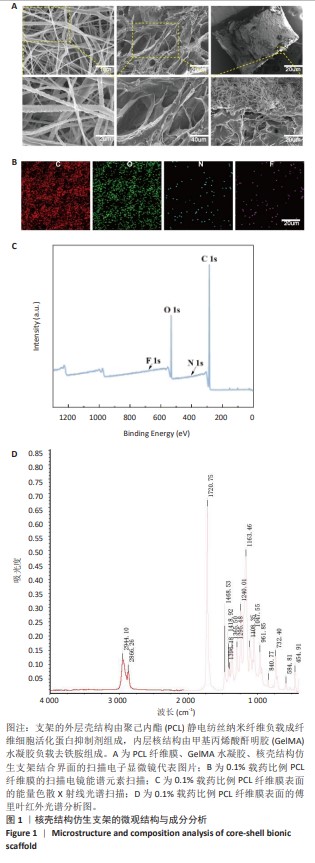
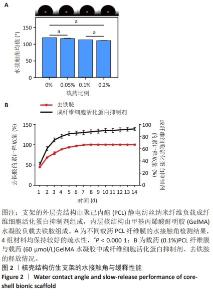
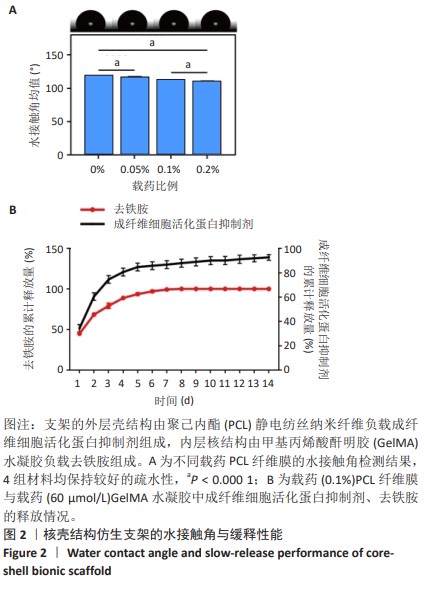
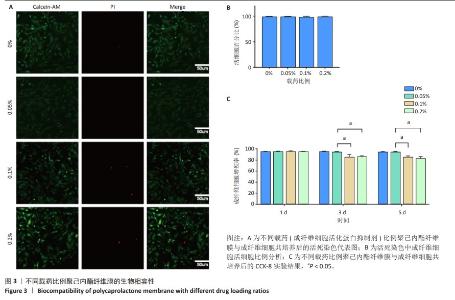
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (16): 3420-3431.doi: 10.12307/2025.418
Previous Articles Next Articles
Critical bone defect repaired with anti-fibrosis and “H”-type core-shell bionic scaffold
Li Yonghang, Li Wenming, Yan Caiping, Wang Xingkuan, Xiang Chao, Zhang Yuan, Jiang Ke, Chen Lu
- Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2023-12-02Accepted:2024-03-13Online:2025-06-08Published:2024-09-04 -
Contact:Corresponding author: Chen Lu, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China Co-corresponding author: Jiang Ke, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Li Yonghang, Master candidate, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China Li Wenming, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China Li Yonghang and Li Wenming contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:Scientific Research Task of Sichuan Medical Association, No. 2015GK012 (to CL); Program of Cooperation between the Schools and Nanchong City in 2022, No. 22SXQT0308 (to JK); Nanchong 2023 Municipal Science and Technology Research and Development Plan, No. 23JCYJPT0036 (to WXK)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Yonghang, Li Wenming, Yan Caiping, Wang Xingkuan, Xiang Chao, Zhang Yuan, Jiang Ke, Chen Lu. Critical bone defect repaired with anti-fibrosis and “H”-type core-shell bionic scaffold[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3420-3431.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
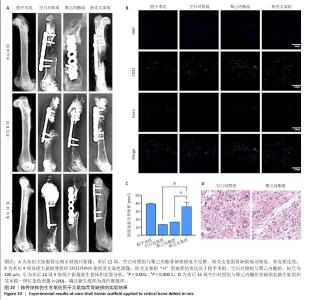
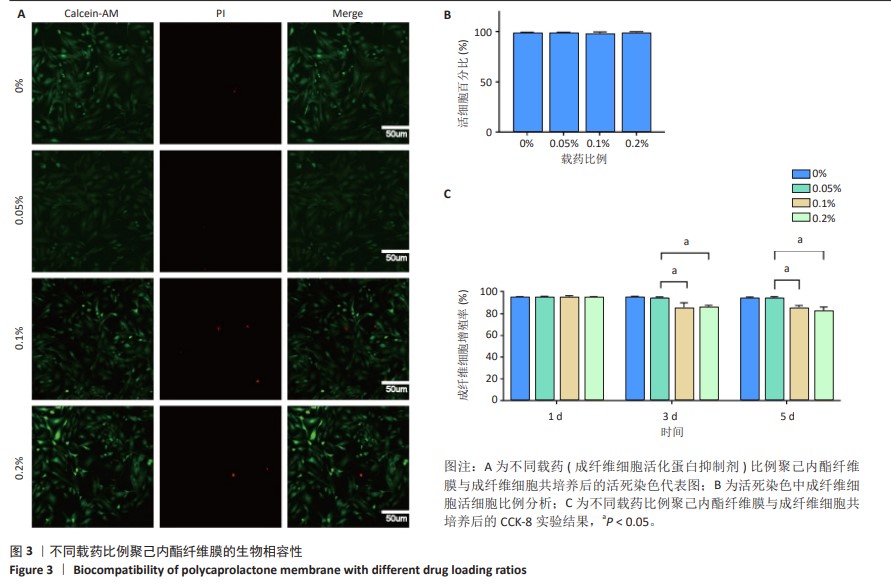
