Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (32): 5238-5242.doi: 10.12307/2024.503
Previous Articles Next Articles
Characterization and mechanism by which nighttime exercise affects sleep
Wang Longteng, Zhou Yuehui
- School of Sports Science, Qufu Normal University, Qufu 273165, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2023-08-23Accepted:2023-10-12Online:2024-11-18Published:2023-12-29 -
Contact:Zhou Yuehui, PhD, Associate professor, School of Sports Science, Qufu Normal University, Qufu 273165, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Wang Longteng, Master candidate, School of Sports Science, Qufu Normal University, Qufu 273165, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the Social Science Planning Research Project of Shandong Province, No, 23CTYJ05 (to ZYH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Longteng, Zhou Yuehui. Characterization and mechanism by which nighttime exercise affects sleep[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5238-5242.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
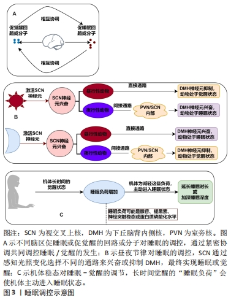
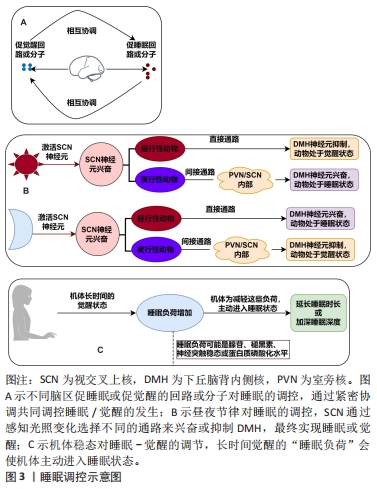
2.1 睡眠与运动 2.1.1 睡眠及调控 根据多导睡眠图,睡眠过程可分为非快速眼动和快速眼动2个时相,非快速眼动睡眠又可分为N1、N2和N3期。在整个睡眠过程中,成人由觉醒先进入非快速眼动睡眠,先后经N1、N2、N3期再进入快速眼动睡眠,睡眠周期最先为90 min,之后持续时间会延长。在非快速眼动阶段,心率和呼吸缓慢且有规律地进行,大脑消耗能量少,并可能伴有思想的发生;而在快速眼动阶段,心率和呼吸进行的更快且无规律,大脑消耗更多的能量,还有肌张力的丧失和体内平衡的暂停,同时梦境也在这一阶段发生,正常情况下睡眠的周期性循环一晚可出现3-6次[6-7]。在睡眠周期中快速眼动睡眠与记忆巩固有关,N1期是从清醒到入睡的一个易醒时期,N2期是真正的入睡阶段,N3期称为慢波睡眠,是睡眠质量最高的深度睡眠,对身体各项功能的恢复有利。睡眠受到个体性别、年龄和身体活动状况、身体健康水平等的影响,同时还与睡眠者的情绪、精神状态、认知活动、免疫功能等息息相关[8],调控好睡眠是进行工作和学习的必要保证。 睡眠调控研究起源于奥地利神经学家ECONOMO提出的睡眠和觉醒受到下丘脑特定区域的调节[9]。随后有研究发现,对麻醉猫的脑干网状结构进行电刺激会引起与清醒时相似的脑电图激活并伴随行为唤醒,提出了一个可产生觉醒的神经网络[10]。目前的研究表明,促进觉醒的神经回路或分子包括γ-氨基丁酸、单胺能神经元、胆碱能神经元、食欲素等;促进睡眠的神经回路或分子存在于视前区、基底前脑、下丘脑后部和脑干。大脑调节睡眠和觉醒正是由分布在大脑和脑干上的促睡眠或促觉醒神经回路和分子紧密协调的[11]。另外,睡眠调控不只依靠大脑的活动,还和昼夜节律以及机体稳态成分相关,这一理论虽然可以追溯到40多年前,但它并没有失去与当今研究的相关性[12]。首先是昼夜节律调控睡眠,白天光照会激活视交叉上核神经元,对夜行性动物来说,视交叉上核主要通过直接通路抑制下丘脑背侧核神经元促进睡眠并抑制觉醒,而对昼行性动物来说,视交叉上核则主要通过室旁核或视交叉上核内部的间接通路兴奋下丘脑背侧核以促进觉醒并抑制睡眠,在夜晚失去光刺激的视交叉上核则会表现出相反的通路选择[13]。其次是机体稳态成分调控睡眠,机体因长时间觉醒状态会导致“睡眠负荷”增加,机体为减轻这种负荷会主动进入睡眠状态并增加睡眠时间或深度[14-15],但睡眠稳态的分子和神经机制目前比较模糊,只知这种“睡眠负荷”可能与褪黑素、腺苷、神经突触稳态或蛋白质磷酸化水平等有关[16-17]。在这2个过程中,稳态过程跟踪睡眠需求并调整睡眠深度,昼夜节律负责调节 24 h内睡眠和觉醒发生的时间[11]。睡眠调控机制见图3。"
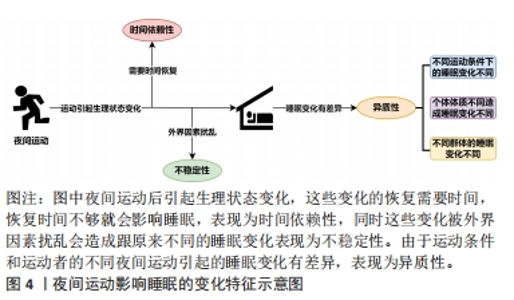
