Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (21): 4492-4498.doi: 10.12307/2025.167
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanical performance of a novel press-fit lumbar intervertebral fusion device
Li Shiwen, Yu Changshui, Liu Qi, Wang Zhibo, Liu Yuliang, Qi Quan
- First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Received:2024-01-04Accepted:2024-03-27Online:2025-07-28Published:2024-12-06 -
Contact:Qi Quan, MD, Chief physician, First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Li Shiwen, MS, Attending physician, First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China Yu Changshui, MS, Associate chief physician, First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China Li Shiwen and Yu Changshui contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:Youth Reserve Talent Foundation of Harbin Science and Technology Bureau, No. 2017RAQXJ185 (to QQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Shiwen, Yu Changshui, Liu Qi, Wang Zhibo, Liu Yuliang, Qi Quan. Mechanical performance of a novel press-fit lumbar intervertebral fusion device[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(21): 4492-4498.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
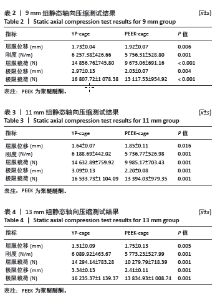
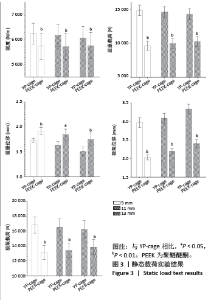
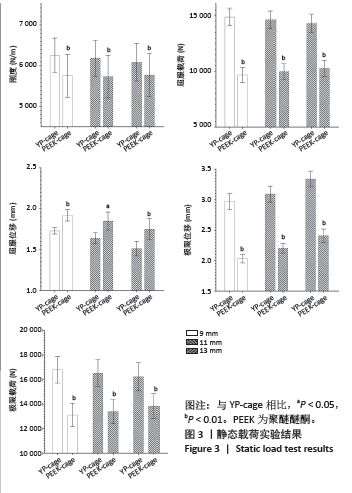
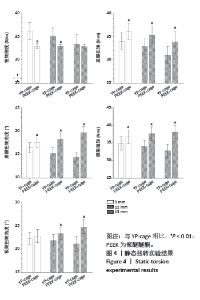
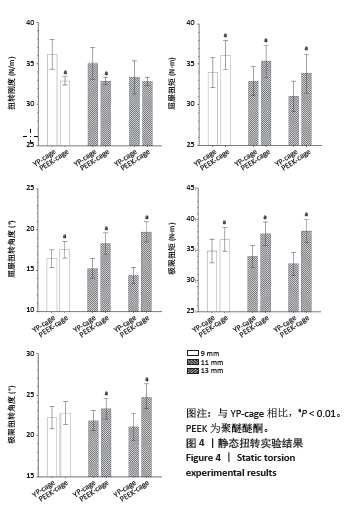
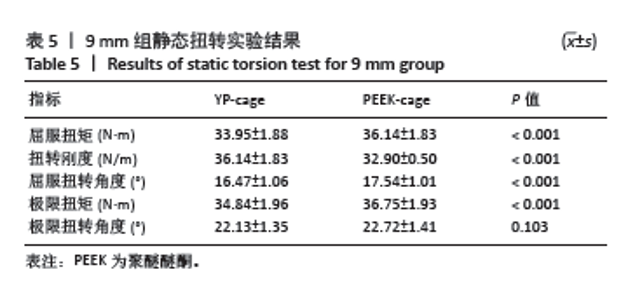
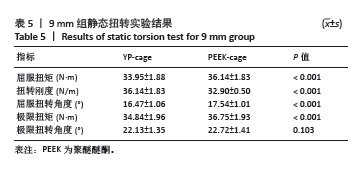
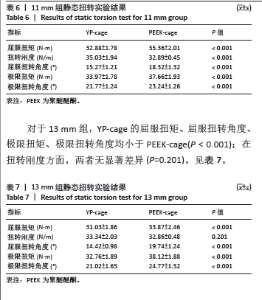
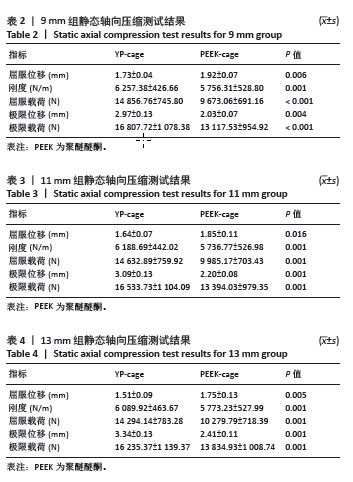
2.1 静态载荷实验结果 静态轴向压缩测试结果如图3所示,进行了对9 mm、11 mm和13 mm组椎间融合器的力学性能评估。 在9 mm组中,YP-cage的屈服位移低于PEEK-cage(P=0.006),表明其在屈服前有较少的形变。YP-cage的刚度高于PEEK-cage(P=0.001),反映了更好的结构抵抗形变的能力。在屈服载荷方面,YP-cage显著高于PEEK-cage(P < 0.001)。YP-cage的极限位移和极限载荷也超过了PEEK-cage(P=0.004,P < 0.001),这表明YP-cage在达到破坏前能够承受更大的形变和载荷。见表2。 在11 mm组中,YP-cage的屈服位移依然低于PEEK-cage(P=0.016),YP-cage刚度更大(P < 0.001)。屈服载荷的对比中,YP-cage同样表现出比PEEK-cage更强的结构承载能力(P < 0.001)。YP-cage在极限位移(P=0.001)和极限载荷(P < 0.001)这2个指标上都优于PEEK-cage。见表3。 在13 mm组中,YP-cage的屈服位移依然低于PEEK-cage(P=0.005),而YP-cage刚度更高(P=0.001)。YP-cage的屈服载荷(P < 0.001)和极限载荷(P < 0.001)均高于PEEK-cage。见表4。"
| [1] ZHANG Q, CHON T, ZHANG Y, et al. Finite element analysis of the lumbar spine in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis subjected to different loads. Comput Biol Med. 2021;136:104745. [2] PENG P, CHEN K, CHEN H, et al. Comparison of O-arm navigation and microscope-assisted minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion and conventional transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of lumbar isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Orthop Translat. 2020;20:107-112. [3] 赵洪顺, 阿尖措, 王德元, 等. 影响外侧入路腰椎椎间融合器置入后早期椎间隙高度的因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(21): 3332-3336. [4] 陈柳旭, 杨函, 杨剑, 等. 椎间融合与双侧经椎弓根经椎间盘螺钉置入后腰椎生物力学的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(12):1815-1822. [5] LOENEN A, PETERS M, BEVERS R, et al. Early bone ingrowth and segmental stability of a trussed titanium cage versus a polyether ether ketone cage in an ovine lumbar interbody fusion model. Spine J. 2022;22(1):174-182. [6] 姚汝斌, 王仕永, 杨开舜. 