Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 2691-2701.doi: 10.12307/2026.129
Previous Articles Next Articles
Isoliquiritigenin inhibits wear particle-induced formation and differentiation of osteoblasts in vitro and in vivo
Tan Fei1, 2, Zeng Jiankang1, 2, Wang Jing1, 2, Liu Jian1, 2, Li Jiahuan1, 2, Li Peijie1, 2, Qiao Yongjie1, Zhou Shenghu1
- 1Department of Joint Surgery, The 940th Hospital of Joint Logistics Support Force of Chinese People’s Liberation Army, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China; 2First School of Clinical Medicine, Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730030, Gansu Province, China
-
Received:2025-03-28Accepted:2025-07-07Online:2026-04-18Published:2025-09-02 -
Contact:Zhou Shenghu, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Joint Surgery, The 940th Hospital of Joint Logistics Support Force of Chinese People’s Liberation Army, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China -
About author:Tan Fei, MS candidate, Physician, Department of Joint Surgery, The 940th Hospital of Joint Logistics Support Force of Chinese People’s Liberation Army, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China; First School of Clinical Medicine, Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730030, Gansu Province, China -
Supported by:Gansu Provincial Key Research & Development Project, No. 25YFFA064 (to ZSH); Gansu Provincial Health Commission Project, No. GSWSKY2024-20 (to ZSH); High-level Talent Training Project at The 940th Hospital of Joint Logistics Force, No. 2024-G3-5 (to QYJ); Lanzhou Science and Technology Plan, No. 2023-ZD-173 (to QYJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tan Fei, Zeng Jiankang, Wang Jing, Liu Jian, Li Jiahuan, Li Peijie, Qiao Yongjie, Zhou Shenghu. Isoliquiritigenin inhibits wear particle-induced formation and differentiation of osteoblasts in vitro and in vivo[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2691-2701.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
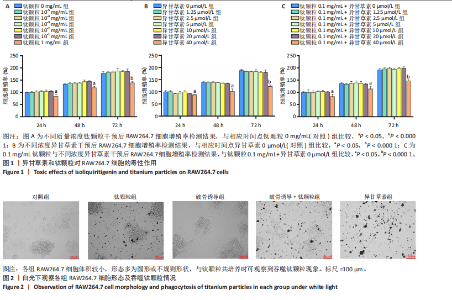
