Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (33): 7055-7062.doi: 10.12307/2025.714
Previous Articles Next Articles
Finite element modeling of knee joint based on semi-automatic segmentation technology
Yan Feng, Zhang Nan, Meng Qinghua, Bao Chunyu, Ye Lixin, Yu Jia
- Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 301617, China
-
Received:2024-06-11Accepted:2024-09-12Online:2025-11-28Published:2025-04-12 -
Contact:Meng Qinghua, PhD, Professor, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 301617, China -
About author:Yan Feng, Lecturer, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 301617, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos. 11372223, 11102135 (to MQH); Tianjin Natural Science Foundation, No. 17JCZDJC36000 (to BCY), 18JCZDJC35900 (to MQH); Science and Technology Innovation Project of General Administration of Sport of China, No. 22KJCX077 (to BCY); Tianjin Graduate Innovation Project, No. 2022SKYZ318 (to ZN)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yan Feng, Zhang Nan, Meng Qinghua, Bao Chunyu, Ye Lixin, Yu Jia. Finite element modeling of knee joint based on semi-automatic segmentation technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7055-7062.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
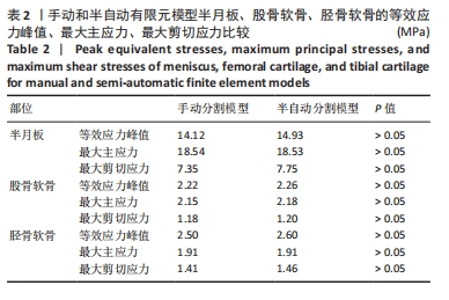
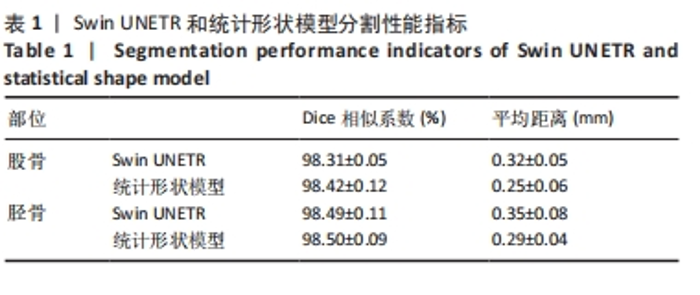
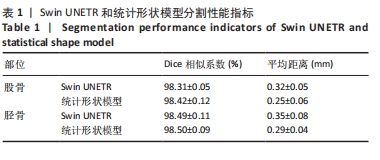
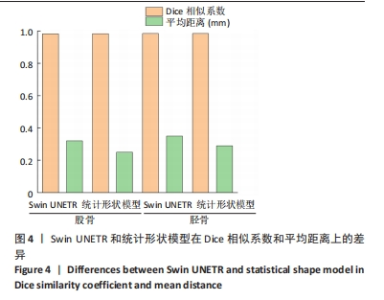
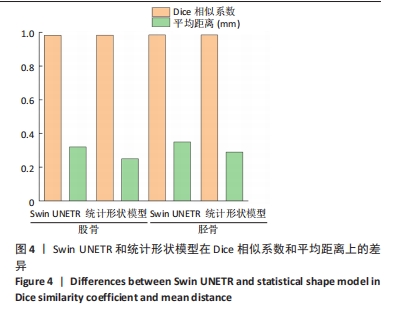
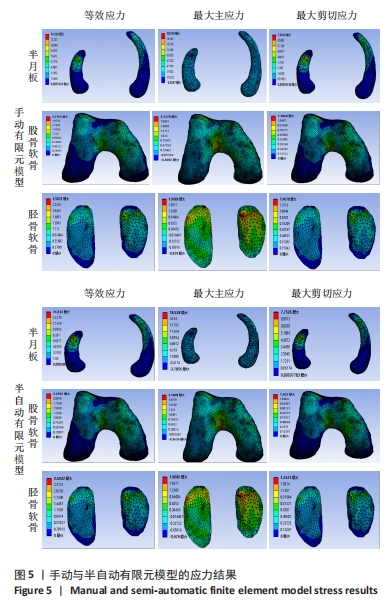
由图5可知,对手动有限元模型股骨顶端施加纵向荷载750 N及10 Nm内翻力矩,半月板等效应力峰值、最大主应力、最大剪切应力为14.12,18.54,7.35 MPa;股骨软骨等效应力峰值、最大主应力、最大剪切应力为2.22,2.15,1.18 MPa;胫骨软骨等效应力峰值、最大主应力、最大剪切应力为2.50,1.91,1.41 MPa。对半自动有限元模型股骨顶端施加纵向荷载750 N及10 Nm内翻力矩,半月板等效应力峰值、最大主应力、最大剪切应力为14.93,18.53,7.75 MPa;股骨软骨等效应力峰值、最大主应力、最大剪切应力为2.26,2.18,1.20 MPa;胫骨软骨等效应力峰值、最大主应力、最大剪切应力为2.60,1.91,1.46 MPa。研究发现手动和半自动有限元模型应力结果基本一致,且与杨骏良等[38]的有限元模型基本一致。由表2可知,通过独立样本t检验发现手动和半自动有限元模型半月板、股骨软骨、胫骨软骨的等效应力峰值、最大主应力、最大剪切应力之间差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。"
| [1] LEGNANI C, VENTURA A, TERZAGHI C, et al. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with synthetic grafts: a review ofliterature. Int Orthop. 2010;34:465-471. [2] DU M, LI J, JIAO C,et al. Distal insertion rupture of lateral ankle ligament as a predictor of weakened and delayed sports recovery after acute ligament repair: mid-term outcomes of 117 cases. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):294. [3] CAMPBELL KJ, MICHALSKI MP, WILSON KJ, et al. The ligament anatomy of the deltoid complex of the ankle: a qualitative and quantitative anatomical study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(8):e62. [4] KIELY PDW, LLOYD ME. Ankle arthritis - an important signpost in rheumatologic practice. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;60(1):23-33. [5] KARITA Y, ISHIBASHI Y, TSUDA E, et al. Mechanisms of anterior cruciate ligament injuries in volleyball. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(4):338-339. [6] TAPASVI S, SHEKHAR A, PATIL S, et al. Limb position influences component orientation in Oxford mobile bearin g unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: an experimental cadaveric study. Bone Joint Res. 2020;9(6):272-278. [7] ARAUZ P, PENG Y, CASTILLO T, et al. In vitro kinematic analysis of single axis radius posterior-substituting total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2021;34(11):1253-1259. [8] KONO K, TOMITA T, YAMAZAKI T, et al. Patellar resurfacing has minimal impact on in vitro tibiofemoral kinematics during deep knee flexion in total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2021;30:163-169. [9] BEIDOKHTI HN, JANSSEN D, VAN DE GROES S, et al. The peripheral soft tissues should not be ignored in the finite element models of the human knee joint. