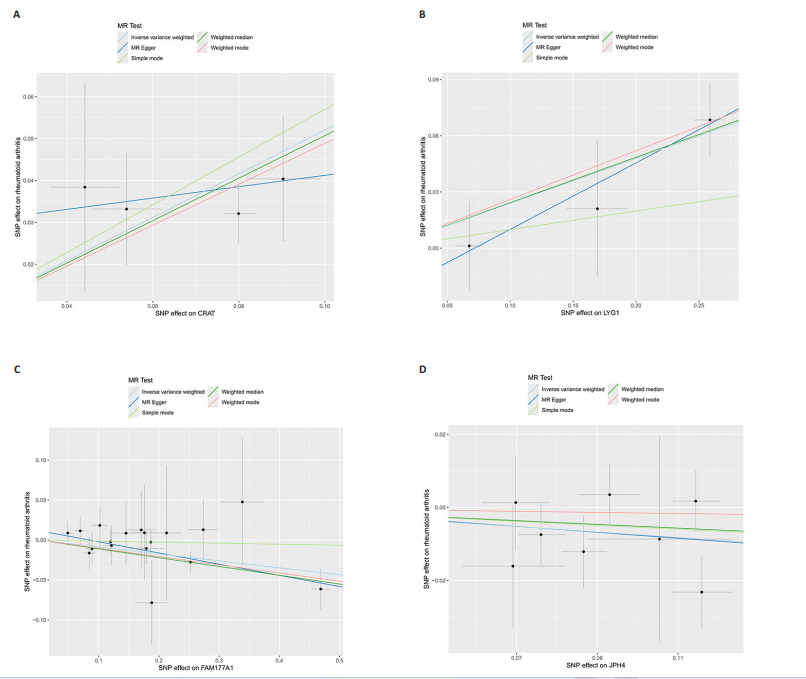
2.1 正向孟德尔随机化分析结果 基于工具变量的筛选标准,4 907种血浆蛋白共获得了34 913个单核苷酸多态性,所纳入单一单核苷酸多态性对应的 F统计量均> 10,故研究不易受到弱工具变量偏倚的影响。研究以逆方差加权法作为主要参考依据,以P < 0.05为标准,对4 907种血浆蛋白进行孟德尔随机化分析,见表1。研究得到5种血浆蛋白可能与类风湿关节炎有关,分别是CRAT、LYG1、SPAG11B、FAM177A1、JPH4,见图2,3。 逆方差加权法分析结果显示,CRAT(OR=1.682 8,95%CI:1.292 6-2.190 8,P=0.000 1)、LYG1(OR=1.270 8,95%CI:1.107 6-1.458 1,P=0.000 6)与类风湿关节炎呈正相关;FAM177A1 (OR=0.882 5,95%CI:0.839 8-0.927 4,P=0.000 1)、JPH4 (OR=0.618 0,95%CI:0.468 5-0.815 3,P=0.000 6)、SPAG11B(OR=0.537 9,95%CI:0.421 5-0.686 4,P=0.000 1)与类风湿关节炎呈负相关,见图4。 敏感性Q检验结果显示,所选的工具变量之间没有明显的异质性;MR-Egger分析结果显示,5种血浆蛋白单核苷酸多态性未表现出水平多效性,见表2。留一法结果未见明显离群值,见图5。 2.2 反向孟德尔随机化分析结果 为了探究类风湿关节炎是否影响这5种血浆蛋白的表达,揭示血浆蛋白与类风湿关节炎之间是否存在反向因果关系,以类风湿关节炎作为暴露因素,5种血浆蛋白(CRAT、LYG1、SPAG11B、FAM177A1、JPH4)作为结局,进行反向孟德尔随机化分析。逆方差加权法结果显示,SPAG11B (OR=0.961 4,95%CI:0.931 7-0.992 1,P=0.014 1),JPH4(OR=0.953 7,"
95%CI:0.910 1-0.999 4,P=0.047 1),LYG1 (OR=1.025 7,95%CI:1.002 9-1.049 0,P=0.002 7)与类风湿关节炎的关联具有统计学意义(P < 0.05),见图6。结果表明这些血浆蛋白的表达可能受到类风湿关节炎疾病进程的影响。敏感性 Q 检验结果显示,所选的工具变量之间没有明显的异质性。留一法结果未见明显离群值。然而SPAG11B和JPH4的MR-Egger分析结果显示类风湿关节炎的单核苷酸多态性具有水平多效性,提示类风湿关节炎可能通过其他生物学途径间接影响SPAG11B、JPH4的表达;LYG1的MR-Egger分析结果显示类风湿关节炎的单核苷酸多态性未表现出水平多效性,表明类风湿关节炎可能直接影响LYG1的表达水平。"
| [1] MUELLER AL, PAYANDEH Z, MOHAMMADKHANI N, et al. Recent Advances in Understanding the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis: New Treatment Strategies. Cells. 2021;10(11):3017. [2] 刘晨旭,郜娜.蛋白质组学在类风湿关节炎中发病机制及诊疗研究中的最新研究进展[J].中国现代医学杂志,2024, 34(7):49-54. [3] JIANG N, LI Q, LI H, et al. Chinese registry of rheumatoid arthritis (CREDIT) V: sex impacts rheumatoid arthritis in Chinese patients. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022;135(18):2210-2217. [4] BENNIKE TB. Advances in proteomics: characterization of the innate immune system after birth and during inflammation. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1254948. [5] 郑梓桐,王美娟,冯育林,等.基于蛋白质组学筛选关节炎相关生物标志物的研究进展[J].中草药,2024,55(18):6383-6392. [6] FIGUS FA, PIGA M, AZZOLIN I, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis: Extra-articular manifestations and comorbidities. Autoimmun Rev. 2021;20(4):102776. [7] LABORDE CM, CASTRO-SANTOS P, DÍAZ-PEÑA R. Contribution of Multiplex Immunoassays to Rheumatoid Arthritis Management: From Biomarker Discovery to Personalized Medicine. J Pers Med. 2020;10(4):202. [8] LOVEGROVE CE, HOWLES SA, FURNISS D, et al. Causal inference in health and disease: a review of the principles and applications of Mendelian randomization. J Bone Miner Res. 2024;39(11):1539-1552. [9] GBD 2021 Gout Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of gout, 1990-2020, and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2024;6(8):e507-e517. [10] CHIU PC, CHATTOPADHYAY A, WU MC, et al. Elucidation of a Causal Relationship Between Platelet Count and Hypertension: A Bi-Directional Mendelian Randomization Study. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8: 743075. [11] LI HB, WU LJ, JIANG N, et al. Treatment satisfaction with rheumatoid arthritis in patients with different disease severity and financial burden: A subgroup analysis of a nationwide survey in China. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020;133(8):892-898. [12] SANDERSON E, GLYMOUR MM, HOLMES MV, et al. Mendelian randomization. Nat Rev Methods Primers. 2022;2:6. [13] STUDENIC P, ALETAHA D, DEWIT M, et al. American College of Rheumatology/EULAR remission criteria for rheumatoid arthritis: 2022 revision. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023;82(1):74-80. [14] FERKINGSTAD E, SULEM P, ATLASON BA, et al. Large-scale integration of the plasma proteome with genetics and disease. Nat Genet. 