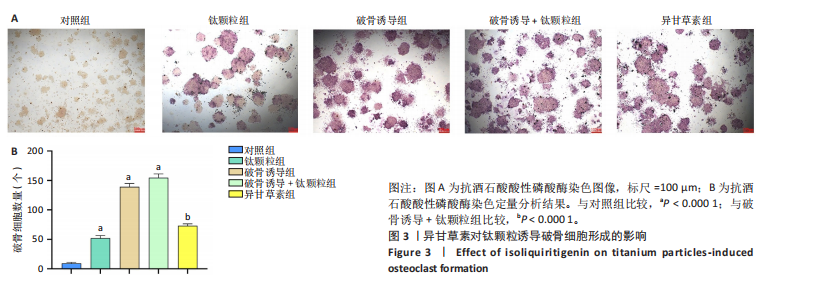
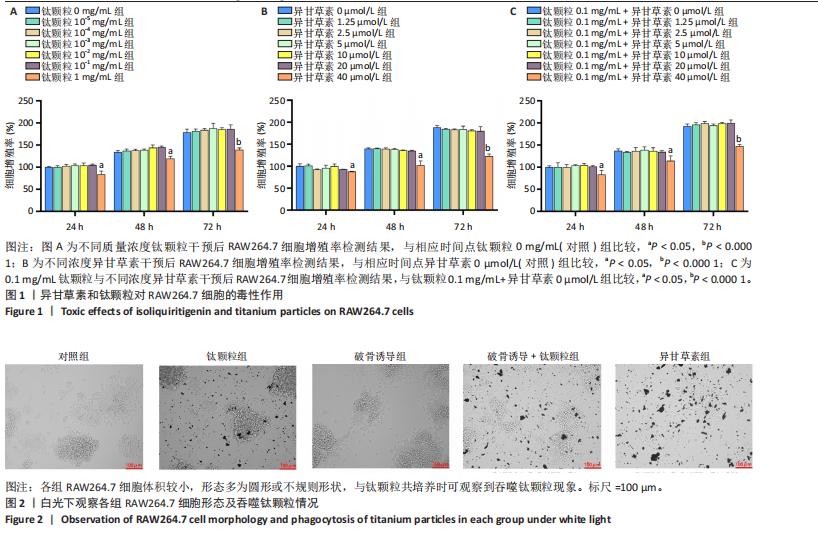
2.1 异甘草素和钛颗粒对RAW264.7细胞的毒性作用 CCK-8检测结果显示,培养24,48,74 h后,与对照组比较,1 mg/mL钛颗粒组细胞增殖率显著降低(P < 0.05或P < 0.000 1),其余浓度钛颗粒组细胞增殖率无明显变化(P > 0.05),见图1A。培养24,48,74 h后,与对照组比较,40 μmol/L异甘草素组细胞增殖率显著降低(P < 0.05或P < 0.000 1),其余浓度异甘草素组细胞增殖率无明显变化(P > 0.05),见图1B。 培养24,48,74 h后,加入钛颗粒干预的情况下,相较于未加入异甘草素组,40 μmol/L异甘草素组细胞增殖率显著降低(P < 0.05或P < 0.000 1),见图1C。综合以上结果,后续实验选择20 μmol/L异甘草素与0.1 mg/mL钛颗粒进行干预。 2.2 细胞实验结果 2.2.1 异甘草素对钛颗粒诱导破骨细胞形态的影响 各组RAW264.7细胞体积较小,形态多为圆形或不规则形状,与钛颗粒共培养时可观察到吞噬钛颗粒现象,见图2。 2.2.2 异甘草素对钛颗粒诱导破骨细胞形成的影响 抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶是破骨细胞分化成熟的标志之一。各组RAW264.7细胞抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶染色图像,见图3A。定量分析结果显示,对照组、钛颗粒组、破骨诱导组、破骨诱导+钛颗粒组、异甘草素组破骨细胞数量分别为(9.18±1.34),(53.80±3.41),(139.76±2.89),(154.80±5.92),(74.29±2.75)个,对照组破骨细胞数量最少,破骨诱导+钛颗粒组破骨细胞数量最多,异甘草素组破骨细胞数量少于破骨诱导+钛颗粒组,见图3B。结果表明异甘草素抑制体外破骨细胞的成熟与分化过程。"
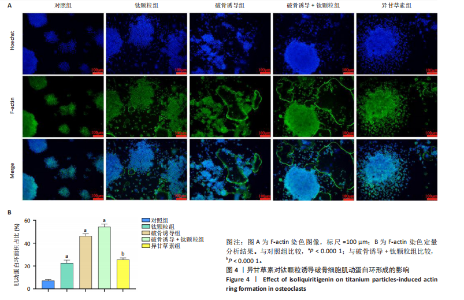
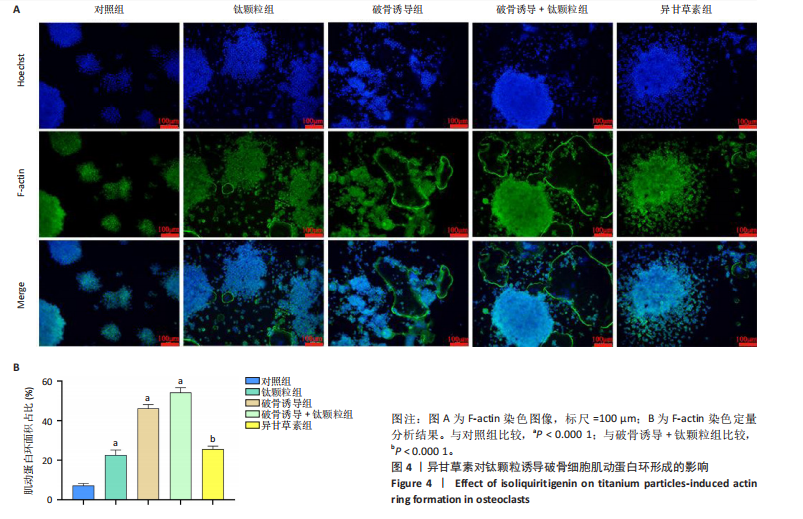
2.2.3 异甘草素对钛颗粒诱导破骨细胞F-actin形成的影响 肌动蛋白环的形成和破骨细胞成熟、吸收及迁移功能密切相关,是反映破骨细胞活性的重要指标。各组RAW264.7细胞肌动蛋白染色图像,见图4A。 定量分析结果显示,对照组、钛颗粒组、破骨诱导组、破骨诱导+钛颗粒组、异甘草素组肌动蛋白环面积占比分别为(7.18±1.05)%,(22.58±2.58)%,(46.19±1.96)%,(54.19±2.50)%,(25.61±1.52)%,对照组肌动蛋白环面积占比最少,破骨诱导+钛颗粒组肌动蛋白环面积占比最多,异甘草素组肌动蛋白环面积占比少于破骨诱导+钛颗粒组(P < 0.000 1),见图4B。结果表明异甘草素抑制破骨细胞肌动蛋白环的形成。"
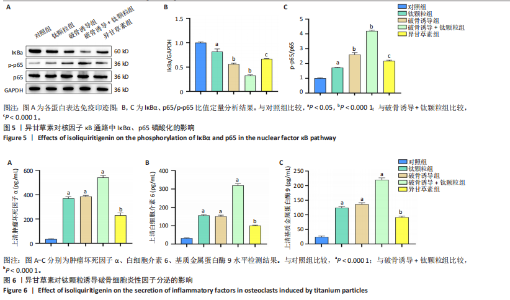
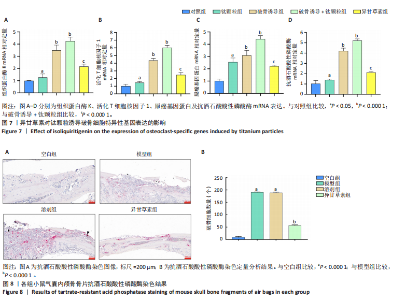
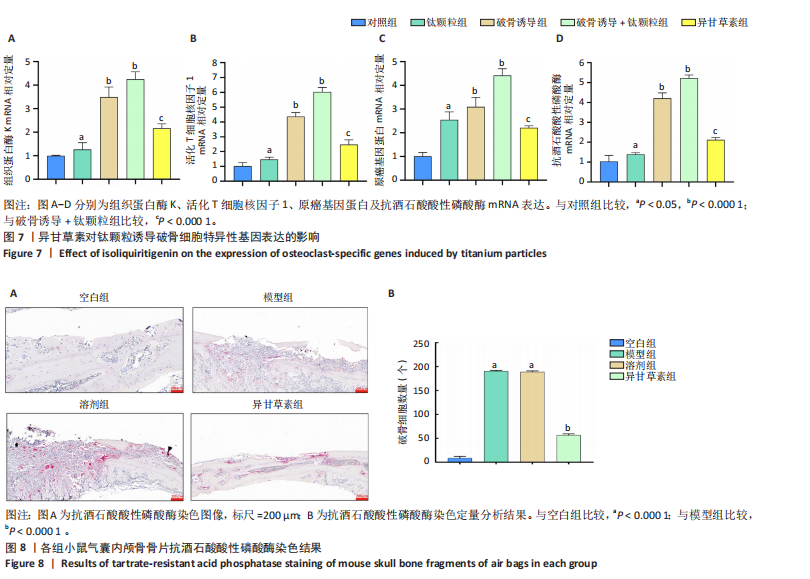
2.2.4 异甘草素对钛颗粒诱导破骨细胞吸收功能的影响 Western Blot检测结果显示,对照组相比,其余4组IκBα、p65磷酸化表达增加(P < 0.05),提示破骨细胞数量增加;破骨诱导+钛颗粒组IκBα、p65磷酸化表达最多,异甘草素组IκBα、p65磷酸化表达较破骨诱导+钛颗粒组降低(P < 0.000 1),见图5。 2.2.5 异甘草素对钛颗粒诱导破骨细胞炎性因子分泌的影响 与对照组比较,钛颗粒组、破骨诱导组、破骨诱导+钛颗粒组、异甘草素组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6和基质金属蛋白酶9水平均升高(P < 0.000 1),其中破骨诱导+钛颗粒组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6和基质金属蛋白酶9水平最高;与破骨诱导+钛颗粒组比较,异甘草素组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6和基质金属蛋白酶9水平降低(P < 0.000 1),见图6。结果表明异甘草素对上述炎性因子的分泌具有明显抑制作用。 