Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (15): 3244-3252.doi: 10.12307/2025.178
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application and development direction of finite element method in biomechanical analysis of thoracolumbar fractures of the spine
He Kai1, Xing Wenhua2, Li Feng2, Liu Shengxiang2, Bai Xianming2, Zhou Chen2, Gao Xu2, Qiao Yu3, He Qiang1, Gao Zhiyu1, Guo Zhen1, Bao Aruhan1, Li Chade1 #br#
- 1Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010110, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; ²Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010020, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; ³Hohhot First Hospital, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-03-21Accepted:2024-05-14Online:2025-05-28Published:2024-11-06 -
Contact:Xing Wenhua, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010020, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:He Kai, Master candidate, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010110, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:a grant from Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Health Commission, No. 2023SGGZ092 (to XWH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
He Kai, Xing Wenhua, Li Feng, Liu Shengxiang, Bai Xianming, Zhou Chen, Gao Xu, Qiao Yu, He Qiang, Gao Zhiyu, Guo Zhen, Bao Aruhan, Li Chade. Application and development direction of finite element method in biomechanical analysis of thoracolumbar fractures of the spine[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(15): 3244-3252.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
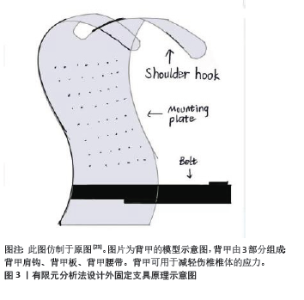
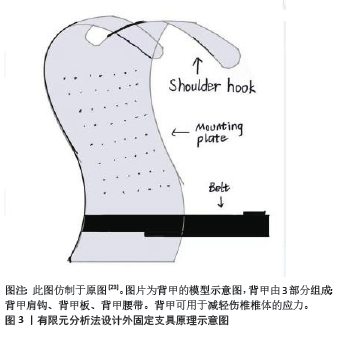
2.1 有限元法在骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折中的应用 胸腰椎单纯压缩性骨折,伤椎的椎体压缩程度小于1/3,且耐受卧床,可采用非手术治疗。保守治疗的主要方法为绝对卧床与佩戴外固定支具,辅以止疼药物等[22]。CHE 等[23]进行了一种新型脊柱保护装置(背甲:背甲肩钩、背甲板、背甲腰带)防治骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折(osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures,OVCFs)的有限元分析。该研究选择1名47岁女性健康志愿者和1名58岁男性L1椎体压缩骨折患者构建T12-L5模型,对模型施加垂直力和扭矩力,研究发现,正常情况下应力主要分布在脊柱的中柱和后柱;当L1椎体前缘骨折塌陷时,由于重心前移,应力分布向前柱移动。后建立了脊柱保护装置的有限元模型,该装置上部是与脊柱支撑板一体并向前延伸的肩钩,下部连接到腰带,当肩钩放在肩膀上并收紧腰带时,向后施加对肩部和腹部的力,同时向前凸出的背甲板对L1周围施加向前的力,经有限元法分析发现,应用新型脊柱保护装置后,中后柱应力呈增大趋势,前柱应力减小,L1、L2椎体终板处的应力均有一定程度的降低,尤其是L1椎体处的应力,L1椎体的最大应力下降了20%。由此得出:新型脊柱保护装置可改变脊柱内的应力分布,有效预防和治疗胸腰椎骨折,尤其是骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折。见图3。"
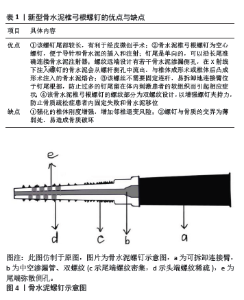
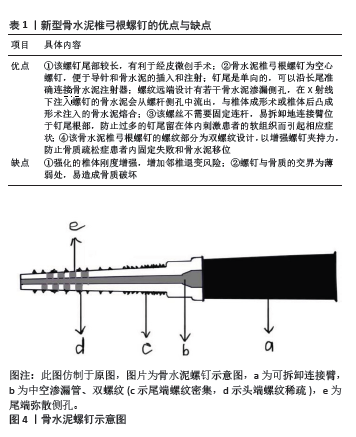
对于胸腰段单纯压缩性骨折,若伤椎的压缩程度大于1/3,往往需要通过手术治疗,骨水泥植入术(即聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯)包括椎体成形术(percutaneous vertebroplasty,PVP)和椎体后凸成形术(percutaneous kyphoplasty,PKP),适用于年龄偏大的患者;而椎弓根螺钉内固定术包括经皮微创和开放手术,适用于全年龄段的患者[24-25]。不同的手术方式治疗效果有何差别?YAN等[26]探究了不同方法治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎椎体压缩骨折的有限元力学表现,该研究对10例骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折患者构建T11-L2模型,其完整纳入了骨松质、骨皮质、韧带、纤维环、髓核、小关节和关节囊结构,依次模拟保守治疗、开放手术(即伤椎骨水泥预填充结合传统椎弓根螺钉固定的6钉2棒技术)、椎体后凸成形术和椎体成形术4种治疗方法,并分析其整体的刚度、抗压强度、椎间隙与小关节的应力变化和最大应力值。