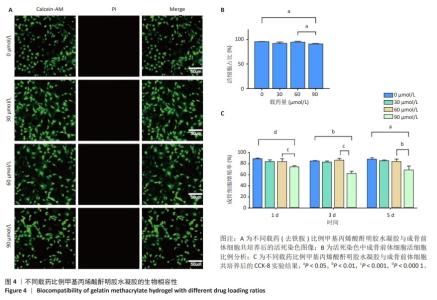
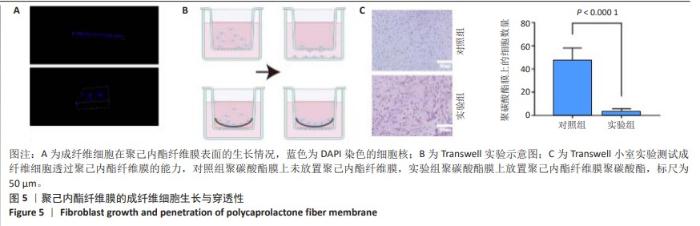
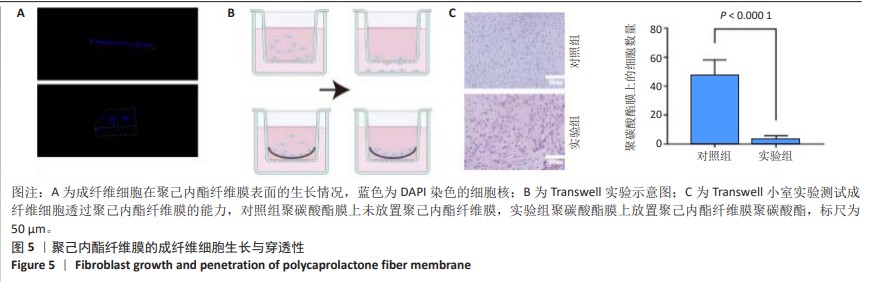
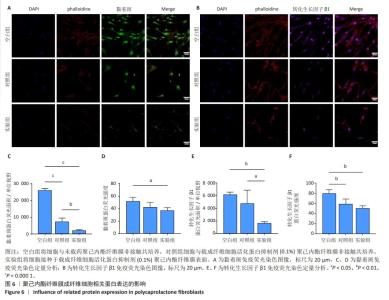
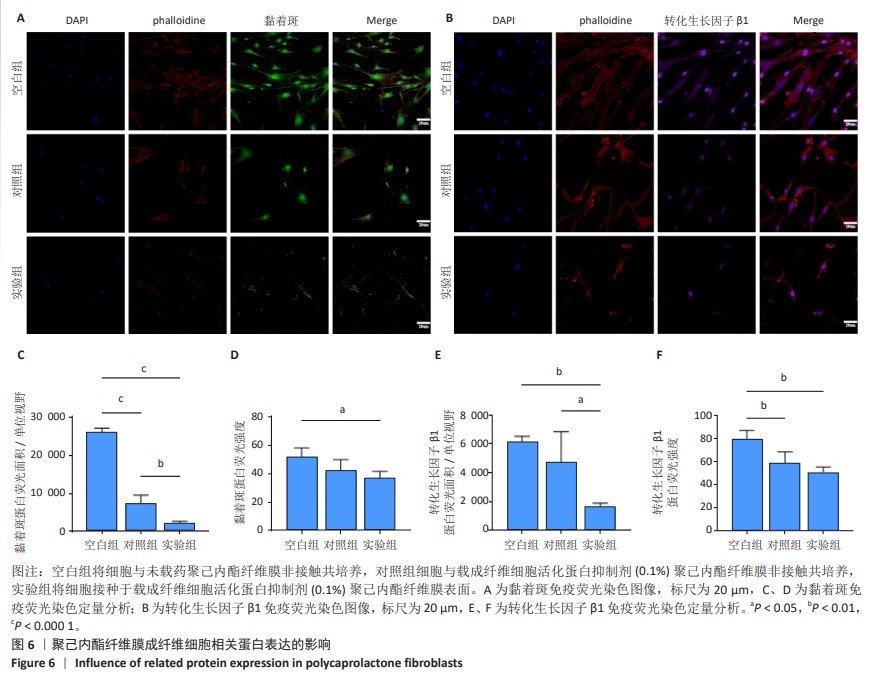
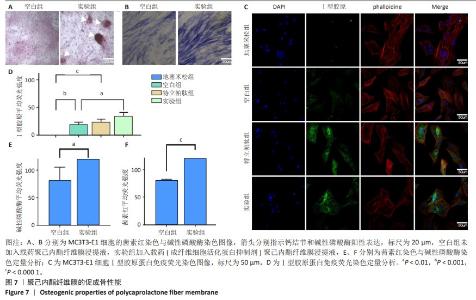
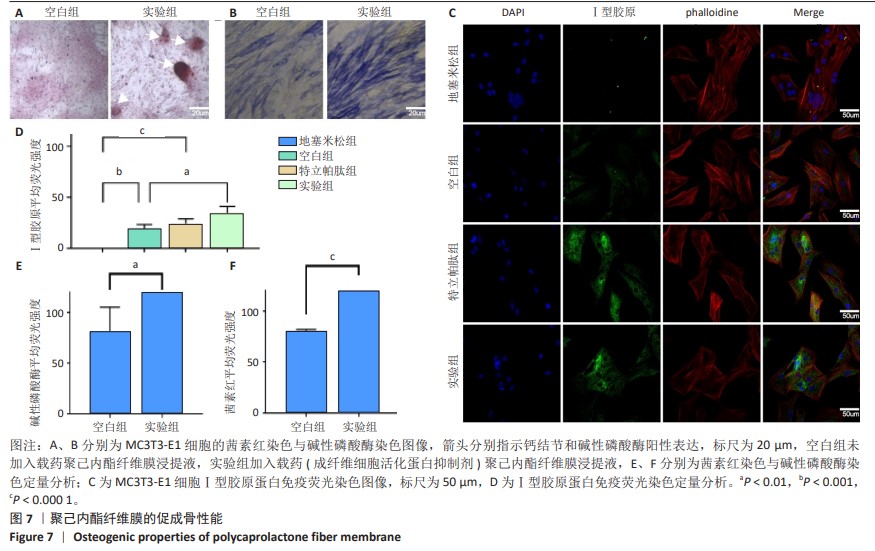
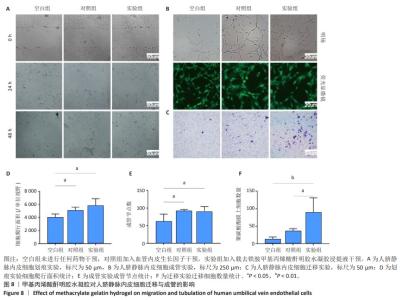
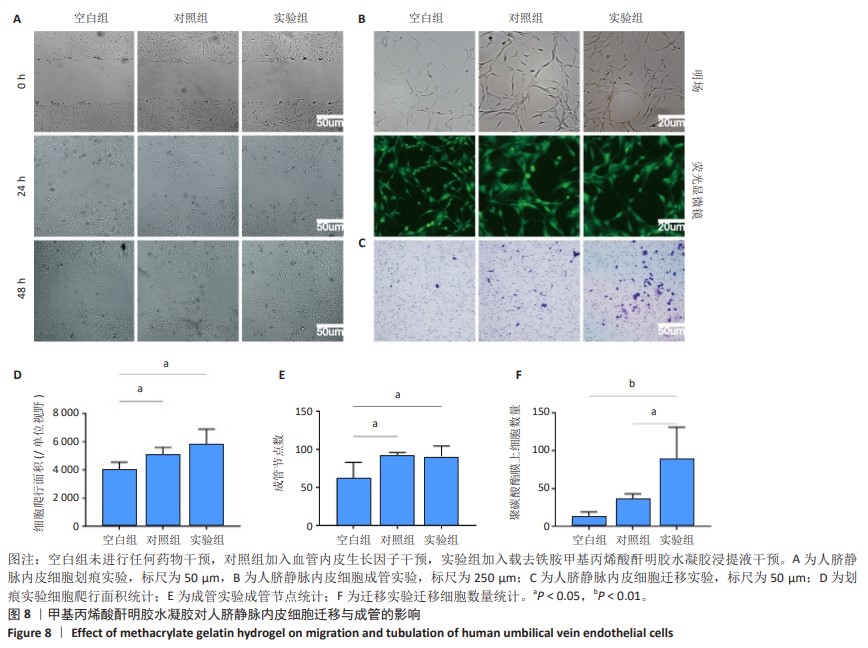
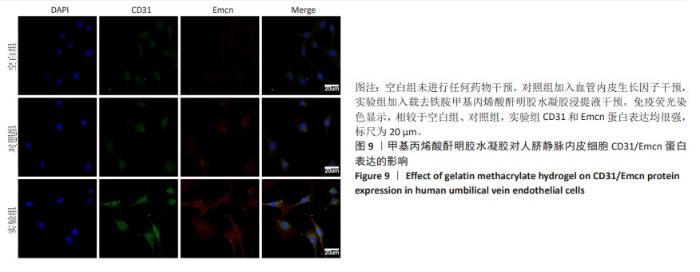
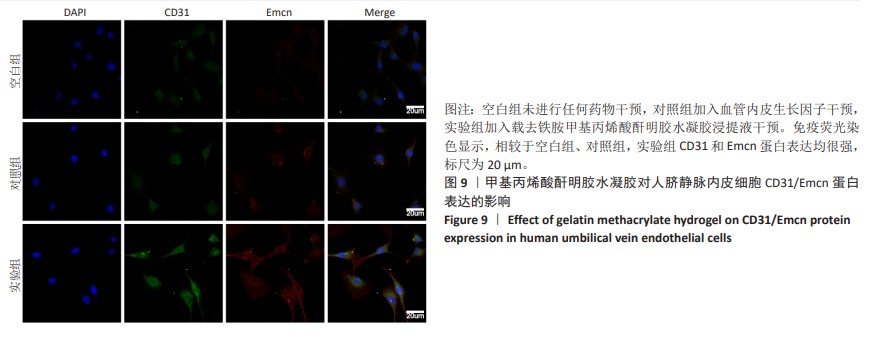
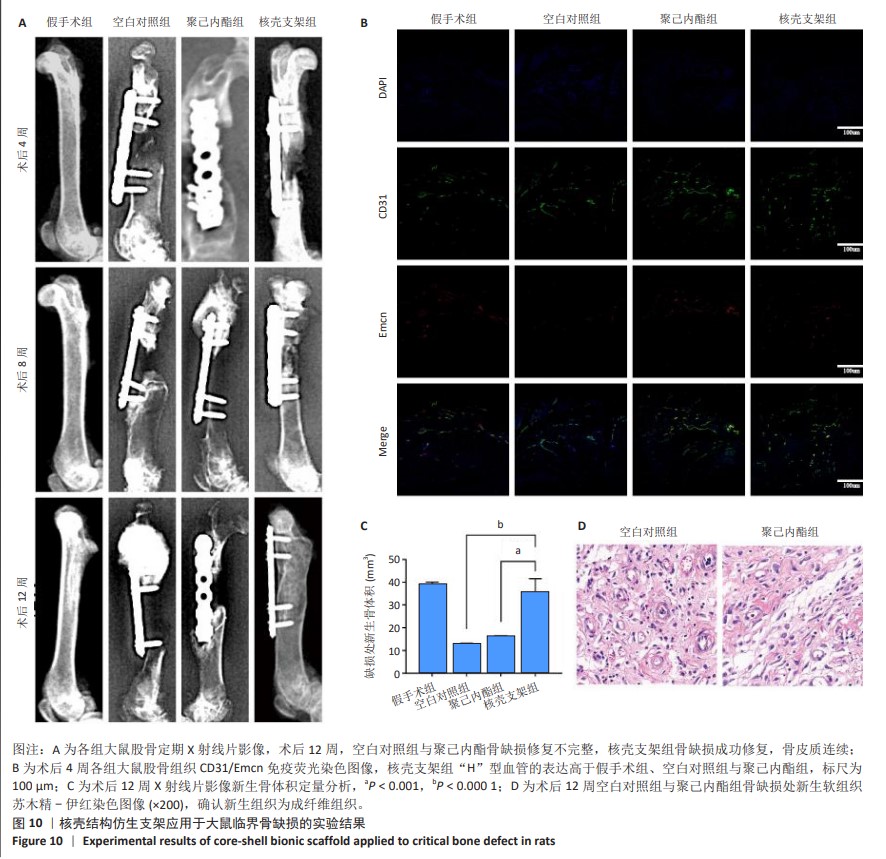
2.6 体内实验结果 2.6.1 实验动物数量分析 36只大鼠全部进入结果分析。 2.6.2 各组大鼠股骨X射线观察 术后4周,各组骨缺损部分都处于原始骨痂时期,新生的骨痂质地稍硬但在影像学图片上并不能显影;术后8周,核壳支架组可见骨折断端有部分连接,空白对照组和聚己内酯组无骨性连接;术后12周,空白对照组与聚己内酯骨缺损修复不完整,核壳支架组骨缺损成功修复,骨皮质连续,见图10。 2.6.3 各组大鼠股骨CD31/Emcn免疫荧光染色 术后4周,核壳支架组“H”型血管的表达高于假手术组、空白对照组与聚己内酯组,见图10。 2.6.4 大鼠股骨组织苏木精-伊红染色 为了确定空白对照组和聚己内酯组股骨修复是否为纤维化组织,对其进行苏木精-伊红染色分析。术后12周苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,对空白对照组和聚己内酯组骨缺损部分的非骨化组织为成纤维组织,见图10。"
| [1] HAK DJ, FITZPATRICK D, BISHOP JA, et al. Delayed union and nonunions: Epidemiology, clinical issues, and financial aspects. Injury. 2014;45: S3-S7. [2] SCHMITZ JP, HOLLINGER JO. The Critical Size Defect as an Experimental Model for Craniomandibulofacial Nonunions. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986:(205):299-308. [3] DALISSON B, CHARBONNIER B, AOUDE A, et al. Skeletal regeneration for segmental bone loss: Vascularised grafts, analogues and surrogates. Acta Biomater. 2021;136:37-55. [4] MA L, WANG X, ZHOU Y, et al. Biomimetic Ti–6Al–4V alloy/gelatin methacrylate hybrid scaffold with enhanced osteogenic and angiogenic capabilities for large bone defect restoration. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(10): 3437-3448. [5] BIGGEMANN J, PEZOLDT M, STUMPF M, et al. Modular ceramic scaffolds for individual implants. Acta Biomater. 