中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (19): 4091-4101.doi: 10.12307/2025.068
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
内皮祖细胞与间充质干细胞治疗血管支架相关疾病
李清音1,2,李林华1,张春乐1,付 平1
- 1四川大学华西医院肾脏内科,肾脏病研究所,四川省成都市 610041;2四川大学疾病分子网络前沿科学中心,四川省成都市 610041
-
收稿日期:2024-02-23接受日期:2024-04-29出版日期:2025-07-08发布日期:2024-09-13 -
通讯作者:付平,博士,教授,主任医师,四川大学华西医院肾脏内科,肾脏病研究所,四川省成都市 610041 -
作者简介:李清音,女,2001 年生,河南省周口市人,汉族,四川大学在读硕士,主要从事生物材料表面改性相关研究。
Endothelial progenitor cell and mesenchymal stem cell therapy for vascular stent-associated diseases
Li Qingyin1, 2, Li Linhua1, Zhang Chunle1, Fu Ping1
- 1Kidney Research Institute, Department of Nephrology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China; 2Frontier Science Center for Disease-related Molecular Network, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2024-02-23Accepted:2024-04-29Online:2025-07-08Published:2024-09-13 -
Contact:Fu Ping, PhD, Professor, Chief physician, Kidney Research Institute, Department of Nephrology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Li Qingyin, Master candidate, Kidney Research Institute, Department of Nephrology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China; Frontier Science Center for Disease-related Molecular Network, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
血管支架相关疾病:①使用血管支架介入治疗的疾病(文中主要介绍的是动脉粥样硬化);②血管支架植入损伤并发症(血栓、内膜增生)。内皮祖细胞与间充质干细胞治疗血管支架相关疾病:①内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞治疗动脉粥样硬化;②内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞治疗血管支架植入损伤并发症;③基于内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞的血管支架用于治疗血管疾病。
摘要
背景:随着干细胞研究的发展,成体干细胞如内皮祖细胞和间充质干细胞在动脉粥样硬化、血管支架植入损伤并发症中的治疗效能逐渐被发现,由于静脉输注成体干细胞治疗疾病存在靶向性差、治疗效率低等问题,近年来对血管支架表面改性以实现内皮祖细胞或间充质干细胞的局部聚集与功能调节一直是研究的焦点。
目的:论述内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞在血管支架相关疾病中的治疗进展,以及基于内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞的血管支架设计方面的研究现状。
方法:在CNKI、万方、PubMed、Web of Science数据库检索建库以来发表的相关文献。中文检索词“内皮损伤,支架植入术,血栓,内膜增生,动脉粥样硬化,内皮修复,内皮祖细胞,间充质干细胞,血管支架”;英文检索词“endothelial injury,stenting,thrombosis,intimal hyperplasia,atherosclerosis,endothelial repair,endothelial regeneration,endothelial progenitor cell,mesenchymal stem cell,vascular stent,vascular scaffold”。根据纳入和排除标准,最终对127篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞能够通过分化以及旁分泌作用治疗动脉粥样硬化及支架植入损伤并发症,其作用机制主要包括保护内皮细胞、调节炎症细胞与炎症因子表达、调节平滑肌细胞增殖和表型等。间充质干细胞在治疗应用中可能伴有血栓、血管钙化等不良反应,使用细胞外囊泡、联合使用肝素进行表面设计是解决这一问题的可行方案。目前基于内皮祖细胞的支架研究较多,主要从内皮祖细胞的募集、捕获、增殖、分化与活性等方面进行支架表面改性;血管领域基于间充质干细胞捕获的支架研究较少,但间充质干细胞来源外泌体洗脱支架被发现具有极高的治疗效能。此外一些基础疾病如糖尿病可能会对成体干细胞活性造成影响,导致基于干细胞设计的支架失去效能,因而未来在设计相应的支架时,应注意考虑这方面的影响因素。
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-9186-8860 (李清音)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
李清音, 李林华, 张春乐, 付 平. 内皮祖细胞与间充质干细胞治疗血管支架相关疾病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(19): 4091-4101.
Li Qingyin, Li Linhua, Zhang Chunle, Fu Ping. Endothelial progenitor cell and mesenchymal stem cell therapy for vascular stent-associated diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(19): 4091-4101.
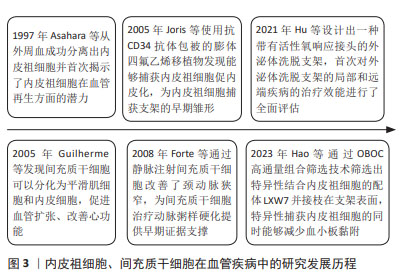
2.2 内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞在血管支架相关疾病中的治疗作用
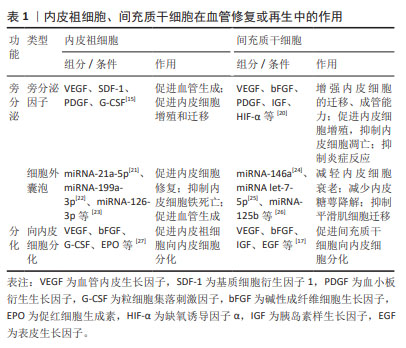
2.2.1 内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞在血管修复或再生中的作用
(1)内皮祖细胞:内皮祖细胞可分为早期内皮祖细胞以及晚期内皮祖细胞[12],它们在血管内皮修复中发挥着至关重要的作用。不论早期还是晚期内皮祖细胞均具有分泌多种细胞因子、生长因子的能力[13],这些旁分泌因子能够促进血管生成、内皮细胞的增殖和迁移,此外内皮祖细胞分泌的细胞外囊泡通过细胞间通讯共同参与旁分泌调节[14]。其中分化程度较低即早期内皮祖细胞主要通过旁分泌作用促进内皮细胞增殖以及晚期内皮祖细胞分化,分化程度较高即晚期内皮祖细胞主要通过黏附、嵌入受损的血管内皮、增殖、分化取代受损内皮细胞,为血管内皮修复提供健康、成熟的细胞原料[15]。
(2)间充质干细胞:血管内皮受损后局部分泌异常水平的细胞、趋化因子能够募集间充质干细胞到损伤部位,分泌多种细胞因子以及细胞外囊泡促进血管内皮再生修复。较多研究认为其重要的功能是炎症调节,可以通过调节T细胞、自然杀伤细胞和巨噬细胞抑制炎症反应[16]。除了旁分泌作用,与内皮祖细胞一样,间充质干细胞具有分化为内皮细胞的能力,它可以在多种因子、缺氧以及剪切应力等条件下分化为内皮细胞[12,17-18],其中血管内皮生长因子和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子诱导间充质干细胞的内皮细胞分化效果较好[19]。除了分化为内皮细胞外,在转化生长因子β1、微小RNA(miRNA-503、miRNA-222-5p)等条件下间充质干细胞还会分化为血管平滑肌细胞[12]。
具体的旁分泌因子、细胞外囊泡功能成分及效能见表1。
2.2.2 内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞治疗动脉粥样硬化
(1)动脉粥样硬化发病机制:内皮细胞功能障碍、血管内皮屏障结构完整性破坏与内皮细胞修复的平衡被打破是动脉粥样硬化发生、发展的关键要素[28]。易发生动脉粥样硬化人群的血管内皮细胞可能受到低密度脂蛋白、高血压、高血糖、促炎因子如肿瘤坏死因子α等影响,在这些因素的作用下内皮细胞功能发生非适应性改变:表达的内皮一氧化氮合酶解偶联,产生一氧化氮能力下降;核因子κB通路被激活进而表达一系列效应蛋白激活炎症细胞、平滑肌细胞、血小板,即内皮细胞出现功能异常[29]。除了功能异常,在炎症与氧化应激的微环境下,参与构成内皮屏障的内皮细胞表面糖萼以及细胞间连接常会被打破,导致血管内皮通透性增加[30],此时被募集的炎症细胞更加容易通过内皮细胞间隙浸润在血管内皮下层,被活化的血小板黏附、聚集,促进单核细胞或巨噬细胞表达多种炎症因子进一步促进炎症发展[31]。浸润于血管内皮下层的单核细胞部分转化为巨噬细胞,而后吞噬大量氧化性低密度脂蛋白,与细胞外脂质共同构成脂质核心,这一脂质核心被发生表型转化、增殖、迁移的平滑肌细胞及其分泌的细胞外基质等成分包裹,与功能异常的内皮细胞共同构成动脉粥样硬化斑块[32-33]。血管内皮细胞自我修复通常以循环或损伤周围常驻的健康内皮细胞为主,以干细胞或其他一些细胞如平滑肌细胞修复为辅。受损的内皮细胞通过激活Notch1信号通路,上调Dlk1表达miRNA-126-5p以分泌更多的促血管生长、迁移因子,促进健康的内皮细胞聚集在损伤部位并增殖;内皮细胞还会通过表达N-钙黏蛋白等修复细胞间连接。干细胞则通过旁分泌多种血管生长、迁移因子或细胞外囊泡调节内皮细胞代谢与增殖,这一旁分泌作用的调节与晚期内皮祖细胞的内皮细胞分化作用共同促进损伤内皮细胞的修复再生[34],当内皮细胞损伤与修复平衡被打破时,血管发生动脉粥样硬化的风险随之升高,若修复始终处于异常状态则会进一步促进动脉粥样硬化的进展。
(2)内皮祖细胞治疗动脉粥样硬化的作用机制:内皮祖细胞参与血管内皮修复主要包括动员、归巢、增殖、分化、旁分泌等过程。损伤部位分泌的高水平血管内皮生长因子、粒细胞集落刺激因子、粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子、基质细胞衍生因子1α等促进着内皮祖细胞的募集、黏附[35-36],WEI等[37]使用超小型超顺磁性氧化铁纳米颗粒标记内皮祖细胞,MRI示踪证实了内皮祖细胞在动脉粥样硬化部位聚集。如前所述晚期内皮祖细胞可以通过增殖、分化替代受损的内皮细胞[38],除了分化作用,内皮祖细胞能够通过呈递细胞外囊泡成分miRNA-126以及多种生长因子促进内皮细胞增殖再生,miRNA-21-5p成分够逆转氧化型低密度脂蛋白诱导的内皮细胞活性下降和自噬功能障碍[39],从而保护内皮细胞受到脂蛋白累积的损害,miRNA-199a-3p可抑制内皮细胞铁死亡并减轻动脉粥样硬化发生[22]。除了对内皮细胞的功能有调节作用,内皮祖细胞还可能对平滑肌细胞的表型转化具有调节作用,有研究将内皮祖细胞和平滑肌细胞共同培养,发现在脂蛋白累积的状态下,内皮祖细胞通过趋化因子CXCL12-CXCR4途径阻碍了平滑肌由收缩表型向合成表型转化,减少了平滑肌细胞分泌释放促炎因子,从而阻碍了动脉粥样硬化的进展[40]。有研究发现内皮祖细胞分泌的细胞外囊泡显著减少糖尿病并发动脉粥样硬化小鼠模型血管斑块数量,降低了细胞黏附分子1、白细胞介素8、C-反应蛋白以及氧化应激因子丙二醛和超氧化物歧化酶水平[21]。
