Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (16): 3486-3493.doi: 10.12307/2025.412
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of MXene-based hydrogels in wound repair
He Rui, Li Chongyi, Wang Ruiyao, Zeng Dan, Fan Daidi
- School of Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Degradable Biomedical Materials, Shaanxi R&D Center of Biomaterials and Fermentation Engineering, Northwest University, Xi’an 710127, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2023-12-20Accepted:2024-03-13Online:2025-06-08Published:2024-09-06 -
Contact:Zeng Dan, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, School of Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Degradable Biomedical Materials, Shaanxi R&D Center of Biomaterials and Fermentation Engineering, Northwest University, Xi’an 710127, Shaanxi Province, China Fan Daidi, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, School of Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Degradable Biomedical Materials, Shaanxi R&D Center of Biomaterials and Fermentation Engineering, Northwest University, Xi’an 710127, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:He Rui, School of Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Degradable Biomedical Materials, Shaanxi R&D Center of Biomaterials and Fermentation Engineering, Northwest University, Xi’an 710127, Shaanxi Province, China Li Chongyi, Master candidate, School of Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Degradable Biomedical Materials, Shaanxi R&D Center of Biomaterials and Fermentation Engineering, Northwest University, Xi’an 710127, Shaanxi Province, China He Rui and Li Chongyi contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:National Key Research & Development Program of China, No. 2019YFA0905200 (to FDD); Youth Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 22108226 (to ZD); Youth Project of Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi Province, No. 2021JQ-439 (to ZD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
He Rui, Li Chongyi, Wang Ruiyao, Zeng Dan, Fan Daidi. Application of MXene-based hydrogels in wound repair[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3486-3493.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
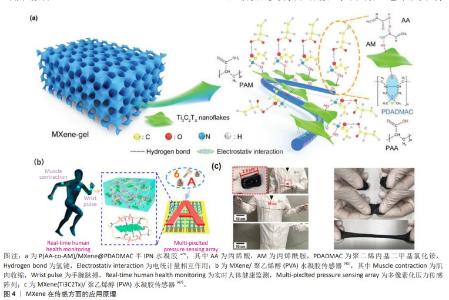
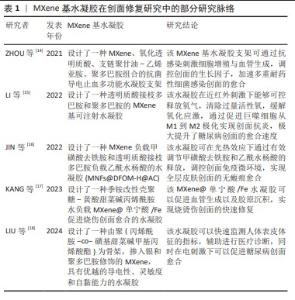
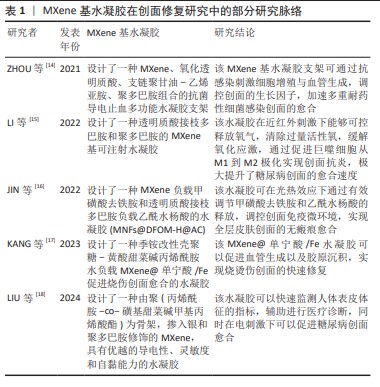
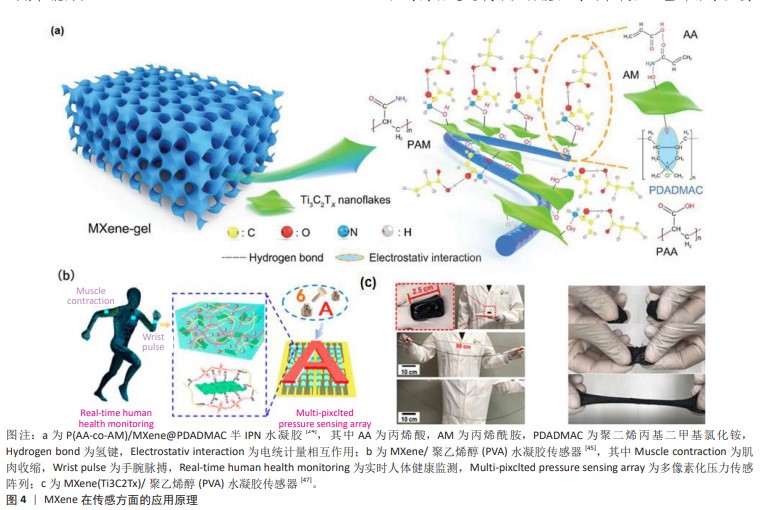
2.2 MXene在创面修复应用中的特性 2.2.1 MXene的导电性 与其他二维材料相比,MXene具有优异的导电性能。SHAHZAD等[19]报道了MXene的电导率为46 S/m,表现出了优异的金属特性。由于MXene内部电子的运动状态和性能传递与金属相同,因此存在电阻率随着温度线性降低的现象。MXene的电子特性主要取决于M位、X位和表面端部的性质。GUAN等[20]开发了一种方法,将2D Ti3C2Tx片转化为具有3D多孔结构的中空Ti3C2Tx-MXene管,同时退火处理后,Ti3C2Tx-MXene上的大多数-F端基被去除,许多-OH端基被-O端基取代,并且O端基的Ti3C2(Ti3C2O2)对K+和Li+表现出更高的吸附能力和更低的扩散势垒,这保证了优异的离子存储能力和快速的离子扩散和传输,使材料具有更好的电化学性能。 研究表明,导电创面敷料可以促进创面部位的细胞行为,与细胞增殖、胶原蛋白沉积、肉芽组织形成和血管生成有关的多个基因表达有关,从而调节创面愈合过程[21-22]。因此,以MXene为主要基材构建的水凝胶将被赋予良好的导电性和促创面修复功效。