微创经椎间孔椎间融合治疗单节段腰椎管狭窄症对腰椎-骨盆平衡的改善作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021,25(9):1387-1392. [7] TAN QC, LIU ZX, ZHAO Y, et al. Biomechanical comparison of four types of instrumentation constructs for revision surgery in lumbar adjacent segment disease: A finite element study. Comput Biol Med. 2021;134: 104477. [8] HUA W, ZHI J, KE W, et al. Adjacent segment biomechanical changes after one- or two-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion using either a zero-profile device or cage plus plate: A finite element analysis. Comput Biol Med. 2020;120:103760. [9] LIU C, ZHAO M, ZHANG W, et al. Biomechanical assessment of different transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion constructs in normal and osteoporotic condition: a finite element analysis. Spine J. 2024;24(6):1121-1131. [10] FOGEL G, MARTIN N, LYNCH K, et al. Subsidence and fusion performance of a 3D-printed porous interbody cage with stress-optimized body lattice and microporous endplates - a comprehensive mechanical and biological analysis. Spine J. 2022;22(6):1028-1037. [11] BASGUL C, MACDONALD DW, SISKEY R, et al. Thermal Localization Improves the Interlayer Adhesion and Structural Integrity of 3D printed PEEK Lumbar Spinal Cages. Materialia (Oxf). 2020;10:100650. [12] LI JX, HSU TJ, HSU SB, et al. Strong association of lumbar disk herniation with diabetes mellitus: a 12-year nationwide retrospective cohort study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1260566. [13] BEUKERS M, GRINWIS G, VERNOOIJ J, et al. Epidemiology of Modic changes in dogs: Prevalence, possible risk factors, and association with spinal phenotypes. JOR Spine. 2023;6(3):e1273. [14] PAN FM, WANG SJ, YONG ZY, et al. Risk factors for cage retropulsion after lumbar interbody fusion surgery: Series of cases and literature review. Int J Surg. 2016;30:56-62. [15] LU T, REN J, SUN Z, et al. Relationship between the elastic modulus of the cage material and the biomechanical properties of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: A logarithmic regression analysis based on parametric finite element simulations. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022;214:106570. [16] LO WC, TSAI LW, YANG YS, et al. Understanding the Future Prospects of Synergizing Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery with Ceramics and Regenerative Cellular Therapies. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(7):3638. [17] WANG R, WU Z. Recent advancement in finite element analysis of spinal interbody cages: A review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11: 1041973. [18] AO S, ZHENG W, WU J, et al. Comparison of Preliminary clinical outcomes between percutaneous endoscopic and minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar degenerative diseases in a tertiary hospital: Is percutaneous endoscopic procedure superior to MIS-TLIF? A prospective cohort study. Int J Surg. 2020;76: 136-143. [19] BOCAHUT N, AUDUREAU E, POIGNARD A, et al. Incidence and impact of implant subsidence after stand-alone lateral lumbar interbody fusion. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2018;104(3):405-410. [20] TSAI CY, SU YF, KUO KL, et al. Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for 2-Level Degenerative Lumbar Disease in Patients With Osteoporosis: Long-Term Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown). 2021;20(6):535-540. [21] CHENG X, ZHANG K, SUN X, et al. Unilateral versus bilateral pedicle screw fixation with transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of lumbar foraminal stenosis. Spine J. 2022;22(10): 1687-1693. [22] ZHAO L, XIE T, WANG X, et al. Comparing the medium-term outcomes of lumbar interbody fusion via transforaminal and oblique approach in treating lumbar degenerative disc diseases. Spine J. 2022;22(6): 993-1001. [23] ALVI MA, KURIAN SJ, WAHOOD W, et al. Assessing the Difference in Clinical and Radiologic Outcomes Between Expandable Cage and Nonexpandable Cage Among Patients Undergoing Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Interbody Fusion: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019;127:596-606.e1. [24] LIU Z, WANG H, YUAN Z, et al. High-resolution 3D printing of angle-ply annulus fibrosus scaffolds for intervertebral disc regeneration. Biofabrication. 