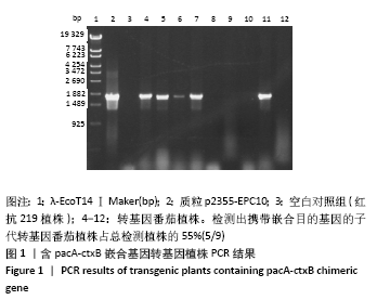
[1] 孙宇辰.基因工程疫苗的研究与应用[J].生物化工,2018,4(6):152-158.
[2] 贺付蒙,李秀钰,赵潇璨,等.转马铃薯StPR1基因烟草抗病性及生理特性分析[J].华北农学报,2020,39(3):39-51.
[3] 王兵,程子义,张蕾,等.过表达毛白杨线粒体 APX 基因烟草提高抗逆能力的研究[J].北京林业大学学报,2020,42(7):33-39.
[4] SARA E,THOMAS J,TIMOTHY D,et al.Decreased bioavailability of aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) in genetically modified corn with activated carbon or calcium montmorillonite clay inclusion in soil. J Environ Sci (China). 2021;100:131-143.
[5] ANASTASIIA B, LYUBOV C, SERGII K, et al. Corrigendum to Transgenic tomato lines expressing human lactoferrin show increased resistance to bacterial and fungal pathogens. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. 2021;31: 101637.
[6] 林丹敏.霍乱毒素样抗肿瘤嵌合蛋白佐剂的设计、制备及活性评价[D].广州:广东工业大学,2015.
[7] 洪献忠,刘建国,吴志刚,连接肽为五肽的Pac-A和CTB嵌合质粒的构建及表达[J].上海口腔医学,2007,16(3):211-212.
[8] 周皓琳.变异链球菌cat-pacA-ctxB-DOCK8/DHR融合基因表达质粒的构建[D].遵义:遵义医学院,2014.
[9] 吴家媛,马欣荣,唐琳,等.变异链球菌表面蛋白PAc 基因A区与霍乱毒素B亚单位融合基因植物表达载体的构建[J].遵义医学院学报,2011,34(4):341-343.
[10] 吴家媛,刘建国,马欣荣,等.变异链球菌表面蛋白A区与霍乱毒素B亚单位嵌合基因转基因黄瓜植株的获得及鉴定[J].口腔医学研究,2016,32(9):902-905.
[11] 张燕,刘建国,陈筑,等.变异链球菌乳酸脱氢酶与霍乱毒素B亚单位嵌合表达质粒的构建和表达[J] .牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2012,22(7):371-406.
[12] CURTISS RI, CARDINEAU CA. Oral immunization by transgenic plants.World Plant Application. 1990;90:107-111
[13] GIRMA B. Review on Vaccine Production Using Transgenic Plants Against Selected Animal and Human Diseases. Advances in life Science and Technologe. 2017;(59):12-20.
[14] 李志亮,黄丛林,刘晓彬,等.转基因植物及其安全性的研究进展[J].北方园艺,2020(8):129-135.
[15] 郎遥玲.pCAMBIA-E8-APB-DOCK8融合基因表达质粒中标记基因的去除及瞬时转化番茄的研究[D].遵义:遵义医学院,2016.
[16] 高佩,尹锐,林彦,等.农杆菌介导的番茄遗传转化研究进展[J] 北方园艺,2016(14):192-197.
[17] 夏丽冬.再谈孟德尔遗传定律的验证[J].中学生物教学,2019(9): 26-28.
[18] 王海慧.转基因植物遗传稳定性影响因素的研究现状[J].贵州农业学,2013,41(9):5-8.
[19] 郭勇,张国锋,刘丽萍,等.基因沉默机制的基因表达式编程[J].计算机工程与应用,2018,54(23):131-136.
[20] 金永梅,马瑞,于志晶,等.转cry1C基因抗虫水稻吉生粳3号外源基因整合分析与品系特异性检测[J].生物技术通报,2019,35(3): 6-12.
[21] WIJEWARDENE I, MISHRA N, SUN L, et al. Improving drought-, salinity-, and heat-tolerance in transgenic plants by co-overexpressing Arabidopsis vacuolar pyrophosphatase gene AVP1 and Larrea Rubisco activase gene RCA. Plant Sci. 2020;296:110499 .
[22] 魏慧慧.玉米不同外植体培养能力、基因表达及遗传转化研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2019.
[23] 谢雯琦,马三梅,王永飞,等.转基因番茄口服疫苗的现状, 问题及对策[J].中国生物工程杂志,2014,34(10):94-100.
[24] MIKI B, MCHUGH S. Selectable marker genes in transgenic plants: applications, alternatives and biosafety. J Biotechnol. 2004;107(3): 193-232.
[25] 魏雪琪.转基因植物口服疫苗的前景分析[J].科技风,2016(22):145.
|