人造皮肤、传感器的快速发展对导电水凝胶的要求越来越高。WAN等[23]为了开发有自供电特性的新型水凝胶,在湿发电技术的基础上设计了一种导电MXene-纤维素纳米晶体-罗望子胶-聚丙烯酰胺水凝胶,具有感应压力、应变、湿度和温度的优势,MXene的加入极大加强了水凝胶的高灵敏度和高导电性。LIU等[18]以聚(丙烯酰胺-co-磺基甜菜碱甲基丙烯酸酯)为水凝胶骨架,将银纳米粒子和聚多巴胺修饰的MXene纳米复合材料以异质结构构型设计合成水凝胶,该水凝胶具有宽范围、高灵敏度、再现性良好、快速响应性和弹性等特性,可以检测人体的各种动作、面部表情和体内心跳信号,在电刺激下可修复糖尿病创面。ZHAO等[24]用丙烯酸和丙烯酰胺为聚合物单体,以MXene负载聚二烯丙基二甲基氯化铵为模板构建的半互穿网络水凝胶,在室温下储存30 d后仍具有优异的应变响应和柔韧性,在1 100次循环后性能也不会下降[25]。 2.2.2 MXene的光热性能 MXene具有的电磁波吸收能力使其能够有效吸收阳光,产生良好的光热效应,未反射的电磁波可以穿过MXene晶格结构在层间进行内部反射,最终被结构吸收,这一特性保证了MXene材料在广阔的太阳光谱范围内的有效光吸收。近红外触发的智能热响应水凝胶可以很好地提高水凝胶对创面的修复效率,MXene的局部表面离子体共振效应和近红外吸收能力使其具有优异的光热转换效率,可达近乎100%[26]。 LI等[15]研究报道的一种可注射性水凝胶,通过H2O2/HbO2体系催化交联透明质酸-多巴胺的邻苯二酚基团和MXene@聚多巴胺氧化偶联形成,其中MXene提供一个由近红外激发产生温和热量的平台,进而激活HbO2氧载体控释氧气,有效促进糖尿病的创面愈合。LIN等[27]的研究证明,Ti3C2纳米薄片具有超高的光热转换效率,但合成的MXene具有亲水性,导致其在生理培养基中的稳定性较差,同时也会造成局部不均匀的光热效应。鉴于此,现阶段的研究考虑采用复合材料改善其性质。在对MXene中Ti3C2片的研究上,通常使用酸性介质如具有强腐蚀性的浓氢氟酸或HCl和氟化物盐的混合物。为了更好地提取Al层,XUAN等[28]使用有机碱四甲基氢氧化铵制备了功能化Ti3C2片,经过铝氧阴离子表面修饰后Ti3C2薄片在近红外区域具有强而宽的吸收,其性能相当甚至优于最先进的光吸收材料(包括金纳米结构、碳基材料和过渡金属双卤代烷),可作为一种有效的光热转换剂。DONG等[29]通过混合、冻干水合的程序制备了壳聚糖-MXene非交联水凝胶,可以快速吸附多重耐药菌细胞,在近红外照射下的抗菌效果可达99.18%。有研究制备了Nb2C-MXene钛板材料,研究了细菌膜和Nb2C-MXene尖锐边缘之间的物理相互作用以及光热行为和光热协同抗菌作用[30]。PARK等[31]将环丙沙星负载在MXene上,同时与海藻酸钠混合制备环丙沙星-MX@海藻酸钠,可通过近红外刺激进行药物递送,加速创面愈合。由以上研究可以看出,MXene具有理想的光热性能。使用近红外光来照射MXene复合材料进而提供热透能量以及氧化应激来针对难愈性创面带来的反复感染,能改善难愈性创面处的微环境,加快创面愈合速度,提高了MXene在创面敷料中的应用价值。 2.2.3 MXene的生物相容性 MXene表面端基含有的羟基(-OH)、氧(-O)以及氟(-F)会决定MXene的表面亲水性质,实验通过去离子水对冷压MXene盘的表面接触角进行测量,证明其具有亲水性,亲水性好意味着生物相容性良好,一些常见的钛基MXene具有生物相容性,如Ti3AlC2。MXene对正常细胞的细胞毒性远小于癌症细胞等非正常细胞,MXene的尺寸在1-100 nm范围内,可以被细胞正常内化[32]。RAFIEERAD等[33]通过将蜂蜜和MXene结合到临床认可的壳聚糖中,所开发的多功能异质结构表现出优异的多孔结构,具有所需的溶胀性和可控的降解性,这种导电复合材料具有高度的生物相容性。ZHU等[34]提出了一种策略,通过将MXene作为纳米填料加入海藻酸盐醛和明胶水凝胶中合成多功能MXene-海藻酸盐醛水凝胶,该水凝胶具有良好的导电性和生物相容性,并且由于海藻酸盐醛凝胶网络的动态亚胺连接而保持了良好的自修复性能。 用于创面敷料的水凝胶需具有良好的生物相容性。经实验证明MXene与红细胞有较好的生物相容性,即使MXene的质量浓度高达200 μg/mL,其引起的溶血百分比仍然可以忽略不计(仅0.8%)。相比之下,在相同处理浓度下石墨烯引起的溶血率达到50.8%[35]。WANG等[36]首次证明了MXene对典型促炎细胞因子白细胞介素6具有超高的去除能力,是传统活性炭吸附剂去除白细胞介素6能力的13.4倍。MXene具有良好的血液相容性,SZUPLEWSKA等[37]系统证明了经过大豆磷脂表面改性的MnOx/MXene具有良好的体外细胞相容性和体内生物安全性。生物医学方面最重要的就是安全性和稳定性,就目前所进行的研究整体来看,MXene在宽浓度范围内具有良好的生物相容性。 2.2.4 MXene的抗菌性能 抗菌性能与材料自身的片层结构性质、片状尺寸和表面电荷等有密切联系[38]。MXene的抗菌特性依靠自身纳米刀的结构以及能氧化还原生成活性氧。所谓纳米刀结构是指MXene的锋利边缘(纳米刀)会对细菌细胞壁造成一定的破坏,引起严重的膜破坏及细胞质泄露,并且随着MXene浓度的增加,细胞会团聚包围在MXene纳米片上。活性氧是指内部结构有不成对电子的活性氧化分子,有着消灭细菌和癌细胞的功能。RASOOL等[39]研究了单层和多层MXene薄片在胶体溶液中的抗菌性能,结果表明与被广泛报道的抗菌剂氧化石墨烯相比,MXene对革兰阴性大肠杆菌和革兰阳性枯草杆菌均表现出更高的抗菌效率和抑菌活性。同石墨烯类似,MXene作为一种高电子传导性的新型材料,在经808 nm的近红外光辐射时,光激发Ti3C2的自由电子传递能量从三线态氧(3O2)产生单线态氧(1O2),活性氧能够氧化细菌内的谷胱甘肽进一步造成氧化应激,导致细菌死亡[40]。 慢性细菌感染的创面修复到目前为止还是一个亟待攻克的难题,临床治疗主要使用抗生素,但此方法对抗感染和创面恢复的效率并没有很大的作用。ZHOU等[14]将MXene引入多功能水凝胶支架用于耐细菌感染的创面愈合研究,结果显示该水凝胶对耐多种常用抗生素甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌的抗菌活性高达99.03%。面对天然来源材料制备的水凝胶孔隙率难以控制的问题,ROZMYS?OWSKA-WOJCIECHOWSKA等[41]在维生素C稳定的壳聚糖-透明质酸基质纳米复合结构中通过添加MXene来降低水凝胶的孔隙率,在改变水凝胶结构的同时也提高了其抗菌能力。