2018;80: 390-400. [6] ZHANG Y, FAN Z, XING Y, et al. Effect of microtopography on osseointegration of implantable biomaterials and its modification strategies. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:981062. [7] WU L, GU Y, LIU L, et al. Hierarchical micro/nanofibrous membranes of sustained releasing VEGF for periosteal regeneration. Biomaterials. 2020;227:119555. [8] PENG F, ZHANG X, WANG Y, et al. Guided bone regeneration in long-bone defect with a bilayer mineralized collagen membrane. Collagen Leather. 2023;36(5). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42825-023-00144-4 [9] SALHOTRA A, SHAH HN, LEVI B, et al. Mechanisms of bone development and repair. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(11): 696-711. [10] PANTELI M, VUN JSH, POUNTOS I, et al. Biological and molecular profile of fracture non-union tissue: A systematic review and an update on current insights. J Cell Mol Med. 2022;26(3):601-623. [11] WANG L, TOWER RJ, CHANDRA A, et al. Periosteal Mesenchymal Progenitor Dysfunction and Extraskeletally-Derived Fibrosis Contribute to Atrophic Fracture Nonunion. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(3):520-532. [12] YU HS, PARK J, LEE HS, et al. Feasibility of Polycaprolactone Scaffolds Fabricated by Three-Dimensional Printing for Tissue Engineering of Tunica Albuginea. World J Mens Health. 2018;36(1):66-72. [13] ZHOU X, HE X, SHI K, et al. Injectable Thermosensitive Hydrogel Containing Erlotinib-Loaded Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as a Localized Drug Delivery System for NSCLC Therapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7(23):2001442. [14] NIRWAN