2022;15(1). doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/aca71f. [25] SCHWEIGER J, EDELHOFF D, GÜTH JF. 3D Printing in Digital Prosthetic Dentistry: An Overview of Recent Developments in Additive Manufacturing. J Clin Med. 2021;10(9):2010. [26] MANI G, PORTER D, GROVE K, et al. A comprehensive review of biological and materials properties of Tantalum and its alloys. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2022;110(6):1291-1306. [27] PRZEKORA A, KAZIMIERCZAK P, WOJCIK M, et al. Mesh Ti6Al4V Material Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting (SLM) as a Promising Intervertebral Fusion Cage. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(7):3985. [28] PRESTAT M, THIERRY D. Corrosion of titanium under simulated inflammation conditions: clinical context and in vitro investigations. Acta Biomater. 2021;136:72-87. [29] LI W, HUANG C, MA T, et al. Low-frequency electromagnetic fields combined with tissue engineering techniques accelerate intervertebral fusion. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):143. [30] HUANG G, PAN ST, QIU JX. The osteogenic effects of porous Tantalum and Titanium alloy scaffolds with different unit cell structure. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022;210:112229. [31] LAUBACH M, KOBBE P, HUTMACHER DW. Biodegradable interbody cages for lumbar spine fusion: Current concepts and future directions. Biomaterials. 2022;288:121699. [32] ZHANG H, DUAN M, QIN S, et al. Preparation and Modification of Porous Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) Cage Material Based on Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(24):5403. [33] JEON IS, LEE MH, CHOI HH, et al. Mechanical Properties and Bioactivity of Polyetheretherketone/Hydroxyapatite/Carbon Fiber Composite Prepared by the Mechanofusion Process. Polymers (Basel). 2021; 13(12):1978. [34] SCHLAGER B, KRUMP F, BOETTINGER J, et al. Morphological patterns of the rib cage and lung in the healthy and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Anat. 2022;240(1):120-130. [35] KUANG B, XIANG X, SU P, et al. Self-assembly of stable and high-performance molecular cage-crosslinked graphene oxide membranes for contaminant removal. J Hazard Mater. 2022;439:129708. [36] YU S, SUN T, LIU W, et al. PLGA Cage-Like Structures Loaded with Sr/Mg-Doped Hydroxyapatite for Repairing Osteoporotic Bone Defects. Macromol Biosci. 2022;22(8):e2200092. [37] WANG K, WANG X, LI Z, et al. The Influence of Screw Positioning on Cage Subsidence in Patients with Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion Combined with Anterolateral Fixation. Orthop Surg. 2023;15(12): 3263-3271. [38] HUANG SF, CHANG CM, LIAO CY, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of an osteoporotic anatomical 3D printed posterior lumbar interbody fusion cage with internal lattice design based on weighted topology optimization. Int J Bioprint. 2023;9(3):697. [39] ABUDOUAINI H, WU T, MENG Y, et al. Biomechanical properties of a novel cervical spine implant with elastic deformation: a cadaveric study. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1214877. [40] PEZZOTTI G, MARIN E, ADACHI T, et al. Incorporating Si(3) N(4) into PEEK to Produce Antibacterial, Osteocondutive, and Radiolucent Spinal Implants. Macromol Biosci. 2018;18(6):e1800033. |