ZHENG等[42]利用MXene的纳米刀抗菌原理开发了一种可注射同时可自我修复的水凝胶,首次将CeO2纳米颗粒负载在MXene表面形成复合材料,提高了抗炎能力,为多重耐药菌感染受损皮肤的有效治疗提供了一种无需抗生素协助的水凝胶敷料新模式。未来联合应用MXene和其他具有生物活性的纳米粒子构建多功能水凝胶,是创面敷料设计的研究热点。 2.3 MXene在创面修复中的应用 2.3.1 创面监测 创面监测是水凝胶敷料智能化革新的一个重要方向。近年来,有关MXene在传感监测方面进行的研究越来越深入,主要有压阻式传感器、生物传感器和物理传感器3个大方向。石墨烯和氧化石墨烯的易团聚会造成自身功能化,使得电导率下降,功能应用受到限制[43];具有类似结构的MoS2,由于自身低电导率和疏水性限制了其在传感器方面的应用[44],而与上述常规传感器材料相比,MXene具有良好稳定的分散性。MXene基水凝胶所具备的柔软可拉伸性、导电性及生物相容性是传感器的基本特性,很适合应用于进行创面修复的可穿戴/植入型器件。MXene在创面监测方面的作用机制是片层间距压缩导致的电导率增加,在经过4 000次循环之后仍保持着敏感的压缩力和应变力,并且具有较高的灵敏度[45](图4)。HU等[46]制备的 MXene/再生丝素蛋白水凝胶表现出良好的导电性和传感功能,可用作压阻式压力传感器用于监测电生理微环境。慢性创面在3个月内无法自己再生受损组织,需多次复诊治疗,耗费额外成本。ZHANG等[47]开发了一种具有出色传感功能的MXene-聚乙烯醇水凝胶传感材料,拥有优异的应变灵敏性、瞬时自修复性和出色的拉伸性能,可以根据拉伸和压缩应变产生不同的电阻值生成电信号,有望应用于人造皮肤或者用于具有释药促愈功能的柔性功能性敷料。但是,同时实现水凝胶优异的导电性能、拉伸性能和低检测阈值仍然是一个极端的挑战。LI等[48]基于Ti3C2Tx/锂盐/聚(丙烯酰胺)/聚乙烯醇在甘油/水二元溶剂中简单浸泡得到了一种超高拉伸和高导电性水凝胶,该水凝胶可以应用8×8像素化传感阵列,通过监测不同部位阻力的变化来反映对目标的精确识别,展示了从微小生理信号到大规模人体运动的人类健康检测潜在能力。 将一些生物材料和生物标志物作为检测指标可以设计为生物传感器,进行身体代谢情况诊断、治疗结果推断以及身体环境的病原体的评估,可分为药物生物传感、免疫检测生物传感、神经递质生物传感等[49],例如目前已报道的全氟磺酸基聚合物MXene传感器[50]、MXene/NiCo层状双氢氧化物传感器[51]、DNA-PNA传感器[52]。光学传感器利用的是MXene的表面等离子共振、荧光共振能量转移等光学传感原理[53],有研究构建的一种凝血酶结合适配体-MXene传感器,可以根据荧光光谱的变化监测凝血酶[54]。 以上研究表明,MXene与其他各种材料的结合显示了良好的结构特点和功能特性,虽然现阶段传感器研究主要出于压力和电阻的物理传感器方向,但在朝着智能化发展的进程中MXene为智能传感提供了更多的可能,已成为创面修复领域极具前景的材料选择。 "
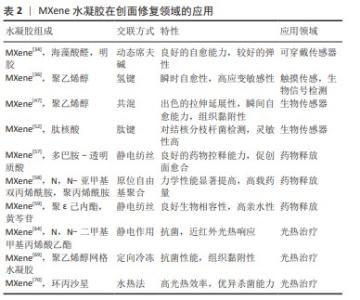
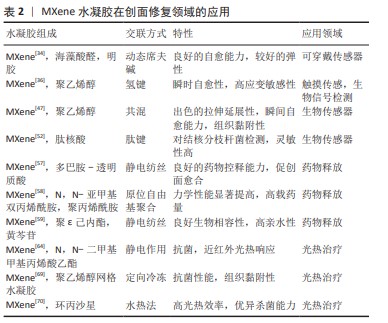
2.3.2 药物递送与缓释 药物递送与缓释是指将不同病理所需的治疗剂以适当的药代动力学运输到体内并释放进行治疗的过程,但是由于代谢和一些不良反应,药物的生物利用度会降低。通过药物负载在纳米结构平台上可以实现药物的持续释放,获得更好的稳定性以及细胞对药物的摄取,降低了药物载体对细胞组织造成的毒性[55],近年来智能型控释的水凝胶发展最为迅速。与其他生物材料相比,MXene上有很多锚定位点,同时也有极高的比表面积,可用作载体递送的优良平台[56]。与MoS2相比,MXene表面含有的羟基(-OH)、氧(-O)以及氟(-F)具有很好的亲水性且可以进一步改性,得到有更好生物相容性的药物递送载体。功能化的纳米氧化石墨烯体系主要通过非共价物理吸附实现载药,仍存在载药量不稳定的问题。 JIN等[16]分别制备了负载甲磺酸去铁胺和乙酰水杨酸两类正向因子的近红外响应MXene纳米纤维和水凝胶双结构体系(MNFs@DFOM-H@AC),双结构体系整合了两类正向因子各自的优势,实现了创面的无瘢痕愈合,光热效应可以调节甲磺酸去铁胺的释放,同时不伤害皮肤;从水凝胶释放的乙酰水杨酸可以调节创面部位的免疫微环境,发挥抗炎和促血管形成功效。另外,LIN等[57]还制备了一种具有核壳结构的促进血管生成和防止瘢痕产生的水凝胶创可贴,它由负载 MXene的纳米纤维为核、多巴胺-透明质酸水凝胶为壳,封装生长因子和H2S供体,该系统连续释放产生的H2S诱导巨噬细胞极化成M2表型,调节免疫微环境并抑制创面部位的过度炎症反应,有利于皮肤细胞的增殖,促进创面愈合。这些研究说明MXene基水凝胶显示出良好的药物递送与缓释效果,有望成为一种构建药物递送载体的极具潜力的纳米平台。ZHANG等[58]将MXene作为交联剂与聚丙烯酰胺有机结合合成了Ti3C2/聚丙烯酰胺水凝胶,该水凝胶的机械性能得到大幅提升且具有稳定的溶胀能力,为氯霉素提供了有效的载体并提高了生物活性。近年来,中草药中抗菌提取物的使用频率大幅增加,例如:ZENG等[59]制备了黄芩苷-聚ε己内酯-MXene三元复合水凝胶,将黄芩苷与MXene相结合极大提高了黄芩苷的亲水性并有助于黄芩苷的释放,此水凝胶表现出良好的抗菌活性。 将药物负载在MXene上通过药物递送载体控制其释放,极大减少了药物在递送过程中的损耗情况以及不良反应,可以使药物的利用度达到最大值[60],通过与光热效应响应、pH值响应等结合实现药物智能控释,在创面处可控调节相关炎症因子,加速创面愈合。 2.3.3 光热治疗 长期服用抗生素会让细菌产生耐药性,导致在突发严重疾病时抗生素失效,同时也会产生胃肠道刺激、呕吐、肠道紊乱等不良反应,因此,如何在不诱发耐药性的情况下切断耐药菌的产生仍是此类创面修复面临的挑战。基于MXene优异光热性能的光热疗法已经成为一种很有希望的解决方法,MXene在近红外区域(700-1 100 nm)表现出很强的吸附性和较高的光热转化率,在近红外光激发下可在380-780 nm范围进行吸收,而氧化石墨烯激在近红外光发下的吸收范围为600-800 nm。MXene会产生局部热能、活性氧、自由基来抵抗细菌感染[61],同时MXene上的光热治疗过程会引起蛋白质的变性和失活,进而破环细菌的完整性,细菌也不会对光热治疗产生依赖性[62]。实验证明,在473 nm或者785 nm激光下的测试中MXene都有100%的内部光热转换效率,高于MoS2纳米片(27.6%)和MoS2纳米薄片(24.4%)的光热转化效率。CHEN等[63]制备了具有0.94 mm的E-MoS2纳米片,实验结果显示其光热转换效率仅达到62%。 