(3)间充质干细胞治疗动脉粥样硬化的作用机制:目前研究证据表明间充质干细胞主要通过4个方面的作用改善动脉粥样硬化:①调节炎症:通过减少T细胞数量、降低血清单核细胞趋化蛋白1水平,促进调节性T细胞的发育和增殖[41-42],通过激活STAT6信号通路等诱导巨噬细胞转变为M2抗炎表型,通过细胞外囊泡成分miRNA-21a-5p[43]、miRNA-let7-5p抑制动脉粥样硬化斑块中巨噬细胞的浸润并减少巨噬细胞凋亡[25,44],最终减少血管炎症反应,炎症因子如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6的表达降低,而抗炎因子白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β的表达增高;②保护内皮细胞,促进内皮细胞增殖并向内皮细胞分化,调节内皮祖细胞功能:通过细胞外囊泡成分miRNA-324-5p、miRNA-146a[24]、miRNA-145等抑制内皮功能障碍[45],通过细胞外囊泡成分FENDRR调节miRNA-28水平逆转内皮细胞损伤[46],抑制斑块炎症,减少内皮细胞凋亡;通过分化为内皮细胞以及促进内皮细胞、内皮祖细胞增殖迁移功能共同促进血管内皮细胞修复[47-49],但研究表明体内非给药条件下单纯向内皮细胞分化的间充质干细胞比例较少,约占8%[50];③降低血脂如总胆固醇、三酰甘油、低密度脂蛋白水平[51];④调节血管平滑肌细胞增殖:有研究认为间充质干细胞能够抑制血管平滑肌增殖[48],在炎症调节过程中生成的转化生长因子β1等是间充质干细胞向平滑肌细胞分化的重要调节因子,在一些研究中间充质干细胞被认为通过分化为平滑肌细胞稳定斑块,减少斑块破裂引起的血栓等问题[52]。由于该方面的报道较少,不同间充质干细胞的培养条件和应用状态的不同是否会导致与④观点的不同尚不可知,未来需要进一步探究。
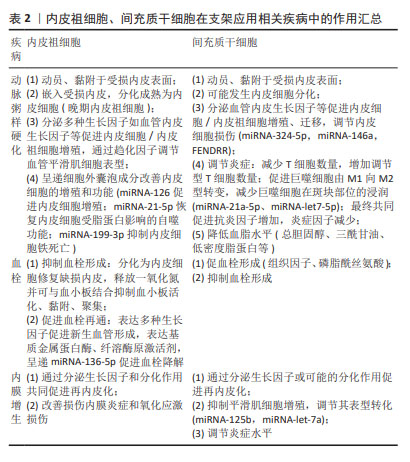
2.2.3 内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞治疗血管支架植入损伤 血栓和内膜增生是导致支架植入后患者远期预后较差的两大原因[53]。血管损伤后内膜增生与动脉粥样硬化发病机制有着相似的本质,支架植入损伤内皮后,部分内皮细胞脱落,暴露出基底面胶原,血小板激活、黏附、聚集并发生级联反应,此时可能导致急性血栓形成,而后中性粒细胞与巨噬细胞等炎症细胞聚集在损伤部位,血管平滑肌细胞由收缩型转变为分泌型并发生增殖,随着基质金属蛋白酶等对细胞外基质降解而向内膜下层迁移,最后细胞外基质重新合成与增殖迁移到内膜下的血管平滑肌细胞共同构成新生内膜[54-55],而晚期支架血栓形成主要是由支架植入后内皮化延迟导致。下面将从内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞在血栓和内膜增生中的作用展开讨论二者在血管支架植入损伤中的治疗效能。
(1)血栓
内皮祖细胞抑制血栓形成并促进血栓再通:已有较多研究发现内皮祖细胞不仅能够抑制血栓形成,还能够促进血栓再通。血管内皮损伤后激活的血小板能够释放多种旁分泌因子(如基质细胞衍生因子1)并表达细胞表面黏附分子P-选择素[56],促进内皮祖细胞的募集和分化,内皮祖细胞具有健康内皮细胞维持血管正常生理状态下的许多重要功能,内皮祖细胞募集到损伤部位可能通过抑制血小板活性来抑制急性血栓形成,并促进再内皮化和血管修复[57]。目前内皮祖细胞对血栓的形成抑制以及再通作用机制主要包括以下5点:①内皮祖细胞能通过修复受损内皮细胞或分化补充丢失的内皮细胞以修复导致血栓形成的根源问题——内皮细胞受损导致的内皮屏障破坏基底胶原暴露;②内皮祖细胞分泌的多种生长因子(血管内皮生长因子、肝细胞生长因子、转化生长因子β等)能够诱导血栓中的新生血管形成以改善血栓中的血供状态[58],这与内皮细胞、巨噬细胞对血栓纤维蛋白网降解形成隧道后内皮祖细胞在局部分化、覆盖形成内皮表面的论点相互印证[59];③内皮祖细胞能够通过释放一氧化氮或通过与血小板结合抑制血小板活化、黏附与聚集[57,60];④内皮祖细胞释放的基质金属蛋白酶、纤溶酶原激活剂能够激活纤溶酶原,促进血栓成分的分解[60];⑤分泌的细胞外囊泡成分如miRNA-136-5p通过抑制硫氧还蛋白互作蛋白表达促进血栓溶解[61]。
间充质干细胞与血栓:在抗血栓方面,间充质干细胞并没有表现出相应的优势,目前主流研究认为间充质干细胞具有促凝血作用,已有较多研究发现使用间充质干细胞会引发凝血和补体途径的双重激活,发生即刻经血液介导的炎症反应(IBMIR)[62]。间充质干细胞通过多种途径调节凝血过程:间充质干细胞分泌的组织因子启动凝血,促进血小板的产生和活化,其分泌的细胞外囊泡中包含的磷脂酰丝氨酸会激活凝血级联反应[63]。但有少量文献研究认为间充质干细胞具有抗凝作用:NETSCH等[64]发表文章指出,不同来源(骨髓、脂肪和脐血)的间充质干细胞具有抗凝血特性,它们能够抑制全血中血小板的活化和聚集。一些学者认为间充质干细胞及其细胞外囊泡均同时具有抗凝血和促凝血的特性,其表达较高水平的促凝血分子的同时表达低水平的抗凝分子,因而也主要表现出促凝的特
点[65],这一观点解释了不同研究中间充质干细胞促凝和抗凝作用的矛盾结果,目前大量人类或动物研究报道的血栓形成事件也证实了间充质干细胞以促凝血为主的特性[66]。
(2)内膜增生
内皮祖细胞抑制内膜增生:研究认为内皮祖细胞可能通过旁分泌细胞因子(如血管内皮生长因子、转化生长因子β1、胰岛素样生长因子1)或增殖分化促进再内皮化而改善支架植入后再狭窄的问题。SUN等[67]将分离出的内皮祖细胞注射至动物模型中,发现实验组血管内皮生长因子和内皮型一氧化氮合酶表达显著升高,炎症调节和脂质过氧化物表达显著低于对照组,即改善了内膜炎症,减少了氧化应激,减轻了内皮功能障碍;WANG等[68]以及XU等[69]通过建立大鼠颈动脉球囊损伤模型证实了内皮祖细胞能够抑制球囊损伤后的内膜增生。内皮祖细胞外泌体也被证实可能通过修复内皮细胞,减慢平滑肌细胞增殖来抑制内膜增生[70]。
间充质干细胞抑制内膜增生:现已有多个研究发现不同来源(脐血、骨髓、脂肪等)的间充质干细胞能够抑制内膜增生,它们可能通过抗炎[71]、促内皮化以及抑制平滑肌细胞增殖周期和炎症表型转化等作用抑制血管内皮损伤后的内膜增生[72-73]。CAI等[74]发现脂肪来源间充质干细胞降低了球囊损伤后血管促炎基因的表达,减少了动静脉瘘球囊治疗术后的内膜增生,改善了血管重塑过程。间充质干细胞外泌体能够介导内皮细胞的血管内皮生长因子表达[75-76],促进内皮细胞增殖、迁移[77],从而加速内皮化进程;其细胞外囊泡组分miRNA-125b[26]、miRNA-let-7a能够下调α-平滑肌肌动蛋白表达抑制平滑肌细胞增殖[78],共同抑制血管内皮损伤后的内膜增生[79]。有部分研究发现损伤后血管内激活的转化生长因子β1/Smad信号转导通路诱导了骨髓间充质干细胞向损伤部位聚集、分化并促进内膜增生[80],间充质干细胞对内膜增生的抑制和促进作用之间是如何相互平衡的,是未来研究值得探索的一个问题。
内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞在支架应用相关疾病中的机制总结见表2。
2.3 基于内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞的血管支架表面改性
2.3.1 基于内皮祖细胞的血管支架表面设计 外周血中循环内皮祖细胞的浓度较低[67],往往不足以实现球囊损伤/支架植入损伤后的快速内皮化恢复,因此研究者往往会对材料表面进行改性以更好地募集、捕获骨髓和循环中的内皮祖细胞,增加内皮祖细胞与损伤部位结合。目前对支架表面改性以实现内皮祖细胞在局部损伤部位的聚集与修复的方式有多种,如何增强内皮祖细胞动员归巢、黏附、增殖、分化以及保护其活性以保证其旁分泌治疗作用等是近年来研究者们重点研究方向。下面将从募集、捕获、增殖与分化等方面展开讨论。
(1)募集:动员内皮祖细胞的因子有多种,如血管内皮生长因子、基质细胞衍生因子1、粒细胞集落刺激因子、HMG-CoA还原酶抑制剂(他汀类药物)、过氧化酶体增殖物激活受体γ激动剂、血管紧张素Ⅱ拮抗剂等 [27,81-82]。此外神经营养因子3也可以诱导内皮祖细胞动员和归巢加速内皮化,并通过抑制平滑肌细胞增生等抑制内膜增生[83]。其中粒细胞集落刺激因子和血管内皮生长因子等因子不仅会募集内皮祖细胞还可能动员炎症细胞。研究表明短期给予粒细胞集落刺激因子治疗能够防止动脉粥样硬化发生发展,而长期或频繁给药可能会促进动脉粥样硬化发展[84]。而基质细胞衍生因子1虽然能够促进内皮化,但是其可能会通过募集平滑肌祖细胞而增加内膜增生的风险[85],因而在设计血管支架表面时应注意避开或不要单独使用这些因子。
目前研究发现一些药物能够募集内皮祖细胞:替米沙坦(一种血管紧张素Ⅱ受体阻滞剂)能够显著募集内皮祖细胞,促进内皮化,减少内膜增生[86];西洛他唑、氯吡格雷等抗血小板药物通过募集内皮祖细胞到血管损伤部位来促进内皮损伤修复[87];人参皂苷Rg1能够募集内皮祖细胞,抑制血管平滑肌细胞的异常增殖,抑制内膜增生[88]。
(2)捕获:捕获内皮祖细胞的方式包括建立纳米表面、提供生物活性结合位点以及捕获分子修饰。纳米表面主要通过相分离、自组装以及静电纺丝等方式建立;生物活性结合位点主要是通过明胶、胶原蛋白等模拟细胞外基质[82];捕获分子表面设计则是目前研究较多的方向,下面将就此方向展开讨论。目前已知的内皮祖细胞表面标志物有多种,包括CD31、CD34、CD133、CD144(VE-钙黏蛋白)、CD146以及血管内皮生长因子2等[89]。尽管已有较多研究利用内皮祖细胞表面标志物与抗体之间的特异性结合反应,在支架表面涂覆这些抗体,成功设计了能够一定程度解决支架内再狭窄问题的血管支架[90],但这些抗体不具备高度特异性:如CD34和CD133在造血干细胞表面存在[91],血管内皮生长因子2在巨噬细胞表面表达[92]。以最经典的内皮祖细胞捕获支架CD34抗体表面包被支架为例,其捕获到的CD34+细胞不仅可以分化为内皮细胞,还可以分化为平滑肌细胞,存在着促内膜增生的风险[93]。因而也逐渐诞生了了联合使用多种表面标志物的设计方式,如CHEN等[94]通过CD34抗体联合VE-钙黏蛋白抗体设计出具有抗血小板黏附、晚期内皮祖细胞特异性捕获等功能的支架。未来通过联合使用多种抗体或其他生物分子有助于减少炎症、内膜增生等由非特异性结合引发的风险。
捕获内皮祖细胞还有许多方式,包括利用特殊的糖、肽/蛋白质或核酸序列以实现内皮祖细胞与支架表面的特异性结合。其中研究最多的为精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸三肽序列(RGD),研究表明环状RGD与受体的亲和力优于线状RGD[95],但RGD会与血小板相互识别结合而导致血栓形成风险增加[96],最近HAO等[97]通过OBOC高通量组合筛选技术筛选出了一种能够特异性结合内皮祖细胞/内皮细胞但不与血小板黏附的配体LXW7,他们使用聚乙二醇接头将内皮祖细胞特异性结合配体LXW7接枝在支架表面,实现内源性内皮祖细胞尤其是晚期内皮祖细胞捕获的同时能够防止血小板黏附[98],不仅促进了再内皮化,还降低了血栓形成和内膜增生的风险,为解决非特异性结合问题提供了很好的思路,这提示即便没有寻找到天然的特异性抗体,也可以通过高通量筛选等方法,从抗原表面的特定结构域着手人工合成特异性结合配体。此外,REDV[99]、TPS[100]、YIGSR等也是研究较多的几类肽[101],层粘连蛋白、胶原[102]、适配体等也是用于实现捕获的有效分子[103]。
(3)增殖与分化:细胞因子/生长因子如血管内皮生长因子、粒细胞集落刺激因子、基质细胞衍生因子1、促红细胞生成素等,这些因子能够促进内皮祖细胞的增殖和分化[27],可以作为联合使用的辅助因子与材料结合用于诱导内皮祖细胞捕获后的增殖与分化,但应用时需要注意,一些因子可能会导致内膜增生。一氧化氮也影响着内皮细胞分化,它不仅兼具着抗血栓的功能还能够抑制内皮祖细胞向平滑肌细胞分化而减少内膜增生。目前实现支架表面稳定递送一氧化氮的方式包括创建催化位点,使内源性内皮一氧化氮前体(S-亚硝基硫醇)与之反应,产生以及利用一氧化氮供体如将S-亚硝基-N-乙酰青霉胺(SNAP)和S-亚硝基谷氨酰谷胱甘肽(GSNO)实现一氧化氮缓释[104-105]。但需要注意的是一氧化氮的疗效具有剂量依赖性,研究发现适当浓度范围内(100 nmol/L-10 μmol/L)的一氧化氮可以抑制干细胞向血管平滑肌细胞分化,但较高的一氧化氮水平(> 1 mmol/L)会产生促成骨分化的作用,从而增加血管钙化的风险[106],因此在设计一氧化氮缓释表面时应注意测定释放速率与释放量以避免不良反应的发生。
研究发现多种他汀类药物如匹伐他汀、阿托伐他汀、辛伐他汀等可以促进内皮祖细胞增殖,这类药物能够维持早期内皮祖细胞的活力并延缓晚期内皮祖细胞衰老的发生,这有助于改善具有糖尿病等基础疾病患者的内皮祖细胞活性,延长内皮祖细胞在这些患者中的治疗有效时长[107],这些他汀类药物可以通过改装成为载药纳米颗粒装配到支架表面[108],在内皮祖细胞归巢后促进其增殖并发挥功能保护作用。
除了从内皮祖细胞的募集、捕获、增殖、分化等方面考虑支架表面改性,维持内皮祖细胞活性,防止其损伤/凋亡亦是一个重要的设计点,有研究发现半夏(Pinellia ternata)能够通过PI3K/AKT信号通路增强内皮祖细胞的活性并减少内膜增生[109];褪黑素可以通过减轻氧化应激保护内皮祖细胞,保证其功能完整性[110]。
基于内皮祖细胞的血管支架表面设计方式汇总见表3。

