Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (12): 1854-1860.doi: 10.12307/2022.507
Previous Articles Next Articles
Patellar suture anchors and semi-tunneling polyetheretherketone suture anchors for double-bundle reconstruction of medial patellofemoral ligament
Han Mingzhan, Maihemuti·Yakufu, Chen Hongtao, Liu Jianjiang, Abudusufu·Kuwan, Aierken·Amudong
- Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2021-06-18Revised:2021-06-30Accepted:2021-08-19Online:2022-04-28Published:2021-12-14 -
Contact:Aierken·Amudong, MD, Associate professor, Chief physician, Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Han Mingzhan, Master candidate, Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Han Mingzhan, Maihemuti·Yakufu, Chen Hongtao, Liu Jianjiang, Abudusufu·Kuwan, Aierken·Amudong. Patellar suture anchors and semi-tunneling polyetheretherketone suture anchors for double-bundle reconstruction of medial patellofemoral ligament[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(12): 1854-1860.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
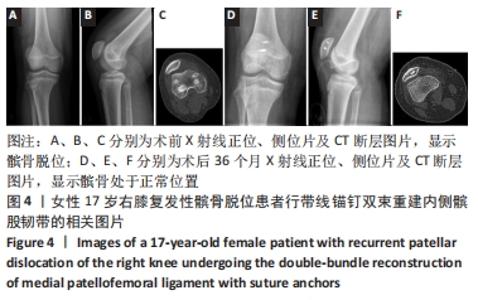
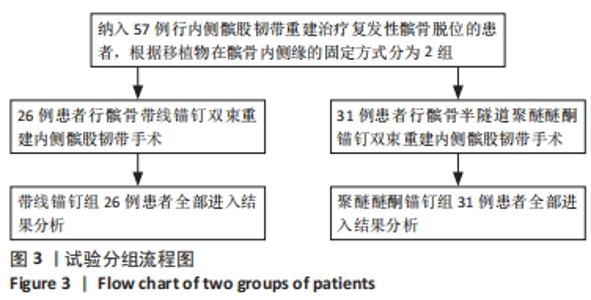
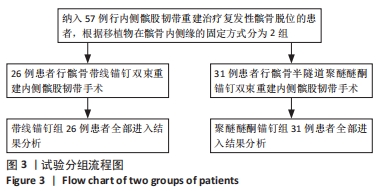
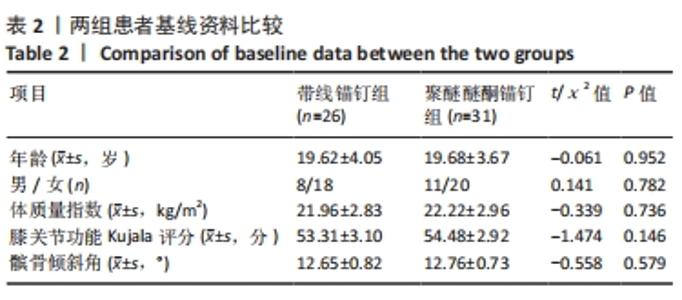
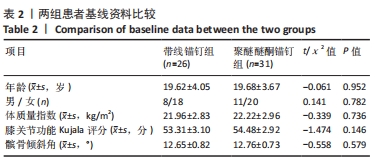
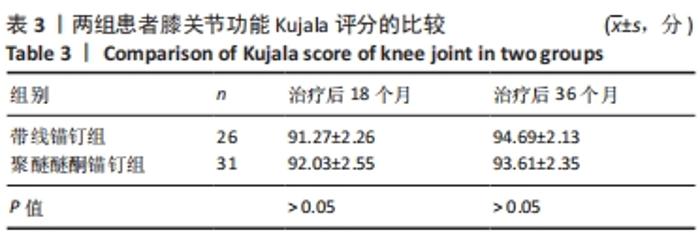
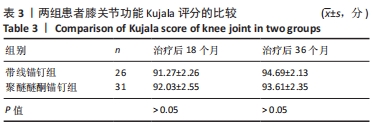
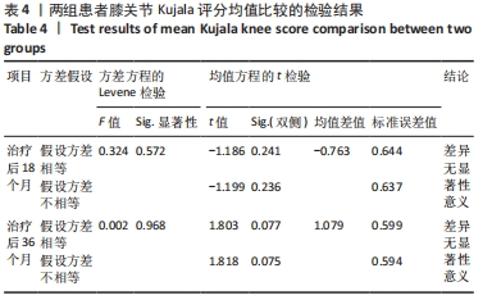
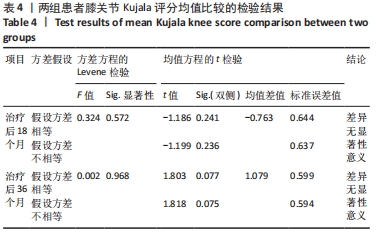
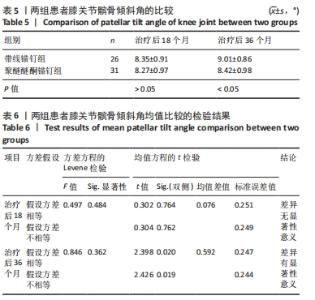
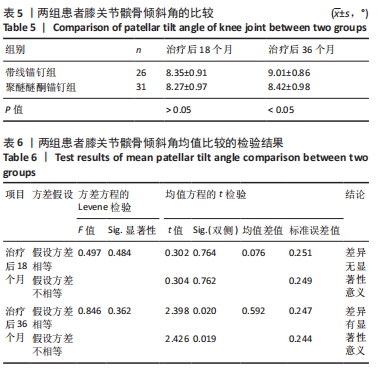
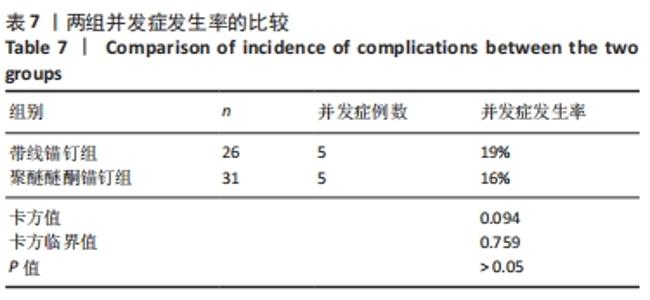
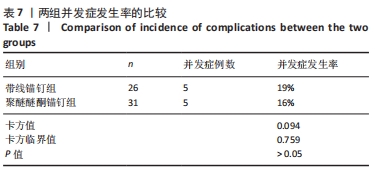
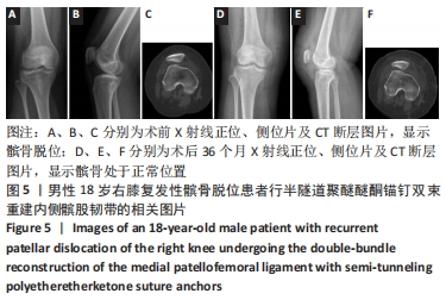
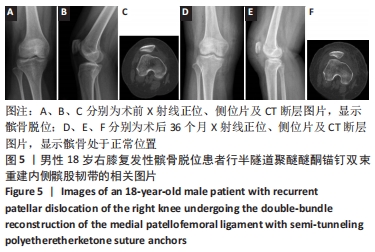
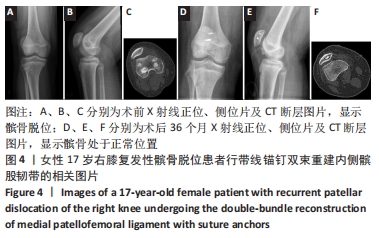
两组总共10例患者出现并发症,带线锚钉组治疗后3个月内出现4例股骨止点疼痛,聚醚醚酮锚钉组治疗后3个月内出现5例股骨止点疼痛,经过物理治疗和康复锻炼疼痛症状均好转;带线锚钉组另有1例患者治疗后14个月运动时患膝再次摔伤,韧带与股骨止点处持续疼痛,经红光、氦氖激光及股骨止点处局部注射复方倍他米松治疗后症状缓解出院。 2.7 植入物与宿主的生物相容性 两组植入物生物相容性良好,未发生局部感染、免疫反应、过敏反应、排斥反应等不良情况。 2.8 典型病例 17岁女性复发性髌骨脱位患者,入院后术前膝关节功能Kujala评分54分,术前膝关节髌骨倾斜角12.6°,髌骨内缘使用带线锚钉固定肌腱治疗复发性髌骨脱位;治疗后随访36个月,膝关节功能Kujala评分95分,膝关节髌骨倾斜角9.1°。该患者治疗前后的影像资料,见图4。"
| [1] SANDERS TL, PAREEK A, HEWETT TE, et al. Incidence of First-Time Lateral Patellar Dislocation: A 21-Year Population-Based Study. Sports Health. 2018;10(2):146-151. [2] ZHENG L, DING H Y, FENG Y, et al. Gender-related differences in concomitant articular injuries after acute lateral patellar dislocation. Injury. 