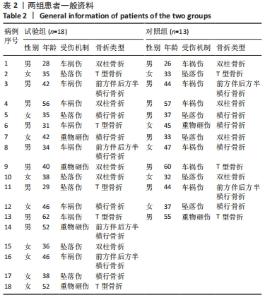
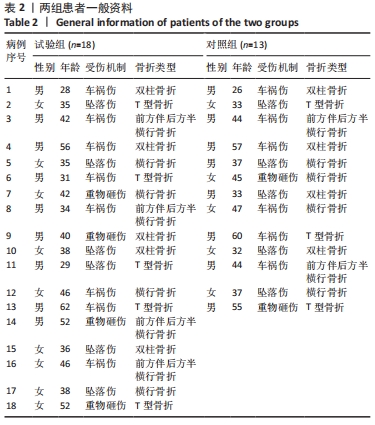
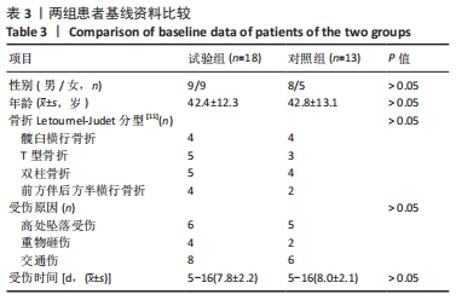
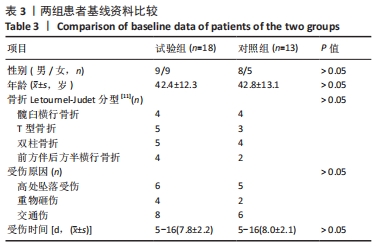
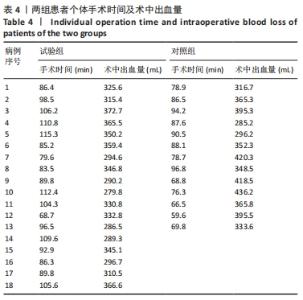
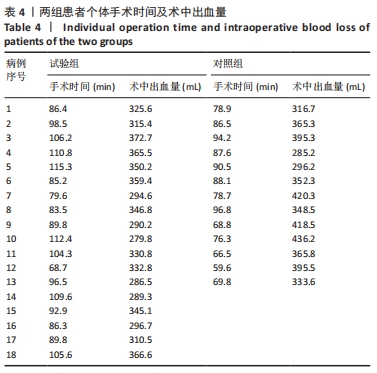
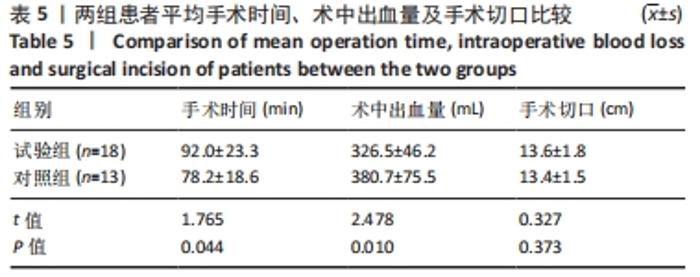
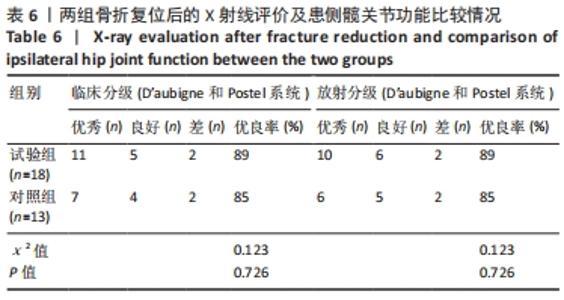
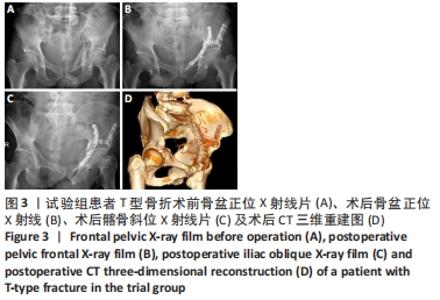
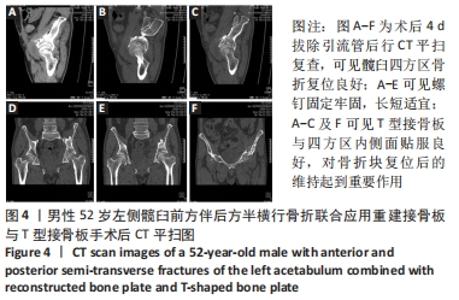
[1] TILE M, HELFET DL, KELLAM JF. Fractures of the pelvis and acetabulum, 3rd edn. Lippincott, Philadelphia. 2003:501.