针对多重耐药菌感染,YANG等[64]利用带负电的MXene和带正电的季铵化含冰片聚合物结合以产生季铵化含冰片聚合物官能化的MXene纳米片,克服了MXene低靶向细菌能力的问题,该纳米片可以在细菌细胞壁原位产生局部热量进行靶向光热治疗。田煜等[65]利用静电作用构筑了MXene与铜铁双金属过氧化物复合材料体系 MXene-CFps,实现光热-光/化双动力协同抗菌疗法,在近红外光激发下MXene-CFps 材料有着优异的光热转化效果以及双动力产活性氧的特征,也具备消灭细菌的能力,这种疗法为组织修复中常见的细菌感染问题提供了一种不使用抗生素且多种方法协同的新思路。LIU等[66]将金纳米颗粒负载在MXene上,再引入壳聚糖和β-甘油磷酸二钠盐交联的水凝胶网络,该复合体系有很强的近红外吸收和光热协同作用,β-甘油磷酸二钠盐是一种具有优良生物相容性的电负性物理交联剂,其降解产物是适合人体的常见磷补充剂,因此该水凝胶有具有协同的近红外、pH值和热多反应药物递送特性。CHENG等[67]提出一种多功能MXene负载锌的氧化纤维素水凝胶,其在近红外照射下持续释放锌离子,抗菌效果达到99.8%,同时也能达到高效止血的作用。在同样的思路下,HU等[68]将MXene-锌复合材料加入到琼脂和海藻酸钠的水凝胶中,得到了光热性能高、光热转换率高杀菌效果好的天然多糖水凝胶。LI等[69]制备了具有各向异性的聚乙烯醇网络水凝胶,将其负载在具有生物相容性的MXene表面,通过光热治疗的近红外照射对细菌造成不可逆破坏,解决了MXene在创面处稳定性差、容易脱落等问题,为细菌感染的创面修复提供了合适的微环境。另外,面对体内细菌反弹导致的抗菌性能无法满足需求的挑战,ZHENG等[70]通过构建包含抗生素环丙沙星的杂化温敏水凝胶,将细菌引入“陷阱和杀死机制”,该水凝胶在近红外的照射下有较高的光热转换效率,同时可以激发环丙沙星的持续释放,避免了光热治疗后细菌的反弹,目前正在研究有效剂量在临床中的具体应用。 针对当前水凝胶创面敷料临床产品存在的生物相容性差、功效不足等问题,MXene基水凝胶材料可根据功能需求进行定向开发,目前研究主要集中在创面监测、药物递送与缓释和光热治疗等新型智能创面敷料领域,实例见表2所示。 "
| [1] POWERS JG, HIGHAM C, BROUSSARD K, et al. Wound healing and treating wounds: Chronic wound care and management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74(4):607-625; quiz 625-606. [2] SUN BK, SIPRASHVILI Z, KHAVARI PA. Advances in skin grafting and treatment of cutaneous wounds. Science. 2014;346(6212):941-945. [3] ZHU Y, CANKOVA Z, IWANASZKO M, et al. Potent laminin-inspired antioxidant regenerative dressing accelerates wound healing in diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(26):6816-6821. [4] 甘丽莉,熊娜,刘燕飞.水凝胶药物支架修复皮肤创面:临床应用可能性的挑战[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(22):3578-3583. [5] ZHANG A, LIU Y, QIN D, et al. Research status of self-healing hydrogel for wound management: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;164:2108-2123. [6] LIU J, YU H, WANG L, et al. Two-dimensional metal-organic frameworks nanosheets: Synthesis strategies and applications. Inorg Chim Acta. 2018; 483:550-564. [7] HEMANTH NR, KANDASUBRAMANIAN B. Recent advances in 2D MXenes for enhanced cation intercalation in energy harvesting Applications: A review. Chem Eng J. 2020;392:12367801-12367815. [8] LEI D, LIU N, SU T, et al. Roles of MXene in Pressure Sensing: Preparation, Composite Structure Design, and Mechanism. Adv Mater. 2022;34(52): e2110608. [9] HALIM J, LUKATSKAYA MR, COOK KM, et al. Transparent Conductive Two-Dimensional Titanium Carbide Epitaxial Thin Films. Chem Mater. 2014;26(7): 2374-2381. [10] GHIDIU M, LUKATSKAYA MR, ZHAO MQ, et al. Conductive two-dimensional titanium carbide ‘clay’ with high volumetric capacitance. Nature. 2014; 516(7529):78-81. [11] LIN H, CHEN Y, SHI J. Insights into 2D MXenes for Versatile Biomedical Applications: Current Advances and Challenges Ahead. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018;5(10):1800518. [12] WON JS, PRASAD C, JEONG SG, et al. Recent advances in the development of MXenes/cellulose based composites: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;240:124477. [13] GUO J, YU Y, ZHANG D, et al. Morphological Hydrogel Microfibers with MXene Encapsulation for Electronic Skin. Research (Washington, DC). 