研究发现骨水泥治疗组的最大应力、轴向受压强度、轴向受压刚度、横向剪切刚度均明显优于保守治疗组和开放治疗组,且开放治疗组与保守治疗组之间,或椎体后凸成形术与椎体成形术治疗组之间,无统计学差异。由此得出:经皮椎体成形术和经皮椎体后凸成形术不仅满足了胸腰椎正常功能运动学的要求,而且恢复了胸腰椎的稳定性,它们具有良好的生物力学性能和显著的应用效果。有限元分析的应用有助于为骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折的临床治疗选择科学、合理、有效的最佳治疗方案。 当对1例骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折患者进行多次椎体手术时,可能会形成夹心椎骨,这是一种完整的、未加固的椎骨夹在2个骨水泥椎体之间。有人认为夹心椎骨承受双重负荷,并假设比其他椎骨更容易出现继发性骨折,对此HUANG等[27]运用有限元法对夹心椎骨的生物力学进行了研究,该研究对1名健康男性志愿者构建T10-L2模型,并使用67%的正常弹性模量模拟骨质疏松症,使用Materialise Magics 21.0软件对T11和L1椎体模拟骨折线,使用SolidWorks 2021软件模拟T11和L1椎体骨水泥置入,对T10、T11、T12、L1、L2椎体施以6个方向(前屈、后伸、左右侧弯、左右旋转)的大小为6.5 N/m的力矩,计算T10、T12、L2椎体的应力值。研究发现,夹心椎骨T12的应力并不是最大的,骨水泥置入椎的上下邻椎和夹心椎的应力值是随患者的弯曲动作而不断变化的,应力损伤的情况见于长期保持固定不变的姿势,使相应椎体血液供应不足,导致椎体骨质流失和损伤,此时才有可能出现继发性骨折,这种情况在上下邻椎和夹心椎体都有可能发生,发生的部位主要取决于长期不良固定姿势的情况。 骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折绝大多数为年龄偏大的患者,由于这类患者身体一般状况差,对开放手术治疗耐受性也差,且多数患者保守治疗的远期不良并发症会出现胸腰段后凸畸形,故骨水泥置入术是这类患者的较优选择,不仅能短期缓解背痛,还能恢复椎体的高度,但骨水泥的硬度远大于骨质流失的邻近椎体的硬度,行骨水泥置入的椎体往往会对邻椎产生较大的应力,出现邻椎退变的并发症[28]。为了减少骨水泥置入术造成远期对邻椎的不良影响,WANG等[29]进行了椎体成形术最优分布模型的有限元分析,该研究选择了1名健康男性构建T11-L2模型,模拟骨质疏松症、L1椎体骨折和注入2,4,6 mL骨水泥的术后模型,然后在模型表面上施加了300 N垂直向下、10 N向前和10 N向后不同组合的压力模拟站立、前屈、后伸,计算不同条件下伤椎和上下邻椎终板的应力变化。研究发现,生物力学变化的影响可能随着骨水泥注入量的增加而增加,椎体成形术显示4 mL是骨水泥注射的最佳量,在保证复位效果的同时能减少远期邻椎退变的风险。 随着人口老龄化,骨质疏松症给治疗爆裂性胸腰椎骨折患者带来了许多挑战。骨质疏松症削弱了螺钉的夹持力,明显增加了器械失败的风险。据报道,患有骨质疏松症的胸腰椎骨折患者的螺钉松动发生率超过60%[30]。不同后路固定技术治疗爆裂性胸腰椎骨折伴骨质疏松症的应用指南仍未达成共识。ZHANG等[31]运用有限元法做了不同后路固定技术治疗老年骨质疏松症患者胸腰椎爆裂性骨折的生物力学评价。该研究对1例健康男性构建T10-L5模型,并通过降低弹性模量模拟骨质疏松,对L1椎体通过SolidWorks进行V形截骨模拟L1骨质疏松性爆裂骨折,之后比较了后路4种手术方式(长节段固定术、皮质骨螺钉固定术、骨水泥增强椎弓根螺钉固定术、皮质骨螺钉固定结合传统椎弓根钉固定术)的差异。经研究发现,皮质骨螺钉固定术提供了最小的稳定性;骨水泥增强椎弓根螺钉固定术和皮质骨螺钉固定结合传统椎弓根钉固定术具有中等稳定性,长节段固定术提供了最大的稳定性,但同时长节段固定会显著增加杆和邻椎的应力,使断棒和邻椎退变的风险增加;骨水泥增强椎弓根螺钉固定术使钉抗拔出力显著增加,皮质骨螺钉固定结合传统椎弓根钉固定术在使用多个连杆时表现出抗旋转的优越性。骨水泥增强椎弓根螺钉固定术和皮质骨螺钉固定结合传统椎弓根钉固定术可能是骨质疏松症患者爆裂性胸腰椎骨折手术治疗的生物力学优势选择。 一些骨质疏松患者受轻微创伤后,经过数周或数月无症状期后,逐渐形成进行性脊柱后凸畸形,可出现慢性的背部疼痛、活动受限和神经功能障碍,称为库莫氏病,近年来这些患者的数量一直在增加。有学者认为,库莫氏病是椎体压缩性骨折的并发症或终末期临床表现,一旦发病会对患者的生命和生活质量产生严重影响,因此需要更积极的手术治疗[32]。无神经系统症状的库莫氏病Ⅰ,Ⅱ,Ⅲ期患者可采用椎体成形术或椎体后凸成形术等微创手术治疗。但椎体成形术和椎体后凸成形术由于骨折裂缝中间常有包膜存在,不能很好地与周围地骨小梁结合,易出现骨水泥松动,甚至移位和断裂[32]。内固定骨水泥锚定是治疗库莫氏病的一种新方法,椎弓根螺钉的置入技术与椎体成形术相结合,将螺钉的前端置入骨水泥中,与骨水泥融合,以稳定骨水泥块,防止骨水泥松动和移位,目前,骨水泥螺钉在临床上常见,但有待长期观察进行评价[33]。现有的椎弓根骨水泥螺钉不能经皮或微孔置入,螺钉尾部呈较大的U形,会对周围的软组织造成很大的干扰,并会引起一些症状,如疼痛、异物感等。为了解决这些临床难题,XU等[34]设计了一种用于治疗库莫氏病的新型骨水泥椎弓根螺钉并进行了有限元分析。该器械特点见表1。该研究选择1名健康人建立T12-L2模型、依次模拟骨质疏松症、L1椎体的库莫氏病和3种骨水泥手术:单纯经皮椎体成形术(A型)、新型经皮单侧单椎体骨水泥螺钉置入术(B型)、新型经皮双侧单椎体骨水泥螺钉置入术(C型),之后分析整体活动范围、T12椎体下终板应力大小、骨水泥螺钉应力大小、骨水泥应力大小以及骨水泥的位移。结果显示3种术后模型整体活动范围无统计学意义,A、B、C型模型的T12椎体下终板应力依次增大(下终板应力增大代表更多高应力区,伴随更大风险),B型骨水泥螺钉应力大于C型(但未达到危险值),C型骨水泥应力大于B型大于A型,B,C型的骨水泥位移小于A型。综上得出新型微创骨水泥螺钉可有效防止库莫氏病治疗中骨水泥的移位,单侧锚定可达到较好的固定效果,对椎体生物力学性能的影响比双侧锚定小,这为术中器械的选择提供了参考。见图4。"