2.3.2 基于间充质干细胞的血管支架表面设计 基于间充质干细胞的血管支架设计发展历程见图4。截至目前基于间充质干细胞的血管支架设计研究较少,现有基于间充质干细胞的支架设计主要是通过形成纳米表面以实现间充质干细胞的非特异性黏附,从而发挥抗炎、血管重塑作用,如YANG等[111]采用静电纺丝技术将聚氨酯和纤维蛋白混合制备的聚氨酯/纤维蛋白血管支架能够促进间充质干细胞的黏附和增殖。早期研究主要通过细胞涂覆或浸渍形成功能支架,2011年有研究将间充质干细胞接种在316L SS支架的蛋白涂层上,表现出促进内皮化、抑制内膜增生的能力[112],2015年HWANG等[113]使用静电纺丝技术构建了间充质干细胞浸渍的纳米纤维支架套管,这些研究初步证明了将间充质干细胞纳入血管支架表面改性设计方案具有一定价值,但并没有讨论这类支架应用时血栓形成等不良反应。随着研究的不断推进,解决间充质干细胞促凝问题的方案也逐渐被提出,研究表明联合使用肝素抗凝治疗能够有效减少急性血栓形成[114],且肝素还具有促间充质干细胞增殖的能力[115]。最近JOSHI等[116]将脂肪来源间充质干细胞与内皮细胞共同接种在肝素化的聚己内酯/明胶共纺纳米纤维上,改善血栓问题的同时实现了快速内皮化;RANGASAMI等[117]通过层层自组装将间充质干细胞涂覆在明胶和肝素形成的聚合物表面,保留间充质干细胞旁分泌功能的同时减少了血栓形成。
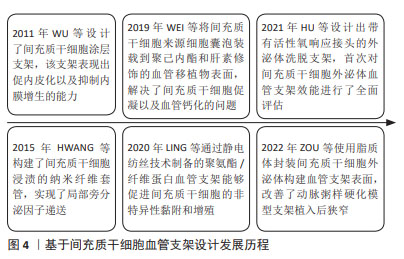
基于间充质干细胞来源细胞外囊泡的血管支架设计是近年来研究较多的内容:2019年WEI等[118]将间充质干细胞衍生的细胞外囊泡装载到聚己内酯和肝素功能化的血管移植物上,发挥间充质干细胞免疫调节功能的同时减少了血栓形成与血管钙化等不良反应,紧接着2021年HU等[119]设计出一种带有活性氧响应接头的外泌体洗脱支架,首次对间充质干细胞外泌体支架的效能进行了全面评价,发现间充质干细胞外泌体洗脱支架不仅能够加速内皮化、减少平滑肌细胞迁移、降低炎症水平,还有助于支架远端缺血以及再灌注损伤组织修复;2022年ZOU等[120]使用对磷脂酶A2具有响应能力的脂质体封装间充质干细胞外泌体构建了生物涂层支架,该支架能够调节低密度脂蛋白刺激的平滑肌细胞以及内皮细胞,通过抑制平滑肌细胞增殖、降低巨噬细胞炎症因子表达等改善动脉粥样硬化条件下的支架植入后狭窄。
此外研究还发现间充质干细胞和内皮祖细胞共培养有助于促进间充质干细胞向内皮细胞分化[121],作者推测设计内皮祖细胞/间充质干细胞两种抗体的支架表面也许在实现修复功能多元化的同时能够一定程度避免间充质干细胞引发的不良反应。CD146是晚期内皮祖细胞和间充质干细胞的共同标志物,一项表面设计研究发现修饰CD146抗体的纳米结构支架具有同时捕获8倍以上内皮祖细胞和3倍以上间充质干细胞的能力,该支架表现出了良好的再内皮化、减少支架内狭窄的能力[122],这一研究也为未来设计同时能够靶向内皮祖细胞和间充质干细胞支架表面提供了有价值的参考。在单纯基于间充质干细胞的血管支架设计时加入肝素、设计能够共捕获内皮祖细胞和间充质干细胞的血管支架以及外泌体洗脱支架是未来研究深入拓展的基础。
| [1] VISHWAKARMA A, SHARPE P, SHI ST, et al. Stem Cell Biology and Tissue Engineering in Dental Sciences. Boston: Academic Press. 2015:1-13. [2] BRIGNIER AC, GEWIRTZ AM. Embryonic and adult stem cell therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;125(2 Suppl 2):S336-344. [3] ROBERTSON JA. Embryo stem cell research: ten years of controversy. J Law Med Ethics. 2010;38(2):191-203. [4] 曹雪洁,陶佳平,曲爱娟,等.血管壁干细胞与血管重塑相关性疾病[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2022,30(11):921-929. [5] BIANCONI V, SAHEBKAR A, KOVANEN P, et al. Endothelial and cardiac progenitor cells for cardiovascular repair: A controversial paradigm in cell therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 2018;181:156-168. [6] SUN LL, LIU Z, RAN F, et al. Non-coding RNAs regulating endothelial progenitor cells for venous thrombosis: promising therapy and innovation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024;15(1):7. [7] WILS J, FAVRE J, BELLIEN J. Modulating putative endothelial progenitor cells for the treatment of endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular complications in diabetes. Pharmacol Ther. 2017;170:98-115. [8] HICKSON LJ, EIRIN A, LERMAN LO. Challenges and opportunities for stem cell therapy in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2016;89(4):767-778. [9] BARQUERA S, PEDROZA-TOBÍAS A, MEDINA C, et al. Global Overview of the Epidemiology of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Arch Med Res. 2015;46(5):328-338. [10] PETRIE JR, GUZIK TJ, TOUYZ RM. Diabetes, Hypertension, and Cardiovascular Disease: Clinical Insights and Vascular Mechanisms. Can J Cardiol. 2018;34(5):575-584. [11] BOBRYSHEV YV, OREKHOV AN, CHISTIAKOV DA. Vascular stem/progenitor cells: current status of the problem. Cell Tissue Res. 2015;362(1):1-7. [12] WANG X, WANG R, JIANG L, et al. Endothelial repair by stem and progenitor cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022;163:133-146. [13] CHENG CC, CHANG SJ, CHUEH YN, et al. Distinct angiogenesis roles and surface markers of early and late endothelial progenitor cells revealed by functional group analyses. BMC Genomics. 2013;14:182. [14] YAN F, LIU X, DING H, et al. Paracrine mechanisms of endothelial progenitor cells in vascular repair. Acta Histochem. 2022;124(1): 151833. [15] MEDINA RJ, BARBER CL, SABATIER F, et al. Endothelial Progenitors: A Consensus Statement on Nomenclature. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(5):1316-1320. [16] AFRA S, MATIN MM. Potential of mesenchymal stem cells for bioengineered blood vessels in comparison with other eligible cell sources. Cell Tissue Res. 2020;380(1):1-13. [17] IKHAPOH I. Regulatory Mechanisms Underlying the Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Endothelial Cells. Creighton University. 2016. [18] WANG C, LI Y, YANG M, et al. Efficient Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Endothelial Cells in Vitro. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2018;55(2):257-265. [19] ZITTERMANN SI, ISSEKUTZ AC. Endothelial growth factors VEGF and bFGF differentially enhance monocyte and neutrophil recruitment to inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 2006;80(2):247-257. [20] LIU Y, CHEN J, LIANG H, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells not only ameliorate blood glucose but also protect vascular endothelium from diabetic damage through a paracrine mechanism mediated by MAPK/ERK signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):258. [21] BAI S, YIN Q, DONG T, et al. Endothelial progenitor cell-derived exosomes ameliorate endothelial dysfunction in a mouse model of diabetes. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110756. [22] LI L, WANG H, ZHANG J, et al. Effect of endothelial progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles on endothelial cell ferroptosis and atherosclerotic vascular endothelial injury. Cell Death Discov. 2021; 7(1):235. [23] MATHIYALAGAN P, LIANG Y, KIM D, et al. Angiogenic Mechanisms of Human CD34+ Stem Cell Exosomes in the Repair of Ischemic Hindlimb. Circ Res. 2017;120(9):1466-1476. [24] XIAO X, XU M, YU H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles mitigate oxidative stress-induced senescence in endothelial cells via regulation of miR-146a/Src. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):354. [25] LI Z, XU Y, LU S, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cell extracellular vesicles delivered miR let-7-5p alleviate endothelial glycocalyx degradation and leakage via targeting ABL2. Cell Commun Signal. 2023;21(1):205. [26] WANG D, GAO B, YUE J, et al. Exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells expressing miR-125b inhibit neointimal hyperplasia via myosin IE. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(2):1528-1540. [27] GOH ET, WONG E, FARHATNIA Y, et al. Accelerating in situ endothelialisation of cardiovascular bypass grafts. Int J Mol Sci. 2014; 16(1):597-627. [28] SIMONCINI S, TOUPANCE S, LABAT C, et al. Functional Impairment of Endothelial Colony Forming Cells (ECFC) in Patients with Severe Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD). Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(16):8969. [29] BLOOM SI, ISLAM MT, LESNIEWSKI LA, et al. Mechanisms and consequences of endothelial cell senescence. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2023; 20(1):38-51. [30] MUNDI S, MASSARO M, SCODITTI E, et al. Endothelial permeability, LDL deposition, and cardiovascular risk factors-a review. Cardiovasc Res. 2018;114(1):35-52. [31] BARRETT TJ, SCHLEGEL M, ZHOU F, et al. Platelet regulation of myeloid suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 accelerates atherosclerosis. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11(517):eaax0481. [32] LIBBY P. The changing landscape of atherosclerosis. Nature. 2021; 592(7855):524-533. [33] JEBARI-BENSLAIMAN S, GALICIA-GARCÍA U, LARREA-SEBAL A, et al. Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(6):3346. [34] EVANS CE, IRUELA-ARISPE ML, ZHAO YY. Mechanisms of Endothelial Regeneration and Vascular Repair and Their Application to Regenerative Medicine. Am J Pathol. 2021;191(1):52-65. [35] NAITO T, SHUN M, NISHIMURA H, et al. Pleiotropic effect of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents on circulating endothelial progenitor cells in dialysis patients. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2021;25(10):1111-1120. [36] YUAN Z, KANG L, WANG Z, et al. 17β-estradiol promotes recovery after myocardial infarction by enhancing homing and angiogenic capacity of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells through ERα-SDF-1/CXCR4 crosstalking. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2018; 50(12):1247-1256. [37] WEI H, TAN T, CHENG L, et al. MRI tracing of ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle‑labeled endothelial progenitor cells for repairing atherosclerotic vessels in rabbits. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(4):3327-3337. [38] ALTABAS V, BILOŠ LSK. The Role of Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Atherosclerosis and Impact of Anti-Lipemic Treatments on Endothelial Repair. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(5):2663. [39] KE X, LIAO Z, LUO X, et al. Endothelial colony-forming cell-derived exosomal miR-21-5p regulates autophagic flux to promote vascular endothelial repair by inhibiting SIPL1A2 in atherosclerosis. Cell Commun Signal. 2022;20(1):30. [40] MAUSE SF, RITZEL E, DECK A, et al. Engagement of the CXCL12-CXCR4 Axis in the Interaction of Endothelial Progenitor Cell and Smooth Muscle Cell to Promote Phenotype Control and Guard Vascular Homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(2):867. [41] MA Y, GU T, HE S, et al. Development of stem cell therapy for atherosclerosis. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04762-8. [42] ZHANG X, REN Z, JIANG Z. EndMT-derived mesenchymal stem cells: a new therapeutic target to atherosclerosis treatment. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023;478(4):755-765. [43] MA J, CHEN L, ZHU X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-21a-5p promotes M2 macrophage polarization and reduces macrophage infiltration to attenuate atherosclerosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021;53(9):1227-1236. [44] LI J, XUE H, LI T, et al. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells attenuate the progression of atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice via miR-let7 mediated infiltration and polarization of M2 macrophage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;510(4):565-572. [45] YANG W, YIN R, ZHU X, et al. Mesenchymal stem-cell-derived exosomal miR-145 inhibits atherosclerosis by targeting JAM-A. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;23:119-131. [46] ZHANG N, LUO Y, ZHANG H, et al. Exosomes Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorate the Progression of Atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- Mice via FENDRR. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2022;22(6):528-544. [47] 刘小春,吴素慧,王文珍,等.人脐带和脂肪来源间充质干细胞培养上清对内皮细胞血管新生作用[J].中华医学杂志,2020,100(6): 456-459. [48] LI Y, SHI G, LIANG W, et al. Allogeneic Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation Alleviates Atherosclerotic Plaque by Inhibiting Ox-LDL Uptake, Inflammatory Reaction and Endothelial Damage in Rabbits. Cells. 2023;12(15):1936. [49] LI Z, YANG A, YIN X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells promote endothelial progenitor cell migration, vascularization, and bone repair in tissue-engineered constructs via activating CXCR2-Src-PKL/Vav2-Rac1. FASEB J. 2018;32(4):2197-2211. [50] LEE J, HENDERSON K, MASSIDDA MW, et al. Mechanobiological conditioning of mesenchymal stem cells for enhanced vascular regeneration. Nat Biomed Eng. 2021;5(1):89-102. [51] FAN M, BAI J, DING T, et al. Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Transplantation Inhibits Vascular Inflammatory Responses and Endothelial Dysfunction in Rats with Atherosclerosis. Yonsei Med J. 2019;60(11):1036-1044. [52] 刘峰涛,于紫英.血管平滑肌细胞与动脉粥样硬化斑块稳定性的研究进展[J].中国心血管杂志,2021,26(3):299-302. [53] BYRNE RA, JONER M, KASTRATI A. Stent thrombosis and restenosis: what have we learned and where are we going? The Andreas Grüntzig Lecture ESC 2014. Eur Heart J. 2015;36(47):3320-3331. [54] WU B, MOTTOLA G, SCHALLER M, et al. Resolution of vascular injury: Specialized lipid mediators and their evolving therapeutic implications. Mol Aspects Med. 2017;58:72-82. [55] MELNIK T, JORDAN O, CORPATAUX JM, et al. Pharmacological prevention of intimal hyperplasia: A state-of-the-art review. Pharmacol Ther. 2022;235:108157. [56] ABOU-SALEH H, HACHEM A, YACOUB D, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells inhibit platelet function in a P-selectin-dependent manner. J Transl Med. 2015;13:142. [57] ABOU-SALEH H, YACOUB D, THÉORÊT JF, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells bind and inhibit platelet function and thrombus formation. Circulation. 2009;120(22):2230-2239. [58] LI WD, LI XQ. Endothelial progenitor cells accelerate the resolution of deep vein thrombosis. Vascul Pharmacol. 2016;83:10-16. [59] MOLDOVAN NI, ASAHARA T. Role of blood mononuclear cells in recanalization and vascularization of thrombi: past, present, and future. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2003;13(7):265-269. [60] CARNEIRO GD, SIELSKI MS, VIEIRA CP, et al. Administration of endothelial progenitor cells accelerates the resolution of arterial thrombus in mice. Cytotherapy. 2019;21(4):444-459. [61] FENG Y, LEI B, ZHANG H, et al. MicroRNA-136-5p from Endothelial Progenitor Cells-released Extracellular Vesicles Mediates TXNIP to Promote the Dissolution of Deep Venous Thrombosis. Shock. 2022; 57(5):714-721. [62] WU X, JIANG J, GU Z, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell therapies: immunomodulatory properties and clinical progress. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 ;11(1):345. [63] GUILLAMAT-PRATS R. Role of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells in Coagulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(18):10393. [64] NETSCH P, ELVERS-HORNUNG S, UHLIG S, et al. Human mesenchymal stromal cells inhibit platelet activation and aggregation involving CD73-converted adenosine. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):184. [65] YANG B, LONG Y, ZHANG A, et al. Procoagulant Properties of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Extracellular Vesicles: A Novel Aspect of Thrombosis Pathogenesis. Stem Cells. 2024;42(2):98-106. [66] COPPIN L, SOKAL E, STÉPHENNE X. Thrombogenic Risk Induced by Intravascular Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Cells. 2019;8(10):1160. [67] SUN H, MORIHARA R, FENG T, et al. Human Cord Blood-Endothelial Progenitor Cells Alleviate Intimal Hyperplasia of Arterial Damage in a Rat Stroke Model. Cell Transplant. 2023;32:9636897231193069. [68] WANG W, ZHANG Y, HUI H, et al. The effect of endothelial progenitor cell transplantation on neointimal hyperplasia and reendothelialisation after balloon catheter injury in rat carotid arteries. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):99. [69] XU RW, ZHANG WJ, ZHANG JB, et al. A Preliminary Study of the Therapeutic Role of Human Early Fetal Aorta-derived Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Inhibiting Carotid Artery Neointimal Hyperplasia. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;128(24):3357-3362. [70] CHEN K, LI Y, XU L, et al. Comprehensive insight into endothelial progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles as a promising candidate for disease treatment. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):238. [71] SHOJI M, OSKOWITZ A, MALONE CD, et al. Human mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) reduce neointimal hyperplasia in a mouse model of flow-restriction by transient suppression of anti-inflammatory cytokines. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2011;18(6):464-474. [72] KIM AK, KIM MH, KIM DH, et al. Inhibitory effects of mesenchymal stem cells in intimal hyperplasia after balloon angioplasty. J Vasc Surg. 2016;63(2):510-517. [73] ISO Y, USUI S, TOYODA M, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and neointimal hyperplasia after arterial injury in rats. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2018;16:79-87. [74] CAI C, KILARI S, ZHAO C, et al. Therapeutic Effect of Adipose Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation in Reducing Restenosis in a Murine Angioplasty Model. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020;31(8):1781-1795. [75] HADE MD, SUIRE CN, SUO Z. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: Applications in Regenerative Medicine. Cells. 2021;10(8):1959. [76] LIU Z, WU C, ZOU X, et al. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells inhibit neointimal hyperplasia by activating the Erk1/2 signalling pathway in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):220. [77] DENG Y, LI Y, CHU Z, et al. Exosomes from umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells combined with gelatin methacryloyl inhibit vein graft restenosis by enhancing endothelial functions. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):380. [78] CHENG G, WANG X, LI Y, et al. Let-7a-transfected mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension by suppressing pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell growth through STAT3-BMPR2 signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):34. [79] 刘指挥.间充质干细胞外泌体对血管损伤后新生内膜形成的影响与机制研究[D].