2.1.2 运动对睡眠的影响 运动对睡眠的研究开始于1966年,研究者们对10名习惯剧烈运动的健康大学生展开研究,得出了单次运动可以增加后续慢波睡眠数量、睡前不久运动会减少后续慢波睡眠数量、习惯性运动可能会增加慢波睡眠3个结论[18],开启了运动影响睡眠研究领域的大门。早期关于运动对睡眠影响的研究主要关注中枢神经系统睡眠,发现运动对睡眠的影响很小,随后的睡眠研究增加了对躯体生理学的探索,因为体力活动会改变内分泌、自主神经系统和躯体功能[19],时至今日,运动影响睡眠的研究仍旧活跃,研究的维度也更加多样。正是如此,运动对睡眠的影响效应逐步被揭开,文章通过梳理既往研究发现运动影响睡眠有多方面的表现:①运动影响主观睡眠质量。有研究发现有氧运动对原发性失眠患者主观睡眠质量的积极改善[20]。②运动影响睡眠连续性。睡眠潜伏期、睡眠效率、入睡后觉醒时长是睡眠连续性的体现。研究发现,中等至剧烈的运动强度及较高的运动量可缩短睡眠潜伏期,而较低的运动量可延长睡眠潜伏期[21];中等强度运动后,入睡后觉醒时长减少、入睡后觉醒次数也减少,但更高的运动量可增加睡后觉醒时长[22-23];运动可提高睡眠效率,提高睡眠质量[24]。③运动影响睡眠数量(即总睡眠时间)。运动对总睡眠时间的影响与运动干预的周期、单次运动干预施加的负荷以及睡眠干预效果的测试方法等有关[25-26]。④运动影响睡眠结构(即快速眼动睡眠以及N1、N2、N3期睡眠的排列和组合)。研究发现运动能减轻失眠患者的过度觉醒状态[25],而过度觉醒状态与N3期睡眠减少有关[27],运动能减轻过度觉醒状态的原因就是之一就是运动增加了N3期睡眠的比例[1]。 2.2 夜间运动影响睡眠的变化特征 夜间与白天的划分大致以4:00-16:00为白天,其余时间为夜间[28],而根据文章纳入的文献,进行夜间运动的时间大约从19:00(±30 min)开始,至22:00(±60 min)结束,符合昼夜划分标准。不同于白天运动,由于夜间运动与睡眠的间隔时间更短,对睡眠产生影响的概率更高。美国睡眠医学学会认为夜间运动不利于后续睡眠,因此不建议在晚上进行体育锻炼[29]。其实在最初运动影响睡眠的研究中就提到了有关夜间运动对睡眠的影响(睡前不久运动会减少后续慢波睡眠的数量[18]),但随着相关研究的展开,发现夜间运动影响睡眠是非常复杂的,不同类型、强度、持续时间的夜间运动对睡眠可能产生不同的影响,同时夜间运动者的情绪、健康水平、年龄、性别、体质等都可能影响睡眠对夜间运动的反应,因此最近关于夜间运动的睡眠指南已经从保守转变为更细致的方法,即从“晚上不要运动”转变为“在这种情况下,夜间运动可能不利于睡眠”[30]。基于此,文章不再论述夜间运动对睡眠的具体效应,而是根据现有文献总结夜间运动影响睡眠变化具备的一些特征,即夜间运动影响睡眠的异质性、时间依赖性和不稳定性,具体影响特征如图4所示。"
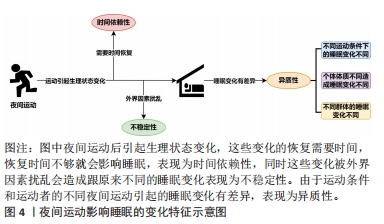
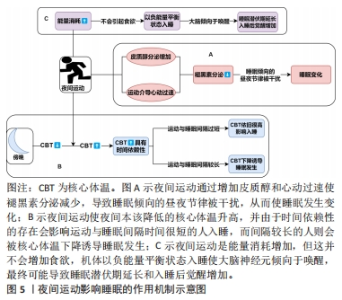
2.2.1 夜间运动影响睡眠变化的异质性 异质性是指一些事物在某些特征上存在差异(百度百科),夜间运动影响睡眠变化的异质性是指夜间运动引起的睡眠变化具有差异性,比如夜间运动可能提高睡眠效率[31],可能增加非快速眼动睡眠、减少快速眼动睡眠[32],也可能对睡眠没有影响[33],产生这些差异的原因可能与运动条件和运动者两方面因素有关。首先,不同的夜间运动条件导致睡眠变化不同,例如:低强度的急性夜间运动最可能缩短睡眠潜伏期,中等强度急性夜间运动对N1和N3期睡眠、睡眠效率、入睡后唤醒有一定的改善,而高强度的急性夜间运动会减少快速眼动睡眠[4],不同运动强度引起的睡眠变化有一定差异,另外选择在周末进行夜间运动可能会比在工作日运动对睡眠的影响更小[34],这也是运动条件不同引起睡眠变化差异的一种体现。其次,不同运动者的睡眠变化亦有差异,单从个体运动者来看,由于个体之间的体质差异会导致不同个体睡眠对夜间运动反应的敏感性不同,显示出个体之间的异质性。一项调查研究证实,与非运动者相比,部分夜间运动者的总睡眠时间、睡眠潜伏期、睡眠质量、醒来时精神不振的感觉没有差异,但也有部分夜间运动者睡眠持续时间更长[35]。另外,不同年龄、性别、身体活动水平、生活习惯等的人群睡眠对夜间运动的反应也存在差异,比如不同性别群体中男性可能比女性更适合夜间运动,夜间运动后女性比男性的睡眠更差[35];在不同身体活动水平群体中,久坐人群睡眠潜伏期缩短、睡眠效率提高、总睡眠时间增加,普通健康人群睡眠效率降低和总睡眠时间减少,但运动员在比赛当晚的睡眠时间会更短、睡眠质量也更差[36],显示出不同群体间的异质性。 2.2.2 夜间运动影响睡眠变化的时间依赖性 夜间运动影响睡眠变化的时间依赖性是指在夜间运动会引起机体生理状态的改变,在不加外界干扰的情况下功体自然恢复这些变化需要一定的时间,如果夜间运动到睡眠的间隔时间比恢复机能改变所需的时间长,则夜间运动可能不会影响睡眠变化,反之则会对睡眠产生各种影响,表现出一定的时间依赖特征。研究发现与不运动相比,睡眠前1 h结束的剧烈运动会增加睡眠潜伏期,同时还会降低总睡眠时间和睡眠效率[37];睡前2.5 h结束的剧烈运动对睡眠没有产生影响[38],睡前不同时间的剧烈运动显示出了不同的睡眠变化,1 h的间隔时间显然不足以恢复夜间剧烈运动引起的生理变化对睡眠的影响,而2.5 h间隔才可能足够,据此可推测支撑恢复夜间剧烈运动对睡眠影响的时间间隔在1-2.5 h内。另外也有研究证明,睡前至少 1.5 h进行一次中等强度的有氧运动或阻力运动不会损害健康年轻男性的睡眠[33],说明夜间中等强度的运动至少需要1.5 h的缓冲时间才不会对睡眠产生影响。时间依赖性的特征与夜间运动引起的核心体温、血压、心率、神经兴奋等变化有关,身体恢复这些功能变化需要一定的时间,强度越高的运动引起的增加幅度越高,如果不施加外界主动干扰可能需要更长时间,表现的时间依赖性也更高。 2.2.3 夜间运动影响睡眠变化的不稳定性 夜间运动影响睡眠变化的不稳定性是指在夜间运动后到睡前的一段时间内,施加或补充一定的外界条件会对机体夜间运动后的恢复过程带来一定影响,干扰夜间运动引起的生理状态变化,进而影响了原来未施加外界条件下夜间运动引起的睡眠变化,体现出一定的不稳定性。