2.2 有限元法在创伤性胸腰椎骨折的应用 对于临床上相对较少选择的非后路微创通道技术,如前路腰椎椎间融合术、斜外侧椎间融合术,常常用于脊柱的椎间盘退行性疾病,很少用于脊柱骨折[35-36]。REN等[37]发明了一种新型椎体侧方锁定板,对胸腰椎爆裂骨折合并前方神经受压的患者采用了前路手术,并运用有限元法将椎体侧方的新型锁定板与侧方传统的钉杆系统进行了生物力学的对比分析。该研究选择1名健康男性构建T12-L4模型,模拟L2椎体爆裂骨折,分析胸腰椎活动范围和固定装置的应力大小。研究发现,这种新锁定板相较于传统的钉杆系统,操作更容易,与骨面贴合更好,稳定性更好,能分散应力,避免固定装置应力集中,且能减少融合节段,由于融合节段越多,邻近节段疾病的风险越高,故能减少邻近节段疾病的发生,对术后脊柱的活动性影响也较小,是一种有待临床实践验证、值得推荐的新装置。 胸腰椎爆裂骨折是椎体后壁骨折后,骨折碎片从椎体后侧转移到椎管内,导致脊髓神经受压或受损,如何防止椎管内骨折碎片的形成并减少骨碎片对神经的影响对于改善胸腰椎爆裂性骨折患者的预后和生活质量至关重要,为此,必须首先阐明管内骨折碎片形成的机制。但目前具体机制存在争议,一种观点是,管内骨折碎片的形成继发于椎体的破裂和由此产生的骨折碎片的移位;另一种观点是,该碎片是特发产生的,接触应力通过关节突传递到椎弓根底部,导致椎体后上侧的应力增加,导致椎体骨折和移位[38]。为此,ZENG等[39]运用有限元法对胸腰椎爆裂骨折的机制展开了研究,该研究选择1名健康男性建立T11-L3模型,骨骼结构被赋予了塑性,椎间盘被赋予超弹性特性,韧带被赋予黏弹性。进行屈曲、后伸、垂直状态下的冲击实验和切除小关节的冲击实验模拟L1椎体爆裂骨折发生过程,结果显示,应力集中在椎弓根、小关节和峡部,位于椎弓根下缘外侧与椎体交界处的皮质骨上的应力最大,此外,在切除小关节的冲击实验中,应力集中的情况显著降低,无应力峰值出现,由此得出,小关节在爆裂性骨折椎管内骨折碎片的形成中起着决定性作用,但小关节如何影响应力的转化和传递需要进一步阐明。 若脊柱仅单纯椎体压缩骨折、无脊髓神经受累,可选择经皮微创或开放手术,椎弓根螺钉经皮固定术与开放式固定术二者效果相同,但前者为微型创口,创伤小、出血小、对椎旁肌肉的神经损伤少,恢复快,而后者创伤大,出血多,对椎旁肌肉的神经损伤多,易引发肌肉僵硬和萎缩,恢复慢[40]。但二者的生物力学有何差别?HUANG等[41]运用有限元法构建了L1椎体压缩性骨折模型,对两种手术方式进行了对比研究,该研究选择1名年轻健康男性构建T12-L2模型,模拟L1椎体压缩骨折的经皮微创与开放手术,二者都是跨伤椎4钉2棒固定,区别仅在于开放手术有横向连接杆,比较微创与开放手术钉杆系统在屈伸、侧弯、旋转时的应力分布与位移大小。经研究发现传统的开放式椎弓根螺钉固定术可以增强脊柱在轴向旋转方向上的稳定性,并且还可以更大程度地降低椎弓根螺钉轴向旋转的最大应力,屈伸和侧弯方向上的应力与位移二者无明显差异,因此有横连的开放手术在临床上治疗胸腰椎不稳定的骨折更具有重要意义,无横连的经皮微创手术需要在康复期间借助支具减少患者旋转时钉杆系统的应力集中和更大位移对骨质的损害。 胸腰椎爆裂骨折是绝对的手术适应证,手术方式包括长节段和短节段内固定手术,短节段包括跨伤椎4钉内固定和经伤椎6钉内固定两种手术方式[42]。LIMTHONGKUL 等[43]运用有限元法对长节段、短节段4钉、短节段6钉的手术方式治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折进行了对比分析,该研究选择1例L1椎体爆裂骨折患者构建T11-L3模型,模拟3种手术方式并比较脊柱的运动范围、钉杆系统与骨骼系统的应力大小。研究发现6钉固定可比长节段固定保留更多的脊柱运动,此外,它能提供比4钉更有利的生物力学性能。在6钉固定中,椎弓根螺钉周围发生的应力是上述3种手术方式中最小的,这可能会减少椎间融合器融合失败等并发症。6钉固定在伤椎中产生的应力比长节段固定和4钉固定更大,根据Wolff定律,这可能有助于骨愈合,6钉固定从脊柱运动、生物力学性能、促进伤椎生长方面都显示出更大优势。 胸腰椎骨折占脊柱骨折的90%,其中10%-20%为爆裂性骨折,当胸腰椎爆裂骨折伴有椎管内有骨块时,后路手术是否需要椎管切口减压仍存在争议[44]。SONG 等[45]进行了胸腰椎爆裂性骨折间接复位后椎弓根螺钉固定的有限元分析,该研究选择了1例L1椎体爆裂骨折患者构建T12-L2模型,并模拟跨伤椎4钉2棒撑开复位固定过程,研究发现进行间接复位时,起主要作用的有椎间盘后纵韧带,其中椎间盘对伤椎的高度恢复起主要作用,尤其是伤椎的上位椎间盘(主要是纤维环),当后路撑开时,上位椎间盘产生向上的拉力时,伤椎椎体高度升高,为突入后方椎管内的碎骨复位创造了空间,并且在撑开过程中,逐渐被拉直的后纵韧带将碎骨推入了原位。此外,T12和L1的复位效果优于L2,这与后纵韧带的柔韧性有关。这种方法不需要融合相关节段,手术后可以最大程度地保留脊柱的运动程度。间接复位消除了大切口分离肌肉的需要,创伤小,出血少,可防止脊髓、神经损伤和术后瘢痕粘连,有利于脊柱功能的恢复,使患者在手术后更早地下床,从而满足快速康复手术的概念,是胸腰椎爆裂骨折合并后纵韧带、椎间盘完整的情况下 首选。 后路短节段螺钉固定术广泛用于创伤性胸腰椎爆裂性骨折的治疗[46],骨折水平的后路中间螺钉固定技术是一种在中间伤椎固定的手术方式,有助于改善和维持脊柱后凸矫正,并且还可以提高生物力学稳定性[47]。多轴椎弓根螺钉(polyaxial pedicle screw,Pps,简称P)与单轴椎弓根螺钉(monoaxial pedicle screw,Mps,简称M)相比由于螺头应力和弯曲强度小,降低了椎弓根螺钉和杆断裂的速率,还可使不在一条直线上的椎弓根螺钉易于连杆,促进了连杆的有效应用。但没有研究比较单轴椎弓根螺钉和多轴椎弓根螺钉混合使用后在后路中间螺钉固定技术的生物力学特征。LIU等[48]运用有限元法进行了混合椎弓根螺钉在后路中间螺钉固定技术治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折的生物力学比较,该研究选择1例40岁健康男性构建T9-L3模型,模拟T12椎体爆裂骨折和混合螺钉固定模型(例如PMM表示最上方椎体的2个钉为多轴椎弓根钉,中间椎体的2个钉和最下方椎体2个钉为单轴椎弓根钉,共8种固定模型:PPP、MMM、PMM、MPM、MMP、MPP、PMP、PPM),比较脊柱的运动范围、固定系统与椎间盘的应力大小,经研究有以下发现,见表2。 "


2.3 有限元法在病理性胸腰椎骨折中的应用 强直性脊柱炎是一种进行性炎症性疾病,主要累及中轴骨骼,炎症使韧带骨化和关节突关节融合,导致脊柱僵硬,同时炎症会导致骨质疏松症,这两个因素都会增加椎体骨折的风险[49]。该病骨折总是累及脊柱的全部三柱,并且可能在低能量损伤下发生,虽然颈椎骨折是强直性脊柱炎骨折最常见的部位,但胸腰椎骨折紧随其后,占20%-40%[50]。ZHANG等[51]进行了强直性脊柱炎胸腰椎骨折的不同固定模式的有限元分析,该研究选择了1例强直性脊柱炎患者构建T9-L5模型,模拟L1椎体骨折和3,4,6个水平跨伤椎固定,分析钉杆系统的应力大小、方向和骨骼系统的位移。研究发现该病胸腰椎骨折固定比正常脊柱胸腰椎骨折承受的应力更大,建议在强直性脊柱炎胸腰椎骨折中使用4个水平(使用骨水泥螺钉)固定或使用普通椎弓根螺钉进行6个水平固定;跨节段的跳跃式水平固定在内固定应力、拉力和屈曲力方面没有表现出优势,因此不建议对强直性脊柱炎脊柱骨折进行跨伤椎固定。脊柱后凸的矫正虽然减少了内固定处的应力,却导致脊柱前柱缺失,产生更大的应力,二者相互抵消,没有明显改变内固定应力和螺钉松动的风险,但却增加了手术并发症的风险,因此,后凸矫形的选择需要考虑利弊。 脊柱转移癌是指原发于甲状腺、前列腺、乳腺等部位的肿瘤经淋巴、血行转移到脊柱部位,形成新的癌症病灶。