2.2.6 异甘草素对钛颗粒诱导破骨细胞特异性基因表达的影响 RT-PCR检测结果显示,与对照组比较,钛颗粒组、破骨诱导组、破骨诱导+钛颗粒组、异甘草素组组织蛋白酶K、活化T细胞核因子1、原癌基因蛋白及抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶mRNA表达均升高(P < 0.000 1),其中破骨诱导+钛颗粒组组织蛋白酶K、活化T细胞核因子1、原癌基因蛋白及抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶mRNA表达最高;与破骨诱导+钛颗粒组比较,异甘草素组组织蛋白酶K、活化T细胞核因子1、原癌基因蛋白及抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶mRNA表达降低(P < 0.000 1),见图7。结果表明异甘草素对这4种破骨特异性基因有显著抑制效果。 2.3 动物实验结果 2.3.1 实验动物数量分析 32只小鼠全部进入结果分析。 2.3.2 各组气囊内颅骨骨片抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶染色结果 各组颅骨骨片抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶染色图像,见图8A。定量分析结果显示,与空白组相比,溶剂组、模型组破骨细胞数量增加(P < 0.000 1);与模型组相比,异甘草素组破骨细胞数量减少(P < 0.000 1), 如图8B。表明异甘草素抑制了由磨损颗粒引发的破骨细胞分化。"
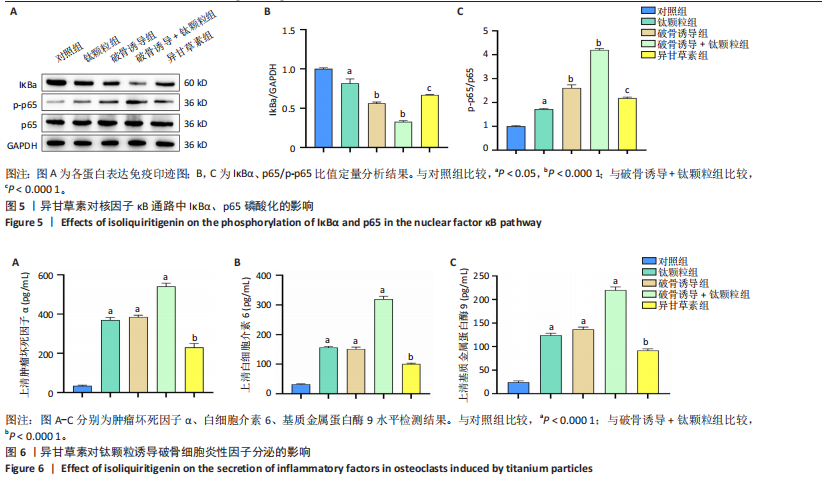
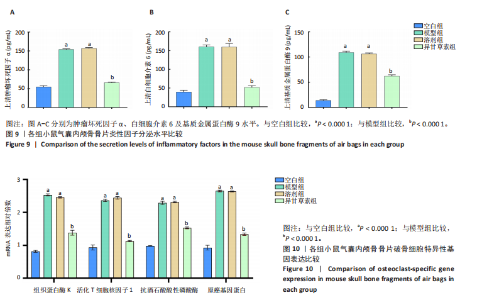
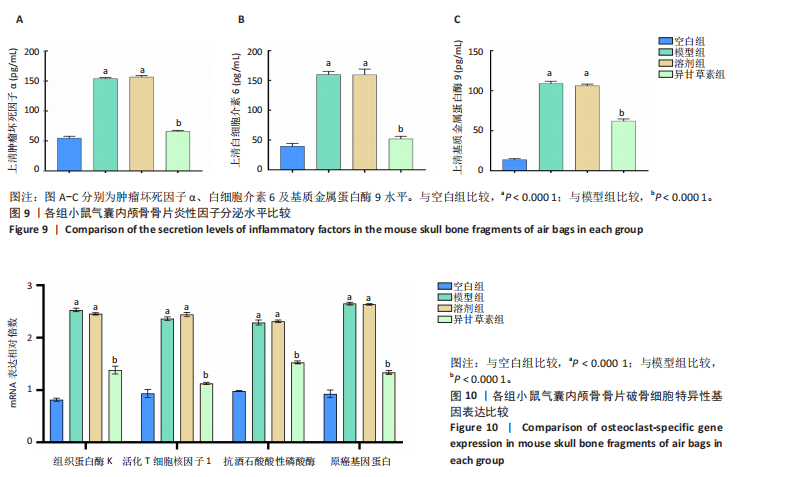
2.3.3 各组气囊内颅骨骨片炎性因子分泌水平比较 与空白组相比,溶剂组、模型组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6和基质金属蛋白酶9水平升高(P < 0.000 1);与模型组相比,异甘草素组肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6和基质金属蛋白酶9水平降低(P < 0.000 1),如图9所示。研究表明异甘草素抑制了由磨损颗粒引起的炎性因子分泌。 2.3.4 各组气囊内颅骨骨片破骨细胞特异性基因表达比较 RT-PCR检测结果显示,与空白组相比,溶剂组、模型组组织蛋白酶K、活化T细胞核因子1、原癌基因蛋白及抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶mRNA表达均升高(P < 0.000 1);与模型组相比,异甘草素组组织蛋白酶K、活化T细胞核因子1、原癌基因蛋白及抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶mRNA表达降低(P < 0.000 1),如图10所示。表明异甘草素抑制了由磨损颗粒引发的破骨细胞分化。"
| [1] MEHDIPOUR S, QOREISHI M, KEIPOURFARD A. Comparison of Clinical, Functional, and Radiological Outcomes of Total Knee Arthroplasty Using Conventional and Patient-Specific Instrumentation. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2020;8(5):625-632. [2] MATTHEW S, AJAY P, SHETH NP. Projected Volume of Primary Total Joint Arthroplasty in the U.S., 2014 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100(17):1455-1460. [3] QOREISHI M, PANAHI M, DORODI O, et al. Involvement of NF-κB/NLRP3 axis in the progression of aseptic loosening of total joint arthroplasties: a review of molecular mechanisms. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022;395(7):757-767. [4] JAGGA S, SHARMA AR, LEE YH, et al. Sclerostin-Mediated Impaired Osteogenesis by Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes in the Particle-Induced Osteolysis Model. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:666295. [5] LU Y, XU X, YANG C, et al. Copper modified cobalt-chromium particles for attenuating wear particle induced-inflammation and osteoclastogenesis. Biomater Adv. 2023;147:213315. [6] DENG Z, ZHANG R, LI M, et al. STAT3/IL-6 dependent induction of inflammatory response in osteoblast and osteoclast formation in nanoscale wear particle-induced aseptic prosthesis loosening. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(4):1291-1300. [7] DAM P AV, VERHOEVEN Y, TRINH XB, et al. RANK/RANKL signaling inhibition may improve the effectiveness of checkpoint blockade in cancer treatment. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2019;133:85-91. [8] PENNANEN P, KALLIONP RA, PELTONEN S, et al. Signaling pathways in human osteoclasts differentiation: ERK1/2 as a key player. Mol Biol Rep. 2021;48(2):1243-1254. [9] KANAZAWA M, SATOMI Y, MIZUTANI Y, et al. Isoliquiritigenin inhibits the growth of prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2003;43(5):580-586. [10] WENFEI Z, XIANG T, CHEN C, et al. Isoliquiritigenin attenuates neuroinflammation after subarachnoid hemorrhage through inhibition of NF‐κB‐mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2024;103(2):e14436. [11] WU S, WANG J. Isoliquiritigenin regulates the circ_0002860/miR-431-5p/RAB9A axis to function as a tumor inhibitor in melanoma. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2023;29:e20220019. [12] 张超,李强强,王雄,等.异甘草素抑制RANKL/RANK/TRAF6信号通路对骨质疏松大鼠成骨细胞分化的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2023,29(4):488-492,508. [13] 薄雨佳,林静,王莉平,等.紫草素干预破骨细胞生成及破骨相关基因的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(32):5126-5131. [14] 刘子歌,刘心蕊,李燕.汉防己甲素干预假体周围磨损颗粒诱导下骨溶解模型的体外实验[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(15): 2358-2363. [15] CHEN D, LI Y, GUO F, et al. Protective effect of p38 MAPK inhibitor on wear debris-induced inflammatory osteolysis through downregulating RANK/RANKL in a mouse model. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14(1):40-52. [16] AHN MY, LIM HH. Effect of Sochungryong-tang Extract on Osteoclast Differentiation and Bone-pit Formation. J Korean Med. 2017;38(3):59-72. [17] PAN B, ZHANG Z, WU X, et al. Macrophage-derived exosomes modulate wear particle-induced osteolysis via miR-3470b targeting TAB3/NF-κB signaling. Bioact Mater. 2023;26:181-193. [18] SHARMA A R, JAGGA S, CHAKRABORTY C, et al. Fibroblast-Like-Synoviocytes Mediate Secretion of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines via ERK and JNK MAPKs in Ti-Particle-Induced Osteolysis. Materials. 2020;13(16):3628. [19] LEE YK, KIM KC, YOON BH, et al. Cementless total hip arthroplasty with delta-on-delta ceramic bearing in patients younger than 30years. Hip Int. 2021;31(2):181-185. [20] NEGAYAMA T, IWATA K, SHIMAMURA M, et al. Total hip arthroplasty after rotational acetabular osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip: a retrospective observational study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):646. [21] 中国药学会医院药学专业委员会,《骨质疏松症治疗药物合理应用专家共识2023》编写组,张玉. 骨质疏松症治疗药物合理应用专家共识(2023)[J].中国医院药学杂志,2024,44(9):985-1006. [22] LIU K, TAN G, SUN W, et al. Percutaneous kyphoplasty combined with zoledronic acid for the treatment of primary osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a prospective, multicenter study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023;143(7):3699-3706. [23] QIAN L, CHEN Q, WANG D, et al. Study on the Relationship between the Use of Bisphosphonates for Antiosteoporosis and Vertebral Re-Fracture after Vertebroplasty. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:3223437. [24] 周龙,陈曦,罗宗平,等.C57BL/6小鼠骨髓单核细胞分离、培养、纯化及向破骨细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(6):940-944. [25] KONG L, SMITH W, HAO D. Overview of RAW264.7 for osteoclastogensis study: Phenotype and stimuli. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(5):3077-3087. [26] DE LA RICA L, GARCÍA-GÓMEZ A, COMET NR, et al. NF-κB-direct activation of microRNAs with repressive effects on monocyte-specific genes is critical for osteoclast differentiation. Genome Biol. 2015;16(1):2. [27] LIU S, ZHU L, ZHANG J, et al. Anti-osteoclastogenic activity of isoliquiritigenin via inhibition of NF-κB-dependent autophagic pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016;106:82-93. [28] ZHANG XY, YU L, WANG K, et al. The combination of berberine and isoliquiritigenin synergistically improved adipose inflammation and obesity‐induced insulin resistance. Phytother Res. 2024;38(8):3839-3855. |
| [1] | Guo Daxin, Fan Susu, Zhu Zhendong, Hou Jianhong, Zhang Xuan. Construction of lentiviral vectors for solute carrier family 1 member 5 overexpression and knockdown and stably transfected RAW264.7 cell line [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1414-1421. |
| [2] | Liu Chunli, Yan Yujuan, Mo Liwen, Wu Zhijie, Zhang Li. Puerarin inhibits the differentiation of Raw264.7 cells into osteoclasts through the Notch signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5636-5641. |
| [3] | Liang Xiaolong, Zheng Kai, Geng Dechun, Xu Yaozeng. Novel programmed cell death in periprosthetic osteolysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(21): 3393-3399. |
| [4] | Zhang Wei, Yu Lei, Yang Peng, Geng Dechun. Tabersonine alleviates wear particle-induced inflammatory osteolysis by inhibiting osteoclast activation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(10): 1519-1525. |
| [5] | Tang Liang, Li Xiheng, Niu Ruijuan, Li Xinyue, Zou Xinying, Mao Tianjiao, Li Jiang. Naringin regulates the function of RAW264.7 macrophages to affect the osteogenic differentiation of MC-3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1205-1210. |
| [6] | Gu Yingchu, Gu Ye, Wu Zerui, Fang Tao, Wang Qiufei, Chen Bingqian, Peng Yuqin, Geng Dechun, Xu Yaozeng. Signaling pathway of osteoblast autophagy in periprosthetic osteolysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(34): 5561-5569. |
| [7] | Liu Chunli, Yan Yujuan, Mo Liwen, Wu Zhijie, Zhang Li. Effects of puerarin on osteoclast differentiation of RAW264.7 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5114-5119. |