施加的外界条件可以是多方面的,可以是与睡眠相关的激素,比如:与仅注射安慰剂的对照组相比,对剧烈深夜运动后健康青少年施加外源性褪黑素(10 mg)后的总睡眠时间、睡眠效率、N3期睡眠和快速眼动睡眠显著提高,睡眠潜伏期、入睡后觉醒时长及N1、N2睡眠持续时间较低,并且主观睡眠质量更好[39],也可一定程度地减缓运动员第2天短期剧烈运动中的肌肉损伤、氧化应激和炎症[40];可以是与睡眠相关的外部条件,比如:夜间运动后对全身进行冷水浸泡可减少夜间前半段的入睡后唤醒、增加睡眠潜伏期比例[41];还可以是睡眠环境,比如:电子设备发出的蓝光会干扰机体恢复运动发生的生理变化,造成疲劳和睡眠质量降低,运动员在夜间比赛后应减少使用电子设备和有意识地防护蓝光[42]。由此可见,夜间运动引起的与睡眠有关的功能改变可被外界因素干扰,这说明夜间运动影响睡眠放入变化并不稳定,这一特点提示夜间运动者运动后可以采取一些措施以减弱对睡眠可能产生的影响。 2.3 夜间运动影响睡眠的作用机制 夜间运动后机体会发生多种生理变化,这些变化会破坏昼夜节律与睡眠的同步作用,使睡眠发生各种变化,并且进行夜间运动消耗的能量需要在睡眠期间恢复,这相当于增加了“睡眠负荷”,会使机体主动进入睡眠状态并增加睡眠的时间和深度,因此可以说这些生理变化与夜间运动影响睡眠的机制紧密相关。而查阅文献发现,与夜间运动影响睡眠机制相关的生理变化包括血浆褪黑素水平、核心体温、能量的消耗以及运动后的骨骼肌状态,但比较遗憾的是运动后的骨骼肌状态相关研究缺乏[1],机制尚不明确,文章不再论述。夜间运动影响睡眠的具体作用机制,如图5所示。"
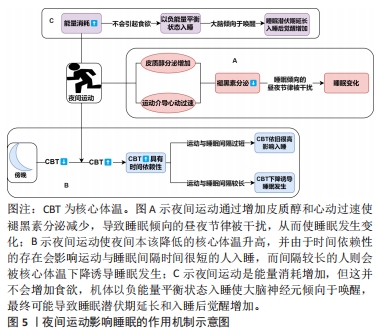

2.3.1 夜间运动减少褪黑素分泌对睡眠的影响 褪黑素属于一类吲哚杂环类激素小分子,内源性褪黑素主要由间脑顶部的松果体分泌,是色氨酸和血清素(5-羟色胺)生物合成途径的终产物。一开始,色氨酸被运送到细胞内,先被羟基化形成5-羟基色氨酸,再经 5-羟色氨酸脱羧酶脱羧作用下形成血清素,血清素被乙酰化形成N-乙酰基-5-羟基色胺,最后被甲基化生成N-乙酰基5-甲氧基色胺,也就是褪黑素[43]。血浆褪黑素水平受到环境光照水平的影响,光会抑制褪黑素的合成,而在光照消失的夜晚褪黑素水平则开始升高,一般在半夜达到峰值。内源性褪黑素的昼夜节律与睡眠倾向的昼夜节律密切相关,目前的研究已证明,褪黑素能够抑制来自昼夜节律起搏器的觉醒动力,并且在睡眠平衡动力不足时诱导睡眠发生,还能诱导昼夜节律时钟的相位变化,使睡眠倾向增强的昼夜节律相位出现在一个新的、理想的时间[44]。但在夜间运动后褪黑素作用的发挥将会被减弱,因为夜间运动能够减少褪黑素的分泌[45],从而干扰了睡眠倾向的昼夜节律,这种减少作用可能是由皮质醇介导的,但具体关系尚未阐明[46];此外,该减少作用还可能与运动介导的心动过速有关[47]。综上可知,褪黑素分泌与睡眠倾向的昼夜节律密切相关,但进行夜间运动会破坏褪黑素分泌的昼夜节律,使其分泌减少,如不能达到睡眠所需水平就会阻碍睡眠的发生,最终影响睡眠变化。 2.3.2 夜间运动升高核心体温对睡眠的影响 核心体温是指人体内部的温度,通常泛指人体胸腔、腹腔、颅腔、肠腔等部位的温度,在静息状态下核心体温约为36.8 ℃。人体核心体温同样具有显著的昼夜节律性,但它与褪黑素的昼夜节律相反,一般为白天温度值较高,以维持正常的生命活动,傍晚时达到一天内的最高温度,之后又开始下降,一直到次日睡眠觉醒前的2 h达到一天内最低,之后白天再次升高[48]。一般来说,核心体温降低发生在睡眠之前和睡眠期间,睡眠前的降低程度与睡眠开始和质量相对应[49],这是因为下丘脑视前区与核心体温调节有关的热感神经元在睡眠开始和非快速眼动睡眠时会自发激活,这可能是自主神经系统和体温效应器活动与睡眠变化相关的基础[50],说明核心体温降低能诱导睡眠的发生。从运动状态中恢复对体温的调节存在明显干扰,使核心体温长时间升高,并伴随出汗、皮肤血流量和皮肤温度降低到运动前的早期基本水平,睡前不久进行1 h的中等强度运动会在睡眠前和睡眠期间升高核心体温,并且无论热疗水平如何,身体散热的生理能力都存在时间依赖性抑制[51]。因此,如果夜间运动与睡眠的时间间隔过短,体温下降幅度小,导致睡眠时体温仍较高,就会对睡眠的诱导发生造成影响;但如果夜间运动与睡眠的时间间隔较长,核心体温下降就能诱导睡眠的发生,此时运动者的睡眠时间较平时可能有所提前,体温下降会成为睡眠发生和深度睡眠的触发因素。 2.3.3 夜间运动增加能量消耗对睡眠的影响 进行夜间运动期间身体会发生多种消耗能量的生理变化,包括肌肉利用葡萄糖和ATP进行舒缩活动、呼吸频率增加以供给更多的氧气、心率增加输送更多的血和氧气到肌肉等,机体为满足增加的能量消耗会加速人体内ATP的合成,体内糖、脂、蛋白质等物质大量减少,由于能量消耗大于能量摄入,夜间运动引起的能量消耗会使身体进入一种急性负能量平衡状态。运动与饮食限制引起的负能量平衡状态所导致的反应并不相同:仅通过饮食限制引起的负能量平衡有利于增加随后的食欲和能量摄入,而运动引起的负能量平衡没有观察到这种反应[52],甚至有更低的饥饿感[53],因此,由于缺少饥饿感夜间运动后人们主动去补充能量的概率就显著减小,导致到准备就寝时机体仍处于负能量平衡状态。但有研究显示在能量负平衡时期,大脑中与睡眠调控和新陈代谢途径相关的一部分神经元为了觅食和生存会倾向于唤醒而不是睡眠[54],这就可能对睡眠产生多种影响,可能的结果是睡眠潜伏期延长和入睡后觉醒增加。另一方面,夜间运动消耗的能量会在睡眠期间得到部分补充,因为研究发现清醒时高分解代谢活动有利于睡眠期间的合成代谢活动[55],以恢复部分能量消耗,并且如果要使能量尽可能多的恢复,机体可能会增加慢波睡眠,因为此期身体的各种代谢活动减慢,消耗的能量会得到恢复。"