2021;52(6):1549-1555. [3] NOMURA E, HORIUCHI Y, INOUE M. Correlation of MR imaging findings and open exploration of medial patellofemoral ligament injuries in acute patellar dislocations. Knee. 2002;9(2):139-143. [4] VOLLNBERG B, KOEHLITZ T, JUNG T, et al. Prevalence of cartilage lesions and early osteoarthritis in patients with patellar dislocation. Eur Radiol. 2012;22(11):2347-2356. [5] ELIAS JJ, COSGAREA AJ. Technical errors during medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction could overload medial patellofemoral cartilage: a computational analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2006;34(9):1478-1485. [6] KIM HK, SHIRAJ S, KANG CH, et al. Patellofemoral Instability in Children: Correlation Between Risk Factors, Injury Patterns, and Severity of Cartilage Damage. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016;206(6):1321-1328. [7] 黄炎,李海鹏,征华勇,等.内侧髌股韧带重建联合外侧支持带松解治疗复发性髌骨脱位[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(8): 743-744. [8] 陈冬,黄炎,李海鹏,等.关节镜下松解联合韧带重建术治疗复发性髌骨脱位的效果分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(10): 1029-1032. [9] BOURAS T, U E, BROWN A, et al. Isolated medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction significantly improved quality of life in patients with recurrent patella dislocation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(11):3513-3517. [10] NIU J, LIN W, QI Q, et al. Anatomical Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction for Recurrent Patella Dislocation: Two-Strand Grafts versus Four-Strand Grafts. J Knee Surg. 2021;34(2):147-154. [11] THOMPSON P, METCALFE AJ. Current concepts in the surgical management of patellar instability. Knee. 2019;26(6):1171-1181. [12] 郭瑞,艾则孜·艾海提, 张浩沙强,等.内侧髌股韧带重建术治疗髌骨不稳的研究回顾[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2018,11(12): 957-960. [13] 戴毅,方钦正,赵家瑞,等.关节镜辅助下内侧支持带紧缩缝合术治疗青少年髌骨脱位[J].局解手术学杂志,2018,27(4):284-288. [14] 任民,甄平,李慎松,等.关节镜下内侧髌股支持带缝合与石膏固定治疗急性髌骨脱位的病例对照研究[J].中国骨伤,2015,28(7): 590-593. [15] 王恒俊,吴世栋,董占引.髌外侧支持带松解术治疗髌骨外侧高压综合征87例报告[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2018,7(12):896-900. [16] 马洪,郭跃明,赵崇智.关节镜辅助带线铆钉与外侧支持带松解加内侧髌股韧带重建术治疗习惯性髌骨脱位的疗效比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2019,21(12):1081-1084. [17] 王承祥,周明旺,颜春鲁,等.臀肌挛缩症患者髌股关节影像学相关指标研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2015,23(3):9-11. [18] KLINGE SA, FULKERSON JP. Fifteen-Year Minimum Follow-Up of Anteromedial Tibial Tubercle Transfer for Lateral and/or Distal Patellofemoral Arthrosis. Arthroscopy. 2019;35(7):2146-2151. [19] 王飞,陈百成,康慧君,等.单束等长重建和双束解剖重建内侧髌股韧带的临床研究[J].