2021; 2021:7065907. [14] ZHOU L, ZHENG H, LIU Z, et al. Conductive Antibacterial Hemostatic Multifunctional Scaffolds Based on Ti3C2Tx MXene Nanosheets for Promoting Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria-Infected Wound Healing. ACS Nano. 2021; 15(2):2468-2480. [15] LI Y, FU R, DUAN Z, et al. Artificial Nonenzymatic Antioxidant MXene Nanosheet-Anchored Injectable Hydrogel as a Mild Photothermal-Controlled Oxygen Release Platform for Diabetic Wound Healing. ACS Nano. 2022;16(5):7486-7502. [16] JIN L, MA Y, WANG R, et al. Nanofibers and hydrogel hybrid system with synergistic effect of anti-inflammatory and vascularization for wound healing. Mater Today Adv. 2022;14:100224. [17] KANG X, LI Y, DUAN Z, et al. A Mxene@TA/Fe dual-nanozyme composited antifouling hydrogel for burn wound repair. Chem Eng J. 2023;476: 146420. [18] LIU D, BI S, WANG H, et al. Polydopamine interface-modulated MXene-based conductive antibacterial hydrogels for on-skin health monitoring and diabetic wound healing. Compos Part A. 2024;180:108065. [19] SHAHZAD F, ALHABEB M, HATTER CB, et al. Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes). Science. 2016; 353(6304):1137-1140. [20] GUAN K, DONG L, XING Y, et al. Structure and surface modification of MXene for efficient Li/K-ion storage. J Energy Chem. 2022;75:330-339. [21] GUO B, MA PX. Conducting Polymers for Tissue Engineering. Biomacromolecules. 2018;19(6):1764-1782. [22] HE J, SHI M, LIANG Y, et al. Conductive adhesive self-healing nanocomposite hydrogel wound dressing for photothermal therapy of infected full-thickness skin wounds. Chem Eng J. 2020;394:124888. [23] WAN B, LIU N, ZHANG Z, et al. Water-dispersible and stable polydopamine coated cellulose nanocrystal-MXene composites for high transparent, adhesive and conductive hydrogels. Carbohydr Polym. 2023;314:120929. [24] ZHAO L, XU H, LIU L, et al. MXene-Induced Flexible, Water-Retention, Semi-Interpenetrating Network Hydrogel for Ultra-Stable Strain Sensors with Real-Time Gesture Recognition. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(30):e2303922. [25] HE J, ZOU H, ZHOU J, et al. Thermoresponsive MXene-based hydrogel for controlled anticancer drug release. J Drug Delivery Sci Technol. 2024;91: 105207. [26] HE L, DI D, CHU X, et al. Photothermal antibacterial materials to promote wound healing. J Control Release. 2023;363:180-200. [27] LIN H, WANG X, YU L, et al. Two-Dimensional Ultrathin MXene Ceramic Nanosheets for Photothermal Conversion. Nano Lett. 2017;17(1):384-391. [28] XUAN J, WANG Z, CHEN Y, et al. Organic‐Base‐Driven Intercalation and Delamination for the Production of Functionalized Titanium Carbide Nanosheets with Superior Photothermal Therapeutic Performance. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2016;55(47):14569-14574. [29] DONG Y, LIU J, CHEN Y, et al. Photothermal and natural activity-based synergistic antibacterial effects of Ti(3)C(2)T(x) MXene-loaded chitosan hydrogel against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;240:124482. [30] 秦苗,CHAIMA M, 苏一蒙,等.MXene及MXene/碳基复合材料在生物医学领域的研究进展[J].新型炭材料(中英文),2023,38(3):496-509. [31] PARK H, KIM JU, KIM S, et al. Sprayable Ti(3)C(2) MXene hydrogel for wound healing and drug release system. Mater Today Bio. 2023;23:100881. [32] LIM GP, SOON CF, MA NL, et al. Cytotoxicity of MXene-based nanomaterials for biomedical applications: A mini review. Environ Res. 2021;201:111592. [33] RAFIEERAD A, SEQUIERA GL, YAN W, et al. Sweet-MXene hydrogel with mixed-dimensional components for biomedical applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020;101:103440. [34] ZHU H, DAI W, WANG L, et al. Electroactive Oxidized Alginate/Gelatin/MXene (Ti3C2Tx) Composite Hydrogel with Improved Biocompatibility and Self-Healing Property. Polymers. 2022;14(18):3908. [35] HUANG J, SU J, HOU Z, et al. Cytocompatibility of Ti(3)C(2)T(x) MXene with Red Blood Cells and Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells and the Underlying Mechanisms. Chem Res Toxicol. 2023;36(3):347-359. [36] WANG T, SUN X, GUO X, et al. Ultraefficiently Calming Cytokine Storm Using Ti3C2Tx MXene. Small Methods. 2021;5(5):2001108. [37] SZUPLEWSKA A, KULPIŃSKA D, JAKUBCZAK M, et al. The 10th anniversary of MXenes: Challenges and prospects for their surface modification toward future biotechnological applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022;182:114099. [38] SEIDI F, ARABI SHAMSABADI A, DADASHI FIROUZJAEI M, et al. MXenes Antibacterial Properties and Applications: A Review and Perspective. Small. 2023;19(14):2206716. [39] RASOOL K, HELAL M, ALI A, et al. Antibacterial Activity of Ti3C2Tx MXene. ACS Nano. 2016;10(3):3674-3684. [40] GE J, LAN M, ZHOU B, et al. A graphene quantum dot photodynamic therapy agent with high singlet oxygen generation. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4596. [41] ROZMYSŁOWSKA-WOJCIECHOWSKA A, KARWOWSKA E, GLOC M, et al. Controlling the Porosity and Biocidal Properties of the Chitosan-Hyaluronate Matrix Hydrogel Nanocomposites by the Addition of 2D Ti3C2Tx MXene. Materials. 2020;13(20):4587. [42] ZHENG H, WANG S, CHENG F, et al. Bioactive anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, conductive multifunctional scaffold based on MXene@CeO2 nanocomposites for infection-impaired skin multimodal therapy. Chem Eng J. 2021;424:130148. [43] YANG G, LIU F, ZHAO J, et al. MXenes-based nanomaterials for biosensing and biomedicine. Coord Chem Rev. 2023;479:215002. [44] KUMAR S, LEI Y, ALSHAREEF NH, et al. Biofunctionalized two-dimensional Ti(3)C(2) MXenes for ultrasensitive detection of cancer biomarker. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;121:243-249. [45] LI Y, HUANG S, PENG S, et al. Toward Smart Sensing by MXene. Small. 2022; 19(14):2206126. [46] HU ZC, LU JQ, ZHANG TW, et al. Piezoresistive MXene/Silk fibroin nanocomposite hydrogel for accelerating bone regeneration by Re-establishing electrical microenvironment. Bioact Mater. 2023;22:1-17. [47] ZHANG YZ, LEE KH, ANJUM DH, et al. MXenes stretch hydrogel sensor performance to new limits. Sci Adv. 2018;4(6):eaat0098. [48] LI Q, ZHI X, XIA Y, et al. Ultrastretchable High-Conductivity MXene-Based Organohydrogels for Human Health Monitoring and Machine-Learning-Assisted Recognition. ACS Appl Mater. 2023;15(15):19435-19446. [49] HO DH, CHOI YY, JO SB, et al. Sensing with MXenes: Progress and Prospects. Adv Mater. 2021;33(47):e2005846. [50] SHAHZAD F, IQBAL A, ZAIDI SA, et al. Nafion-stabilized two-dimensional transition metal carbide (Ti3C2Tx MXene) as a high-performance electrochemical sensor for neurotransmitter. J Ind Eng Chem. 2019;79: 338-344. [51] SUN Q, ZHANG Y, GAO P, et al. Three-dimensional NiO/Co(3)O(4)@C composite for high-performance non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Anal Sci. 2023;39(1):33-42. [52] ZHANG J, LI Y, DUAN S, et al. Highly electrically conductive two-dimensional Ti(3)C(2) Mxenes-based 16S rDNA electrochemical sensor for detecting Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Anal Chim Acta. 2020;1123:9-17. [53] ZHU X, ZHANG Y, LIU M, et al. 2D titanium carbide MXenes as emerging optical biosensing platforms. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021;171:112730. [54] CUI H, FU X, YANG L, et al. 2D titanium carbide nanosheets based fluorescent aptasensor for sensitive detection of thrombin. Talanta. 2021; 228:122219. [55] RAMASAMY T, RUTTALA HB, GUPTA B, et al. Smart chemistry-based nanosized drug delivery systems for systemic applications: A comprehensive review. J Control Release. 2017;258:226-253. [56] LU B, ZHU Z, MA B, et al. 2D MXene Nanomaterials for Versatile Biomedical Applications: Current Trends and Future Prospects. Small. 2021;17(46): 2100946. [57] JIN L, GUO X, GAO D, et al. An NIR photothermal-responsive hybrid hydrogel for enhanced wound healing. Bioact Mater. 2022;16:162-172. [58] ZHANG P, YANG XJ, LI P, et al. Fabrication of novel MXene (Ti3C2)/polyacrylamide nanocomposite hydrogels with enhanced mechanical and drug release properties. Soft Matter. 2020;16(1):162-169. [59] ZENG W, CHENG NM, LIANG X, et al. Electrospun polycaprolactone nanofibrous membranes loaded with baicalin for antibacterial wound dressing. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):10900. [60] QIN M, JIN J, SAIDING Q, et al. In situ inflammatory-regulated drug-loaded hydrogels for promoting pelvic floor repair. J Control Release. 2020;322: 375-389. [61] 徐静,吕慧欣,鲍鑫,等.