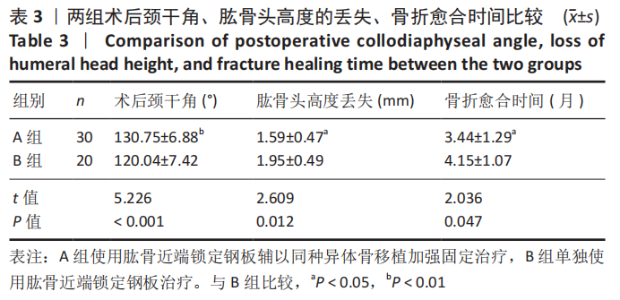
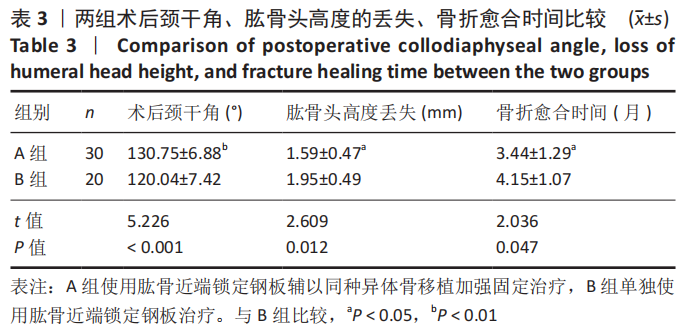
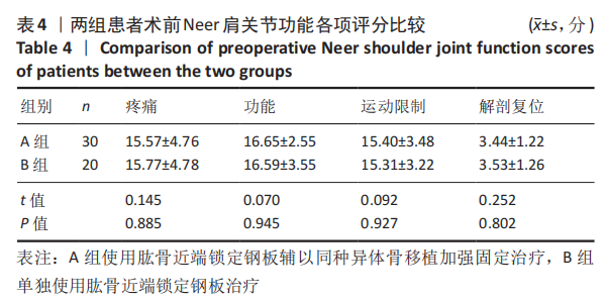
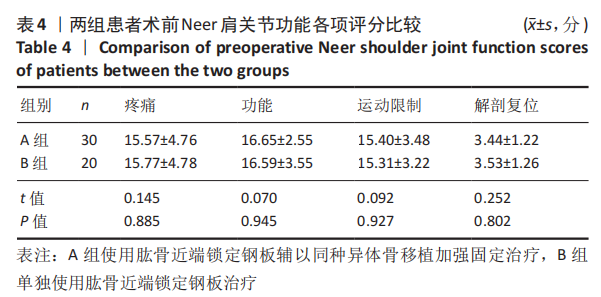
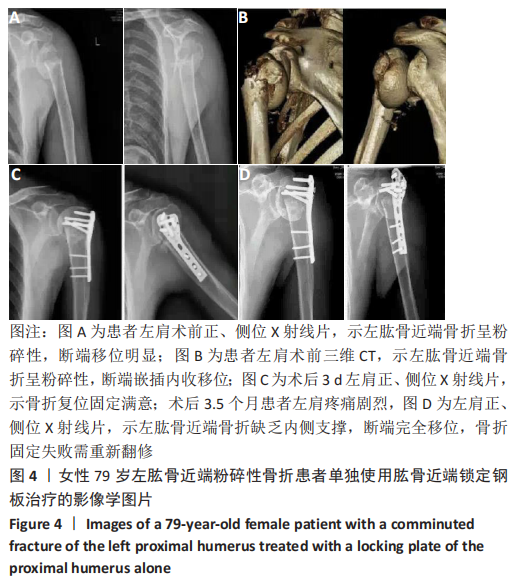
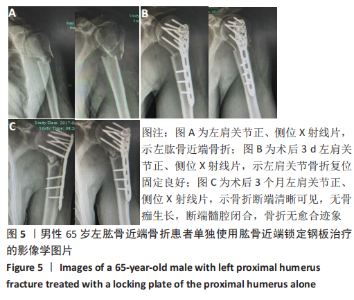
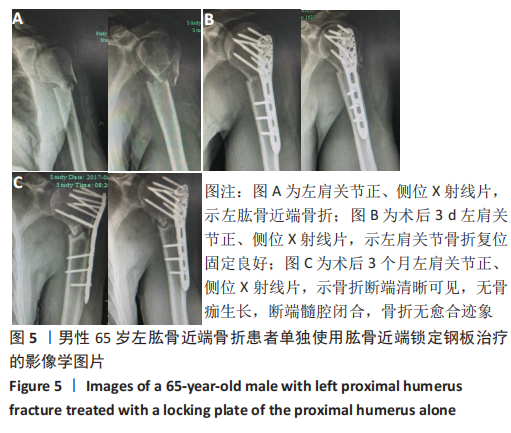
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (27): 4368-4373.doi: 10.12307/2021.198
Previous Articles Next Articles
Proximal humerus locking plate combined with allogeneic bone graft in the treatment of proximal humerus osteoporotic fractures
Pan Dongxu, Yang Jing, Li Yaohua, Liu Yuzhang, Duan Yonggang, Zhong Aiyun, Tang Xiaolong, Ding Yingqi
- Department of Orthopedics, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou 075100, Hebei Province, China