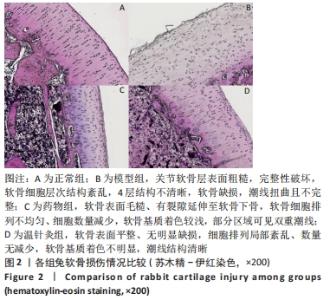
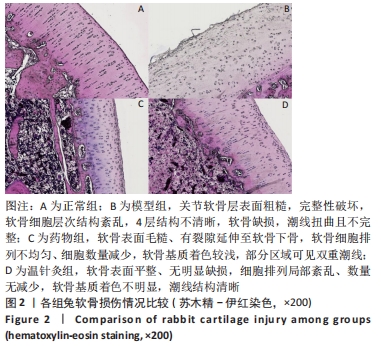
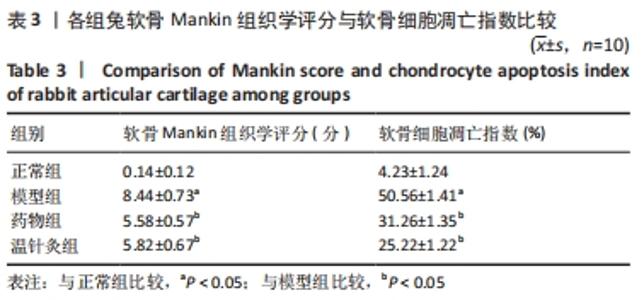
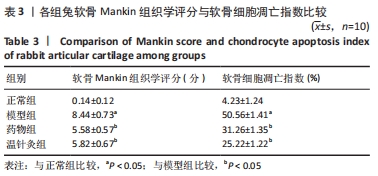
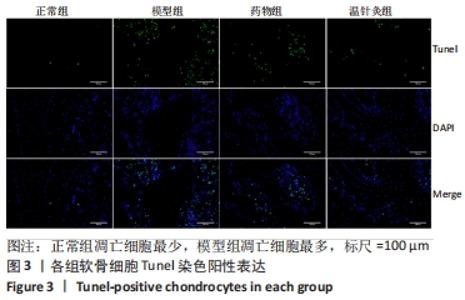
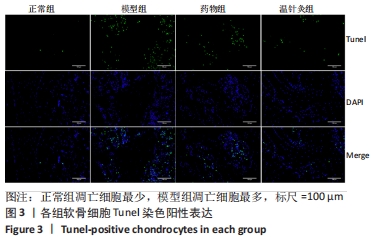
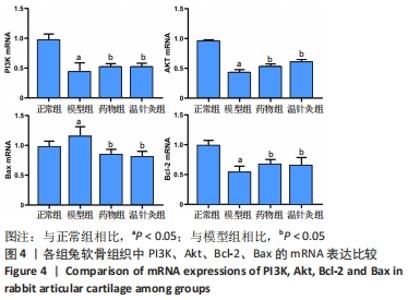
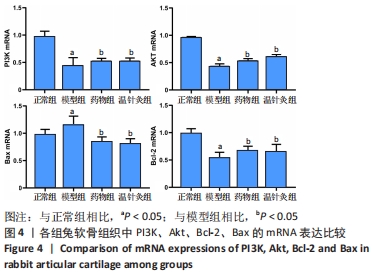
[1] 王新军,袁银鹏,王越,等.软骨细胞凋亡引发骨关节炎的机制研究进展[J].山东医药,2020,60(2):109-112.
[2] 李盛华,吴献毅,周明旺,等.细胞凋亡在膝骨性关节炎半月板损伤中的作用研究[J].西部中医药,2018,31(2):131-134.
[3] 于楠.温针灸治疗膝关节骨性关节炎对患者临床疗效及JOA评分的影响[J].当代医学,2021,27(20):179-180.
[4] 吴福春,陈捷,余德标,等.温针灸对兔膝骨关节炎软骨细胞及Lubricin的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2019,41(8):565-569.
[5] HHARIKRISHNAN, HJANTAN I, HAQUE MA, et al. Anti -inflammatory effects of hypophyllanthin and niranthin through downregulation of NF-κB/MAPKs/PI3K-Akt signaling pathways. Inflammation. 2018;41(3): 984-995.
[6] YANG J, SONG Q, CAI Y, et al. RLIP76-dependent suppression of PI3K/Akt/Bcl-2 pathway by miR-101 induces apoptosis in prostate cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;463(4):900-906.
