Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (15): 3253-3261.doi: 10.12307/2025.807
Previous Articles Next Articles
Characteristics and advantages in finite element analysis techniques in knee biomechanics
Guo Huanxuan1, Kang Zhijie2, Bai Xiaolong1, Tian Xiaoyan1, Jin Feng1
- 1Department of Diagnostic Imaging, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 2Graduate School of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-05-22Accepted:2024-07-01Online:2025-05-28Published:2024-11-06 -
Contact:Jin Feng, Chief physician, Department of Diagnostic Imaging, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Guo Huanxuan, Master candidate, Department of Diagnostic Imaging, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Health Science and Technology Project of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, No. 202201266 (to JF); Joint Project of Inner Mongolia Medical University, No. YKD2021LH008 (to JF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guo Huanxuan, Kang Zhijie, Bai Xiaolong, Tian Xiaoyan, Jin Feng. Characteristics and advantages in finite element analysis techniques in knee biomechanics[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(15): 3253-3261.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
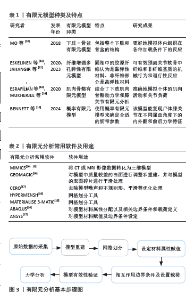
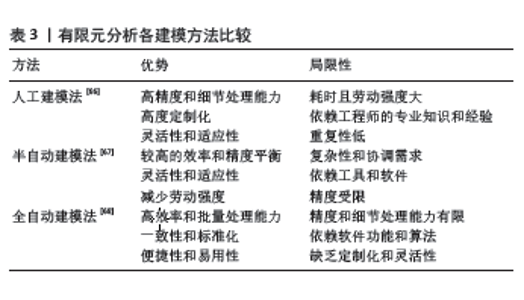
2.1 膝关节有限元模型的构建 膝关节的有限元模型是一种数值模拟工具,可以提供常规影像资料以外的力学生物特征资料,帮助临床医生更好地了解疾病的力学机制,评估不同治疗方法的效果以及制定个性化治疗方案,为膝关节疾病的临床治疗和预防提供理论支持。随着计算机技术的不断发展,膝关节有限元模型变得更加精细化,从二维线性模型发展到三维非线性模型;从单独的骨性结构发展到包括半月板、韧带及关节软骨等软组织在内的解剖模型;从静态分析到动态分析,使得研究者们更全面地理解膝关节的生物力学行为。 目前常见的膝关节有限元模型有下肢-骨盆有限元模型、纤维增强多孔弹性有限元模型、肌肉骨骼有限元模型和概率有限元模型等[10-15],详情见表1。构建有限元模型软件种类繁多,常用软件是Mimics,Geomagic,Hypermensh和Abaqus软件[16-18],具体用途详见表2,有限元分析基本步骤包括7个重要步骤:收集影像学数据、重建有限元模型、有限元模型网格化、材料属性定义、设定载荷及应力方向、模型有效性验证、有限元计算,见图3。其中计算机断层扫描(computed tomography,CT)图像、核磁共振成像(magnetic resonance imaging,MRI)图像为重要的数据来源,CT能清晰地显示骨组织的形态及病变,具有定位精确和空间分辨率高等优势;MRI对关节软骨、半月板、韧带等软组织结构分辨率高,可对人体组织进行三维成像[19-20]。最早由于受到影像技术的限制,是由成人的X射线图像提供影像数据,所构建的是膝关节2D模型[8]。随着影像技术和计算机技术的进步,BENDJABALLAH等[21]应用CT图像和测量方法构建了膝关节有限元模型。之后PE?A等[22]开始使用MRI获取更加准确、涵盖更多解剖部位的影像学数据,利用CT和MRI图像建立了包括膝关韧带在内的更完整的三维模型,使膝关节的模型更接近人体的真实结构。"

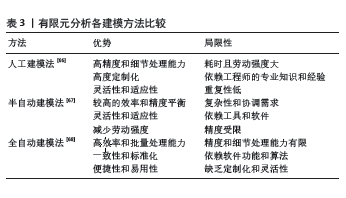
为了准确显示膝关节骨性结构和非骨性结构的特定解剖学特征,研究者利用图像配准融合技术,将CT和MRI影像数据相结合,得到完整、精准的膝关节三维模型[23]。 而建立准确可靠的有限元模型是评估膝关节生物力学特征的关键,其中网格划分、材料属性、参数设定和边界条件是构建精确模型的重要因素。Geomagic和Hypermesh 软件是目前常用的有限元网格划分软件,网格划分通常采用四面体或六面体单元,网格划分的单元数量越多,计算精度越高,相应的计算数量、研究时间及成本也越多,因此网格划分需考虑结构的复杂性和计算的准确性,目前研究都简化操作步骤,将不同组织结构视为各向同性、均匀、连续的线弹性材料,以构建简单的膝关节有限元模型,但这种简化的模型只能提供膝关节力学行为的近似信息,而不能完全真实反映其生物力学特点[24]。因此,国内外研究者不断改进模型,考虑膝关节结构的复杂性,将简单的单一均质、各向同性材料转向非均质、多属性、各向异性材料,从而准确地探究膝关节的生物力学特 征[25]。LAMPEN等[26]通过T2弛豫时间来定义关节软骨材料属性,相较于均匀材料模型,此模型在大多数软骨区域表现出更高的主应力和剪切应变。此外,研究表明,通过利用T2弛豫时间细化材料属性构建的有限元模型可用于预测哪些区域可能因为应力集中而容易发生组织结构改变,从而有助于临床医生在病变尚未显著之前进行临床干预[27]。 然而,膝关节有限元模型生物材料参数的设定仍缺乏统一的标准,国内研究多参照国外文献设定的参数,但不同年龄段、不同人群的解剖结构、生理特征存在差异,会影响模型的构建及生物力学分析结果的准确性。此外,目前构建的膝关节有限元模型大多基于青壮年,仅有少部分研究基于儿童与老年人,KARIMI DASTGERDI等[28]和MALLINOS等[29]开发了儿童膝关节有限元模型,有助于了解各种儿童膝关节损伤机制。有限元模型的有效性验证是确保力学分析结果科学性的关键步骤,有效性验证虽缺乏统一的标准,但通常可以通过生物力学实验或文献中已验证的膝关节有限元模型进行比较验证。例如SUN等[30]构建了肥胖儿童内翻膝关节的模型,通过与传统的运动学测量方法对比来验证其有效性。张刘会等[31]将有限元模型在特定工况下的活动范围与尸体标本生物力学实验结果进行比较,从而验证了模型的有效性。