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2018;56:1189-1199. [10] NAGHIBI H, JANSSEN D, GROES S, et al. The influence of ligament modelling strategies on the predictive capability of finite element models of the human knee joint. J Biomech. 2017;65:1-11. [11] BALDWIN MA, LAZ PJ, STOWE JQ, et al. Efficient probabilistic representation of tibiofemoral soft tissue constraint. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2009;12(6):651-659. [12] HUANG X. Sports injury modeling of the anterior cruciate ligament based on the intelligent finite element algorithm. J Healthc Eng. 2021; 2021:3606863. [13] MAHMOOD H, ECKOLD D, STEAD I, et al. A method for the assessment of the coefficient of friction of articula r cartilage and a replacement biomaterial. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020;103:103580. [14] ESTELL EG, MURPHY LA, GANGI LR, et al. Attachment of cartilage wear particles to the synovium negatively impacts friction properties. J Biomech. 2021;127:110668. [15] RADIN EL, PAUL IL. A consolidated concept of joint lubrication. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1972;54(3):607-613. [16] FARROKHI S, KEYAK JH, POWERS CM. Individuals with patellofemoral pain exhibit greater patellofemoral joint stress: a finite element analysis study. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2011;19(3):287-294. [17] LIUKKONEN MK, MONONEN ME, TANSKA P, et al. Application of a semi-automatic cartilage segmentation method for biomechanical modeling of the knee joint. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2017;20(13):1453-1463. [18] MYLLER KAH, KORHONEN RK, TÖYRÄS J, et al. Clinical Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography With Semi-Automatic Segmentation Provides Feasible Input for Computational Models of the Knee Joint. J Biomech Eng. 2020;142(5):051001. [19] ERDEMIR A, BESIER TF, HALLORAN JP, et al. Deciphering the “Art” in Modeling and Simulation of the Knee Joint: Overall Strategy. J Biomech Eng. 2019;141(7):0710021-07100210. [20] KOO S, GOLD GE, ANDRIACCHI TP. Considerations in measuring cartilage thickness using MRI: Factors influencing reproduc-ibility and accuracy. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2005;13(9):782-789. [21] KANG KT, KIM SH, SON J, et al. In vivo evaluation of the subject-specific finite element model for knee joint cartilage contact area. Int J Precis Eng Manuf. 2015;16:1171-1177. [22] BALDWIN MA, LANGENDERFER JE, RULLKOETTER PJ. Development of subject-specific and statistical shape models of the knee using an efficient segmentation and mesh-morphing approach. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2010;97(3):232-240. [23] COOTES TF, TAYLOR CJ, COOPER DH, et al. Active shape models-their training and application. Comput Vis Image Underst.1995;61(1):38-59. [24] CLOUTHIER AL. The effect of articular geometry features identified using statistical shape modelling on knee biomechanics. Med Eng Phys. 2019;66:47-55. [25] PRÖVE PL, JOPP-VAN WELL E, STANCZUS B, et al. Automated segmentation of the knee for age assessment in 3D MR images using convolutional neural networks. Int J Legal Med. 2019;133(4):1191-1205. [26] KIM-WANG SY. Auto-segmentation of the tibia and femur from knee MR images via deep learning and its application to cartilage strain and recovery. J Biomech. 2023;149:111473. [27] AMBELLAN F, TACK A, EHLKE M, et al. Automated segmentation of knee bone and cartilage combining statistical shape knowledge and convolutional neural networks: Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Med Image Anal. 2019;52:109-118. [28] PAPROKI A. Automated segmentation and analysis of normal and osteoarthritic knee menisci from magnetic resonance images–data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2014;22(9):1259-1270. [29] TACK A, MUKHOPADHYAY A, ZACHOW S. Knee menisci segmentation using convolutional neural networks: Data from the Osteo-arthritis Initiative. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2018;26(5): 680-688 [30] RONG Y, XIANG D, ZHU W, et al. Deriving external forces via convolutional neural networks for biomedical image segmentation. Biomed Opt Express. 2019;10(8):3800-3814. [31] BURTON W II, MYERS C, RULLKOETTER P. Semi-supervised learning for automatic segmentation of the knee from MRI with con-volutional neural networks. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020;189: 105328 [32] HATAMIZADEH A. Unetr: Transformers for 3d medical image segmentation. in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. 2022:574-584. [33] HATAMIZADEH A, NATH V, TANG Y, et al. Swin unetr: Swin transformers for semantic segmentation of brain tumors in mri images. Int MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop. 2021:272-284. [34] DOSOVITSKIY A. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2010:11929. [35] ÇIÇEK Ö, ABDULKADIR A, LIENKAMP SS, et al. 3D U-Net: Learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. in Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2016: 19th International Conference, Athens, Greece, October 17-21, 2016, Proceedings, Part II 19,2016:424-432. [36] LIU Z. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision,2021:10012-10022. [37] 鲍春雨,郭宝川,孟庆华.人体膝关节有限元模型建立及其有效性验证[J].应用力学学报,2017,34(3):559-563+615. [38] 杨骏良,路坦,徐彪,等.前交叉韧带部分断裂对膝关节应力影响的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(9):1347-1353. [39] 任爽,时会娟,张家豪,等.前交叉韧带重建术后移植物应力的有限元分析[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2021,53(5):865-870. [40] 张楠,孟庆华,鲍春雨,等.脑卒中患者运动过程中动力学特征的智能预测[J].医用生物力学,2024,39(3):489-496. [41] 王冬梅, 郭文霞, 袁书芳, 等. 基于主成分分析和小波神经网络预测跑步中垂直地面反作用力[J]. 医用生物力学,2022,37(4):706-712. [42] FOURMENT M, SWANEPOEL CJ, GALLOWAY JG, et al. Automatic Differentiation is no Panacea for Phylogenetic Gradient Computation. Genome Biol Evol. 2023;15(6):evad099. [43] FABIANO S, TORELLI N, PAPP D. A novel stochastic optimization method for handling misalignments of proton and photon doses in combined treatments. Phys Med Biol. 2022;67(18). doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ac858f. [44] PIETRONI N, TARINI M, CIGNONI P. Almost isometric mesh parameterization through abstract domains. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph. 2009;16(4):621-635. [45] RÖHRICH E, THALI M, SCHWEITZER W. Skin injury model classification based on shape vector analysis. BMC Med Imaging. 2012;12:32. [46] GANG GJ, STAYMAN JW. Universal orbit design for metal artifact elimination. Phys Med Biol. 2022;67(11):10.1088/1361-6560/ac6aa0. [47] LUO C, GE X, WANG Y. Uniformization and density adaptation for point cloud data via graph Laplacian. Comp Graph Forum. 2018;325-337. [48] MYRONENKO A, SONG X. Point set registration: Coherent point drift. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010;32(12):2262-2275. [49] MONTECCHI M, CARA G, BENEDETTI A. VISproPT: A high-precision instrument for 3D shape analysis of parabolic trough panels. Open Res Eur. 2023;3:111. [50] BOOKSTEIN FL, GREEN WDK. A thin-plate spline and the decomposition of deformations. Math Methods Med. 1993:14-28. [51] ZHOU Z, ZHAO G, KIJOWSKI R, et al. Deep convolutional neural network for segmentation of knee joint anatomy. Magn Reson Med. 2018;80(6):2759-2770. [52] LATIF MHA, FAYE I. Automated tibiofemoral joint segmentation based on deeply supervised 2D-3D ensemble U-Net: Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Artif Intell Med. 2021;122:102213. [53] RODRIGUEZ-VILA B, SÁNCHEZ-GONZÁLEZ P, OROPESA I, et al. Automated hexahedral meshing of knee cartilage structures - application to data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2017;20(14):1543-1553. [54] EBRAHIMKHANI S, JAWARD MH, CICUTTINI FM, et al. A review on segmentation of knee articular cartilage: from conventional methods towards deep learning. Artif Intell Med. 2020;106:101851. |
