[1] THAM YC, LI X, WONG TY, et al. Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2014;121(11):2081-2090.
[2] TAMM ER. 70-The trabecular meshwork outflow pathways: Surgical aspects. Glaucoma (Second Edition). 2015;2:695-698.
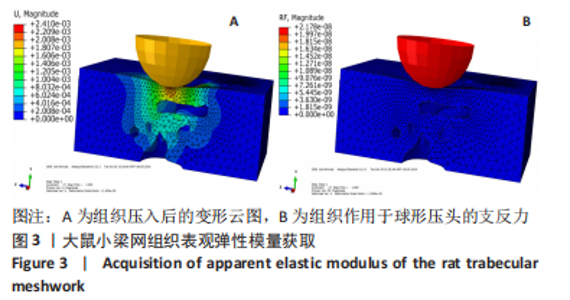
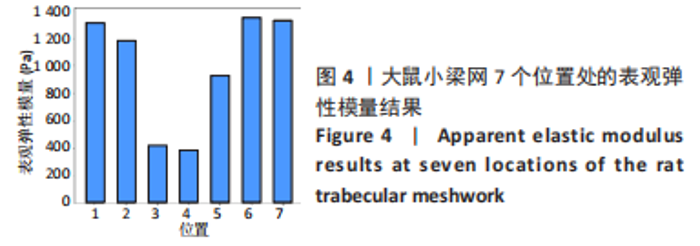
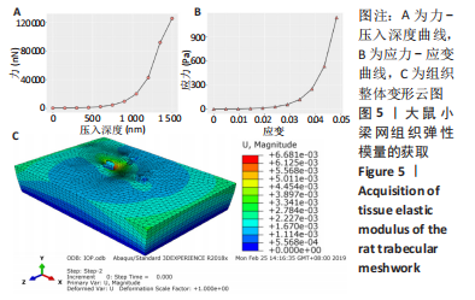
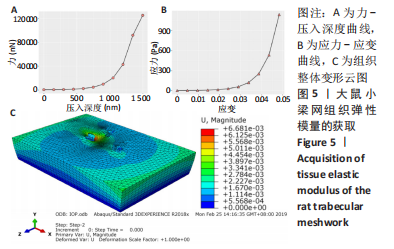
[3] 王川,李林,刘志成.基于原子力显微镜压痕技术的大鼠小梁网组织弹性模量测定[J].北京生物医学工程,2021,40(4):354-359.
[4] BRAUNGER BM, FUCHSHOFER R, TAMM ER. The aqueous humor outflow pathways in glaucoma: A unifying concept of disease mechanisms and causative treatment. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015;95(Pt B):173-181.
[5] SBARDELLA D, TUNDO GR, COLETTA M, et al. Dexamethasone downregulates autophagy through accelerated turn-over of the ulk-1 complex in a trabecular meshwork cells strain: Insights on steroid-induced glaucoma pathogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(11):5891.
[6] WANG K, READ AT, SULCHEK T, et al. Trabecular meshwork stiffness in glaucoma. Exp Eye Res. 2017;158:3-12.
[7] CAMRAS LJ, STAMER WD, EPSTEIN D, et al. Differential effects of trabecular meshwork stiffness on outflow facility in normal human and porcine eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53(9):5242-5250.
[8] PANT AD, KAGEMANN L, SCHUMAN JS, et al. An imaged-based inverse finite element method to determine in-vivo mechanical properties of the human trabecular meshwork. J Model Ophthalmol. 2017;1(3):100-111.
[9] YUAN F, CAMRAS L J, GONZALEZ P. Trabecular meshwork stiffness in ex vivo perfused porcine eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(14):6693.
[10] LAST JA, PAN T, DING Y, et al. Elastic modulus determination of normal and glaucomatous human trabecular meshwork. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(5):2147-2152.
[11] CHUNG HW, PARK JH, YOO C, et al. Effects of trabecular meshwork width and schlemm’s canal area on intraocular pressure reduction in glaucoma patients. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2021;35(4):311-317.
[12] CHOLKAR K, TRINH HM, PAL D, et al. Discovery of novel inhibitors for the treatment of glaucoma. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2015;10(3):293-313.
[13] ZHANG J, REN L, MEI X, et al. Microstructure visualization of conventional outflow pathway and finite element modeling analysis of trabecular meshwork. Biomed Eng Online. 2016;15(Suppl 2):162.
[14] BUFFAULT J, LABBÉ A, HAMARD P, et al. The trabecular meshwork: Structure, function and clinical implications. A review of the literature. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2020;43(7):e217-e230.
[15] ISVILANONDA V, IAQUINTO JM, PAI S, et al. Hyperelastic compressive mechanical properties of the subcalcaneal soft tissue: An inverse finite element analysis. J Biomech. 2016;49(7):1186-1191.
[16] SHRIVASTAVA A, GUNDIAH N. Crosslinks increase the elastic modulus and fracture toughness of gelatin hydrogels. 2022. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2203.08693
[17] VINCKIER A, SEMENZA G. Measuring elasticity of biological materials by atomic force microscopy. FEBS Lett. 1998;430(1-2):12-16.
[18] WANG C, LI L, LIU Z. Experimental research on the relationship between the stiffness and the expressions of fibronectin proteins and adaptor proteins of rat trabecular meshwork cells. BMC Ophthalmol. 2017;17(1):268.
[19] MASIHZADEH O, AMMAR DA, KAHOOK MY, et al. Direct trabecular meshwork imaging in porcine eyes through multiphoton gonioscopy. J Biomed Opt. 2013;18(3):036009.
[20] 王川,董建鑫,张静,等.大鼠小梁网组织压痕实验有限元模拟研究[J].北京生物医学工程,2022,41(5):454-457,464.
[21] TANE N, DHAR S, ROY S, et al. Effect of excess synthesis of extracellular matrix components by trabecular meshwork cells: Possible consequence on aqueous outflow. Exp Eye Res. 2007;84(5):832-842.
[22] RAGHUNATHAN VK, MORGAN JT, PARK SA, et al. Dexamethasone stiffens trabecular meshwork, trabecular meshwork cells, and matrix. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015; 56(8):4447-4459.
[23] MALLICK S, SHARMA M, KUMAR A, et al. Cell-based therapies for trabecular meshwork regeneration to treat glaucoma. Biomolecules. 2021;11(9):1258.
[24] DIBAS A, YORIO T. Glucocorticoid therapy and ocular hypertension. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016;787:57-71. |