这样的验证过程确保了有限元模型的可靠性,使其在生物力学研究和临床应用具有很高的可信度。目前,膝关节有限元模型的精细化和复杂性方面的研究已有显著进步,在膝关节疾病研究和临床治疗方面发挥了重要作用,但仍需加强针对不同年龄段和不同人群的模型构建,进一步探索膝关节生物力学特征。 2.2 有限元分析法在膝骨关节炎的应用 膝骨关节炎是膝关节最常见的慢性疾病之一,据报道是全球致残的主要原因之一[32]。45岁以上的成年人每5人中约有一人患病[33]。膝骨关节炎引起的关节僵硬、慢性疼痛和功能障碍会严重影响患者的生活质量及身心健康[34]。膝关节的生物力学主要依赖于正常软组织的结构或功能,在正常的膝关节中,内侧和外侧间室的应力分布相对平衡,这有助于膝关节在各种活动中均匀地分散载荷[35]。无论是由于外部创伤和疾病还是其他因素引起的膝关节软组织损伤或结构的改变,都可能导致关节内的载荷分配发生变化,无法维持正常的平衡状态,导致膝骨关节炎的发生或病情加重。该疾病是以关节软骨、软骨下骨的退行性改变和滑膜炎症为特征性改变[36]。因此,了解膝关节退变的生物力学因素对于制定有效的预防或治疗策略至关重要。有限元分析法已广泛应用于膝骨关节炎的病因研究、保守治疗及手术治疗。 2.2.1 有限元分析法在膝骨关节炎发病机制中的应用 关节软骨及半月板对膝骨关节炎的影响:关节软骨的机械性退变是膝骨关节炎的标志,也是关节功能障碍的主要原因[36]。关节软骨的完整性影响着关节的稳定性和承载能力,前人研究表明了当发生膝骨关节炎,关节软骨厚度减少和表面磨损不光整等几何形状的变化会显著降低半月板载荷传递的作用及改变半月板与软骨之间的接触面积[37]。半月板在保护关节软骨方面起着重要作用,它具有分布压力、吸收冲击、增强一致性以及稳定关节的功能[38-39]。WILLINGER等[40]研究发现行膝关节半月板切除后膝骨关节炎的患病率增高,因此半月板切除术后的康复治疗是研究重点。DASZKIEWICZ等[41]发现膝骨关节炎患者由于关节软骨几何结构发生变化,使得内侧半月板后部环向应力增加,因此发生内侧半月板径向撕裂的概率增大。然而,外伤性半月板纵向撕裂后会改变关节间隙,增加股骨和胫骨软骨下骨的应力,这会加速骨关节炎的发展[42]。因此,膝关节内各解剖结构存在相互作用的载荷分布,软骨损伤会加重半月板损伤,同时,半月板损伤能导致软骨损伤,两者之间存在紧密的相互依赖和影响的关系,共同促进膝骨关节炎的 发生。 韧带及骨对膝骨关节炎的影响:前交叉韧带通过抑制胫骨相对于股骨的过度向前运动以及防止膝关节的过伸和限制胫骨的内旋来维持膝关节的稳定性[43],DONG等[44]利用正常膝关节影像资料构建的有限元模型可模拟前交叉韧带损伤,行应力分析后发现前交叉韧带损伤可引起膝关节屈曲时股骨和胫骨相对位移增大,影响股骨远端与胫骨平台关节软骨接触摩擦运动的稳定性,表现出关节软骨的应力增加和峰值应力集中的重新分布,损害了关节软骨的自然生理和生物特性,从而促进了膝骨关节炎的进展。CHEUNG等[45]研究发现前交叉韧带撕裂患者行韧带重建术后半数患者在10-14年内会出现明显的膝骨关节炎临床症状,这说明韧带重建术后接受全膝关节置换的患者平均年龄比未接受的患者小10岁。因此SPIERINGS等[46]利用有限元分析法研究发现行前交叉韧带重建术的患者术后膝骨关节炎患病率高的原因除前交叉韧带断裂同时会伴有关节软骨或半月板损伤,另外的原因是移植物的机械性能的改变导致膝关节运动学改变,移植物的刚度降低和松弛度增加会增加关节前滑和内旋,这些运动是前交叉韧带所限制的,因此改变了关节的正常运动,增加了关节的不稳定性,引发膝骨关节炎的早期发作。ARJMAND等[47]利用有限元分析法比较了正常人群和膝骨关节炎患者胫骨近端的生物力学差异,发现了膝骨关节炎患者胫骨近端的最小主应力较高,这有助于膝骨关节炎患者早期制定治疗策略。 综上所述,通过有限元分析研究,膝关节各解剖结构间复杂的相互作用和对膝骨关节炎的影响得以揭示,当膝关节内部的正常载荷分配平衡发生改变时,会导致关节软骨的过度载荷及部分区域的负荷下降,关节软骨长期在异常应力作用下会产生变形及磨损,最终导致缺失,这有助于制定更精准的诊断和治疗策略。 2.2.2 有限元分析法在膝骨关节炎保守治疗中的应用 过去数十年间世界各地为改善膝骨关节炎的进展制定了多种治疗策略。在膝骨关节炎的初期,临床医生提倡保守治疗以减轻患者症状、改善功能及延缓病情进展。保守治疗方法主要包括药物治疗和物理治疗,药物治疗在膝骨关节炎管理中扮演着重要角色,例如非类固醇类抗炎药等被广泛应用于缓解疼痛和减轻炎症,然而药物只能缓解膝关节炎患者疼痛的症状,无法延缓病情的进展,并且可能会引起药物的依赖性。随着生物力学理论的深入理解,物理治疗方法变得越来越受重视。物理治疗旨在通过康复运动、器械辅助来改善关节功能,以增强关节稳定性,从而提高患者生活质量[48]。LIU等[49]采用有限元法分析了陈氏太极拳典型下肢运动中膝关节软骨和半月板的负荷和应力分布,结果发现陈氏太极拳的特定动作中,例如单鞭、搂膝拗步与行走相比,可降低胫骨股骨内侧与总接触力的比率,有助于改善应力分布,并且适度的机械应力有利于保持软骨基质合成代谢和分解代谢之间的平衡,有助于软骨的健康和完整性,此外,特定动作可以增强膝关节周围的肌肉力量和平衡能力,因此,有助于预防和缓解轻度膝关节内侧骨关节炎。然而,该研究受试者主要为青壮年,后续研究应该包括不同年龄段的患者做进一步探究,以全面评估陈氏太极拳对不同年龄段人群的膝关节生物力学影响。 步态调整是一种重要的物理治疗方法,它通过改变膝关节内外侧接触力分布,缓解患者疼痛、改善膝关节的功能。ESRAFILIAN等[50]结合了运动学分析和有限元分析法,研究了两种不同的常规步态条件(即赤足和穿鞋)和6种步态调整(即 0°,5° 和 10°外侧楔形鞋垫、趾入、趾出和宽站立)对膝关节软骨组织力学的影响,“趾入”“趾出”和“大步”中胫骨内侧和股骨软骨的力学变化明显。步态调整能有效改变胫骨内侧软骨的最大主应力和剪切应变,但由于个体差异,个性化步态调整会对膝关节的组织力学特征产生不同影响,因此在评估疾病时,应根据患者实际情况制定个性化的治疗方案。综上所述,有限元分析研究为理解膝关节在物理治疗手段的力学响应提供了重要见解,有助于临床个体化的治疗方案,然而这些研究仍需在不同年龄段和更广泛的人群进行验证,以确保治疗方案的普遍性和有效性。 2.2.3 有限元分析法在膝骨关节炎手术治疗中的应用 由于关节软骨不可再生,膝骨关节炎是一种不可逆性的疾病,当疾病发展至终末期,人工膝关节置换是治疗严重膝骨关节炎的首选方法[51]。人工膝关节置换可以减轻膝骨关节炎患者的疼痛,改善身体功能和生活质量[52],但术后患者会出现功能障碍和并发症[53]。在植入假体治疗中,如果假体的弹性模量高于周围骨组织,这会导致应力集中在植入的假体上,会出现应力屏蔽现象,导致周围骨组织吸收,引起骨萎缩及假体松动,而假体松动及假体磨损等术后并发症是骨科医生面临的重大挑战。为了避免和改善这些问题,国内外学者使用有限元分析法进行相关研究,STODDART等[54]通过有限元分析法研究不同膝关节置换方案对骨负荷转移的影响,研究结果显示,全膝关节置换导致的平均应力屏蔽比部分膝关节置换和多间室膝关节置换高出3倍以上,这会导致假体承担了大部分的应力,从而减少了邻近骨骼的应力,导致骨骼的负载减少,这会影响骨骼的正常生长和重建,最终导致假体无菌松动。 而有限元分析法可以帮助改进假体设计,以减少应力集中和磨损,提高假体与骨骼之间的支配性,从而提高手术成功率并延长假体的使用寿命。