[2] KISTLER BJ, SAGI HC. Reduction of the posterior column in displaced acetabulum fractures through the anterior intrapelvic approach. J Orthop Trauma. 2015; 29(Suppl. 2):S14-19.
[3] 陈开放,姚升,万意州,等.跨弓状缘髋臼四方区阻挡钢板治疗复杂髋臼骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2020,40(5):294-300.
[4] 张志海,孙思佳,张绍安.单一髂腹股沟入路治疗髋臼双柱骨折的疗效分析[J].现代临床医学,2021,47(2):103-105.
[5] 王慧彪,王武超.单一髂腹股沟入路治疗复杂髋臼骨折[J].创伤外科杂志, 2018,20(5):363-366.
[6] 樊仕才,刘涵,黄复铭.髋臼骨折手术入路选择的原则与复位固定技巧[J].中华骨科杂志,2021,41(1):58-66.
[7] 孙晓,殷建,霍永峰,等.应用单一髂腹股沟入路治疗复杂髋臼骨折的疗效分析[J].重庆医科大学学报,2018,43(10):1360-1363.
[8] 朱仕文,吴新宝,王满宜.髋臼骨折手术入路的恰当选择[J].骨科临床与研究杂志,2019,4(6):382-384.
[9] 黄复铭,温湘源,刘源城,等.直接后方入路治疗髋臼后部骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2019,39(13):789-795.
[10] VON RÜDEN C, WENZEL L, BECKER J, et al. The pararectus approach for internal fixation of acetabular fractures involving the anterior column: evaluating the functional outcome. Int Orthop. 2019;43(6):1487-1493.
[11] 王忠正,田思宇,赵阔,等.髋臼骨折分型的研究进展[J].中华创伤杂志, 2020,36(11):966-971.
[12] 孙建,郝连升,房义辉.不同入路方式对骨盆合并髋臼骨折患者疗效及功能恢复的影响[J].医学综述,2019,25(17):3522-3525,3531.
[13] 曹奇勇,吴宏华,孙旭.等.髋臼骨折合并髋关节前脱位的分型及治疗[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2020,22(12):1041-1047.
[14] 蒋侃凌, 季斌, 戴利明, 等. 髋臼前柱螺钉通道的解剖学参数[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2021,24(1):84-87.
[15] CHUI KH, CHAN CCD, IP KC, et al. Three-dimensional navigation-guided percutaneous screw fixation for nondisplaced and displaced pelvi-acetabular fractures in a major trauma centre. Int Orthop. 2018;42(6):1387 -1395.
[16] KARIM MA, ABDELAZEEM AH, YOUNESS M, et al. Fixation of quadrilateral plate fractures of the acetabulum using the buttress screw: A novel technique. Injury. 2017;48(8):1813-1818.
[17] SEBAALY A, JOUFFROY P, EMMANUEL MP, et al. Intraoperative cone beam tomography and navigation for displaced acetabular fractures: a comparative study. J Orthop Trauma. 2018;32(12):612-626.
[18] ASKAM B, SIMS S. Supplemental Superior Buttress Plating for the Treatment of Posterosuperior Wall Acetabulum Fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;3(2):S27-31.
[19] 刘涵,汪灿彬,陈家辉,等.经腹直肌外侧入路髋臼翼形全万向锁定钢板固定治疗老年髋臼骨[J].中华骨科杂志,2019,39(10):596-603.
[20] 谷诚. 金属3D打印个性化髋臼翼状接骨板的研发及实验研究[D]. 广州:南方医科大学, 2017.
[21] 陈开放,杨帆,郭晓东,等.髋臼四方区组合钢板治疗髋臼双柱骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(5):295-300.
[22] WONG JM, BEWSHER S, YEW J, et al. Fluoroscopically assisted computer navigation enables accurate percutaneous screw placement for pelvic and acetabular fracture fixation. Injury. 2015;46:1064-1068.
[23] 陈开放,杨帆,郭晓东,等. 髋臼四方区组合钢板治疗老年 髋臼骨折的有效性[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2018,34(4):323-330.
[24] SHON HC, CHOI S, YANG JY. Three-dimensional printing-assisted surgical technique with limited operative exposure for both-column acetabular fractures. Turk J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2018;24(4):369-375.
[25] ALY TA, HAMED H. Posterior Acetabular Column and Quadrilateral Plate Fractures: Fixation With Tension Band Principles. Orthopedics. 2013;36(7):e844-848.
[26] BYUN Y, CHO O, KIM K. Less Invasive Anterior Iliac Approach and CompressLess Invasive Anterior Iliac Approach and Compression Osteosynthesis for the Treatment of High Anterior Column Fractures of the Acetabulum. Clin Orthop Surg. 2018;10:279-285.
|