| [8] | Liu Guanjuan, Song Na, Huo Hua, Luo Shanshan, Cheng Yuting, Xiong Yue, Hong Wei, Liao Jian. Zoledronic acid inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoclast differentiation by regulating NLRP3 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(29): 4677-4683. |
| [9] | Hu Weifan, Zheng Li, Li Dadi, Sun Yang, Zhao Fengchao. Overexpression of miR-25 downregulates titanium particle-induced osteoclast differentiation through the NFATc1 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 682-687. |
| [10] | Yang Ruijuan, Li Yangyang, Cai Ruiyan, Liu Huibin, Guo Chun. Interleukin-1 alpha induces osteoclast activation and bone loss [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3691-3699. |
| [11] | Wang Qiufei, Gu Ye, Peng Yuqin, Xue Feng, Ju Rong, Zhu Feng, Wang Yijun, Geng Dechun, Xu Yaozeng. Effect of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway on osteoblasts under the action of wear particles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3894-3901. |
| [12] | Jiang Shengyuan, Li Dan, Jiang Jianhao, Shang-you Yang, Yang Shuye. Biological response of Co2+ to preosteoblasts during aseptic loosening of the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3292-3299. |
| [13] | Fan Siqi, Zeng Ping, Nong Jiao, Liu Jinfu, Qian Xiaofen. Effect of Tongluo Shenggu Capsule-containing serum on osteoclasts and Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2155-2160. |
| [14] | Zhao Xiangyu, Zhang Guirong, Guo Chuanbo, Shi Chun, Wu Liuzhong. Increased expression of long-chain non-coding RNA LINC00511 in periodontitis promotes osteoclast proliferation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(33): 5360-5365. |
| [15] | Jia Peng, Zhang Tao. Biological cage in intervertebral bone integration: histocytological properties of interface and healing mechanism of osseointegration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(26): 4249-4254. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||