中华外科杂志,2010,48(12):891-895. [20] KANG H, ZHENG R, DONG C, et al. No influence of patellar fixation technique on clinical outcomes of double-bundle medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction: a systematic review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018;139(1):79-90. [21] MIGLIORINI F, TRIVELLAS A, COLAROSSI G, et al. Single- versus double-bundle patellar graft insertion for isolated MPFL reconstruction in patients with patellofemoral instability: a systematic review of the literature. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020;140(6):769-776. [22] GURUSAMY P, PEDOWITZ JM , CARROLL AN, et al. Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction for Adolescents With Acute First-Time Patellar Dislocation With an Associated Loose Body. Am J Sports Med. 2021;49(8):2159-2164. [23] ZHANG Z, ZHANG H, SONG G, et al. A High-Grade J Sign Is More Likely to Yield Higher Postoperative Patellar Laxity and Residual Maltracking in Patients With Recurrent Patellar Dislocation Treated With Derotational Distal Femoral Osteotomy. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48(1):117-127. [24] MULLIEZ A, LAMBRECHT D, VERBRUGGEN D, et al. Clinical outcome in MPFL reconstruction with and without tuberositas transposition. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(9):2708-2714. [25] BANKE IJ, KOHN LM, MEIDINGER G, et al. Combined trochleoplasty and MPFL reconstruction for treatment of chronic patellofemoral instability: a prospective minimum 2-year follow-up study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(11):2591-2598. [26] SAPPEY-MARINIER E, SONNERY-COTTET B, O’LOUGHLIN P, et al. Clinical Outcomes and Predictive Factors for Failure With Isolated MPFL Reconstruction for Recurrent Patellar Instability: A Series of 211 Reconstructions With a Minimum Follow-up of 3 Years. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(6):1323-1330. [27] KANG HJ, WANG F, CHEN BC, et al. Functional bundles of the medial patellofemoral ligament. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010; 18(11):1511-1516. [28] 董江涛,王飞,孙然,等.骨性结构改良与软组织重建治疗髌股关节对合不良的初期临床疗效比较[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2011, 19(17):1423-1426. [29] 张磊,岳娜,张太良,等.保留残端与不保留残端重建前交叉韧带腱骨愈合情况比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(51):7634-7641. [30] 史丰田,魏民,张梅,等.韧带固定器械在促进腱骨愈合方面的研究进展[J].