目前,用于脊柱转移癌的评分系统,例如脊柱不稳定性肿瘤评分可指导有高骨折风险的脊柱转移癌患者进行手术治疗,但该评分系统特异性不高,一部分患者未能识别[52]。为此,COSTA等[53]运用有限元法对脊柱转移癌进行了生物力学分析,探索有助于补充上述评分系统不足的方法,该研究选择了8例脊柱转移癌患者构建T11-L5肿瘤浸润椎及其邻椎的模型,通过定量CT将建模与骨密度表达结合,研究发现转移癌浸润椎的平均密度虽与邻椎的平均密度相似,但转移癌浸润椎的骨密度具体可分为过高或过低,若用不同的颜色表示有限元模型的骨密度,转移癌浸润椎颜色不一,正常邻椎的颜色一致,是否有癌浸润、癌浸部位可直观看到,但该方法不适用于原发性脊柱肿瘤。 胸腰椎是脊柱结核的主要受累部位之一,低热、盗汗、消瘦无力、后背部疼痛伴活动受限是前期典型症状,若结核杆菌侵袭椎管,则会产生下肢疼痛、麻木、截瘫等症状,为避免后期脊髓、神经受累,需早期行病灶清除和后路钉棒系统固定术[54]。李翔等[55]运用有限元法进行了胸腰椎结核后路短节段短钉和长节段长钉的生物力学分析,该研究选择1例健康男性构建T12-L3模型,模拟4钉短节段短钉和4钉跨节段长钉两种手术方式,给予500 N垂直向下的力和10 N不同方向的力模拟屈伸、侧弯、旋转状态,比较活动范围和螺钉生物力学,结果显示,短节段短钉与长节段长钉相比,前者在各个方向的活动范围更大,钉棒系统应力值更小,但抗拔出力相同。短节段短钉对脊柱活动影响小、断钉断棒风险低、有着良好的稳定性,是胸腰椎结核后路固定的较优选择之一。 有限元分析法在胸腰椎骨折领域的应用时间轴见表3。"

| [1] ZHANG Q, CHON T, ZHANG Y, et al. Finite element analysis of the lumbar spine in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis subjected to different loads. Comput Biol Med. 2021;136:104745. [2] WANG W, BARAN GR, BETZ RR, et al. The Use of Finite Element Models to Assist Understanding and Treatment For Scoliosis: A Review Paper. Spine Deform. 2014;2(1):10-27. [3] NAOUM S, VASILIADIS AV, KOUTSERIMPAS C, et al. Finite Element Method for the Evaluation of the Human Spine: A Literature Overview. J Funct Biomater. 2021;12(3):43. [4] CAI XY, SANG D, YUCHI CX, et al. Using finite element analysis to determine effects of the motion loading method on facet joint forces after cervical disc degeneration. Comput Biol Med. 2020;116:103519. [5] BREKELMANS WA, POORT HW, SLOOFF TJ. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972; 43(5):301-317. [6] BELYTSCHKO T, KULAK RF, SCHULTZ AB, et al. Finite element stress analysis of an intervertebral disc. J Biomech. 1974;7(3):277-285. [7] MIZRAHI J, SILVA MJ, KEAVENY TM, et al. Finite-element stress analysis of the normal and osteoporotic lumbar vertebral body. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(14):2088-2096. [8] WEI W, ZHANG T, YANG J, et al. Material sensitivity of patient-specific finite element models in the brace treatment of scoliosis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1111449. [9] WANG R, WU Z. Recent advancement in finite element analysis of spinal interbody cages: A review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1041973. [10] SPIEGL UJA, SCHNAKE KJ, HARTMANN F, et al. Traumatic Fractures of the Thoracic Spine. Z Orthop Unfall. 2021;159(4):373-382. [11] MURPHY J, MCLOUGHLIN E, DAVIES AM, et al. Is T9-11 the true thoracolumbar transition zone? J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020;11(5): 891-895. [12] WAN SHT, GULDENIZ O, YEUNG MHY, et al. Inter-screw index as a novel diagnostic indicator of tether breakage. Spine Deform. 2023;11(4): 887-895. [13] SMITH CJ, ABDULAZEEZ MM, ELGAWADY M, et al. The Effect of Thoracolumbar Injury Classification in the Clinical Outcome of Operative and Non-Operative Treatments. Cureus. 