Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (33): 7048-7054.doi: 10.12307/2025.852
Previous Articles Next Articles
Finite element analysis of biomechanical characteristics of three internal fixation methods in treatment of inferior patellar fracture
Wang Lei1, Li Chengsong2, Zhang Shenshen2, Wang Qing2
- 1Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350108, Fujian Province, China; 2Mindong Hospital Affiliated to Fujian Medical University, Fuan 355000, Fujian Province, China
-
Received:2024-07-22Accepted:2024-10-11Online:2025-11-28Published:2025-04-12 -
Contact:Zhang Shenshen, MS, Chief physician, Mindong Hospital Affiliated to Fujian Medical University, Fuan 355000, Fujian Province, China -
About author:Wang Lei, MS, Associate chief physician, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350108, Fujian Province, China Li Chengsong, Master candidate, Mindong Hospital Affiliated to Fujian Medical University, Fuan 355000, Fujian Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Lei, Li Chengsong, Zhang Shenshen, Wang Qing. Finite element analysis of biomechanical characteristics of three internal fixation methods in treatment of inferior patellar fracture[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7048-7054.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
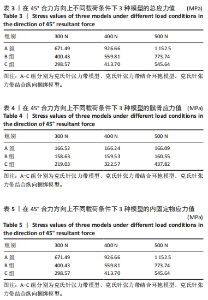
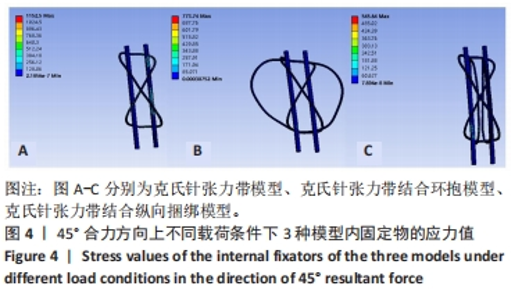
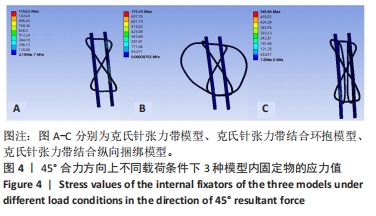
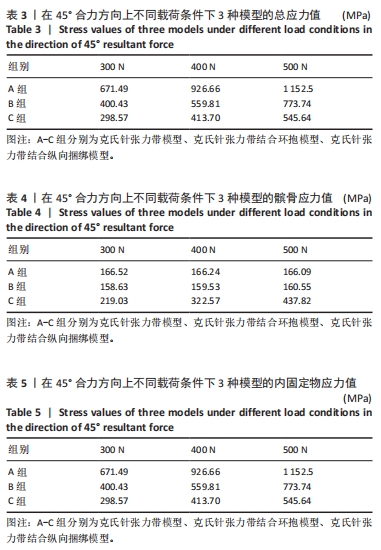
2.1 45°合力方向上不同载荷条件下3种模型的应力分布及应力值 45°合力方向分别施加300,400,500 N载荷下3种模型总应力分布:3组模型的结果呈现一个清晰的趋势,A组> B组> C组;完整髌骨应力分布:C组> A组> B组;内固定物应力分布:A组> B组> C组。在有限元分析结构中钢丝最大应力达到1 234 MPa(材料屈服强度)时,内固定物可能发生不可逆的形变[26-28]。在此组数据结果中,3种内固定模型的内固定应力均小于1 234 MPa,表示3组内固定方式均不会发生内固定物不可逆的形变;从应力分布情况上看,当施加载荷增大的情况下,髌骨模型和内固定物的应力也随之增加,300 N载荷应力最小,500 N载荷应力最大;3种模型总的等效应力及内固定物等效应力最大为A组,最小为C组;完整髌骨等效应力最大为C组,最小为B组,A组与B组的髌骨等效应力无显著差异。有限元分析结果表明,C组在45°角300,400,500 N载荷条件下整体模型及内固定物的等效应力最低。见表3-5及图4。"
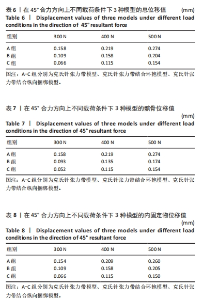
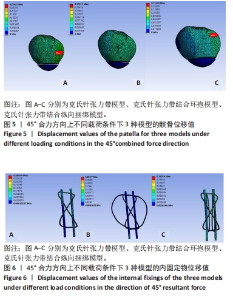
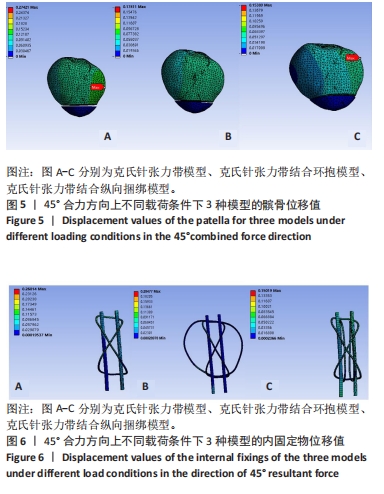
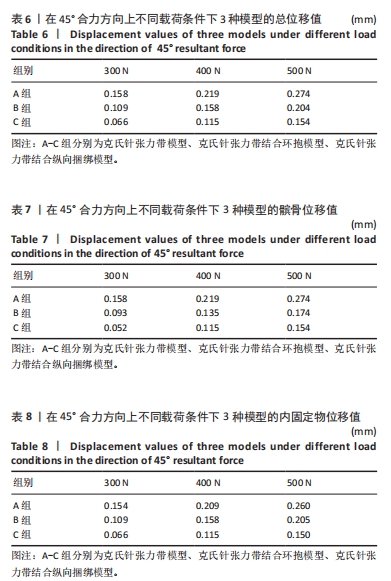
2.2 45°合力方向上不同载荷条件下3种模型的位移分布 45°合力方向300,400,500 N载荷下3种模型总位移为:A组> B组> C组;完整髌骨位移:A组> B组> C组;内固定物位移:A组> B组> C组。3种模型总位移、髌骨及内固定物位移上最大均为A组,最小均为C组,C组与A、B组相比,在300 N载荷下最大位移分别减低了58% (0.158 mm:0.066 mm)和39%(0.109 mm:0.066 mm);在400 N载荷下最大位移分别减低了47%(0.274 mm:0.154 mm)和27%(0.158 mm:0.115 mm);在500 N载荷下最大位移分别减低了47%(0.219 mm:0.115 mm)和25% (0.204 mm:0.154 mm)。有限元分析结果表明,当施加载荷增大的情况下,髌骨模型和内固定物位移也随之增加,300 N载荷位移最小,500 N载荷位移最大;C组在45°合力方向300,400,500 N载荷条件下整体模型、髌骨及内固定物的位移最小。见表6-8及图5,6。"
| [1] HEUSINKVELD MH, DEN HAMER A, TRAA WA, et al. Treatment of transverse patellar fractures: a comparison between metallic and non-metallic implants. Br Med Bull. 2013:107:69-85. [2] PU S, CHEN Y, LIANG J, et al. Treatment of inferior pole fracture of the patella with tension-free external immobilization. BMC Surg. 2022; 22(1):337. [3] ZHU W, XU L, XIE K, et al. Design and Validation of a Smile‐Necklace Plate for Treating Inferior Patellar Pole Avulsion Fractures: A Review and Hypothesis. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(11):2799-2808. [4] ALLEN C, JIN LM. Fracture of the inferior pole of the patella. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2012;42(7):658. [5] FAN W, XIAO Y, XIANG F, et al. Research progress of inferior-pole patellar fracture: A systematic review. Asian J Surg. 2023;46(6):2450-2451. [6] WATANABE H, MURASE K, KIM D, et al. A posterior tibial slope angle over 12 degrees is critical to epiphyseal fracture of the proximal tibia: Three-dimensional finite element analysis. Heliyon. 