中国医药导报,2018,15(9):22-25. [31] RAOULIS VA, ZIBIS A, CHIOTELLI MD, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of three patellar fixation techniques for MPFL reconstruction: Load to failure did not differ but interference screw stabilization was stiffer than suture anchor and suture-knot fixation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021: doi: 10.1007/s00167-020-06389-4. [32] RUSS SD, TOMPKINS M, NUCKLEY D, et al. Biomechanical comparison of patellar fixation techniques in medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(1):195-199. [33] ATESOK K, FU FH, WOLF MR, et al. Augmentation of tendon-to-bone healing. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(6): 513-521. [34] 赵宗峤,吴萍,孙磊.生长因子对前交叉韧带重建后腱-骨愈合影响的研究现状[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2011,19(6): 471-474. [35] ZHANG C, LIU YJ. Biomechanic and histologic analysis of fibroblastic effects of tendon-to-bone healing by transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) in rotator cuff tears. Acta Cirurgica Brasileira. 2017;32(12): 1045-1055. [36] WU GB, XU PC, WU P, et al. Advances in the treatment of rotator cuff lesions by cytokines. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2017;22: 516-529. [37] HEE CK, DINES JS, DINES DM, et al. Augmentation of a rotator cuff suture repair using rhPDGF-BB and a type I bovine collagen matrix in an ovine model. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(8):1630-1639. [38] 王亚斌,于绍斌,董启榕.富血小板血浆凝胶在同种异体肌腱重建前交叉韧带后腱-骨愈合中的作用[J].中华创伤杂志,2010,26(3): 280-284. |
| [1] | Tan Xinfang, Guo Yanxing, Qin Xiaofei, Zhang Binqing, Zhao Dongliang, Pan Kunkun, Li Yuzhuo, Chen Haoyu. Effect of uniaxial fatigue exercise on patellofemoral cartilage injury in a rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [2] | Li Jie, Zhang Haitao, Chen Jinlun, Ye Pengcheng, Zhang Hua, Zhou Bengen, Zhao Changqing, Sun Youqiang, Chen Jianfa, Xiang Xiaobing, Zeng Yirong. Anterior cruciate ligament rupture and patellofemoral joint stability before sagittal and axial measurement using MRI [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 969-972. |
| [3] | Huang Hao, Hong Song, Wa Qingde. Finite element analysis of the effect of femoral component rotation on patellofemoral joint contact pressure in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 848-852. |
| [4] | Lin Chaosheng, Liu Yuwei, Zhu Weimin, Xiong Jianyi. Reconstruction of medial patellofemoral ligament: selection of single- and double-bundle graft and fixation technique of patellar and femoral insertion point [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(26): 4217-4222. |
