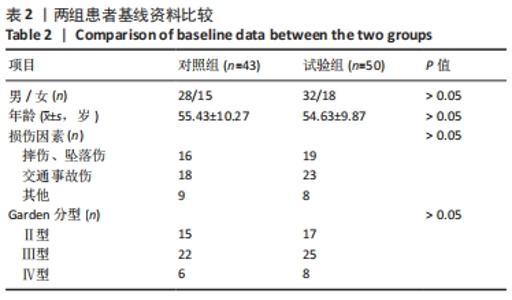
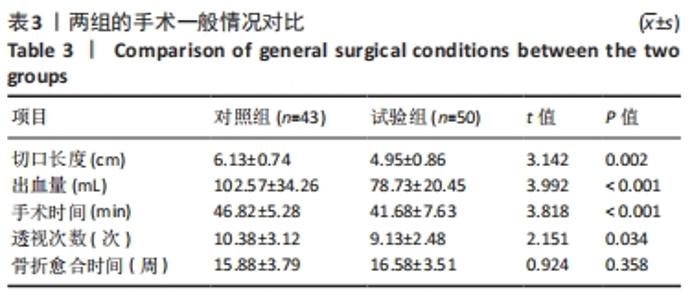
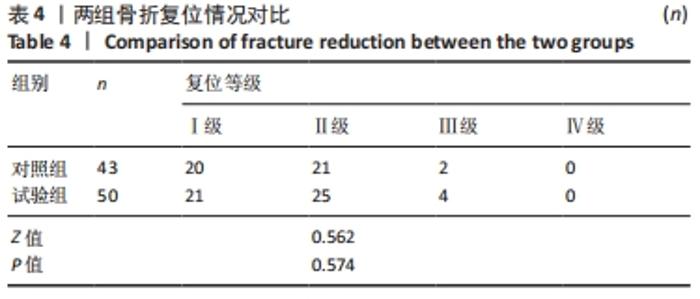
[1] 李兴国,邓叶龙,刘朝晖,等.中国老年髋部骨折流行性病学特征分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2021,27(7):601-606.
[2] 魏志辉,马坤龙,张铭华. 4枚空心钉与动力髋螺钉结合防旋螺钉内固定治疗股骨颈骨折的疗效比较[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2017,32(2):187-188.
[3] LICHSTEIN PM, KLEIMEYER JP, GITHENS M, et al. Does the Wat-son-Jones or Motlified Smith-Petersen approach provide superior exposure for femoral neck fracture fixation? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018;476(7): 1468-1476.
[4] STOFFEL K, ZDERIC I, GRAS F, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of the Femoral Neck System in Unstable Pauwels III Femoral Neck Fractures: A Comparison with the Dynamic Hip Screw and Cannulated Screws. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(3):131-137.
[5] 李建涛,张里程,徐高翔,等.股骨近端三角形结构重建失效对骨折手术失败的影响[J].中华骨科杂志,2020,40(14):928-935.
[6] 崔爽爽,赵丽坤,马信龙.中国老年髋部骨折流行病学和疾病经济负担研究现状[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2020,26(3):567-570.
[7] BASTARD C. Fracture du col du fémur [Femoral neck fracture. Rev Prat. 2019;69(10):1124-1128.
[8] 毕郑刚,王旭明.再谈老年股骨颈骨折的手术治疗策略[J].中华外科杂志,2019,57(11):804-806.
[9] DUFFIN M, PILSON HT. Technologies for young femoral neck fracture fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;33 Suppl 1:S20-S26.
[10] SLOBOGEAN GP, STOCKTON DJ, ZENG BF, et al. Femoral neck shortening in adult patients under the age of 55 years is associated with worse functional outcomes: Analysis of the prospective multi-center study of hip fracture outcomes in China (SHOC). Injury. 2017;48(8):1837-1842.
[11] LI M, COLE PA. Anatomical considerations in adult femoral neck fractures: how anatomy influences the treatment issues? Injury. 2015; 46(3):453-458.
[12] JONES CB, WALKER JB. Diagnosis and Management of Ipsilateral Femoral Neck and Shaft Fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2018; 26(21):e448-e454.
[13] PANTELI M, RODHAM P, GIANNOUDIS PV. Biomechanical rationale for implant choices in femoral neck fracture fixation in the non-elderly. Injury. 2015;46(3):445-452.
[14] MOROCHOVIČ R, TAKÁČOVÁ K, TOMČOVČÍK Ľ, et al. Factors influencing femoral neck fracture healing after internal fixation with dynamic locking plate. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019;139(5):629-638.
[15] LI J, ZHAO Z, YIN P, et al. Comparison of three different internal fixation implants in treatment of femoral neck fracture-a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):76.
[16] YE Y, CHEN K, TIAN K, et al. Medial buttress plate augmentation of cannulated screw fixation in vertically unstable femoral neck fractures: Surgical technique and preliminary results. Injury. 2017;48(10):2189-2193.
[17] STOFFEL K, ZDERIC I, GRAS F, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of the femoral neck system in unstable pauwels III femoral neck fractures: A comparison with the dynamic hip screw and cannulated screws. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(3):131-137.
[18] SCHOPPER C, ZDERIC I, MENZE J, et al. Higher stability and more predictive fixation with the Femoral Neck System versus Hansson Pins in femoral neck fractures Pauwels II. J Orthop Translat. 2020;24:88-95.
[19] YANG Y, MA T, ZHANG X, et al. Short-term effectiveness of femoral neck system in the treatment of femoral neck fracture. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021;35(5):539-543.
[20] 陈志兵,王光林,林佳生,等.空心螺钉与动力髋螺钉加防旋螺钉治疗股骨颈骨折疗效比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2011,25(1): 26-29.
[21] LI Z, ZHANG X, LI Z, et al. Comparative study of Pauwels type III femoral neck fractures managed by short dynamic hip screw with fibula bone graft or cannulated screws in young adults. Ann Transl Med. 2020; 8(11):681.
[22] 范智荣,苏海涛,周霖,等.新型股骨颈内固定系统治疗不稳定性股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(15): 2321-2328.
[23] 杨亚军,马涛,张小钰,等.股骨颈动力交叉钉系统治疗股骨颈骨折近期疗效[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(5):539-543.
|