2023;9(8):e18854. [7] MELVIN JS, MEHTA S. Patellar fractures in adults. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011; 19(4): 198-207. [8] 张健, 蒋协远, 黄晓文. 纵向钢丝捆绑结合克氏针张力带治疗髌骨下极粉碎骨折[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版),2016,48(3):534-538. [9] ZHAO QM, YANG HL, WANG L, et al. Treatment of comminuted patellar fracture with the nitinol patellar concentrator. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2016;25(3):171-175. [10] LIU F, WANG S, ZHU Y, et al. Patella rings for treatment of patellar fracture. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24(1):105-109. [11] GU H, ZHU S, LI T, et al. Combination of Cable Cerclage and Hook Plate for the Fixation of Comminuted Fractures of Inferior Patellar Pole: A Review of 16 Consecutive Patients Followed Up for a Minimum of 1 Year. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(11):3111-3118. [12] LI M, QI H, MA T, et al. Outcomes for a custom-made anchor-like plate combined with cerclage in the treatment of inferior pole patellar fracture. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):452. [13] CHEN R, CAO H, SUN Z, et al. The clinical outcome of the reduction of the patellar inferior pole fracture with wire cerclage through a generated bone hole, in combination with patellar concentrator: a retrospective comparative study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):117. [14] LIU Y. Mechanical Analysis and Clinical Application of Butterfly-Shaped Patellar Claw. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022;2022:2008668. [15] 李广磊, 刘平. 髌骨骨折手术治疗方式的研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(8):1057-1062. [16] 李志帅, 张红倩, 李丽, 等. 膝关节有限元分析的研究热点及趋势[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(15):2412-2418. [17] 肖琦科, 张力鹏, 张永峰. 髌韧带编织缝合联合克氏针钢丝张力带内固定治疗髌骨下极骨折疗效观察[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2021,36(6):605-607. [18] 尼玛平措, 唐剑飞, 李坛珠, 等. 髌骨骨折钢板内固定研究进展[J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2022,43(1):22-26. [19] LI G, LIU P. Progress in the surgical treatment of the patellar fracture. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021;35(8):1057-1062. [20] 白晓东, 芦重尧, 张英泽, 等. 髌骨骨折的内固定治疗进展[J]. 河北医科大学学报,2020,41(7):865-868. [21] MONACO E, BRUNI G, DAGGETT M, et al. Patellar Fracture Fixation Using Suture Tape Cerclage. Arthrosc Tech. 2020;9(6):e783-e789. [22] 杨匡洋, 王昌兵. MRI评价自体骨-髌韧带-骨与股四头肌腱行前交叉韧带重建后移植物成熟度及膝关节的功能[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(6):963-968. [23] 何双建. 改良SVW技术治疗髌骨下极骨折的有限元分析及临床研究[D]. 南京:南京医科大学,2018. [24] DEMIRTAŞ Y, KATI YA. A novel patella fracture fixation technique: finite element analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023;143(8):5105-5115. [25] GAO Y, CHENG Y, ZHU H, et al. A modified separate vertical fixation by wires and titanium cables for comminuted inferior patella fracture: A technique note and finite element analysis. Injury. 2023:S0020-1383(23)00178-X. [26] FAN W, LIU J, TAN X, et al. Candy box technique for the fixation of inferior pole patellar fractures: finite element analysis and biomechanical experiments. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1): 835. [27] FAN W, DANG S, TAN X, et al. Computational evaluation of wire position using separate vertical wire technique and candy box technique for the fixation of inferior pole patellar fractures: a finite element analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1353901. [28] AMIROUCHE F, CHOI KW, GOLDSTEIN WM, et al. Finite element analysis of resurfacing depth and obliquity on patella stress and stability in TKA. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(6):978-984. [29] WHITTAKER JL, LOSCIALE JM, JUHL CB, et al. Risk factors for knee osteoarthritis after traumatic knee injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials and cohort studies for the OPTIKNEE Consensus. Br J Sports Med. 2022;56(24):1406-1421. [30] YAN SG, LI D, CUI Y, et al. Management of comminuted inferior patellar pole fractures with cerclage-wire-augmented separate vertical wiring: a retrospective clinical study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023;143(1): 247-254. [31] SONG HK, YOO JH, BYUN YS, et al. Separate vertical wiring for the fixation of comminuted fractures of the inferior pole of the patella. Yonsei Med J. 2014;55(3):785-791. [32] MASSEY PA, MYERS M, MCCLARY K, et al. Biomechanical Analysis of Patellar Tendon Repair With Knotless Suture Anchor Tape Versus Transosseous Suture. Orthop J Sports Med. 2020;8(10): 2325967120954808. [33] AMIS AA. Current concepts on anatomy and biomechanics of patellar stability. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2007;15(2):48-56. [34] DARGEL J, GICK S, MADER K, et al. Biomechanical comparison of tension band- and interfragmentary screw fixation with a new implant in transverse patella fractures. Injury. 2010;41(2):156-160. [35] DU B, MA T, BAI H, et al. Efficacy comparison of Kirschner-wire tension band combined with patellar cerclage and anchor-loop plate in treatment of inferior patellar pole fracture. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:1010508. [36] AMIROUCHE F, SOLITRO GF, WALIA A, et al. Segmental acetabular rim defects, bone loss, oversizing, and press fit cup in total hip arthroplasty evaluated with a probabilistic finite element analysis. Int Orthop. 2017; 41(8):1527-1533. [37] PETTERSEN SH, WIK TS, SKALLERUD B. Subject specific finite element analysis of stress shielding around a cementless femoral stem. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2009;24(2):196-202. [38] GARABANO G, RODRIGUEZ J, PEREZ ALAMINO L, et al. Stress shielding in total knee replacements: Comparative analysis between titanium and all-polyethylene bases at 10 years follow-up. J Orthop. 2022;34: 276-281. [39] 姜亚琼, 路坦, 徐彪, 等. 内侧副韧带不同程度损伤时膝关节的应力变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024,28(33):5270-5275. [40] FERRER MA, LOBO MO, ALMEIDA LMP, et al. Patellar fracture in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: in vitro analysis. Acta Ortop Bras. 2023;31(2):e259557. [41] TRAVASCIO F, BULLER LT, MILNE E, et al. Mechanical performance and implications on bone healing of different screw configurations for plate fixation of diaphyseal tibia fractures: a computational study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2021;31(1):121-130. [42] WIERER G, WINKLER PW, POMWENGER W, et al. Transpatellar bone tunnels perforating the lateral or anterior cortex increase the risk of patellar fracture in MPFL reconstruction: a finite element analysis and survey of the International Patellofemoral Study Group. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022;30(5):1620-1628. [43] KERNS J, PIPONOV H, HELDER C, et al. Mechanical Properties of the Human Tibial and Peroneal Nerves Following Stretch With Histological Correlations. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2019;302(11):2030-2039. [44] LIU S, LIU S, GU F, et al. Novel screw-cable integrated system(SCIS) for minimally invasive treatment of patella transverse fractures: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):818. |