2021;53(12):1712-1721. [15] SMOLEN JS, LANDEWÉ RBM, BERGSTRA SA, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2022 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023;82(1):3-18. [16] BHAK Y, TENESA A. Mendelian randomization study of whole blood viscosity and cardiovascular diseases. PLoS One. 2024;19(4):e0294095. [17] ÁLVARO-GRACIA ÁLVARO JM, DÍAZ DEL CAMPO FONTECHA P, ANDRÉU SÁNCHEZ JL, et al. Update of the Consensus Statement of the Spanish Society of Rheumatology on the use of biological and synthetic targeted therapies in rheumatoid arthritis. Reumatol Clin (Engl Ed). 2024;20(8):423-439. [18] 缪怡,胡朝英,钱柳,等.类风湿性关节炎免疫学研究进展[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版),2011,31(7):1035-1040. [19] BOERS M, HARTMAN L, OPRIS-BELINSKI D, et al. Low dose, add-on prednisolone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis aged 65+: the pragmatic randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled GLORIA trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022;81(7):925-936. [20] 林滢,沈楚楚,徐森磊,等.针灸治疗类风湿关节炎的研究进展[J].中国针灸, 2024,44(12):1479-1488. [21] ROODENRIJS NMT, KEDVES M, HAMAR A, et al. Diagnostic issues in difficult-to-treat rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic literature review informing the EULAR recommendations for the management of difficult-to-treat rheumatoid arthritis. RMD Open. 2021;7(1):e001511. [22] HU C, DAI Z, XU J, et al. Proteome Profiling Identifies Serum Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:865425. [23] WATANABE R, HASHIMOTO M, MURATA K, et al. Prevalence and predictive factors of difficult-to-treat rheumatoid arthritis: the KURAMA cohort. Immunol Med. 2022; 45(1):35-44. [24] ANDONIAN BJ, KOSS A, KOVES TR, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis T cell and muscle oxidative metabolism associate with exercise-induced changes in cardiorespiratory fitness. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):7450. [25] NAGY G, ROODENRIJS NMT, WELSING PMJ, et al. EULAR points to consider for the management of difficult-to-treat rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022; 81(1):20-33. [26] ZHU X, LONG W, ZHANG J, et al. Integrated multi-omics revealed that dysregulated lipid metabolism played an important role in RA patients with metabolic diseases. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024;26(1):188. [27] CONRAN C, KOLFENBACH J, KUHN K, et al. A Review of Difficult-to-Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis: Definition, Clinical Presentation, and Management. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2023;25(12):285-294. [28] ZHAO Z, REN J, XIE S, et al. Identification of biomarkers associated with CD8+ T cells in rheumatoid arthritis and their pan-cancer analysis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1044909. [29] VAN MULLIGEN E, WEEL AE, HAZES JM, et al. Tapering towards DMARD-free remission in established rheumatoid arthritis: 2-year results of the TARA trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(9):1174-1181. [30] SHARMA S, SUN X, AGARWAL S, et al. Role of carnitine acetyl transferase in regulation of nitric oxide signaling in pulmonary arterial endothelial cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2012; 14(1):255-272. [31] EULER N, HELLBACHER E, KLINT EA, et al. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma in rheumatoid arthritis patients is associated with elevated B-cell driving factors including CXCL13. Clin Immunol. 2025;275:110476. [32] TRAGNI V, PRIMIANO G, TUMMOLO A, et al. Personalized Medicine in Mitochondrial Health and Disease: Molecular Basis of Therapeutic Approaches Based on Nutritional Supplements and Their Analogs. Molecules. 