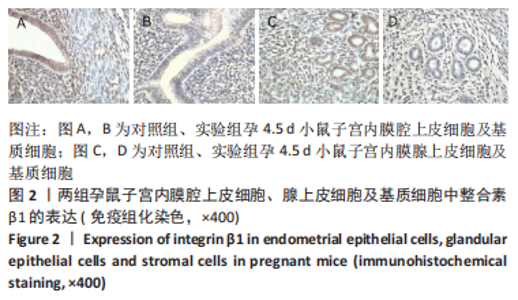
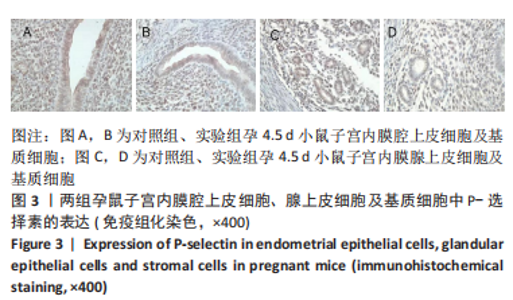
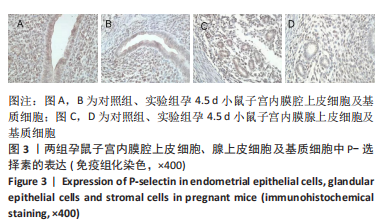
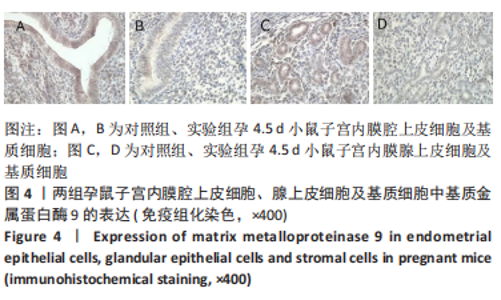
[1] MUSAK L, SMERHOVSKY Z, HALASOVA E, et al.Chromosomal damage among medical staff occupationally exposed to volatile anesthetics,antineoplastic drugs,and formaldehyde. Scand J Work Environm Health. 2013;39(6):618-630.
[2] CASALE T, CACIARI T, ROSATI MV, et al.Anesthetic gases and occupationally exposed workers. Environm Toxicol Pharmacol. 2014; 37(1):267- 274.
[3] HUANG L, HUANG K, NING H. Hispidulin prevents sevoflurane- Induced memory dysfunction in aged rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;97: 412-422.
[4] DOGRU S, DOGRU HY, BUTUN I, et al. Effects of sevoflurane on female reproductive functions in Wistar rats. J Pakist Med Ass. 2017;67(6):877.
[5] MOLINA ARAGONES JM, AYORA A, BARBARA RIBALTA A, et al. Occupational exposure to volatile anaesthetics: A systematic review.Occupat Med. 2015;66(3):202-207.
[6] TANKO B,MOLNAR L,FULESDI B,et al.Occupational hazards of halogenated volatile anesthetics and their prevention: Review of the literature. J Anesth Clin Res. 2014;5(7):1-7.
[7] LUCIO LMC, BRAZ MG, DO NASCIMENTO JUNIOR P, et al. Occupational hazards, DNA damage, and oxidative stress on exposure to waste anesthetic gases. Rev Bras Anestesiol. 2018;68:33-41.
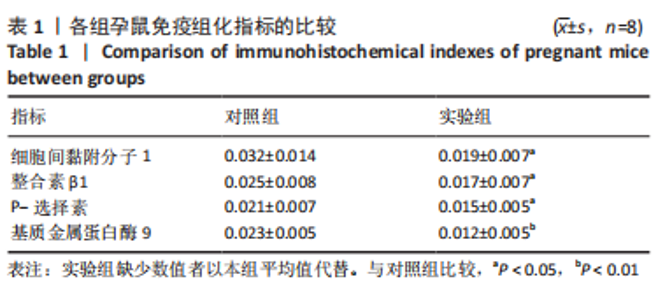
[8] 舒蕤,张成明,丁国建.长期吸入低浓度七氟醚对雌性小鼠早期胚胎及妊娠结果的影响[J].实用医学杂志,2020;36(19):2625-2629.
[9] 李大金.生殖免疫学[M].上海:复旦大学出版社,2008:119-148
[10] SHARMA S,GODBOLE G,MODI D. Decidual Control of Trophoblast Invasion. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2016;75(3):341-350.
[11] SOHN JO, PARK HJ, KIM SH, et al. Integrins expressed on the surface of human endometrial stromal cells derived from a female patient experiencing spontaneous abortion. Hum Cell. 2020;33(1):29-36.
[12] BALCI M, ÖZDEMIR G. Differential Expression of EGFR-1, MMP-3, and MMP-9 in Spontaneous Abortions, Induced Abortions, and Tubal Pregnancies. Turk Patoloji Derg. 2019;35(1):1-8.
[13] 张武文,黄丽丽.子宫内膜容受性相关调控因子的时序表达及功能[J].国外医学(妇产科学分册),2007,34(1):12-15.
[14] MATSUMOTO L, HIROTA Y, SAITO-FUJITA T, et al. A hypoxia-induced Rab pathway regulates embryo implantation by controlled trafficking of secretory granules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020;117(25): 14532-14542.
[15] TANG B, WU K, MENG Q, et al. Comparison of the Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Xiaoyuningkun Decoction with Cynanchum Paniculatum and Fukeqianjin in a Mouse Model of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:9094-9102.
[16] SALAFIA CM, HEYNES N, MERLURZI VJ, et al. Distribution of ICAM-1 within decidual and placenta and 1st gestational age associated changes. Padiatr Pathol. 1991;11:381-388.