| [1] | Liu Xiaoyin, Zhang Jianqun, Chen Zhen, Liang Simin, Wang Zhiqiang, Ma Zongjun, Ma Rong, Ge Zhaohui. Short-term efficacy of oblique lateral interbody fusion combined with lateral plate fixation in treatment of single-level lumbar degenerative disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 531-537. |
| [2] | Xi Jintao, Lu Qilin, Wang Yang, Wang Xiaojuan, Lyu Peng, Chen Long, Shi Zhen, Xie Wei, Zhu Yiliang, Li Xugui. Risk factors for cage retropulsion following transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1394-1398. |
| [3] | Li Ke, Cao Shuai, Zhang Qiongchi, He Xijing, Li Haopeng, Li Jie. Finite element analysis of biomechanical effect of lumbar range of motion on the implants after lumbar fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5747-5752. |
| [4] | Li Ting, Liao Wenao, Zhong Wenjie, Liu Xilin, Wang Fei, Hu Jiang. Robot-assisted minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(12): 1855-1862. |
| [5] | Wang Yanjin, Zhou Yingjie, Chai Xubin, Zhuo Hanjie. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of 3D printed porous titanium alloy fusion cage in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1434-1440. |
| [6] | Xu Shicai, Ma Fei, Tang Chao, Liao Yehui, Tang Qiang, Chen Shiyu, Li Yang, Zhou Jiajun, Wang Qing, Zhong Dejun. Effect of nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide-66 intervertebral fusion cage shape on the efficacy of anterior cervical discectomy and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(30): 4830-4835. |
| [7] | Long Zhisheng, Fu Liuxiang, Gong Feipeng, Wen Jiabin, Deng Ying, Min Huan, Deng Zhuan, Chen Gang. Expression and significance of pyroptosis associated protein in peripheral tissues with tantalum cage loosening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(25): 4057-4062. |
| [8] | Ma Maoxiao, Cui Guofeng, Zhang Xue, Zhang Hong, Liu Youwen, Yue Chen. Complications after spinal fusion in patients with metabolic syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(22): 3602-3608. |
| [9] | Cai Yuanqing, Liu Mozhen, Li Zhonghai. Application of allograft bone materials in spinal fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(16): 2571-2579. |
| [10] | Yang Jun, Yang Qun, Zhang Rui, Jiang Chang. A novel slidable pedicle screw-rod system for lumbar tuberculosis: promoting bone graft fusion by producing stress stimulation to fused segment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 914-918. |
| [11] | Li Jian, Bao Zhengqi, Zhou Pinghui, Zhu Ruizhi, Li Zhixiang, Wang Jinzi. Effects of posterior single open-door laminoplasty and anterior cervical corpectomy fusion on cervical sagittal balance parameters in the treatment of multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 949-953. |
| [12] | Li Ting, Liu Xilin, Wang Fei, Hu Jiang. Robot-assisted minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases: accuracy and safety of screw placement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(36): 5812-5818. |
| [13] | Lin Boying, Shen Mao. Biomechanical stability of endoscopic transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with unilateral pedicle screw combined with contralateral translaminar facet screw fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 329-333. |
| [14] | Jin Herong, Cui Jingbin, Shao Cang. Materials of interbody fusion cage: advantages and focus of clinical application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3592-3597. |
| [15] | Yao Rubin, Wang Shiyong, Yang Kaishun. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of single-segment lumbar spinal stenosis improves lumbar-pelvic balance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1387-1392. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||