| [1] STUTZ J, EIHOLZER R, SPENGLER CM. Effects of Evening Exercise on Sleep in Healthy Participants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2019;49(2):269-287. [2] CHAPUT JP, MCHILL AW, COX RC, et al. The role of insufficient sleep and circadian misalignment in obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2023;19(2):82-97. [3] BLOOMBERG M, BROCKLEBANK L, HAMER M, et al. Joint associations of physical activity and sleep duration with cognitive ageing: longitudinal analysis of an English cohort study. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2023;4(7):e345-e53. [4] YUE T, LIU X, GAO Q, et al. Different Intensities of Evening Exercise on Sleep in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Nat Sci Sleep. 2022;14:2157-2177. [5] RAMOS-CAMPO DJ, ÁVILA-GANDíA V, LUQUE AJ, et al. Effects of hour of training and exercise intensity on nocturnal autonomic modulation and sleep quality of amateur ultra-endurance runners. Physiol Behav. 2019;198:134-139. [6] 韩芳.人为什么要睡眠?[J].科学通报,2018,63(1):16-21. [7] 邓佳慧,黄筱琳,刘晓星,等.中国睡眠医学的过去、现在和未来[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2023,55(3):567-573. [8] TROYNIKOV O, WATSON CG, NAWAZ N. Sleep environments and sleep physiology: A review. J Therm Biol. 2018;78:192-203. [9] VON ECONOMO C. Sleep as a problem of localization. Nerv Ment Dis.1930;71:249-259. [10] MORUZZI G, MAGOUN HW. Brain stem reticular formation and activation of the EEG. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1949;1(4):455-473. [11] VANINI G, TORTEROLO P. Sleep-Wake Neurobiology. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1297:65-82. [12] BORBéLY A. The two-process model of sleep regulation: Beginnings and outlook. J Sleep Res. 2022;31(4):e13598. [13] 崔素颖,秦宇,张永鹤.睡眠调控与睡眠调节药物研究进展[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2022,36(11):801-811. [14] ZADA D, SELA Y, MATOSEVICH N, et al. Parp1 promotes sleep, which enhances DNA repair in neurons. Mol Cell. 2021;81(24):4979-4993.e7. [15] WANG Z, MA J, MIYOSHI C, et al. Quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis of the molecular substrates of sleep need. Nature. 2018;558(7710):435-439. [16] DUHART JM, INAMI S, KOH K. Many faces of sleep regulation: beyond the time of day and prior wake time. FEBS J. 2023;290(4):931-950. [17] FIFEL K, YANAGISAWA M, DEBOER T. Mechanisms of Sleep/Wake Regulation under Hypodopaminergic State: Insights from MitoPark Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(5):e2203170. [18] BAEKELAND F, LASKY R. Exercise and sleep patterns in college athletes. Percept Mot Skills. 