Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (18): 3413-3420.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.18.025
Recurrent patellar dislocation in children treated with different soft tissue transplantation: A comparative study
Zhu Jun, Zhu Yun-li, Wu Hai-shan, Wu Yu-li, Fu Pei-liang
- Department of Joint Surgery, Shanghai Changzheng Hospital, Shanghai 200003, China
-
Received:2012-12-29Revised:2013-02-25Online:2013-04-30Published:2013-04-30 -
Contact:Zhu Yun-li, Doctor, Associate chief physician, Department of Joint Surgery, Shanghai Changzheng Hospital, Shanghai 200003, China joint_zhu@126.com -
About author:Zhu Jun☆, Doctor, Attending physician, Department of Joint Surgery, Shanghai Changzheng Hospital, Shanghai 200003, China xlgy1@sina.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhu Jun, Zhu Yun-li, Wu Hai-shan, Wu Yu-li, Fu Pei-liang. Recurrent patellar dislocation in children treated with different soft tissue transplantation: A comparative study[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(18): 3413-3420.
share this article

2 文章分析结果与其他研究结果的比较 2.1 资料来源 检索数据库有关软组织移植治疗儿童复发性髌骨脱位的文献[26-27],研究文献范围1990至2011年,检索词为“软组织移植(Soft tissue transplantation);复发性髌骨脱位(Recurrent patellar dislocation);髌韧带(Patellar tendon);髌股韧带(Patellofemoral ligament);髌骨高位(Patellar high);软组织挛缩(Soft tissue contracture);膝关节脱位(The knee joint dislocation)”,检索到相关文献37篇,结果分析相关文献12篇[5-16]。 2.2 纳入标准 ①股骨远端、胫骨近端骨骺未闭。②移植前均为复发性髌骨脱位。 2.3 排除标准 ①既往有髌骨不稳外科治疗史。②严重高位髌骨、滑车发育不良等发育异常。③单纯髌骨不稳患者,无脱位史。④移植后出现感染、血管、神经损伤等并发症。 2.4 分析指标 ①不同软组织移植物治疗儿童复发性髌骨脱位的效果。②软组织移植对儿童复发性髌骨脱位髌股关节适应性的影响。③软组织移植后早期康复训练对治疗儿童复发性髌骨脱位的中期疗效影响。 2.5 软组织移植治疗儿童复发性髌骨脱位的远期随访效果分析 儿童复发性髌骨脱位是临床上比较常见的膝关节损伤,严重影响患者的运动能力和日常生活。治疗儿童复发性髌骨脱位的方法很多,其目的都是为了控制髌骨不稳,恢复髌骨的正常运动轨道[28]。近年来,随着软组织移植相关研究的深入,软组织移植治疗儿童复发性髌骨脱位取得了良好的临床效果,多数文献报道的移植后成功率很高,主要区别在于所使用的软组织移植物和固定的方法[29]。应用不同来源软组织移植治疗儿童复发性髌骨脱位相关研究分析,见表3。"

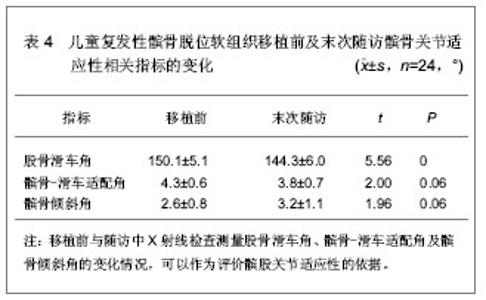
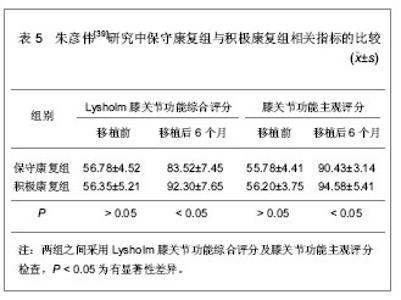
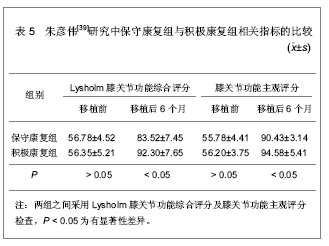
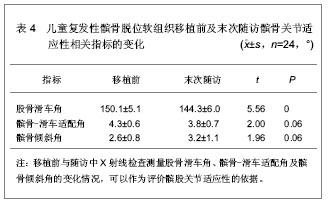
2.6 软组织移植对儿童复发性髌骨脱位髌股关节适应性的影响 儿童复发性髌骨脱位的病理改变为股骨滑车窝发育低平、股内侧肌萎缩、内侧髌股韧带薄弱,经常合并有高位髌骨等异常解剖形态[34]。由于儿童骨骺及生长板的存在,对于儿童复发性髌骨脱位的治疗主要为软组织移植,并且取得了较好的效果,但是对于移植后髌股关节适应性相关报道较少[35]。吕学敏等[36]研究了软组织移植治疗不同年龄段儿童复发性髌骨脱位后,髌股关节适应性的变化情况。对24例患者行软组织移植治疗,患者年龄平均5.4岁(3-8岁),男6例,女18例,移植前及随访中分别行髌骨轴位和侧位X射线片检查,测量股骨滑车角、髌骨-滑车适配角及髌骨倾斜角的变化情况,以评价髌股关节适应性,相关指标测量结果,见表4。"
| [1] Beasley LS, Vidal AF.Traumatic patellar dislocation in children and adolescents treatment update and literature review.Curr Opin Pediatr.2004;16(1):29-36.[2] Larsen E,Lauridsen F.Conservative treatment of patellar dislocations. Influence of evident factors on the tendency to redislocation and the therapeutic result.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1982;(171):131-136.[3] Hing CB,Shepstone L,Marshall T,et al.A laterally positioned concave trochlear groove prevents patellar dislocation.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2006;447:187-194.[4] Fukui N,Nakagawa T,Murakami S,et al.A modified system of stress radiography for patellofemoral instability.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2003;85(8):1128-1133.[5] Deie M,Ochi M,Sumen Y,et al.Reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament for the treatment of habitual or recurrent dislocation of the patella in children.