2022;27(11):3494. [33] CHEN L, XU L, ZHANG Y, et al. Dioscin alleviates the dysfunction of fibroblast-like synoviocytes by circ_0008267/miR-942-5p/FKBP5 axis during rheumatoid arthritis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03872-y. [34] LEE SY, PARK JL, KIM K, et al. Identification of NIFTP-Specific mRNA Markers for Reliable Molecular Diagnosis of Thyroid Tumors. Endocr Pathol. 2023; 34(3):311-322. [35] LI Y, PRADEEP SINGH S. Computational Screening of IL-1 and IL-6 Inhibitors for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Insights from Molecular Docking and Dynamics Analysis. Curr Pharm Des. 2025. doi: 10.2174/0113816128344776250222043907. [36] LIU H, YU Z, TANG B, et al. LYG1 Deficiency Attenuates the Severity of Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease via Skewing Allogeneic T Cells Polarization Towards Treg Cells. Front Immunol. 2021;12:647894. [37] SUR D, PRAMANIK R. The TIM-3/Gal-9 Pathway: A Promising Therapeutic Target for Regulation of Immune Checkpoint in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2025. doi: 10.2174/0115733971330865250312075719. [38] GUIMARÃES ES, MARTINS JM, GOMES MTR, et al. Lack of Interleukin-6 Affects IFN-γ and TNF-α Production and Early In Vivo Control of Brucella abortus Infection. Pathogens. 2020;9(12):1040. [39] HUANG H, WEI X. Therapeutic potential of CD20/CD3 bispecific antibodies in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Rheumatol Immunol Res. 2025;5(4): 209-216. [40] PANG X, XU F, FAN C, et al. Global research trends of MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: bibliometrics and visualization analysis. Clin Rheumatol. 2025;44(1):53-66. [41] ALI S, ZEHRA A, KHALID MU, et al. Role of C-reactive protein in disease progression, diagnosis and management. Discoveries (Craiova). 2023;11(4):e179. [42] YANG C, LI D, TENG D, et al. Epigenetic Regulation in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:859400. [43] KYRIAKIDI M, VETSIKA EK, FRAGOULIS GE, et al. Identification and Clinical Correlation of Circulating MAIT, γδ T, ILC3, and Pre-Inflammatory Mesenchymal Cells in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Spondyloarthritis. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2023;35(2):312-315. [44] LIAO BW, ZHANG HY, DU WT, et al. FAM177A1 Inhibits IL-1β-Induced Signaling by Impairing TRAF6-Ubc13 Association. J Immunol. 2021;207(12):3090-3097. [45] BYKERK VP. Clinical implications of synovial tissue phenotypes in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024;10:1093348. [46] CHEN S, WANG Q, WANG H, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in T cell-mediated diseases. Scand J Immunol. 2023; 98(3):e13307. [47] PIGGOTT CA, JIN Y. Junctophilins: Key Membrane Tethers in Muscles and Neurons. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021;14:709390. [48] GHODOOSIFAR S, DEHGHAN G, SAFARALIZADEH R, et al. The Association between the Expression of MicroRNA-4270 and MicroRNA-4441 with some Metabolic Factors in Iranian Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023;22(6):536-550. [49] NARMADHA G, YENUGU S. Molecular modeling of the human sperm associated antigen 11 B (SPAG11B) proteins. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2015;61(2):78-88. [50] WANG J, LIU J. Correlation between protein expression profiling of inflammation and bone metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Afr Health Sci. 2023;23(3):624-634. [51] DENADAI-SOUZA A, RIBEIRO CM, ROLLAND C, et al. Effect of tryptase inhibition on joint inflammation: a pharmacological and lentivirus-mediated gene transfer study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):124. |