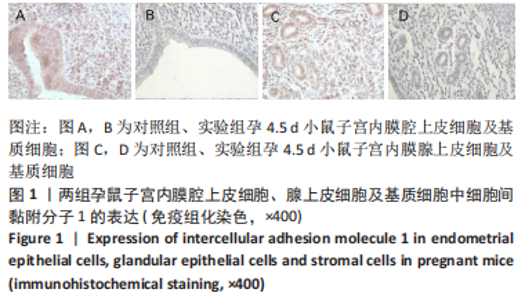
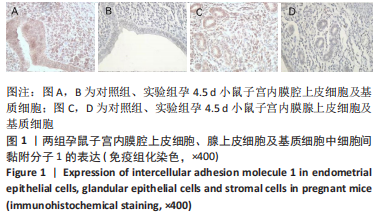
[17] 张炜,周剑萍,张俊慧.细胞间粘附分子-1在着床前小鼠胚胎培养液中的表达[J].生殖医学杂志,1999,3(8):33-36.
[18] 郝翠芳,郎翠红,沈肖方,等.不同浓度的瘦素在胚胎着床中对细胞间粘附分子-1和金属蛋白酶-9 的影响[J].中国优生与遗传杂志, 2011,19(2):95-97.
[19] LU DP, TIAN L, O’NEILL C, et al. Regulation of cellular adhesion molecule expression in murine oocytes,peri-implantation and post-implantation embryos. Cell Res. 2002;12(5-6):373-383.
[20] DEFRERE S, VAN LA, MOULIN P, et al.Human endometrial cells (EEC) constitutively express more intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM) -1 than endometrial stromal cells (ESC) in culture. Am J ReprodImmunol. 2005;54(1):5.
[21] 张炜,刘银坤.细胞间黏附分子-1在小鼠早孕期子宫内膜的表达规律及调节的研究[J].生殖与避孕,2000,20(1):12-16.
[22] 张炜,刘银坤.小鼠孕早期子宫内膜ICAM-1 mRNA的表达及调节[J].中国免疫学杂志,2000,16(12):678-680.
[23] 盛敏, 任春娥, 韩海艳, 等.种植窗口期子宫内膜中MMP-9、TIMP-1及ICAM-1的表达与体外受精-胚胎移植妊娠结局的关系[J].中国卫生检验杂志,2012,22(8):1827-1830.
[24] XIONG T, ZHAO Y, HU D, et al. Integrins β1 and β3 are biomarkers of uterine condition for embryo transfer. J Transl Med. 2016;14(1):303.
[25] KANRKO Y, LINDSAY LA, MURPHY CR. Uterine focal adhesions are retained at implantation after rat ovarian hyperstimulation. Reproduction. 2016;152(6):753-763.
[26] 谢芬芬. 植入前小鼠子宫内膜形态学及整合素α4、β1表达的研究[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2008.
[27] XU B, MAKRIS A, LIU CC, et al. Galectin-1-Related Modulation of Trophoblast Endothelial Interactions by Integrins α1 and β1. Reprod Sci. 2020;27(5):1097-1109.
[28] ERIKSON DW, BURGHARDT RC, BAYLESS KJ, et al. β(1) and β(3) integrins disassemble from basal focal adhesions and β(3) integrin is later localised to the apical plasma membrane of rat uterine luminal epithelial cells at the time of implantation. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2011; 23(3):481-495.
[29] FENG Y, MA X, DENG L, et al. Role of selectins and their ligands in human implantation stage. Glycobiology. 2017;27(5):385-391.
[30] 曾国良,彭健,张忠栋,等. P-选择素基因多态性与可溶性P选择素浓度、心房颤动血栓栓塞的相关性研究[J].实用医学杂志, 2009,25(11):1757-1760.
[31] 李争,史俊玲,马立庆,等.充血性心力衰竭患者体内血清选择素家族水平的变化[J].实用医学杂志,2010,26(18):3364-3366.
[32] KAUTZKY-WILLER A, FASCHING P, JILMA B, et al. VCAM-1, ICAM-1 and selectins in gestational diabetes mellitus and the risk for vascular disorders. Future Cardiol. 2019;15(5):339-346.
[33] 王志萍.二氧化硫对作业女工早期妊娠影响及其作用机理的研究[D].济南:山东大学,2005.
[34] 高丽丽.Ley、Lex、MMP-2、MMP-9和TGFβ1在妊娠1-8天小鼠子宫内膜的分布[D].大连:大连医科大学,2003.
[35] 孟艳岑, 张明敏, 崔丹丹, 等.补肾、活血对超促排卵小鼠着床期间子宫内膜MMP-2、MMP-9、TIMP-3表达的影响[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2013,42(6):627-632.
[36] HE Y, SUN Q. IFN-γ induces upregulation of TNF-α, downregulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 expressions in abortion rat. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(15):4762-4767.
[37] BAGHERI D, KAZEMI P, SARMADI F, et al. Low oxygen tension promotes invasive ability and embryo implantation rate. Reprod Biol. 2018;18(3):295-300.
[38] ZHANG S, MESALAM A, JOO MD, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases improves trophoblast invasion and pregnancy potential in mice.Theriogenology. 2020;151:144-150.
[39] 张冬雅,郭红军,邱海峰. GnRH-α联合曼月乐治疗子宫腺肌症患者的疗效及对血清复发相关指标的影响[J].实用医学杂志, 2019,35(1):84-87.
[40] LEA RG, MCINTYRE S, BAIRD JD, et al. IFN-γ induces upregulation of TNF-α, downregulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 expressions in abortion rat. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(15):4762-4767. |