2021;13(1): e12428. [14] VACCARO AR, KIM DH, BRODKE DS, et al. Diagnosis and management of thoracolumbar spine fractures. Instr Course Lect. 2004;53: 359-373. [15] LIU B, ZHU Y, LIU S, et al. National incidence of traumatic spinal fractures in China: Data from China National Fracture Study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(35):e12190. [16] COSCIA MF, TRAMMELL TR, HAINES N. Thoracolumbar spinal fractures--concepts of treatment. Indiana Med. 1991;84(11): 92-796. [17] LI Y, FENG X, PAN J, et al. Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Versus Kyphoplasty for Thoracolumbar Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures in Patients with Distant Lumbosacral Pain. Pain Physician. 2021;24(3):E349-E356. [18] TANASANSOMBOON T, KITTIPIBUL T, LIMTHONGKUL W, et al. Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture without Neurological Deficit: Review of Controversies and Current Evidence of Treatment. World Neurosurg. 2022;162:29-35. [19] ROBLESGIL-MEDRANO A, TELLEZ-GARCIA E, BUENO-GUTIERREZ LC, et al. Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Anterior and Posterior Approaches. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2022;6(2):99-108. [20] HAYOUN T, SIBONI R, OHL X, et al. Treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: comparison of the clinical and radiological outcomes of percutaneous versus open surgery. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2023;33(6):2393-2397. [21] LIU G, TAN JH, KONG JC, et al. Thoracolumbar Injury Classification and Severity Score Is Predictive of Perioperative Adverse Events in Operatively Treated Thoracic and Lumbar Fractures. Asian Spine J. 2022;16(6):848-856. [22] GAVIRA N, AMELOT A, COOK AR, et al. Thoracolumbar spinal fracture in children: Conservative or surgical treatment? Neurochirurgie. 2022;68(3):309-314. [23] CHE M, WANG Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Finite Element Analysis of a New Type of Spinal Protection Device for the Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. Orthop Surg. 2022; 14(3):577-586. [24] SPIEGL UJ, JOSTEN C, DEVITT BM, et al. Incomplete burst fractures of the thoracolumbar spine: a review of literature. Eur Spine J. 2017; 26(12):3187-3198. [25] NEELEY OJ, KAFKA B, TECLE NE, et al. Percutaneous screw fixation versus open fusion for the treatment of traumatic thoracolumbar fractures: A retrospective case series of 185 Patients with a single-level spinal column injury. J Clin Neurosci. 2022;101:47-51. [26] YAN J, LIAO Z, YU Y. Finite element analysis of dynamic changes in spinal mechanics of osteoporotic lumbar fracture. Eur J Med Res. 2022;27(1):142. [27] HUANG S, ZHOU C, ZHANG X, et al. Biomechanical analysis of sandwich vertebrae in osteoporotic patients: finite element analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1259095. [28] ZHANG L, LI J, YANG H, et al. Histological evaluation of bone biopsy results during PVP or PKP of vertebral compression fractures. Oncol Lett. 2013;5(1):135-138. [29] WANG D, LI Y, YIN H, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of optimal distribution model of vertebroplasty. Ann Palliat Med. 2020;9(3):1062-1072. [30] MURATORE M, ALLASIA S, VIGLIERCHIO P, et al. Surgical treatment of traumatic thoracolumbar fractures: a retrospective review