ZHAO等[55]使用有限元分析法评估正常骨密度受试者和骨质疏松患者中聚醚醚酮和CoCr合金植入物的生物力学性能,结果显示在正常胫骨中,聚醚醚酮和CoCr合金胫骨植入物的应力分布和应力屏蔽程度相似,但聚醚醚酮植入物的应力峰值较低,在骨质疏松患者的胫骨模型中,聚醚醚酮植入物相比CoCr合金植入物在胫骨平台显示出更高的等效应力,减少了应力屏蔽区域,因此可以更好地维持生理条件下的负载平衡,有利于保护植入物周围的骨组织,所以聚醚醚酮有望成为全膝关节置换中的一种替代材料。FILIP等[56]通过有限元法分析在静态和动态压力下有/无胫骨干延长部对于膝关节应力的影响,结果表明在结构受损的骨骼中添加胫骨干延长部,在静态和动态状况下均可使压缩疲劳减少1/2,因此,对于骨骼物理性质降低的患者,应使用胫骨干延长部增强关节稳定性、固定性及延长假体的寿命。 有限元分析法还可帮助外科医生规划最佳的假体位置和固定方式,以减少术后并发症。BORI等[57]对膝关节股骨假体柄进行的有限元分析法发现,压入式骨干的应力屏蔽效应更大,比骨水泥固定的应力屏蔽高出38.5%,骨水泥结构比压入式结构引起的微动较低,因此骨水泥固定比压入式固定更有优势。综上所述,有限元分析法在膝骨关节炎的治疗中发挥着重要作用,不仅可以帮助临床医生更好地理解膝关节力学特征,指导治疗方案的制定,提高患者的治疗效果,还有助于优化人工膝关节置换的假体设计,提高假体使用寿命,减少术后并发症。然而有限元分析法在临床应用中的普及仍面临操作复杂性等挑战,后续研究应进一步简化操作步骤,以便更多临床医生使用。 2.3 有限元分析法在膝关节胫骨平台骨折中的应用 胫骨平台是膝关节重要的承重结构,胫骨平台骨折是临床常见的膝关节损伤,占成人骨折的1%-2%[58]。由于胫骨平台骨折属于关节内骨折,需恢复关节面的解剖结构以及正常下肢稳定的关节功能,并且尽可能的恢复膝关节的负重和运动功能,因此治疗难度大。如果处理不当,患者在治疗后易出现创伤性关节炎、畸形愈合和膝关节不稳定等严重的功能障碍[59]。有限元分析法可以在术前对骨折进行三维重建、数据测量和模拟手术,并优化计算机辅助计划和手术技术,显著提高手术治疗效果,有利于减少术后并发症[60]。Schatzker Ⅱ型是胫骨平台骨折中最常见的类型,其特点是胫骨外侧平台劈裂合并中央塌陷骨折,因此治疗时需要填充物进行固定增量,以填补骨内空隙,并为关节面提供机械支撑。BELAID等[61]通过有限元分析法证明,骨水泥增量可以提高种植体的稳定性,降低再次塌陷的风险。上述研究虽然比较了不同类型填充物的效果,但研究疾病单一,并没有考虑到Schatzker Ⅱ型自身的形态多样性,骨折形态的多样性会影响术后关节的稳定性。ZENG等[62]通过改变碎片的大小来代表4种不同的骨折亚型,每个亚型使用了螺钉结合不同类型类型的填充物进行固定,通过计算螺钉的应力分布、凹陷碎片的应变分布,以评估植入物的稳定性和二次下陷的风险,从中得出无论是何种亚型缺损部位使用填充物都可以有效减少种植体应力集中和塌陷块的减少,为治疗Schatzker Ⅱ型骨折提供良好的稳定性;但对于不同亚型填充物的模量对稳定性的影响不同,因此应在患者术前根据影像等数据,选择合适的填充物硬度。有限元分析法不仅可以指导手术材料的选择,还可指导患者术式的选择。FERRE等[63]利用有限元技术对Schatzker Ⅴ型胫骨平台的冲击性骨折行生物力学研究,分析两种不同固定方法后发现与有限接触动态加压钢板相比,锁定加压钢板在骨折部位的骨块之间具有更小的相对位移,从而提供了更好的稳定性和低组织应变,这有利于骨的生成,因此,对于Schatzker Ⅴ型胫骨平台骨折锁定加压钢板固定效果更好。综上所述,有限元分析法为膝关节损伤的治疗提供了有力的科学支持,优化了治疗方案,提升患者手术治疗效果。 2.4 人工智能在膝关节有限元分析领域的研究进展 智能化是有限元分析领域发展的必然趋势,人工智能是一门将计算机科学与大量数据集结合起来的学科,用于模仿人类的智能[64]。深度学习作为人工智能最为广泛的一种人工智能技术,极大地推动了计算机科学的发展[65]。构建膝关节有限元模型的方法主要有人工建模法、半自动建模法和全自动建模法[66-68],见表3。从影像图像中精确分割出膝关节的各解剖结构对于构建模型非常重要,手动分割是最传统的方法,但由于手动分割耗时大、效率低,并且分割的质量取决于操作者的专业知识及经验,容易因阈值设定不当引起结构的丢失,因此受到很大限制。近年来,人工智能技术的出现,为有限元模型的构建提供了新的思路,人工智能广泛应用于图像分割,节省了人工分割的时间,其准确率与手工分割相当。KAKAVAND等[69]有效整合了深度学习和有限元建模技术,将Swin UNETR与统计形状建模结合,研发了一个半自动化方法来分割膝关节并构建生物力学模型,Swin UNETR用于初步的3D分割,统计形状建模用于进一步模型表面的优化处理,与传统的手动分割相比,这种半自动化方法显著提高了分割效率,同时提高了模型的精确度,为膝关节疾病的诊治提供了精确的技术支持。BURTON等[70]提出了一种基于卷积神经网络的半监督学习方法,用于分割MRI图像中膝关节解剖结构,显著提高了图像分割的准确性和效率。AX-FEM是一个开源的有限元方法库。JAX-FEM能够利用GPU加速进行高性能数值计算,并采用了自动微分技术,可以自动化设置和解决有限元分析问题中的许多复杂步骤。因此,JAX-FEM能够快速模拟复杂的生物结构(如膝关节),协助临床实现个性化医学、外科计划和医疗设备设计[71]。另有研究表明,自动病灶分割是一个尚未解决的问题,因此,使用深度学习技术进行病变特征量化仍然具有挑战性[72]。人工智能除了在有限元建模过程中展现出很大优势外,PAZ等[73]提出了一种基于模板的有限元建模方法,通过结合神经网络预测的膝关节在行走过程中的最大载荷,结合个体的软骨厚度,可对膝骨关节炎发展准确预测,此方法减少了传统方法中对复杂运动的捕捉,并提高了软骨图像分割的效率。 综上所述,人工智能在有限元分析领域展现出了巨大价值,特别是在自动化建模、提高分割准确性、个性化医疗方面,未来随着人工智能技术的不断进步和完善,可进一步探索人工智能在膝关节有限元分析的应用潜力,提升有限元模型构建的精确度和实用性,促进其在临床实践中更广泛的应用。"
| [1] BENOS L, STANEV D, SPYROU L, et al. A review on finite element modeling and simulation of the anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:967. [2] HASSEBROCK JD, GULBRANDSEN MT, ASPREY WL, et al. Knee ligament anatomy and biomechanics. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2020;28(3): 80-86. [3] YAN M, LIANG T, ZHAO H, et al. Model properties and clinical application in the finite element analysis of knee joint: a review. Orthop Surg. 2024;16(2):289-302. [4] POPESCU R, HARITINIAN EG, CRISTEA S. Relevance of finite element in total knee arthroplasty-literature review. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2019; 114(4):437-442. [5] WELCH-PHILLIPS A, GIBBONS D, AHERN DP, et al. What is finite element analysis? Clin Spine Surg. 2020;33(8):323-324. [6] BREKELMANS WA, POORT HW, SLOOFF TJ. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972; 43(5):301-317. [7] RYBICKI EF, SIMONEN FA, WEIS EB JR. On the mathematical analysis of stress in the human femur. J Biomech. 1972;5(2):203-215. [8] CHAND R, HAUG E, RIM K. Stresses in the human knee joint. J Biomech. 1976;9(6):417-422. [9] SHU L, YAMAMOTO K, YOSHIZAKI R, et al. Multiscale finite element musculoskeletal model for intact knee dynamics. Comput Biol Med. 2022;141:105023. [10] MO F, LI F, BEHR M, et al. A lower limb-pelvis finite element model with 3D active muscles. Ann Biomed Eng. 2018;46(1):86-96. [11] ESKELINEN ASA, TANSKA P, FLOREA C, et al. Mechanobiological model for simulation of injured cartilage degradation via pro-inflammatory cytokines and mechanical stimulus. PLoS Comput Biol. 2020;16(6):e1007998. [12] JAHANGIR S, ESRAFILIAN A, EBRAHIMI M, et al. Sensitivity of simulated knee joint mechanics to selected human and bovine fibril-reinforced poroelastic material properties. J Biomech. 2023; 160:111800. [13] ESRAFILIAN A, STENROTH L, MONONEN ME, et al. EMG-assisted muscle force driven finite element model of the knee joint with fibril-reinforced poroelastic cartilages and menisci. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):3026. [14] MUKHERJEE S, NAZEMI M, JONKERS I, et al. Use of computational modeling to study joint degeneration: a review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:93. [15] BENNETT KJ, FOROUTAN P, FAIRWEATHER E, et al. Development and validation of a biomechanically fidelic surgical training knee model. J Orthop Res. 2024. doi:10.1002/jor.25873. [16] REN S, SHI H, LIU Z, et al. Finite element analysis and experimental validation of the anterior cruciate ligament and implications for the injury mechanism. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022;9(10):590. [17] 刘清华,蔡永强,金凤,等.CT数据建立12岁儿童全颈椎有限元模型及有效性验证[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(4):500-504. [18] ZHU LY, LI L, LI ZA, et al. Design and biomechanical characteristics of porous meniscal implant structures using triply periodic minimal surfaces. J Transl Med. 2019;17(1):89. [19] SODHI N, JACOFSKY DJ, CHEE A, et al. Benefits of CT scanning for the management of knee arthritis and arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2021; 34(12):1296-1303. [20] OMOUMI P, MERCIER GA, LECOUVET F, et al. CT arthrography, MR arthrography, PET, and scintigraphy in osteoarthritis. Radiol Clin North Am. 2009;47(4):595-615. [21] BENDJABALLAH MZ, SHIRAZI-ADL A, ZUKOR DJ. Finite element analysis of human knee joint in varus-valgus. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 1997;12(3):139-148. [22] PEÑA E, CALVO B, MARTÍNEZ MA, et al. A three-dimensional finite element analysis of the combined behavior of ligaments and menisci in the healthy human knee joint. J Biomech. 