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2003;85(6):887-890.[6] Kuroda R,Kambic H,Valdevit A,et al.Articular cartilage contact pressure after tibial tuberosity transfer.A cadaveric study.Am J Sports Med.2001;29(4):403-409.[7] 吕征,吕天润,万斌.半腱肌腱股薄肌腱在重建前交叉韧带中的运用[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2005,25(11): 786-788.[8] 王宁,刘玉杰,杨玉明,等.自体腘绳肌腱移植治疗复发性髌骨脱位[J].军医进修学院学报,2009,30(5):603-605.[9] Schöttle PB,Fucentese SF,Romero J.Clinical and radiological outcome of medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction with a semitendinosus autograft for patella instability.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2005;13(7):516-521.[10] Deie M,Ochi M,Sumen Y,et al.A long-term follow-up study after medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction using the transferred semitendinosus tendon for patellar dislocation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2005;13(7):522-528.[11] Letts RM,Davidson D,Beaule P.Semitendinosus tenodesis for repair of recurrent dislocation of the patella in children.J Pediatr Orthop.1999;19(6):742-747.[12] 刘阳,郑江,张明宇,等.半腱肌肌腱移植双束解剖重建治疗复发性髌骨脱位[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(2):111-115.[13] 周红星,李钦宗,张保健,等.关节镜下自体腘绳肌腱重建内侧髌股韧带治疗复发性髌骨脱位[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012, 26 (6):683-685.[14] Drez D Jr,Edwards TB,Williams CS.Results of medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction in the treatment of patellar dislocation.Arthroscopy.2001;17(3):298-306.[15] Woods GW,Elkousy HA,O'Connor DP.Arthroscopic release of the vastus lateralis tendon for recurrent patellar dislocation. Am J Sports Med.2006;34(5):824-831.[16] Nomura E,Horiuchi Y,Kihara M.Medial patellofemoral ligament restraint in lateral patellar translation and reconstruction. Knee.2000;7(2):121-127.[17] Cossey AJ,Paterson R.A new technique for reconstructing the medial patellofemoral ligament.Knee.2005;212(2):93-98.[18] Irrgang JJ,Ho H,Harner CD,et al.Use of the International Knee Documentation Committee guidelines to assess outcome following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.1998; 6(2):107-114.[19] Lysholm J,Gillquist J.Evaluation of knee ligament surgery results with special emphasis on use of a scoring scale.Am J Sports Med.1982;10(3):150-154.[20] 李付彬,徐向峰,李杰峰,等.关节镜结合内侧髌骨股骨韧带重建治疗复发性髌骨脱位[J].中国现代药物应用,2012,6(13):52-53.[21] 张学胜, 韩宝生.自体半腱肌重建内侧支持带并松解外侧支持带治疗复发性髌骨脱位[J].医学信息,2012,25(2):135-136.[22] 黄炎,李海鹏,征华勇,等.内侧髌股韧带重建联合外侧支持带松解治疗复发性髌骨脱位[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(8): 743-744.[23] 田红光,范小平,贺两平,等.半腱肌重建内侧髌股韧带治疗复发性髌骨脱位[J].临床医学,2011,31(2):78-80.[24] 郭氧,郭秋菊,徐华,等.股薄肌腱双束重建内侧骸股韧带治疗12例复发性髌骨脱位临床分析[J].福建医药杂志,2011,33(2): 42-44.[25] 张羽飞,王寿宇,王立德,等.游离半腱肌腱髌旁锚钉固定加强膝内侧髌股韧带治疗复发性髌骨脱位[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2010, 12(9):819-823.[26] 中国知网.中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2012-08-10. httpswww.cnki.net[27] SCI数据库.Web of Sciencevia ISI Web of Knowledge[DB/OL]. 2012-08-10.httpip-science.thomsonreuters.commjl[28] 柯陈荣,李皓桓,叶恒,等.重建MPFL治疗复发性髌骨脱位的临床疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011,26(12):1115-1116.