VP, KOWALCZYK T, BAR J, et al. Advances in Electrospun Hybrid Nanofibers for Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022;12(11):1829. [15] WANG W, ZHAO J, YAO Z, et al. Oriented inner fabrication of bi-layer biomimetic tendon sheath for anti-adhesion and tendon healing. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2020;11:2040622320944779. [16] ZHANG X, REAGAN MR, KAPLAN DL. Electrospun silk biomaterial scaffolds for regenerative medicine. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009;61(12): 988-1006. [17] LOKTEV A, LINDNER T, BURGER EM, et al. Development of Fibroblast Activation Protein-Targeted Radiotracers with Improved Tumor Retention. J Nucl Med. 2019;60(10):1421-1429. [18] GIESEL FL, KRATOCHWIL C, LINDNER T, et al. (68)Ga-FAPI PET/CT: Biodistribution and Preliminary Dosimetry Estimate of 2 DOTA-Containing FAP-Targeting Agents in Patients with Various Cancers. J Nucl Med. 2019;60(3):386-392. [19] CHEN Q, LI J, HAN F, et al. A Multifunctional Composite Hydrogel That Rescues the ROS Microenvironment and Guides the Immune Response for Repair of Osteoporotic Bone Defects. Adv Funct Mater. 2022;32(27):2201067.1-2201067.18. [20] WEI Z, XIONG C, LIU Z, et al. Release characteristics and processing-structure-performance relationship of electro-spinning curcumin-loaded polyethersulfone based porous ultrafine fibers. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2018;29(15):1825-1838. [21] PATTNAIK S, SWAIN K, RAMAKRISHNA S. Optimal delivery of poorly soluble drugs using electrospun nanofiber technology: Challenges, state of the art, and future directions. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2023;15(2):e1859. [22] PENG Y, WU S, LI Y, et al. Type H blood vessels in bone modeling and remodeling. Theranostics. 2020;10(1):426-36. [23] XU R, YALLOWITZ A, QIN A, et al. Targeting skeletal endothelium to ameliorate bone loss. Nat Med. 2018;24(6):823-833. [24] RUAN Z, YIN H, WAN TF, et al. Metformin accelerates bone fracture healing by promoting type H vessel formation through inhibition of YAP1/TAZ expression. Bone Res. 2023;11(1):45. [25] YANG M, LI CJ, XIAO Y, et al. Ophiopogonin D promotes bone regeneration by stimulating CD31(hi) EMCN(hi) vessel formation. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(3):e12784. [26] LU W, ZENG M, LIU W, et al. Human urine-derived stem cell exosomes delivered via injectable GelMA templated hydrogel accelerate bone regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2023;19:100569. [27] GHERASIM O, GRUMEZESCU AM, GRUMEZESCU V, et al. Bioactive Coatings Based on Hydroxyapatite, Kanamycin, and Growth Factor for Biofilm Modulation. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021;10(2):160. [28] ZENG Y, HUANG C, DUAN D, et al. Injectable temperature-sensitive hydrogel system incorporating deferoxamine-loaded microspheres promotes H-type blood vessel-related bone repair of a critical size femoral defect. Acta Biomater. 2022;153:108-123. [29] BAYANZAY K, ALZOEBIE L. Reducing the iron burden and improving survival in transfusion-dependent thalassemia patients: current perspectives. J Blood Med. 2016;7:159-169. [30] HADJIZADEH A, GHASEMKHAH F, GHASEMZAIE N. Polymeric Scaffold Based Gene Delivery Strategies to Improve Angiogenesis in Tissue Engineering: A Review. Polym Rev. 2017;57(3): 505-556. [31] CHEN S, YU Y, XIE S, et al. Local H2 release remodels senescence microenvironment for improved repair of injured bone. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):7783. [32] YUE K, TRUJILLO-DE SANTIAGO G, ALVAREZ MM, et al. Synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2015;73:254-271. [33] CHEN YC, LIN RZ, QI H, et al. Functional Human Vascular Network Generated in Photocrosslinkable Gelatin Methacrylate Hydrogels. Adv Funct Mater. 2012;22(10):2027-2039. [34] KLOTZ BJ, GAWLITTA D, ROSENBERG AJWP, et al. Gelatin-Methacryloyl Hydrogels: Towards Biofabrication-Based Tissue Repair. Trends Biotechnol. 2016;34(5):394-407. [35] REICHERT JC, WULLSCHLEGER ME, CIPITRIA A, et al. Custom-made composite scaffolds for segmental defect repair in long bones. Int Orthop. 2010;35(8): 1229-1236. [36] CAI C, WANG W, LIANG J, et al. MMP-2 Responsive Unidirectional Hydrogel‐Electrospun Patch Loading TGF‐β1 siRNA Polyplexes for Peritendinous Anti‐Adhesion. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;31(6). doi: org/10.1002/adfm.202008364. [37] JOHNSON KA. Healing large bone defects. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 2014;27(6): V.doi: 10.3415/VCOT-14-10-0162. [38] AGARWAL R, GARCÍA AJ. Biomaterial strategies for engineering implants for enhanced osseointegration and bone repair. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;94:53-62. [39] HO-SHUI-LING A, BOLANDER J, RUSTOM LE, et al. Bone regeneration strategies: Engineered scaffolds, bioactive molecules and stem cells current stage and future perspectives. Biomaterials. 2018;180:143-162. [40] CAO J, JIN L, YAN ZQ, et al. Reassessing endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in mouse bone marrow: insights from lineage tracing models. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):8461. |