2006;39(9):1686-1701. [23] DONG Y, MOU Z, HUANG Z, et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction of subject-specific knee joint using computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging image data fusions. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2013;227(10):1083-1093. [24] 张吉超,董万鹏,董跃福,等.膝关节有限元模型参数设置[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(30):4781-4786. [25] LIU W, SUN X, LIU W, et al. Finite element study of a partial meniscectomy of a complete discoid lateral meniscus in adults. Med Eng Phys. 2022;107:103855. [26] LAMPEN N, SU H, CHAN DD, et al. Finite element modeling with subject-specific mechanical properties to assess knee osteoarthritis initiation and progression. J Orthop Res. 2023;41(1):72-83. [27] LAMPEN N, SU H, CHAN DD, et al. T2 mapping refined finite element modeling to predict knee osteoarthritis progression. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2021;2021:4592-4595. [28] KARIMI DASTGERDI A, ESRAFILIAN A, CARTY CP, et al. Validation and evaluation of subject-specific finite element models of the pediatric knee. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):18328. [29] MALLINOS A, JONES K, DAVIS B. Pivot shift and lachman test simulation-based exploration in juvenile populations for accurately predicting anterior tibial translation. J Biomech. 2022;136:111069. [30] SUN J, YAN S, JIANG Y, et al. Finite element analysis of the valgus knee joint of an obese child. Biomed Eng Online. 2016;15(Suppl 2):158. [31] 张刘会,刘丹平.膝关节三维有限元模型建立和验证及模拟后交叉韧带重建术[J].生物医学工程与临床,2020,24(5):508-513. [32] CROSS M, SMITH E, HOY D, et al. The global burden of hip and knee osteoarthritis: estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(7):1323-1330. [33] LAWRENCE RC, FELSON DT, HELMICK CG, et al. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the united states. part II. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(1):26-35. [34] IIJIMA H, AOYAMA T, FUKUTANI N, et al. Psychological health is associated with knee pain and physical function in patients with knee osteoarthritis: an exploratory cross-sectional study. BMC Psychol. 2018;6(1):19. [35] 黄振宇,董跃福,胡广洪,等.基于有限元方法的正常和早期OA膝关节生物力学行为比较[J].中国数字医学,2015,10(5):6-9. [36] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and treatment of hip and knee osteoarthritis: a review. JAMA. 2021;325(6):568-578. [37] ŁUCZKIEWICZ P, DASZKIEWICZ K, CHRÓŚCIELEWSKI J, et al. The influence of articular cartilage thickness reduction on meniscus biomechanics. PLoS One. 2016;11(12):e0167733. [38] KRAUSE WR, POPE MH, JOHNSON RJ, et al. Mechanical changes in the knee after meniscectomy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976;58(5): 599-604. [39] WALKER PS, ERKMAN MJ. The role of the menisci in force transmission across the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1975;(109): 184-192. [40] WILLINGER L, FOEHR P, ACHTNICH A, et al. Effect of lower limb alignment in medial meniscus-deficient knees on tibiofemoral contact pressure. Orthop J Sports Med. 2019;7(2): 2325967118824611. [41] DASZKIEWICZ K, ŁUCZKIEWICZ P. Biomechanics of the medial meniscus in the osteoarthritic knee joint. Peer J. 2021;9:e12509. [42] LI L, YANG X, YANG L, et al. Biomechanical analysis of the effect of medial meniscus degenerative and traumatic lesions on the knee joint. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(2):542-556. [43] PERRIMAN A, LEAHY E, SEMCIW AI. The effect of open- versus closed-kinetic-chain exercises on anterior tibial laxity, strength, and function following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2018;48(7): 552-566. [44] DONG Z, YANG C, ZHANG D, et al. The application of human medical image-based finite element analysis in the construction of mouse osteoarthritis models. Heliyon. 2024;10(4):e26226. [45] CHEUNG EC, DILALLO M, FEELEY BT, et al. Osteoarthritis and ACL reconstruction-myths and risks. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2020; 13(1):115-122. [46] SPIERINGS J, VAN DEN HENGEL M, JANSSEN RPA, et al. Knee instability caused by altered graft mechanical properties after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: the early onset of osteoarthritis? Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1244954. [47] ARJMAND H, NAZEMI M, KONTULAINEN SA, et al. Mechanical metrics of the proximal tibia are precise and differentiate osteoarthritic and normal knees: a finite element study. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):11478. [48] NGUYEN C, LEFÈVRE-COLAU MM, POIRAUDEAU S, et al. Rehabilitation (exercise and strength training) and osteoarthritis: a critical narrative review. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2016;59(3):190-195. [49] LIU H, GONG H, CHEN P, et al. Biomechanical effects of typical lower limb movements of chen-style tai chi on knee joint. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2023;61(11):3087-3101. [50] ESRAFILIAN A, HALONEN KS, DZIALO CM, et al. Effects of gait modifications on tissue-level knee mechanics in individuals with medial tibiofemoral osteoarthritis: a proof-of-concept study towards personalized interventions. J Orthop Res. 2024;42(2):326-338. [51] HUNTER DJ, FELSON DT. Osteoarthritis. BMJ. 2006;332(7542):639-642. [52] SHAN L, SHAN B, GRAHAM D, et al. Total hip replacement: a systematic review and meta-analysis on mid-term quality of life. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(3):389-406. [53] WISE BL, NIU J, FELSON DT, et al. Functional impairment is a risk factor for knee replacement in the multicenter osteoarthritis study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(8):2505-2513. [54] STODDART JC, GARNER A, TUNCER M, et al. Load transfer in bone after partial, multi-compartmental, and total knee arthroplasty. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1274496. [55] ZHAO G, LUO J, MA J, et al. Decreased stress shielding with poly-ether-ether-ketone tibial implant for total knee arthroplasty - A preliminary study using finite element analysis. Heliyon. 2024; 10(5):e27204. [56] FILIP AC, CUCULICI SA, CRISTEA S, et al. Tibial stem extension versus standard configuration in total knee arthroplasty: a biomechanical assessment according to bone properties. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022; 58(5):634. [57] BORI E, ARMAROLI F, INNOCENTI B. Biomechanical analysis of femoral stems in hinged total knee arthroplasty in physiological and osteoporotic bone. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022; 213:106499. [58] LI K, ZHANG S, QIU X, et al. Optimal surgical timing and approach for tibial plateau fracture. Technol Health Care. 2022;30(S1): 545-551. [59] PARKKINEN M, LINDAHL J, MÄKINEN TJ, et al. Predictors of osteoarthritis following operative treatment of medial tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 2018;49(2):370-375. [60] SHEN QJ, ZHANG JL, XING GS, et al. Surgical treatment of lateral tibial plateau fractures involving the posterolateral column. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(6):1029-1038. [61] BELAID D, VENDEUVRE T, BOUCHOUCHA A, et al. Utility of cement injection to stabilize split-depression tibial plateau fracture by minimally invasive methods: a finite element analysis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2018;56:27-35. [62] ZENG C, REN X, XU C, et al. Stability of internal fixation systems based on different subtypes of schatzker II fracture of the tibial plateau: a finite element analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022; 10:973389. [63] FERRE LS, DI NISIO FG, MENDONÇA CJA, et al. Comparative analysis of tibial plateau fracture osteosynthesis: a finite element study. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2022;134:105392. [64] ZUHAIR V, BABAR A, ALI R, et al. Exploring the impact of artificial intelligence on global health and enhancing healthcare in developing nations. J Prim Care Community Health. 2024;15:21501319241245847. [65] LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, HINTON G. Deep learning. Nature. 2015;521(7553): 436-444. [66] BARTEL DL, BURSTEIN AH, SANTAVICCA EA, et al. Performance of the tibial component in total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982;64(7):1026-1033. [67] GALBUSERA F, CINA A, PANICO M, et al. Image-based biomechanical models of the musculoskeletal system. Eur Radiol Exp. 2020;4(1):49. [68] CAPRARA S, CARRILLO F, SNEDEKER JG, et al. Automated pipeline to generate anatomically accurate patient-specific biomechanical models of healthy and pathological fsus. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:636953. [69] KAKAVAND R, PALIZI M, TAHGHIGHI P, et al. Integration of swin unetr and statistical shape modeling for a semi-automated segmentation of the knee and biomechanical modeling of articular cartilage. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):2748. [70] BURTON W 2ND, MYERS C, RULLKOETTER P. Semi-supervised learning for automatic segmentation of the knee from MRI with convolutional neural networks. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020;189:105328. [71] XUE T, LIAO S, GAN Z, et al. JAX-FEM: a differentiable gpu-accelerated 3D finite element solver for automatic inverse design and mechanistic data science. Comput Phys Comm. 2023;291:108802. [72] ATAEI A, EGGERMONT F, VERDONSCHOT N, et al. The effect of deep learning-based lesion segmentation on failure load calculations of metastatic femurs using finite element analysis. Bone. 2024;179: 116987. [73] PAZ A, LAVIKAINEN J, TURUNEN MJ, et al. Knee-loading predictions with neural networks improve finite element modeling classifications of knee osteoarthritis: data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Ann Biomed Eng. 2024. doi:10.1007/s10439-024-03549-2. [74] 陈彦飞,赵勇,鲁超.有限元分析技术在膝关节生物力学研究中的应用现状[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2019,27(8):81-83, 88. [75] ZHANG ZH, QI YS, WEI BG, et al. Application strategy of finite element analysis in artificial knee arthroplasty. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023; 11:1127289. |