| [1] | Xu Hao, Ding Lu, Li Xiao. Investigating the effect of the mechanical wear on abutment screw in Morse taper connection implant implant system by using finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Zhang Hao, Wang Qing, Zhang Jian, Li Guangzhou, Wang Gaoju. Comparison of posterior C2-3 fixation combined with bucking bar technique and posterior C2-3 fixation alone in treatment of unstable Hangman fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1848-1854. |
| [3] | Su Lintao, Jiang Jianfeng, Ma Jun, Huang Liangliang, Lei Changyu, Han Yaozheng, Kang Hui. Precise application of O-arm navigation system in thoracolumbar fractures with developmental pedicle stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1855-1862. |
| [4] | Gao Zhenyang, Zeng Xiuan, Yang Qibing, Kou Xianshuai, Wang Kejing, Li Meng. Computer-simulated repositioning combined with pelvic reduction frame for treatment of anteroposterior compression-III pelvic fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1870-1875. |
| [5] | Zhou Jiajun, Ma Fei, Leng Yebo, Xu Shicai, He Baoqiang, Li Yang, Liao Yehui, Tang Qiang, Tang Chao, Wang Qing, Zhong Dejun. Assessing distribution characteristics and clinical significance of vertebral fractures in patients with osteoporosis based on whole spine MRI [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1883-1889. |
| [6] | Sun Xiaojun, Wang Huaming, Zhang Dehong, Song Xuewen, Huang Jin, Zhang Chen, Pei Shengtai. Effect of finite element method in treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1897-1904. |
| [7] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [8] | Li Liangkui, Huang Yongcan, Wang Peng, Yu Binsheng. Effect of anterior controllable anteriodisplacement and fusion on vertebrae-ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament complex and implants: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1761-1767. |
| [9] | Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao. Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1768-1774. |
| [10] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [11] | Chen Xi, Tang Tao, Chen Tongbing, Li Qing, Zhang Wen. Mechanical stability of intertrochanteric fracture of femur with different internal fixation systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1783-1788. |
| [12] | Fu Enhong, Yang Hang, Liang Cheng, Zhang Xiaogang, Zhang Yali, Jin Zhongmin. OpenSim-based prediction of lower-limb biomechanical behavior in adolescents with plantarflexor weakness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1789-1795. |
| [13] | Huang Haobo, Liang Xinyuan, Ye Guozhong, Xie Qingxiang, Su Boyuan. Suture tape and headless compression screws in treatment of Lisfranc injury with comminuted fractures of the first and second proximal metatarsal bones [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1803-1809. |
| [14] | Liu Yan, Wang Kai, Wu Min. Relationship between coronal angle fluctuation of ankle point and recovery of joint function after ankle fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1820-1826. |
| [15] | Lu Jieming, Li Yajing, Du Peijie, Xu Dongqing. Effects of artificial turf versus natural grass on biomechanical performance of the lower limbs in young females during jump-landing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1101-1107. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||