| [1] | Sun Xianjuan, Wang Qiuhua, Zhang Jinyi, Yang Yangyang, Wang Wenshuang, Zhang Xiaoqing. Adhesion, proliferation, and vascular smooth muscle differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on different electrospinning membranes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 661-669. |
| [2] | Zhao Zengbo, Li Chenxi, Dou Chenlei, Ma Na, Zhou Guanjun. Anti-inflammatory and osteogenic effects of chitosan/sodium glycerophosphate/sodium alginate/leonurine hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 678-685. |
| [3] | Dong Meilin, Du Haiyu, Liu Yuan. Quercetin-loaded carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel promotes wound healing in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 692-699. |
| [4] |
Zhang Bo, Zhang Zhen, Jiang Dong.
Tannic acid modified interpenetrating network hydrogel promotes tissue remodeling of ruptured Achilles tendon after surgery#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 721-729.
|
| [5] | Wu Chen, Jiang Jiahui, Su Dou, Liu Chen, Ci Chao. Decellularized skin matrix/polyurethane blended fibrous scaffolds promote repair of skin defects in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 745-751. |
| [6] | Wang Zilin, Mu Qiuju, Liu Hongjie, Shen Yuxue, Zhu Lili. Protective effects of platelet-rich plasma hydrogel on oxidative damage in L929 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 771-779. |
| [7] | Zhao Hongxia, Sun Zhengwei, Han Yang, Wu Xuechao , Han Jing. Osteogenic properties of platelet-rich fibrin combined with gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 809-817. |