| [1] | Xu Hao, Ding Lu, Li Xiao. Investigating the effect of the mechanical wear on abutment screw in Morse taper connection implant implant system by using finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Li Liangkui, Huang Yongcan, Wang Peng, Yu Binsheng. Effect of anterior controllable anteriodisplacement and fusion on vertebrae-ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament complex and implants: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1761-1767. |
| [3] | Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao. Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1768-1774. |
| [4] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [5] | Chen Xi, Tang Tao, Chen Tongbing, Li Qing, Zhang Wen. Mechanical stability of intertrochanteric fracture of femur with different internal fixation systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1783-1788. |
| [6] | Fu Enhong, Yang Hang, Liang Cheng, Zhang Xiaogang, Zhang Yali, Jin Zhongmin. OpenSim-based prediction of lower-limb biomechanical behavior in adolescents with plantarflexor weakness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1789-1795. |
| [7] | Ma Chi, Wang Ning, Chen Yong, Wei Zhihan, Liu Fengji, Piao Chengzhe. Application of 3D-printing patient-specific instruments combined with customized locking plate in opening wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1863-1869. |
| [8] | Sun Xiaojun, Wang Huaming, Zhang Dehong, Song Xuewen, Huang Jin, Zhang Chen, Pei Shengtai. Effect of finite element method in treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1897-1904. |
| [9] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [10] | Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Wan Haili, Chang Ying, Xiong Wenjuan, Xia Yuan. Effect of neuromuscular exercise for knee osteoarthritis pain and function: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [11] | Yu Jingbang, Wu Yayun. Regulatory effect of non-coding RNA in pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1659-1666. |
| [12] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [13] | Yuan Weibo, Liu Chan, Yu Limei. Potential application of liver organoids in liver disease models and transplantation therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [14] | Wang Juan, Wang Guanglan, Zuo Huiwu. Efficacy of exercise therapy in the treatment of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients: #br# a network meta-analysis #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1714-1726. |
| [15] | Wang Peiguang, Zhang Xiaowen, Mai Meisi, Li Luqian, Huang Hao. Generalized equation estimation of the therapeutic effect of floating needle therapy combined with acupoint embedding on different stages of human knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1565-1571. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||