1966;23(3):1203-1207. [19] UCHIDA S, SHIODA K, MORITA Y, et al. Exercise effects on sleep physiology. Front Neurol. 2012;3:48. [20] 赵春玲,欧阳松云,陈兰兰,等.有氧运动对原发性失眠病人睡眠质量、睡眠结构及炎症因子的影响[J].护理研究,2022,36(1):154-157. [21] PLEKHANOVA T, ROWLANDS AV, DAVIES M, et al. Effect of exercise on sleep and bi-directional associations with accelerometer-assessed physical activity in men with obesity. Appl Physiol Nutr Me. 2021;46(6):597-605. [22] WANG XW, YOUNGSTEDT SD. Sleep quality improved following a single session of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise in older women: Results from a pilot study. J Sport Health Sci. 2014;3(4):338-342. [23] SIU PM, YU AP, TAM BT, et al. Effects of Tai Chi or Exercise on Sleep in Older Adults With Insomnia: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Jama Netw Open. 2021;4(2):e2037199. [24] 谢璞,马园艳,聂应军.运动锻炼对老年人睡眠干预效果分析——基于Meta系统综述[J].武汉体育学院学报,2023,57(7):69-78. [25] 龚明俊,谭思洁,孙亚麒,等.运动干预睡眠障碍成年人的睡眠结构的Meta分析[J].首都体育学院学报,2021,33(3):276-284. [26] PESONEN AK, KAHN M, KUULA L, et al. Sleep and physical activity - the dynamics of bi-directional influences over a fortnight. Bmc Public Health. 2022;22(1):1160. [27] 赵文瑞,李陈渝,陈军君,等.失眠障碍与过度觉醒:来自静息态脑电和睡眠脑电的证据[J].中国科学:生命科学,2020,50(3):270-286. [28] VALDEZ P. Circadian Rhythms in Attention. Yale J Biol Med. 2019;92(1):81-92. [29] BREUS M. Healthy Sleep Tips. 2023-06-01. https://www.sleepassociation.org/about-sleep/sleep-hygiene-tips/ [30] MILLER DJ, ROACH GD, LASTELLA M, et al. Hit the gym or hit the hay: can evening exercise characteristics predict compromised sleep in healthy adults? Front Physiol. 2023;14:1231835. [31] RAMOS-CAMPO DJ, ÁVILA-GANDíA V, LUQUE AJ, et al. Effects of hour of training and exercise intensity on nocturnal autonomic modulation and sleep quality of amateur ultra-endurance runners. Physiol Behav. 2019;198:134-139. [32] ALOULOU A, DUFOREZ F, BIEUZEN F, et al. The effect of night-time exercise on sleep architecture among well-trained male endurance runners. J Sleep Res. 2020;29(6):e12964. [33] MILLER DJ, SARGENT C, ROACH GD, et al. Moderate-intensity exercise performed in the evening does not impair sleep in healthy males. Eur J Sport Sci. 2020;20(1):80-89. [34] KAHN M, KORHONEN T, LEINONEN L, et al. Is It Time We Stop Discouraging Evening Physical Activity? New Real-World Evidence From 150,000 Nights. Front Public Health. 