重庆:西南大学,2020. [80] 郑仕杰,周敬群,杨维华,等.血管损伤后TGF-β1/Smad信号通路在诱导BMSCs分化参与血管再狭窄的相关性研究[J].中国医药科学,2019,9(17):50-54. [81] ZENG W, WEN C, WU Y, et al. The use of BDNF to enhance the patency rate of small-diameter tissue-engineered blood vessels through stem cell homing mechanisms. Biomaterials. 2012;33(2):473-484. [82] ZHUANG Y, ZHANG C, CHENG M, et al. Challenges and strategies for in situ endothelialization and long-term lumen patency of vascular grafts. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(6):1791-1809. [83] CHEN Y, CAO J, PENG W, et al. Neurotrophin-3 accelerates reendothelialization through inducing EPC mobilization and homing. Open Life Sci. 2020;15(1):241-250. [84] LIU P, ZHOU B, GU D, et al. Endothelial progenitor cell therapy in atherosclerosis: a double-edged sword? Ageing Res Rev. 2009 ;8(2):83-93. [85] HU A, SHUAI Z, LIU J, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 prevents vascular intimal hyperplasia involved by SDF-1α/CXCR4, SCF/c-kit and FKN/CX3CR1 axes in a rat balloon injury. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;260:113046. [86] LEE CH, LIU KS, ROTH JG, et al. Telmisartan Loaded Nanofibers Enhance Re-Endothelialization and Inhibit Neointimal Hyperplasia. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(11):1756. [87] FUKAWA N, UEDA T, OGOSHI T, et al. Vascular Endothelial Repair and the Influence of Circulating Antiplatelet Drugs in a Carotid Coil Model. J Cent Nerv Syst Dis. 2021;13:11795735211011786. [88] XU S, HU A, CHEN J, et al. The role of calcium-sensing receptor in ginsenoside Rg1 promoting reendothelialization to inhibit intimal hyperplasia after balloon injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;163:114843. [89] SALYBEKOV AA, KOBAYASHI S, ASAHARA T. Characterization of Endothelial Progenitor Cell: Past, Present, and Future. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(14):7697. [90] XIAO ST, KUANG CY. Endothelial progenitor cells and coronary artery disease: Current concepts and future research directions. World J Clin Cases. 2021;9(30):8953-8966. [91] CHRISTOPHER AC, VENKATESAN V, KARUPPUSAMY KV, et al. Preferential Expansion of Human CD34+CD133+CD90+ Hematopoietic Stem Cells Enhances Gene-Modified Cell Frequency for Gene Therapy. Hum Gene Ther. 2022;33(3-4):188-201. [92] LAI YS, WAHYUNINGTYAS R, AUI SP, et al. Autocrine VEGF signalling on M2 macrophages regulates PD-L1 expression for immunomodulation of T cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(2):1257-1267. [93] ROTMANS JI, HEYLIGERS JM, VERHAGEN HJ, et al. In vivo cell seeding with anti-CD34 antibodies successfully accelerates endothelialization but stimulates intimal hyperplasia in porcine arteriovenous expanded polytetrafluoroethylene grafts. Circulation. 2005;112(1):12-18. [94] CHEN H, WANG X, ZHOU Q, et al. Preparation of Vascular Endothelial Cadherin Loaded-Amphoteric Copolymer Decorated Coronary Stents for Anticoagulation and Endothelialization. Langmuir. 2017;33(46): 13430-13437. [95] KÄMMERER PW, HELLER M, BRIEGER J, et al. Immobilisation of linear and cyclic RGD-peptides on titanium surfaces and their impact on endothelial cell adhesion and proliferation. Eur Cell Mater. 2011;21: 364-372. [96] SÁNCHEZ-CORTÉS J, MRKSICH M. The platelet integrin alphaIIbbeta3 binds to the RGD and AGD motifs in fibrinogen. Chem Biol. 2009;16(9): 990-1000. [97] HAO D, LIN J, LIU R, et al. A bio-instructive parylene-based conformal coating suppresses thrombosis and intimal hyperplasia of implantable vascular devices. Bioact Mater. 2023;28:467-479. [98] HAO D, XIAO W, LIU R, et al. Discovery and Characterization of a Potent and Specific Peptide Ligand Targeting Endothelial Progenitor Cells and Endothelial Cells for Tissue Regeneration. ACS Chem Biol. 2017;12(4):1075-1086. [99] DUAN Y, YU S, XU P, et al. Co-immobilization of CD133 antibodies, vascular endothelial growth factors, and REDV peptide promotes capture, proliferation, and differentiation of endothelial progenitor cells. Acta Biomater. 2019;96:137-148. [100] YANG Z, ZHAO X, HAO R, et al. Bioclickable and mussel adhesive peptide mimics for engineering vascular stent surfaces. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(28):16127-16137. [101] LEE JS, LEE K, MOON SH, et al. Mussel-inspired cell-adhesion peptide modification for enhanced endothelialization of decellularized blood vessels. Macromol Biosci. 2014;14(8):1181-1189. [102] II M, TAKESHITA K, IBUSUKI K, et al. Notch signaling regulates endothelial progenitor cell activity during recovery from arterial injury in hypercholesterolemic mice. Circulation. 2010;121(9):1104-1112. [103] CHEN W, ZENG W, SUN J, et al. Construction of an Aptamer-SiRNA Chimera-Modified Tissue-Engineered Blood Vessel for Cell-Type-Specific Capture and Delivery. ACS Nano. 2015;9(6):6069-6076. [104] LI L, CAO Z, ZHANG C, et al. A Versatile Passivated Protein-Adsorption Platform for Rapid Healing of Vascular Stents by Modulating the Microenvironment. Adv Funct Mater. 2024;34:2312243. [105] DE MEL A, NAGHAVI N, COUSINS BG, et al. Nitric oxide-eluting nanocomposite for cardiovascular implants. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25(3):917-929. [106] WANG F, QIN K, WANG K, et al. Nitric oxide improves regeneration and prevents calcification in bio-hybrid vascular grafts via regulation of vascular stem/progenitor cells. Cell Rep. 2022;39(12):110981. [107] ANTÓNIO N, SOARES A, FERNANDES R, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells in diabetic patients with myocardial infarction - can statins improve their function? Eur J Pharmacol. 2014;741:25-36. [108] LIU H, BAO P, LI L, et al. Pitavastatin nanoparticle-engineered endothelial progenitor cells repair injured vessels. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1): 18067. [109] LU HK, HUANG Y, LIANG XY, et al. Pinellia ternata attenuates carotid artery intimal hyperplasia and increases endothelial progenitor cell activity via the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway in wire-injured rats. Pharm Biol. 2020;58(1):1184-1191. [110] LEE FY, SUN CK, SUNG PH, et al. Daily melatonin protects the endothelial lineage and functional integrity against the aging process, oxidative stress, and toxic environment and restores blood flow in critical limb ischemia area in mice. J Pineal Res. 2018;65(2):e12489. [111] YANG L, LI X, WU Y, et al. Preparation of PU/Fibrin Vascular Scaffold with Good Biomechanical Properties and Evaluation of Its Performance in vitro and in vivo. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:8697-8715. [112] WU X, WANG G, TANG C, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell seeding promotes reendothelialization of the endovascular stent. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2011;98(3):442-449. [113] HWANG CW, JOHNSTON PV, GERSTENBLITH G, et al. Stem cell impregnated nanofiber stent sleeve for on-stent production and intravascular delivery of paracrine factors. Biomaterials. 2015;52: 318-326. [114] LIAO L, SHI B, CHANG H, et al. Heparin improves BMSC cell therapy: Anticoagulant treatment by heparin improves the safety and therapeutic effect of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell cytotherapy. Theranostics. 2017;7(1):106-116. [115] LING L, CAMILLERI ET, HELLEDIE T, et al. Effect of heparin on the biological properties and molecular signature of human mesenchymal stem cells. Gene. 2016;576(1 Pt 2):292-303. [116] JOSHI A, XU Z, IKEGAMI Y, et al. Co-culture of mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells on heparinized polycaprolactone/gelatin co-spun nanofibers for improved endothelium remodeling. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;151:186-192. [117] RANGASAMI VK, ASAWA K, TERAMURA Y, et al. Biomimetic polyelectrolyte coating of stem cells suppresses thrombotic activation and enhances its survival and function. Biomater Adv. 2023;147: 213331. [118] WEI Y, WU Y, ZHAO R, et al. MSC-derived sEVs enhance patency and inhibit calcification of synthetic vascular grafts by immunomodulation in a rat model of hyperlipidemia. Biomaterials. 2019;204:13-24. [119] HU S, LI Z, SHEN D, et al. Exosome-eluting stents for vascular healing after ischaemic injury. Nat Biomed Eng. 2021;5(10):1174-1188. [120] ZOU D, YANG P, LIU J, et al. Exosome-Loaded Pro-efferocytic Vascular Stent with Lp-PLA2-Triggered Release for Preventing In-Stent Restenosis. ACS Nano. 2022;16(9):14925-14941. [121] PARK KS, KANG SN, KIM DH, et al. Late endothelial progenitor cell-capture stents with CD146 antibody and nanostructure reduce in-stent restenosis and thrombosis. Acta Biomater. 2020;111:91-101. [122] WANG CH, CHERNG WJ, YANG NI, et al. Late-outgrowth endothelial cells attenuate intimal hyperplasia contributed by mesenchymal stem cells after vascular injury. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008;28(1):54-60. [123] THANASKODY K, JUSOP AS, TYE GJ, et al. MSCs vs. iPSCs: Potential in therapeutic applications. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:1005926. [124] GAO A, HANG R, LI W, et al. Linker-free covalent immobilization of heparin, SDF-1α, and CD47 on PTFE surface for antithrombogenicity, endothelialization and anti-inflammation. Biomaterials. 2017;140: 201-211. [125] PELLICCIA F, ZIMARINO M, DE LUCA G, et al. Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Coronary Artery Disease: From Bench to Bedside. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2022;11(5):451-460. [126] XIANG Q, TIAN F, XU J, et al. New insight into dyslipidemia-induced cellular senescence in atherosclerosis. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2022; 97(5):1844-1867. [127] BASMAEIL YS, BAHATTAB E, ALSHABIBI MA, et al. Human Decidua Basalis mesenchymal stem/stromal cells reverse the damaging effects of high level of glucose on endothelial cells in vitro. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(4):1838-1850. |
| [1] | 张艺博, 卢健棋, 毛美玲, 庞 延, 董 礼, 杨尚冰, 肖 湘. 类风湿关节炎与冠状动脉粥样硬化的因果关系:GWAS数据库血清代谢物和炎症因子数据[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | 杨治航, 孙祖延, 黄文良, 万 喻, 陈仕达, 邓 江. 神经生长因子促进兔骨髓间充质干细胞软骨分化并抑制肥大分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [3] | 胡涛涛, 刘 兵, 陈 诚, 殷宗银, 阚道洪, 倪 杰, 叶凌霄, 郑祥兵, 严 敏, 邹 勇. 过表达神经调节蛋白1的人羊膜间充质干细胞促进小鼠皮肤创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1343-1349. |
| [4] | 金 凯, 唐 婷, 李美乐, 谢裕安. 人脐带间充质干细胞条件培养基及外泌体对肝癌细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭和凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [5] | 李帝均, 酒精卫, 刘海峰, 闫 磊, 李松岩, 王 斌. 明胶三维微球装载人脐带间充质干细胞修复慢性肌腱病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1356-1362. |
| [6] | 刘 琪, 李林臻, 李玉生, 焦泓焯, 杨 程, 张君涛. 淫羊藿苷含药血清促进3种细胞共培养体系中软骨细胞增殖和干细胞成软骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [7] | 章镇宇, 梁秋健, 杨 军, 韦相宇, 蒋 捷, 黄林科, 谭 桢. 新橙皮苷治疗骨质疏松症的靶点及对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [8] | 李佳林, 张耀东, 娄艳茹, 于 洋, 杨 蕊. 间充质干细胞分泌组发挥作用的分子机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1512-1522. |
| [9] | 何 波, 陈 文, 马岁录, 何志军, 宋 渊, 李金鹏, 刘 涛, 魏晓涛, 王威威, 谢 婧. 皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的发病机制及治疗进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [10] | 高 洋, 秦合伟, 刘丹丹. ACSL4介导铁死亡及在动脉粥样硬化性心血管病中的潜在作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1239-1247. |
| [11] | 孙现娟, 王秋花, 张锦艺, 杨杨杨, 王文双, 张晓晴. 不同静电纺丝膜上骨髓间充质干细胞的黏附、增殖与成血管平滑肌分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(4): 661-669. |