[29] Nakagawa K,Wada Y,Minamide M,et al.Deterioration of long-term clinical results after the Elmslie-Trillat procedure for dislocation of the patella.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2002; 84(6): 861-864.[30] 冯超,王玉琨,张建立,等.大收肌腱移位重建内侧髌股韧带治疗儿童复发性髌骨脱位初期效果分析[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2012, 33(6):429-433.[31] 王月光,周宏艳,左玉明,等.综合手术治疗儿童复发性髌骨脱位的疗效观察[J].中国医师杂志,2011,13(1):65-66.[32] 王来喜,袁芳.重建髌骨内侧韧带治疗儿童复发性髌骨脱位[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(1):37-38.[33] 于振武,刘玉昌,马文校,等.联合术式治疗儿童习惯性髌骨脱位的疗效评价[J].山东医药,2004,44(21):23-24.[34] Fleming BC,Beynnon BD,Renstrom PA,et al.The strain behavior of the anterior cruciate ligament during bicycling. An in vivo study.Am J Sports Med.1998;26(1):109-118.[35] Tyler TF,McHugh MP,Gleim GW,et al.The effect of immediate weightbearing after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1998;(357):141-148.[36] 吕学敏,闫桂森,郭源,等.复合软组织手术对儿童习惯性髌骨脱位髌股关节适应性的影响[J].中华骨科杂志,2010,30(9): 870-875.[37] Weiler A,Peine R,Pashmineh-Azar A,et al.Tendon healing in a bone tunnel. Part I Biomechanical results after biodegradable interference fit fixation in a model of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in sheep.Arthroscopy.2002;18(2):113-123.[38] Hantes ME,Mastrokalos DS,Yu J,et al.The effect of early motion on tibial tunnel widening after anterior cruciate ligament replacement using hamstring tendon grafts. Arthroscopy. 2004;20(6):572-580.[39] 朱彦伟.体腘绳肌腱重建前交叉韧带术后两种康复方案效果的比较[D].山西:山西医科大学, 2009:1-30.[40] 韵向东,夏亚一,吴萌,等.重建内侧髌股韧带治疗复发性髌骨脱位[J].中国骨伤,2012,25(2):124-127.[41] 张力丹,张辉,冯华.急性创伤性髌骨脱位的早期手术治疗[J].山东医药,2010,50(44):7-9.[42] Avikainen VJ,Nikku RK,Seppänen-Lehmonen TK.Adductor magnus tenodesis for patellar dislocation. Technique and preliminary results.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1993;(297):12-16.[43] Ghanem I, Wattincourt L, Seringe R.Congenital dislocation of the patella. Part I pathologic anatomy.J Pediatr Orthop.2000; 20(6):812-816.[44] Garth WP Jr,Pomphrey M Jr,Merrill K.Functional treatment of patellar dislocation in an athletic population.Am J Sports Med. 19960;24(6):785-791.[45] Goorens CK,Robijn H,Hendrickx B,et al.Reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament for patellar instability using an autologous gracilis tendon graft.Acta Orthop Belg.2010;76(3): 398-402.[46] Benoit B,Laflamme GY,Laflamme GH,et al.Long-term outcome of surgically-treated habitual patellar dislocation in children with coexistent patella alta. Minimum follow-up of 11 years.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2007;89(9):1172-1177.[47] Matthews JJ,Schranz P.Reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament using a longitudinal patellar tunnel technique.Int Orthop.2010;34(8):1321-1325.[48] Deie M,Ochi M,Adachi N,et al.Medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction fixed with a cylindrical bone plug and a grafted semitendinosus tendon at the original femoral site for recurrent patellar dislocation.Am J Sports Med.2011;39(1): 140-145.[49] Larson RL,Cabaud HE,Slocum DB,et al.The patellar compression syndrome surgical treatment by lateral retinacular release.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1978;(134): 158-167.