| [8] | An Jiangru, Zhang Jinyi, Wang Qiuhua, Yang Yangyang, Wang Wenshuang, Zhang Xiaoqing. Mesenchymal stem cells combined with polycaprolactone-hyaluronic acid electrospinning membrane in repair of endometrial injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3369-3379. |
| [9] | He Rui, Li Chongyi, Wang Ruiyao, Zeng Dan, Fan Daidi. Application of MXene-based hydrogels in wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3486-3493. |
| [10] | Liu Zhongyu, Li Wenya, Fan Yonghong, Lyu Shuang, Pei Juan, Chen Yaqin, Liu Beiyu, Sun Hongyu. Methacrylated dermal extracellular matrix hydrogel promotes repair of abdominal wall defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2074-2082. |
| [11] | Zhao Wenqi, Yu Haichi, Song Yiru, Yuan Tianyang, Liu Qinyi. Platelet-rich plasma and hydrogel for spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2189-2200. |
| [12] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [13] | Cheng Mingguang, Zhang Chaoyu, Zhuang Kangle, Ruan Peng, Zuo Yi, Zhou Zhengchun, Kong Xiang, Ge Jianjun, Cheng Guangcun. In vitro construction of Stanford type A aortic dissection 3D dynamic simulation diagram and individual tissue-engineered blood vessels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 335-338. |
| [14] | Liu Liang, Hu Gaoquan, Wei Zhao, Chen Lin, Hong Feng. Potential of bacterial nanocellulose/polydopamine composite tubes as small-diameter artificial blood vessel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3535-3542. |
| [15] | Zhou Shicheng, Han Hongguang, Ji Fang, Xu Liying, Zhang Xiaohui, Sun Chang. Effect and histocompatibility of expended polytetrafluoroethylene in modified Blalock-Taussig shunt [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(21): 3394-3400. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||