of 101 cases. Musculoskelet Surg. 2021;105(1):49-59. [31] ZHANG G, DU Y, JIANG G, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of different posterior fixation techniques for treating thoracolumbar burst fractures of osteoporosis old patients: a finite element analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1268557. [32] VENMANS A, KLAZEN CA, LOHLE PN, et al. Natural history of pain in patients with conservatively treated osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: results from VERTOS II. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33(3):519-521. [33] PAWAR A, BADHE V, GAWANDE M. Treatment of Osteoporotic Compression Fractures at Thoracolumbar Spine With Neurodeficit: Short-Segment Stabilization With Cement-Augmented Fenestrated Pedicle Screws and Vertebroplasty by Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Technique. Int J Spine Surg. 2022;16(3):465-471. [34] XU H, FENG Q, MA X, et al. Biomechanical behaviour of a novel bone cement screw in the minimally invasive treatment of Kummell’s disease: a finite element study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023; 24(1):967. [35] AHN Y, YOUN MS, HEO DH. Endoscopic transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a comprehensive review. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2019;16(5):373-380. [36] SUN H, ZHU Y, HE QF, et al. Reinforcement strategy for lateral rafting plate fixation in posterolateral column fractures of the tibial plateau: The magic screw technique. Injury. 2017;48(12):2814-2826. [37] REN P, CHENG X, LU C, et al. Finite Element Analysis of a Novel Anterior Locking Plate for Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture. Biomed Res Int. 2021; 2021:2949419. [38] LANGRANA NA, HARTEN RR, LIN DC, et al. Acute thoracolumbar burst fractures: a new view of loading mechanisms. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(5):498-508. [39] ZENG ZL, ZHU R, LI SZ, et al. Formative mechanism of intracanal fracture fragments in thoracolumbar burst fractures: a finite element study. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013;126(15):2852-2858. [40] LEE KH, YUE WM, YEO W, et al. Clinical and radiological outcomes of open versus minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(11):2265-2270. [41] HUANG C, ZHANG C, SU F, et al. Finite element analysis of minimally invasive nail placement and traditional nail placement in the treatment of lumbar 1 vertebral compression fracture. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023;102(26):e34145. [42] ALTAY M, OZKURT B, AKTEKIN CN, et al. Treatment of unstable thoracolumbar junction burst fractures with short- or long-segment posterior fixation in magerl type a fractures. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(8): 1145-1155. [43] LIMTHONGKUL W, WANNARATSIRI N, SUKJAMSRI C, et al. Biomechanical Comparison Between Posterior Long-Segment Fixation, Short-Segment Fixation, and Short-Segment Fixation With Intermediate Screws for the Treatment of Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture: A Finite Element Analysis. Int J Spine Surg. 2023;17(3):442-448. [44] MITTAL S, IFTHEKAR S, AHUJA K, et al. Outcomes of Thoracolumbar Fracture-Dislocation Managed by Short-Segment and Long-Segment Posterior Fixation: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. Int J Spine Surg. 2021;15(1):55-61. [45] SONG Y, PANG X, ZHU F. Finite element analysis of the indirect reduction of posterior pedicle screw fixation for a thoracolumbar burst fracture. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(41):e30965. [46] WANG H, ZHANG Y, XIANG Q, et al. Epidemiology of traumatic spinal fractures: experience from medical university-affiliated hospitals in Chongqing, China, 2001-2010. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;17(5):459-468. [47] YE C, LUO Z, YU X, et al. Comparing the efficacy of short-segment pedicle screw instrumentation with and without intermediate screws for treating unstable thoracolumbar fractures. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(34):e7893. [48] LIU H, WANG H, LIU J, et al. Biomechanical comparison of posterior intermediate screw fixation techniques with hybrid monoaxial and polyaxial pedicle screws in the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fracture: a finite element study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):122. [49] PRAY C, FEROZ NI, NIGIL HAROON N. Bone Mineral Density and Fracture Risk in Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Meta-Analysis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2017;101(2):182-192. [50] WESTERVELD LA, VERLAAN JJ, ONER FC. Spinal fractures in patients with ankylosing spinal disorders: a systematic review of the literature on treatment, neurological status and complications. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(2):145-156. [51] ZHANG T, WANG Y, ZHANG P, et al. Different fixation pattern for thoracolumbar fracture of ankylosing spondylitis: A finite element analysis. PLoS One. 2021;16(4):e0250009. [52] FOURNEY DR, FRANGOU EM, RYKEN TC, et al. Spinal instability neoplastic score: an analysis of reliability and validity from the spine oncology study group. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(22):3072-3077. [53] COSTA MC, ELTES P, LAZARY A, et al. Biomechanical assessment of vertebrae with lytic metastases with subject-specific finite element models. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2019;98:268-290. [54] RICHTERMAN A, RICHARD-GREENBLATT M, WHITAKER K. Back Pain, Fever, and Cough in a 46-Year-Old Man. JAMA. 2021;326(20): 2070-2071. [55] 李翔, 司建炜. 脊柱结核病灶清除术中单节段短椎弓根钉固定的三维有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(28):4552-4557. |
| [1] | Sun Xiaojun, Wang Huaming, Zhang Dehong, Song Xuewen, Huang Jin, Zhang Chen, Pei Shengtai. Effect of finite element method in treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1897-1904. |
| [2] | Li Liangkui, Huang Yongcan, Wang Peng, Yu Binsheng. Effect of anterior controllable anteriodisplacement and fusion on vertebrae-ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament complex and implants: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1761-1767. |