2021;9:772376. [35] BUMAN MP, PHILLIPS BA, YOUNGSTEDT SD, et al. Does nighttime exercise really disturb sleep? Results from the 2013 National Sleep Foundation Sleep in America Poll. Sleep Med. 2014;15(7):755-761. [36] FRIMPONG E, MOGRASS M, ZVIONOW T, et al. The effects of evening high-intensity exercise on sleep in healthy adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med Rev. 2021;60:101535. [37] ODA S, SHIRAKAWA K. Sleep onset is disrupted following pre-sleep exercise that causes large physiological excitement at bedtime. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2014;114(9):1789-1799. [38] ROBEY E, DAWSON B, HALSON S, et al. Effect of evening postexercise cold water immersion on subsequent sleep. Med Sci Sport Exer. 2013;45(7):1394-1402. [39] CHEIKH M, HAMMOUDA O, GAAMOURI N, et al. Melatonin ingestion after exhaustive late-evening exercise improves sleep quality and quantity, and short-term performances in teenage athletes. Chronobiol Int. 2018;35(9):1281-1293. [40] CHEIKH M, MAKHLOUF K, GHATTASSI K, et al. Melatonin ingestion after exhaustive late-evening exercise attenuate muscle damage, oxidative stress, and inflammation during intense short term effort in the following day in teenage athletes. Chronobiol Int. 2020; 37(2):236-247. [41] CHAUVINEAU M, PASQUIER F, GUYOT V, et al. Effect of the Depth of Cold Water Immersion on Sleep Architecture and Recovery Among Well-Trained Male Endurance Runners. Front Sports Act Living. 2021;3:659990. [42] RICHARD NA, KOEHLE MS. Optimizing recovery to support multi-evening cycling competition performance. Eur J Sport Sci. 2019;19(6):811-823. [43] ASEY C, MCBRIDE J, PENTA K. Circadian Rhythm Dysregulation and Restoration: The Role of Melatonin. Nutrients. 2021;13(10):3480. [44] CAJOCHEN C, KRäUCHI K, WIRZ-JUSTICE A. Role of melatonin in the regulation of human circadian rhythms and sleep. J Neuroendocrinol. 2003;15(4):432-437. [45] CARLSON LA, POBOCIK KM, LAWRENCE MA, et al. Influence of Exercise Time of Day on Salivary Melatonin Responses. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2019;14(3):351-353. [46] MONTELEONE P, FUSCHINO A, NOLFE G, et al. Temporal relationship between melatonin and cortisol responses to nighttime physical stress in humans. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1992;17(1):81-86. [47] MARRIN K, DRUST B, GREGSON W, et al. Diurnal variation in the salivary melatonin responses to exercise: relation to exercise-mediated tachycardia. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011;111(11):2707-2714. [48] 董毅.