[7] 曾俊华,马笃军,彭力平,等.实验兔膝骨关节炎模型的建立及鉴定[J].中国临床研究,2016,29(5):679-682.
[8] 李忠仁.实验针灸学[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2003.
[9] 聂永胜,杨立峰,林美琼,等.动物实验中常用麻醉药应用[J].畜牧兽医科技信息,2019(4):34-35.
[10] MATSUI H, SHIMIZU M, TSUJI H. Cartilage and subchondral bone interaction in osteoarthrosis of human knee joint: a histological and histomorphometric study. Microsc Res Tech. 1997;37(4):333-342.
[11] 许学猛,刘文刚,詹红生,等.肌肉训练康复治疗膝痹(膝骨关节炎)专家共识[J].按摩与康复医学,2020,11(19):1-4.
[12] 詹红生,潘富伟.膝骨关节炎治疗中不可或缺的基础治疗——《膝骨关节炎中医诊疗指南(2020年版)》解读[J].中医正骨,2021, 33(8):1-6.
[13] 徐玲琳.温针灸联合穴位贴敷治疗阳虚寒凝型膝骨性关节炎的临床疗效观察[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2018.
[14] 刘君伟.温针灸联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植对兔膝骨关节炎软骨组织影响的研究[D].银川:宁夏医科大学,2019.
[15] SHEN PC, CHOU SH, LU CC, et al. Shockwave Treatment Enhanced Extracellular Matrix Production in Articular Chondrocytes Through Activation of the ROS/MAPK/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Cartilage. 2021; 13(2_suppl):238S-253S.
[16] GUILAK F, NIMS RJ, DICKS A, et al. Osteoarthritis as a disease of the cartilage pericellular matrix. Matrix Biol. 2018;71-72:40-50.
[17] 关尚琪,滕菲,张志毅,等.骨关节炎流行病学研究进展[J].中华内科杂志,2017,56(6):450-452.
[18] 乌云额尔敦,郭长青,王彤,等.针刀干预对KOA兔关节软骨细胞功能及细胞外基质代谢的影响[J].中医学报,2020,35(12):2612-2618.
[19] XU J, YI Y, LI L, et al. Osteopontin induces vascular endothelial growth factor expression in articular cartilage through PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signaling. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(3):4708-4712.
[20] CHEN NY, LU K, YUAN JM, et al. 3-Arylamino-quinoxaline-2-carboxamides inhibit the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways to activate P53 and induce apoptosis. Bioorg Chem. 2021;114:105101.
[21] CAMPBELL KJ, TAIT S. Targeting Bcl-2 regulated apoptosis in cancer. Open Biol. 2018;8(5):180002.
[22] XU K, HE Y, MOQBEL SAA, et al. SIRT3 ameliorates osteoarthritis via regulating chondrocyte autophagy and apoptosis through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;175:351-360.
[23] FAN Y, YANG F, CAO X, et al. Gab1 regulates SDF-1-induced progression via inhibition of apoptosis pathway induced by PI3K/AKT/Bcl-2/BAX pathway in human chondrosarcoma. Tumour Biol. 2016;37(1):1141-1149.
[24] SAIJO K, IMAMURA J, NARITA K, et al. Biochemical, biological and structural properties of romidepsin (FK228) and its analogs as novel HDAC/PI3K dual inhibitors. Cancer Sci. 2015;106(2):208-215.
[25] MAO Y, XI L, LI Q, et al. Regulation of cell apoptosis and proliferation in pancreatic cancer through PI3K/Akt pathway via Polo-like kinase 1. Oncol Rep. 2016;36(1):49-56.
[26] 毛滔,李木清,程学荣,等.NEAT1通过PI3K/AKT/Bcl-2信号通路抑制骨质疏松[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2020,39(2):758-762.
[27] 田胜兰,王国延,杨扬.人甲壳质酶蛋白40通过PI3K/Akt信号通路调控膝骨性关节炎兔软骨细胞的凋亡[J].中国组织工程研究, 2020,24(32):5108-5113.
[28] 熊勇,彭锐,王华.“双固一通”温针灸实验性膝骨性关节炎模型兔Bcl-2及Bax蛋白的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(2):261-264.
[29] SUN Y, WANG C, GONG C. Repairing effects of glucosamine sulfate in combination with etoricoxib on articular cartilages of patients with knee osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):150.
[30] 黄泽灵,施珊妮,何俊君,等.温针灸治疗阳虚寒凝型膝骨关节炎疗效Meta分析及选穴规律研究[J].康复学报,2021,31(4):341-350.
|