| [3] | Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao. Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1768-1774. |
| [4] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [5] | Fu Enhong, Yang Hang, Liang Cheng, Zhang Xiaogang, Zhang Yali, Jin Zhongmin. OpenSim-based prediction of lower-limb biomechanical behavior in adolescents with plantarflexor weakness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1789-1795. |
| [6] | Lu Jieming, Li Yajing, Du Peijie, Xu Dongqing. Effects of artificial turf versus natural grass on biomechanical performance of the lower limbs in young females during jump-landing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1101-1107. |
| [7] | Yang Yicheng, Zheng Zhizhen, Liang Shuangxue, Wu Chengliang, Du Yunyun. Influence and implications of basketball shoes' functional parameters on human biomechanics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7620-7628. |
| [8] | Song Xubin, Wu Dou, Zhao Enzhe, Zhang Xingyu, Zhang Xiaolun, Wang Chuheng. Finite element analysis of a new femoral neck spiral blade system to treat femoral intertrochanteric fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7041-7047. |
| [9] | Wang Lei, Li Chengsong, Zhang Shenshen, Wang Qing. Finite element analysis of biomechanical characteristics of three internal fixation methods in treatment of inferior patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7048-7054. |
| [10] | Xu Xin, Wurikaixi·Aiyiti, Lyu Gang, Maimaiaili·Yushan, Ma Zhiqiang, Ma Chao. Finite element analysis of four different internal fixation methods for complex acetabular double-column fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7063-7071. |
| [11] | Liang Cheng, Zhuo Chuanchuan, Zhang Xiaogang, Wang Guan, Duan Ke, Li Zhong, Lu Xiaobo, Zhuo Naiqiang, Jin Zhongmin. Biomechanical characteristics of a novel sacroiliac lag screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7080-7086. |
| [12] | Ma Shuangshuang, Gao Dedong, Shan Zhongshu, Xu Wenxu, Lu Zhirui. Finite element analysis and biomechanical validation of revision pedicle screw placement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7087-7095. |
| [13] | Yang Yu, Li Yinghao, Duo Zhuangzhi, Zhou Dingrong. Effect of overall functional physical exercise on lumbar biomechanics in patients with lumbar disc herniation after surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7096-7101. |
| [14] | Zhang Ziyi, Qin Qi, Alimujiang·Yusufu, Liu Yuzhe, Yusufu·Reheman, Ran Jian. Biomechanical analysis of three internal fixation schemes for Pauwels type III femoral neck fractures in young adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7102-7108. |
| [15] | Ma Tao, Li Xing, Wei Yajun, Deng Juncai. Effects of lateral screw-rod placement positions on segmental range of motion, internal fixation and cage stress during oblique lumber interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7165-7172. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||