生物节律与运动[J].中国体育科技,2019,55(4):22-30. [49] BIGALKE JA, CLEVELAND EL, BARKSTROM E, et al. Core body temperature changes before sleep are associated with nocturnal heart rate variability. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2023;135(1):136-145. [50] SZYMUSIAK R. Body temperature and sleep. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;156:341-351. [51] KENNY GP, MCGINN R. Restoration of thermoregulation after exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017;122(4):933-944. [52] THIVEL D, METZ L, JULIAN V, et al. Diet- but not exercise-induced iso-energetic deficit induces compensatory appetitive responses. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2021;75(10):1425-1432. [53] THIVEL D, FINLAYSON G, MIGUET M, et al. Energy depletion by 24-h fast leads to compensatory appetite responses compared with matched energy depletion by exercise in healthy young males. Br J Nutr. 2018;120(5):583-592. [54] NORTHEAST RC, VYAZOVSKIY VV, BECHTOLD DA. Eat, sleep, repeat: the role of the circadian system in balancing sleep-wake control with metabolic need. Curr Opin Physiol. 2020;15:183-191. [55] FLAUSINO NH, DA SILVA PRADO JM, DE QUEIROZ SS, et al. Physical exercise performed before bedtime improves the sleep pattern of healthy young good sleepers. Psychophysiology. 2012;49(2):186-192. |
| [1] | Liu Luxing, Di Mingyuan, Yang Qiang. Signaling pathways in the mechanism underlying active ingredients of Chinese medicine in the treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 609-614. |
| [2] | Chen Jixin, Yu Weijie, Guo Tianci, Zhou Qinxin, Niu Puyu, Ye Yuntian, Liu Aifeng. Sleep characteristics and risk of osteoarthritis: a two-sample and multivariate Mendelian randomization study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5203-5209. |
| [3] | Yao Yuan, Zhang Shizhen, Jin Lei, Yang Yunxiao, Yu Wenqiang, Xu Yuanjing, Wang Jinwu. Effect of photon cervical vertebra massage instrument on improving neck pain and related functions in patients with chronic neck pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(30): 4876-4880. |
| [4] | Li Weizhao, Zhou Hui, Peng Xinsheng, Li Baohong. Preparation, characterization, and application of acylated collagen with anhydride [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(15): 2430-2436. |
| [5] | Zhu Xunpeng, Xu Hui, Wang Lin, Wang Jun, Zhang Hui. Relationship of preoperative sleep quality and early rehabilitation after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5806-5811. |