| [1] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [2] | Wang Juan, Wang Guanglan, Zuo Huiwu. Efficacy of exercise therapy in the treatment of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients: #br# a network meta-analysis #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1714-1726. |
| [3] | Chen Jing, Zhang Nan, Meng Qinghua, Bao Chunyu. Material characterization of finite element computational models of knee joints at different ages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7369-7375. |
| [4] | Ye Xiaolong, Zhang Yuxuan, Fu Rongchang, Liu Yun, Yusanjiang·Wuhuer, Escar·Aimer, Ma Yuan. A three-dimensional finite element modal analysis on adolescent idiopathic scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7072-7079. |
| [5] | Jiang Tao, Zhang Chuankai, Hao Liang, Liu Yong. MAKO robot- and navigation-assisted knee replacement: comparison of lower limb force alignment and prosthesis position accuracy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7150-7157. |
| [6] | Su Dejun, Dong Wanpeng, Dong Yuefu, Zhang Jichao, Zhang Zhen. Design of asymmetric prosthesis and mechanical analysis of total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 510-516. |
| [7] | Hu Zhenghui, Zhang Wen, Heng Hongquan, Ren Weizhi, Wu Chenying, Gu Zenghui, Peng Jian, Li Liubing, Xu Wei. Finite element analysis of application of variable angle screws in posterolateral tibial plateau fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5735-5742. |
| [8] | Wei Changqiang, Yu Hongjian, Liu Ningning, Zhang Yinxiao. Effect of line adjustment area of lower limbs on knee joint function and kinematics after high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5743-5749. |
| [9] | Zhao Yuhan, Li Yamei, Yan Shifang, Jiang Huabei. Immediate effects of different stretching methods on knee joint muscle strength and vertical jump performance of healthy adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3784-3790. |
| [10] | Wu Yue, Ren Shuang, Huang Hongshi, Dai Ruilan, Ao Yingfang, Gou Bo. Gluteal muscle activation exercise therapy improves lower limb muscle strength in young male patients with anterior knee pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3798-3803. |
| [11] | Tang Xiran, Chen Weijian, Jiang Tao, Tan Xianyun, Liu Wengang . Types and contents of fatty acids and the risk of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3724-3731. |
| [12] | Li Hongtao, Pan Hongyu, Lei Yang, Xiao Changming. Finite element analysis of percutaneous vertebroplasty combined with pedicle augmentation in treatment of severe osteoporotic vertebral fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(15): 3089-3094. |
| [13] | Pan Hao, Yang Meng, Liu Guoqiang. Timing of total knee arthroplasty with tourniquet under navigation system: a single-center, retrospective analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(15): 3159-3164. |
| [14] | Guo Huanxuan, Kang Zhijie, Bai Xiaolong, Tian Xiaoyan, Jin Feng. Characteristics and advantages in finite element analysis techniques in knee biomechanics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(15): 3253-3261. |
| [15] | Xu Zhen, Zhang Mengru, Lyu Ke, Xia Zhongyu, Zhang Caiwei, Xu Jianda. Application and value of acoustic emission technique in joint surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(15): 3262-3270. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||