[50] Hautamaa PV,Fithian DC,Kaufman KR,et al.Medial soft tissue restraints in lateral patellar instability and repair.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1998;(349):174-182.[51] Fulkerson JP.Anteromedialization of the tibial tuberosity for patellofemoral malalignment.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1983; (177):176-181.[52] Fulkerson JP,Becker GJ,Meaney JA,et al.Anteromedial tibial tubercle transfer without bone graft.Am J Sports Med.1990; 18(5):490-496.[53] Boden BP,Pearsall AW,Garrett WE Jr,et al.Patellofemoral Instability Evaluation and Management.J Am Acad Orthop Surg.1997;5(1):47-57.[54] Conlan T,Garth WP Jr,Lemons JE.Evaluation of the medial soft-tissue restraints of the extensor mechanism of the knee.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1993;75(5):682-693.[55] Hautamaa PV,Fithian DC,Kaufman KR,et al.Medial soft tissue restraints in lateral patellar instability and repair.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1998;(349):174-182.[56] Baldwin JL.The anatomy of the medial patellofemoral ligament.Am J Sports Med.2009;37(12):2355-2361.[57] Guerrero P,Li X,Patel K,et al.Medial patellofemoral ligament injury patterns and associated pathology in lateral patella dislocation an MRI study.Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Ther Technol.2009;1(1):17.[58] Bicos J,Fulkerson JP,Amis A.Current concepts review the medial patellofemoral ligament.Am J Sports Med.2007; 35(3):484-492. |
| [1] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [2] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [3] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [4] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [5] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [6] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [7] | Shen Jinbo, Zhang Lin. Micro-injury of the Achilles tendon caused by acute exhaustive exercise in rats: ultrastructural changes and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1190-1195. |
| [8] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [9] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [10] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [11] | Zhong Hehe, Sun Pengpeng, Sang Peng, Wu Shuhong, Liu Yi. Evaluation of knee stability after simulated reconstruction of the core ligament of the posterolateral complex [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 821-825. |
| [12] | Zhao Zhongyi, Li Yongzhen, Chen Feng, Ji Aiyu. Comparison of total knee arthroplasty and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of traumatic osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 854-859. |
| [13] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Influence of anterior cruciate ligament defect on the mid-term outcome of fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 860-865. |
| [14] | Zhang Nianjun, Chen Ru. Analgesic effect of cocktail therapy combined with femoral nerve block on total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 866-872. |
| [15] | Yuan Jun, Yang Jiafu. Hemostatic effect of topical tranexamic acid infiltration in cementless total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 873-877. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||