| [6] | Zhang Qi, Yu Mei, Liu Lei, Tian Weidong. Recent advances of engineered exosomes and challenges on clinical translational research [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(19): 3052-3060. |
| [7] | He Junjun, Huang Zeling, Hong Zhenqiang. Interventional effect of Yanghe Decoction on synovial inflammation in a rabbit model of early knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 694-699. |
| [8] | Luo Shiren, Xie Yan, Zhang Li, Yin Na. miRNA screening for targeted regulation of bone growth by semen ziziphi spinosae extract [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(35): 5658-5664. |
| [9] | Yuan Xixi, Zhao Zirui, Zhang Yanyan, Huang Yu, Shi Kaikai, Fan Dengying, Zhu Yahui, Liu Chunyan. Effect of mandibular advancement device on mitochondrial ultrastructure of the genioglossus in the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(35): 5626-5632. |
| [10] | Xu Yixin, Wang Yixin, Li Yongming. Autophagy level of the mandible in nasal obstruction rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(35): 5633-5638. |
| [11] | Wang Xiao, Liu Qing, Hu Yaorui, Gu Chengxu, Guo Qixuan, Zhu Yonglin, Zhang Luping. Preparation of wogonoside polycaprolactone-polyethylene glycol micelles delivered by adipose stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 4996-5001. |
| [12] | Qiao Qiqi, Wu Yixin, Wang Xin, Xia Zhongliang. Effect of high-definition transcranial direct current stimulation on human dynamic balance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4192-4198. |
| [13] | Wang Xinyuan, Huang Xiabing, Li Juan, Deng Xin. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on Taohong Siwu Decoction for rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis based on the concept of “Treating Different Diseases with the Same Therapeutic Principle” [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(15): 2419-2425. |
| [14] | Jing Huimin, Yu Wenjuan, Wang Sijia, Chen Cong, Li Yifan, Wang Yonglan, Li Xin, Zhang Juan, Liang Meng. Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of the brain’s default mode network in patients with sleep bruxism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 685-689. |
| [15] | Wen Mingtao, Xu Bo, Li Jiacheng, Liu Jinbao, Li Gang. Tanshinone IIA treats vascular system injury: possible molecular mechanism and biological processes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(35): 5656-5661. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||