| [12] | 郑伊桐, 汪永新, 刘 文, 阿木吉特, 秦 虎. 神经内镜下人脐带间充质干细胞外泌体鞘内移植修复脊髓损伤的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(36): 7743-7751. |
| [13] | 郭 昭, 庄浩岩, 史学文. 间充质干细胞衍生外泌体在结直肠癌治疗中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(36): 7872-7879. |
| [14] | 葛 霄, 赵状状, 郭舒瑜, 徐荣耀. HOXA10基因修饰骨髓间充质干细胞促进骨再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(36): 7701-7708. |
| [15] | 张熊劲夫, 陈奕达, 程歆怡, 刘岱珲, 施 勤. 年轻大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体逆转老龄大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞衰老[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(36): 7709-7718. |
动脉粥样硬化是导致全球心血管疾病死亡的主要原因之一[9],动脉粥样硬化斑块导致管腔狭窄或闭塞会影响重要器官的生理功能,严重者可危及生命,临床中常通过支架介入扩张狭窄的管腔以改善组织器官缺血情况。目前血管支架介入治疗中,不论是单纯球囊扩张成形术还是支架植入术均会引起血管内皮损伤,引发一系列并发症如支架植入后内膜增生以及晚期血栓形成,并最终导致远期预后不良。而血管介入治疗对象常伴有高血脂、高血压、高血糖以及慢性肾脏病等基础疾病,它们可致血管内皮处于慢性炎性状态[10],并会加速支架植入后再狭窄的进程。目前具有血管损伤修复作用且被较多应用于血管支架设计的主要是内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞这两类干细胞[4],已有不少研究发现它们在动脉粥样硬化和支架植入损伤中的治疗效能[11]。
此综述主要阐述内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞治疗血管支架相关动脉疾病(动脉粥样硬化、支架植入损伤并发症等问题)以及基于两类成体干细胞的血管支架表面设计研究进展,旨在综合最新的研究观点,总结阐述研究现状并汇集目前研究的前沿问题,为推动成体干细胞治疗血管疾病研究进展以及未来设计基于成体干细胞的血管支架提供研究策略和方向。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人与检索时间 由第一、二、三作者于2023年11月至2024年2月进行计算机文献检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 自各数据库建库以来至2024-02-20前发表的所有文献。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中文数据库包括CNKI、万方数据库;英文数据库包括PubMed、Web of Science数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词:“内皮损伤,支架植入术,血栓,内膜增生,动脉粥样硬化,内皮修复,内皮祖细胞,间充质干细胞,血管支架”;英文检索词:“endothelial injury,stenting,thrombosis,intimal hyperplasia,atherosclerosis,endothelial repair,endothelial regeneration,endothelial progenitor cell,mesenchymal stem cell,vascular stent,vascular scaffold”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究型论文、综述、学位论文。
1.1.6 检索策略 以PubMed数据库为例,具体检索策略见图1。
1.1.7 检索文献量 中文文献5篇,英文文献122篇。
1.2 入选标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①与内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞治疗血管疾病相关度高的文献;②与基于内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞血管支架设计相关度高的文献;③论证严谨、逻辑清楚、数据和观点可信度高的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①内容相关性不高、陈旧、重复的文献;②缺乏详细数据或重要内容的文献;③论证不严谨、可信度低或质量较差的文献。
1.3 文献质量评估与数据提取 首先根据研究的主题和目的进行文献检索和初步分析,确定论述具体要点;其次根据要点进行文献筛选,优先选择来自权威学术期刊或由专业机构发布的文献,以确保文献质量;然后对所选文献选择性地全文粗读或精读,评估其研究设计、方法、样本、数据和分析过程等方面的严谨性,同时关注文献的研究对象、样本量、实验操作等细节,以确定数据的可靠性,对于重复或类似主题的文献观点进行筛选、合并、双重检查和验证,检查数据或观点的一致性和可信度;最后,对最终筛选出的127篇文献的数据、观点进行分析、整理和汇总,其中中文文献5篇(CNKI数据库1篇,万方数据库4篇),英文文献122篇(PubMed数据库106篇,Web of Science数据库16篇)。文献筛选流程见图2。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
在支架植入损伤并发症中,内皮祖细胞与间充质干细胞均能通过促进内皮细胞/内皮祖细胞增殖而加速内皮化进程,从而抑制内膜增生进程,但二者在血栓方面的效能有所差别,内皮祖细胞能够抑制血栓形成并促进血栓再通,而间充质干细胞被认为具有促血栓形成的作用。越来越多的研究探索了血管支架表面改性以实现内皮祖细胞/间充质干细胞局部聚集和调节方面的应用,其中以内皮祖细胞研究居多,主要是通过募集、捕获、增殖分化以及活性等方面设计支架表面,其中研究最多的是内皮祖细胞捕获支架,由于内皮祖细胞表面标志物的非特异性,单一的标志物抗体很可能会造成一系列不良反应如内膜增生或炎症反应,联合使用多种抗体或高通量筛选出特异性抗体是目前解决非特异性捕获问题的可行思路。目前血管领域基于间充质干细胞设计的支架研究减少,这一现象可能与间充质干细胞的促血栓反应以及成骨分化作用(促血管钙化)有关,联合使用肝素已被证明能够改善血栓形成,而分离的细胞外囊泡则可以解决血管钙化等问题,通过脂质体封装外泌体或将其接枝在活性氧响应接头可以实现炎症状态下的调控释放。
目前研究存在问题:①间充质干细胞可能导致血管钙化、血栓的发生,且部分研究并未证明间充质干细胞抗内膜增生能力。目前较少有研究分析或解释这些矛盾或问题,多数证明间充质干细胞治疗价值的研究可能遗漏了这方面的问题。间充质干细胞的负面和正向的作用是如何平衡以及间充质干细胞发挥正向作用、避免负面事件发生的条件和机制尚不清楚。②目前基于内皮祖细胞的血管支架设计中存在一些问题,如内皮祖细胞的动员因子基质细胞衍生因子1α虽然能够通过募集内皮祖细胞促进内皮化,但是同样会促进支架植入后内膜增生,内皮祖细胞的表面标记物较多不具有特异性,若使用根据这些动员/捕获分子设计支架表面可能引发一系列预期外的不良反应如炎症等。③间充质干细胞及其分泌的细胞外囊泡具有较高的治疗潜力,且已有一定的相关支架设计理论研究基础,但目前相关的支架表面设计仍然较少。④使用血管支架治疗的患者通常还具有其他一些基础疾病如高血糖、高血压、高血脂等,这些因素很可能是基于成体干细胞设计的血管支架治疗效能显著降低的原因,现研究多考虑如何尽可能的将间充质干细胞或内皮祖细胞从骨髓或循环或血管壁募集到靶部位发挥作用,但常忽略了储量不足或生成不足的问题。
由于静脉注射内皮祖细胞或间充质干细胞治疗血管疾病存在低靶向性、免疫不相容性等问题,因而局部或精准递送治疗型成体干细胞并改善这些不良并发症逐渐成为研究热点。对支架进行表面改性以实现内皮祖细胞或间充质干细胞的局部聚集发挥治疗作用已逐渐成为研究者们治疗血管疾病聚焦的一个话题,目前基于内皮祖细胞的血管支架设计的主要原理是对接受治疗者内源性内皮祖细胞募集、捕获以实现局部功能的发挥,因而其不良反应通常较少,但接受治疗者血液循环异常状态往往会导致内皮祖细胞功能活性下降;目前血管领域基于间充质干细胞的血管支架特异性捕获设计较少,将间充质干细胞接种在血管支架上而移植到体内是目前较多研究证实的一种可行方案,但这一策略可能伴随有补体激活、血栓形成、血管钙化等问题,虽然已有多个研究报道了间充质干细胞的低免疫原性和致瘤性[123],但这种同种异体移植还是在一定程度上会导致免疫不相容和肿瘤风险增加,与内皮祖细胞一样,接受治疗者的血液异常状态同样会影响间充质干细胞的表达和功能,解决这些问题的可行的方式包括使用细胞外囊泡,在移植前对间充质干细胞的凝血因子表达以及血小板活化情况进行检测[63],联合使用改善血液异常状态或干细胞功能活性的药物等。
3.2 作者综述区别于他篇的特点 该综述首次涵盖了血管支架介入治疗中可能遇到的多种问题,综合阐述了内皮祖细胞与间充质干细胞在常见血管疾病动脉粥样硬化以及支架植入血管损伤等问题中的应用,并总结了基于这两类成体干细胞支架设计的研究现状与前沿问题,为未来研究内皮祖细胞与间充质干细胞治疗血管支架相关疾病提供了参考和研究方向。
3.3 综述局限性 目前应用于血管损伤修复的成体干细胞不仅包括间充质干细胞和内皮祖细胞,此综述仅摘取了目前研究较多、能够相互印证的研究方向加以综合阐述和论证,对于报道较少的研究领域,其价值可能被忽略了。
3.4 展望 未来通过联合使用多种因子、抗体以及其他具有治疗作用的生物活性分子或药物是改良支架表面设计的可行方案,如联合使用肝素、CD47和基质细胞衍生因子1α[124],这有助于实现特异性的募集捕获以及功能的多元化,提高支架治疗效率,降低血管不良反应的发生风险,改善远期预后。对于使用的抗体非特异性等问题,可以使用高通量筛选肽类解决,通过筛选出能够与所需靶细胞特异性结合的肽类或结构是解决因非特异性结合产生的不良反应的有效方法。但应当注意的一点是,使用捕获类支架时应补充说明远期预后情况,以避免短期过度募集而长期产生不足导致的预后不良等问题。研究表明内皮祖细胞的修复活性会因高血压、糖尿病等因素降低[125],高血脂也被证实会促进内皮祖细胞衰老[126],在介入治疗时这些基础疾病不仅会使基于内皮祖细胞设计的支架失去效能,还可能进一步促进动脉粥样硬化的发生发展,因而未来在设计相应的支架时,应注意考虑其背景疾病,如对存在高血脂的患者可以考虑使用他汀类药物,降脂的同时能够实现内皮祖细胞快速募集、增殖和保护。对于糖尿病患者而言,已有研究报道人足月胎盘母体蜕膜基底组织中获得的间充质干细胞能够保护内皮细胞功能免受氧化应激,可以修复糖尿病中葡萄糖诱导的内皮细胞损伤[127],这提示设计时考虑间充质干细胞可能有助于减少由于高血糖持续刺激损伤而导致的不良结局,改善患者的长期预后。这些研究提示设计支架时可以考虑患者的疾病背景,提高治疗效率的同时减轻患者因非指向性治疗而增加的医疗负担。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
文题释义:
血管支架相关疾病:①使用血管支架介入治疗的疾病(文中主要介绍的是动脉粥样硬化);②血管支架植入损伤并发症(血栓、内膜增生)。#br#内皮祖细胞与间充质干细胞治疗血管支架相关疾病:①内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞治疗动脉粥样硬化;②内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞治疗血管支架植入损伤并发症;③基于内皮祖细胞、间充质干细胞的血管支架用于治疗血管疾病。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
内皮祖细胞和间充质干细胞作为两大成体干细胞,通过分化或旁分泌作用在血管疾病治疗中发挥着重要作用。目前较多研究通过注射内皮祖细胞或间充质干细胞来治疗血管疾病如动脉粥样硬化及支架植入损伤并发症,并由此发现了这些干细胞的治疗作用机制。但由于静脉输注成体干细胞存在治疗效率低、靶向性差、不良反应发生率较高等问题,因此成体干细胞逐渐被开发应用于支架表面,近年来的研究表明,基于内皮祖细胞和间充质干细胞的血管支架表现出良好的治疗效果。这种治疗方法可以提高成体干细胞治疗的靶向性,高效作用于损伤部位修复损伤的血管内皮。
#br#
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||