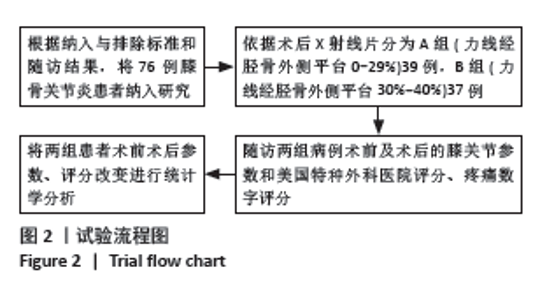
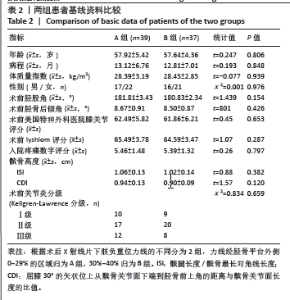
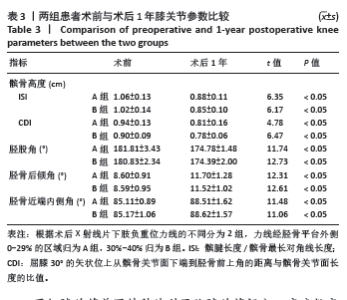
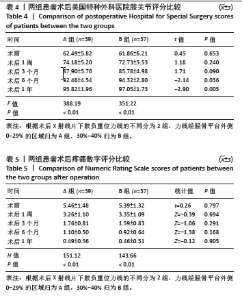
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (27): 5743-5749.doi: 10.12307/2025.196
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of line adjustment area of lower limbs on knee joint function and kinematics after high tibial osteotomy
Wei Changqiang1, Yu Hongjian2, Liu Ningning2, Zhang Yinxiao3
- 1First Clinical Medical College of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Joint and Sports Medicine, Binzhou People’s Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China; 3Graduate School of Shandong First Medical University, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2024-04-10Accepted:2024-06-11Online:2025-09-28Published:2025-03-03 -
Contact:Yu Hongjian, MD, Chief physician, Department of Joint and Sports Medicine, Binzhou People’s Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Wei Changqiang, Master candidate, First Clinical Medical College of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, No. ZR2021MH084 (to YHJ); Shandong Provincial Medical and Health Science and Technology Development Plan Project, No. 202204070588 (to LNN)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wei Changqiang, Yu Hongjian, Liu Ningning, Zhang Yinxiao. Effect of line adjustment area of lower limbs on knee joint function and kinematics after high tibial osteotomy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5743-5749.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] WHITTAKER JL, KALSOUM R, BILZON J, et al. Toward designing human intervention studies to prevent osteoarthritis after knee injury: A report from an interdisciplinary OARSI 2023 workshop. Osteoarthr Cartil Open. 2024;6(2):100449. [2] LI J, ZHAO F, DONG W, et al. Medial open-wedge high tibial osteotomy for the treatment of degenerative varus knee osteoarthritis in geriatric patients: a retrospective study. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):16848. [3] MURRAY R, WINKLER PW, SHAIKH HS, et al. High Tibial Osteotomy for Varus Deformity of the Knee. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2021;5(7):e21.00141. [4] 付琨朋,张中斌,朱凯,等.两种截骨方法联合关节镜治疗内侧膝骨关节炎的早期疗效分析[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2022,28(10):879-883. [5] PÉRIÉ D, HOBATHO MC. In vivo determination of contact areas and pressure of the femorotibial joint using non-linear finite element analysis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 1998;13(6):394-402. [6] BODE G, VON HEYDEN J, PESTKA J, et al. Prospective 5-year survival rate data following open-wedge valgus high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(7):1949-1955. [7] FUJISAWA Y, MASUHARA K, SHIOMI S. The effect of high tibial osteotomy on osteoarthritis of the knee. An arthroscopic study of 54 knee joints. Orthop Clin North Am. 1979;10(3):585-608. [8] 俞颖豪,赵继军,刘冬铖,等. 个体化开放楔形胫骨高位截骨治疗内侧间 室膝骨关节炎的优势 [J]. 中国组织工程研究 ,2020,24(27):4310-4316. [9] ZHANG B, QIAN H, WU H, et al. Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty versus high tibial osteotomy for medial knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2023;31(1):10225536231162829. [10] GHASEMI SA, KOLESNICK E, MURRAY BC, et al. High tibial osteotomy combined with cartilage restoration: A systematic review of clinical outcomes and prognostic factors. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2024;50: 102360. [11] SAITO T, KUMAGAI K, AKAMATSU Y, et al. Five- to ten-year outcome following medial opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy with rigid plate fixation in combination with an artificial bone substitute. Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(3):339-344. [12] MARTAY JL, PALMER AJ, BANGERTER NK, et al. A preliminary modeling investigation into the safe correction zone for high tibial osteotomy. Knee. 2018;25(2):286-295. [13] MURRAY DW, FITZPATRICK R, ROGERS K, et al. The use of the Oxford hip and knee scores. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89(8):1010-1014. [14] JI S, GAO Y, ZHANG J, et al. High tibial lateral closing wedge and opening wedge valgus osteotomy produce different effects on posterior tibial slope and patellar height. Front Surg. 2023;10:1219614. [15] MOON DK, SEO MS, KIM CW, et al. The influence of different hinge position on pts during HTO: comparison between open-wedge and closed-wedge HTO. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2023;33(4): 1341-1347. [16] SUH DW, NHA KW, HAN SB, et al. Biplane Medial Opening-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy Increases Posterior Tibial Slope more than Uniplane Osteotomy. J Knee Surg. 2022;35(11):1229-1235. [17] 李军. 胫骨内侧开放楔形高位截骨术中矢状位截骨倾斜角度对胫骨平台后倾角的影响[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2022,25(4):559. [18] 吴克亮,叶鹏程,冯文俊,等.开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术中矫正角度对胫骨后倾角及髌骨高度的影响分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2018, 24(10):894-898+903. [19] KHASIAN M, MECCIA BA, LACOUR MT, et al. Effects of Posterior Tibial Slope on a Posterior Cruciate Retaining Total Knee Arthroplasty Kinematics and Kinetics. J Arthroplasty. 2021;36(7):2379-2385. [20] GUY S, SAITHNA A, FERREIRA A, et al. The Influence of Tibial Tubercle-Sparing Slope-Reducing Osteotomy on Patellar Height in Patients Undergoing Revision ACL Reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2024;52(4):919-927. [21] XU H, TU H, ZHAO T, et al. Comparison of the clinical effects for different positions of the weight-bearing axis after high tibial osteotomy. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):423. [22] BENZAKOUR T, HEFTI A, LEMSEFFER M, et al. High tibial osteotomy for medial osteoarthritis of the knee: 15 years follow-up. Int Orthop. 2010;34(2):209-215. [23] YIN Y, LI S, ZHANG R, et al. What is the relationship between the “Fujisawa point” and postoperative knee valgus angle? A theoretical, computer-based study. Knee. 2020;27(1):183-191. [24] HERNIGOU P. Recul à plus de 20 ans de la gonarthrose fémoro-tibiale interne après ostéotomie tibiale de valgisation. Ostéotomie unique versus ostéotomie itérative [A 20-year follow-up study of internal gonarthrosis after tibial valgus osteotomy. Single versus repeated osteotomy]. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1996;82(3): 241-250. [25] HERNIGOU P, MEDEVIELLE D, DEBEYRE J, et al. Proximal tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis with varus deformity. A ten to thirteen-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987;69(3):332-354. [26] 徐奎帅,张靓,陈进利,等. 内侧开放楔形胫骨高位截骨后早期力线改变对下肢关节的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(6): 821-826. [27] DOMNICK C, GARCIA P, RASCHKE MJ, et al. Trends and incidences of ligament-surgeries and osteotomies of the knee: an analysis of German inpatient records 2005-2013. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017;137(7):989-995. [28] WEIDENHIELM L, SVENSSON OK, BROSTRÖM LÅ. Change of adduction moment about the hip, knee and ankle joints after high tibial osteotomy in osteoarthrosis of the knee. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 1992;7(3):177-180. [29] CHOI GW, YANG JH, PARK JH, et al. Changes in coronal alignment of the ankle joint after high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(3):838-845. [30] GOSHIMA K, SAWAGUCHI T, SHIGEMOTO K, et al. Comparison of Clinical and Radiologic Outcomes Between Normal and Overcorrected Medial Proximal Tibial Angle Groups After Open-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy. Arthroscopy. 2019;35(10):2898-2908. [31] KRAUSE M, DRENCK TC, KORTHAUS A, et al. Patella height is not altered by descending medial open-wedge high tibial osteotomy (HTO) compared to ascending HTO. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(6):1859-1866. [32] 闫加鹏,张洪飞,刘焕彩,等.单髁置换术与全膝关节置换术治疗膝关节内侧间室骨性关节炎的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(4):393-395. [33] KATAOKA K, WATANABE S, NAGAI K, et al. Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis Progresses After Medial Open-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy: A Systematic Review. Arthroscopy. 2021;37(10): 3177-3186. [34] WU K, ZENG J, HAN L, et al. Effect of the amount of correction on posterior tibial slope and patellar height in open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2021;29(3): 23094990211049571. [35] EL-AZAB H, GLABGLY P, PAUL J, et al. Patellar height and posterior tibial slope after open- and closed-wedge high tibial osteotomy: a radiological study on 100 patients. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(2): 323-329. [36] LI M, LU Z, ZHANG H, et al. Effect of open-wedge high tibial osteotomy and lateral patellofemoral retinacular release on patellar position: an X-ray imaging-based comparative study. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023;13(5):2860-2870. [37] 李明,张浩军,方超华,等.开放楔开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术对髌骨位置与关节功能的影响[J].中国骨伤,2022,35(11):1037-1041. [38] NGUYEN TT, LE HDT, HOANG NT, et al. Morphologic Evaluation of the Patella: The Impact of Gender and Age. Orthop Res Rev. 2024;16: 59-66. [39] PRIMEAU CA, BIRMINGHAM TB, LEITCH KM, et al. Total knee replacement after high tibial osteotomy: time-to-event analysis and predictors. CMAJ. 2021;193(5):E158-E166. [40] AGARWALLA A, CHRISTIAN DR, LIU JN, et al. Return to Work Following Isolated Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy. Cartilage. 2021;12(4):468-474. |
| [1] | Ma Chi, Wang Ning, Chen Yong, Wei Zhihan, Liu Fengji, Piao Chengzhe. Application of 3D-printing patient-specific instruments combined with customized locking plate in opening wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1863-1869. |
| [2] | Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Wan Haili, Chang Ying, Xiong Wenjuan, Xia Yuan. Effect of neuromuscular exercise for knee osteoarthritis pain and function: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [3] | Wang Peiguang, Zhang Xiaowen, Mai Meisi, Li Luqian, Huang Hao. Generalized equation estimation of the therapeutic effect of floating needle therapy combined with acupoint embedding on different stages of human knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1565-1571. |
| [4] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [5] | Ma Haoyu, Qiao Hongchao, Hao Qianqian, Shi Dongbo. Causal effects of different exercise intensities on the risk of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1305-1311. |
| [6] | Wu Guangtao, Qin Gang, He Kaiyi, Fan Yidong, Li Weicai, Zhu Baogang, Cao Ying . Causal relationship between immune cells and knee osteoarthritis: a two-sample bi-directional Mendelian randomization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1081-1090. |
| [7] | Li Jia, Liu Qianru, Xing Mengnan, Chen Bo, Jiao Wei, Meng Zhaoxiang. A network meta-analysis on therapeutic effect of different types of exercise on knee osteoarthritis patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 609-616. |
| [8] | Shi Lei, Shi Song, Lu Yue, Tao Ran, Ma Hongdong. Comparison of unicondylar knee arthroplasty and high tibial osteotomy in treatment of medial knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 503-509. |
| [9] | Zhang Yunyi, Liu Songtao, Xie Shaodong, Zhu Haifeng, Qian Guifeng, Huo Ming, Zhou Jie, Deng Zixuan. Platelet rich plasma versus hyaluronic acid in treatment of knee osteoarthritis: an overview of systematic reviews [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 6138-6145. |
| [10] | Sun Yingjin, Liu Ning, Huang Long, Feng Shuo, Chen Xiangyang. Effect of patellar morphology on functional recovery and patellofemoral joint alignment after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5826-5832. |
| [11] | Ding Yuan, Gong Jianbao, Zhang Jie, Qiao Yuan, Xu Wenlong. Characteristic analysis of isometric muscle strength of knee joint in patients after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5833-5838. |
| [12] | Shaban Amiri Nzelekela, Yang Lianbo, Li Peng. Objective accuracy of six degree of freedom gait analysis system in evaluating the severity of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5890-5896. |
| [13] | Li Yongjie, Liu Mengling, Zhang Dakuan, Fu Shenyu, Liu Hongju. Effect of unilateral knee osteoarthritis on gait dynamics and muscle activation asymmetry in elderly women [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5750-5756. |
| [14] | Sun Hailiang, Pang Jian, Shi Wanzhong, Shi Ying. Protective effect of Huaizhen Yanggan Capsule on knee osteoarthritis induced by sodium iodoacetate in model mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5579-5587. |
| [15] | Chen Yixin, Lu Yan, Zhang Xuan, Chen Xiaoli, Tan Liangyuan, Xu Zhangjie, Chen Wanglong, Su Shaoting, Liang Jiyao, Zhou Honghai. Mechanism by which Tongan Decoction regulates synovial macrophage polarization in rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5621-5631. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||