| [5] | Chen Xiaolong, Zhao Heng, Hu Rong, Luo Guanghua, Liu Jincai . Correlation of infrapatellar fat pad edema with trochlear and patellofemoral joint morphology: MRI evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2410-2415. |
| [6] | Ai Di. Absorbable suture anchors for treating femoroacetabular impingement syndrome combined with acetabular labral tears [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 499-504. |
| [7] | Lin Yuan, Xu Bin, Tu Jun, Xu Honggang, Guo Ruipeng. Effect of different femoral tunnel locations on patellofemoral joint during single-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(14): 2140-2146. |
| [8] | Yuan Ling-li, Xu Bin, Xu Wen-di, Geng Chun-hui. Reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament in the treatment of adolescent acute patellar dislocation using “double-pulley” technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(20): 3158-3163. |
| [9] | Chen Hui, Wang Qun, Yan Shuang-xi, Dong Tian-yun, Zou Hai-bing . Lateral retinacular release and patella ligament reconstruction under arthroscopy for recurrent patellar dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(29): 4747-4751. |
| [10] | Sui Jin-po, Ge Bang-rong, Xie Shi-cheng, Duan Guo-qing, Zhang Yuan-min, Zhao Xiao-wei. Lateral retinacular release: changes in knee joint parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(11): 1722-1726. |
| [11] | Luo Sheng-fei, Qu You, Chen Jian, Li Ping. Effect of McConnell Taping on the quadriceps muscle strength and patellofemoral pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(25): 4078-4083. |
| [12] | Sui Jin-po, Ge Bang-rong, Yang Wen-feng, Duan Guo-qing, Zhang Yuan-min, Zhao Xiao-wei, Xie Shi-cheng. Knee joint parameters are significant for anterior knee pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(9): 1633-1640. |
| [13] | Hou Bo, Wang Yi, Shen Yu-hui. Mechanical analysis of knee dynamic finite element model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(22): 3998-4004. |
| [14] | Zhu Jun, Zhu Yun-li, Wu Hai-shan, Wu Yu-li, Fu Pei-liang. Recurrent patellar dislocation in children treated with different soft tissue transplantation: A comparative study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(18): 3413-3420. |
| [15] | Pan Yong-qian, Li Jian, Yang Bo, Zhang Ping, Wang Le, Zhong Zhi-hong. Treatment for patellofemoral maltracking in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(13): 2327-2332. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||