近红外光响应水凝胶在组织工程领域的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(3):486-492. [62] HAO S, HAN H, YANG Z, et al. Recent Advancements on Photothermal Conversion and Antibacterial Applications over MXenes-Based Material. Nanomicro Lett. 2022;14(1):178. [63] CHEN F, LUO Y, LIU X, et al. 2D Molybdenum Sulfide-Based Materials for Photo-Excited Antibacterial Application. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(13): e2200360. [64] YANG L, CHEN S, WEI H, et al. Low-Temperature Photothermal Therapy Based on Borneol-Containing Polymer-Modified MXene Nanosheets. ACS Appl Mater. 2022;14(40):45178-45188. [65] 田煜,张姝婷,邓怡,等.MXene/过氧化物复合材料的制备及抗菌性能研究[J].应用化工,2023,52(6):1619-1625. [66] LIU C, YANG P, LI J, et al. NIR/pH-responsive chitosan hydrogels containing Ti(3)C(2)/AuNRs with NIR-triggered photothermal effect. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;295:119853. [67] CHENG F, YI X, DAI J, et al. Photothermal MXene@Zn-MOF-decorated bacterial cellulose-based hydrogel wound dressing for infectious wound healing. Cell Rep Phys Sci. 2023;4(10):101619. [68] HU Y, ZENG Q, HU Y, et al. MXene/zinc ion embedded agar/sodium alginate hydrogel for rapid and efficient sterilization with photothermal and chemical synergetic therapy. Talanta. 2024;266:125101. [69] LI Y, HAN M, CAI Y, et al. Muscle-inspired MXene/PVA hydrogel with high toughness and photothermal therapy for promoting bacteria-infected wound healing. Biomater Sci. 2022;10(4):1068-1082. [70] ZHENG Y, YAN Y, LIN L, et al. Titanium carbide MXene-based hybrid hydrogel for chemo-photothermal combinational treatment of localized bacterial infection. Acta Biomater. 2022;142:113-123. |
| [1] | Zhao Hongxia, Sun Zhengwei, Han Yang, Wu Xuechao , Han Jing. Osteogenic properties of platelet-rich fibrin combined with gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 809-817. |
| [2] | Zhao Zengbo, Li Chenxi, Dou Chenlei, Ma Na, Zhou Guanjun. Anti-inflammatory and osteogenic effects of chitosan/sodium glycerophosphate/sodium alginate/leonurine hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 678-685. |
| [3] | Dong Meilin, Du Haiyu, Liu Yuan. Quercetin-loaded carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel promotes wound healing in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 692-699. |
| [4] |
Zhang Bo, Zhang Zhen, Jiang Dong.
Tannic acid modified interpenetrating network hydrogel promotes tissue remodeling of ruptured Achilles tendon after surgery#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 721-729.
|
| [5] | Liu Zhongyu, Li Wenya, Fan Yonghong, Lyu Shuang, Pei Juan, Chen Yaqin, Liu Beiyu, Sun Hongyu. Methacrylated dermal extracellular matrix hydrogel promotes repair of abdominal wall defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2074-2082. |
| [6] | Zhao Wenqi, Yu Haichi, Song Yiru, Yuan Tianyang, Liu Qinyi. Platelet-rich plasma and hydrogel for spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2189-2200. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||