| [1] | Guo Ying, Tian Feng, Wang Chunfang. Potential drug targets for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: large sample analysis from European databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1549-1557. |
| [2] | Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [3] | Zhang Qingfeng, Wang Chaoyi, Yang Jingyan, Li Hanyu, Zhao Yuyang, Hao Huatao, Yu Dong. Potential target genes for spondylolisthesis: drugable genome analysis based on the European population-based biodatabase [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1592-1601. |
| [4] | Liu Hongtao, Wu Xin, Jiang Xinyu, Sha Fei, An Qi, Li Gaobiao. Causal relationship between age-related macular degeneration and deep vein thrombosis: analysis based on genome-wide association study data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1602-1608. |
| [5] | Zheng Yin, Wu Zhenhua, Zhang Cheng, Ruan Kexin, Gang Xiaolin, Ji Hong. Safety and efficacy of immunoadsorption therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: a network meta-analysis and systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1260-1268. |
| [6] | Gao Zengjie, , Pu Xiang, Li Lailai, Chai Yihui, Huang Hua, Qin Yu. Increased risk of osteoporotic pathological fractures associated with sterol esters: evidence from IEU-GWAS and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1302-1310. |
| [7] | Liu Fengzhi, Dong Yuna, Tian Wenyi, Wang Chunlei, Liang Xiaodong, Bao Lin. Gene-predicted associations between 731 immune cell phenotypes and rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1311-1319. |
| [8] | Zhang Cuicui, Chen Huanyu, Yu Qiao, Huang Yuxuan, Yao Gengzhen, Zou Xu. Relationship between plasma proteins and pulmonary arterial hypertension and potential therapeutic targets [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1331-1340. |
| [9] | Bao Zhuoma, Hou Ziming, Jiang Lu, Li Weiyi, Zhang Zongxing, Liu Daozhong, Yuan Lin. Effect and mechanism by which Pterocarya hupehensis skan total flavonoids regulates the proliferation, migration and apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 816-823. |
| [10] | Zeng Hao, Sun Pengcheng, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong, Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun. Association between thyroid function and osteoporosis: genome-wide data analysis of European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1019-1027. |
| [11] | Rong Xiangbin, , Zheng Haibo, Mo Xueshen, Hou Kun, Zeng Ping, . Plasma metabolites, immune cells, and hip osteoarthritis: causal inference based on GWAS data from European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1028-1035. |
| [12] | He Qiwang, , , Chen Bo, Liang Fuchao, Kang Zewei, Zhou Yuan, Ji Anxu, Tang Xialin, . Relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and sarcopenia and body mass index: analysis of GWAS datasets for European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1036-1046. |
| [13] | Ding Yu, Chen Jingwen, Chen Xiuyan, Shi Huimin, Yang Yudie, Zhou Meiqi, Cui Shuai, . Circulating inflammatory proteins and myocardial hypertrophy: large sample analysis of European populations from GWAS Catalog and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1047-1057. |
| [14] | Zhao Feifan, Cao Yujing. An artificial neural network model of ankylosing spondylitis and psoriasis shared genes and machine learning-based mining and validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 770-784. |
| [15] | Liu Chu, Qiu Boyuan, Tong Siwen, He Linyuwei, Chen Haobo, Ou Zhixue. A genetic perspective reveals the relationship between blood metabolites and osteonecrosis: an analysis of information from the FinnGen database in Finland [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 785-794. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||