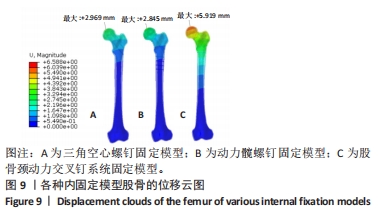
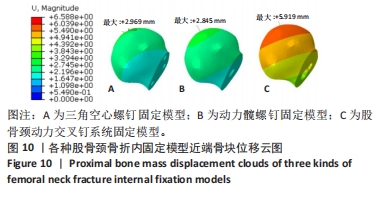
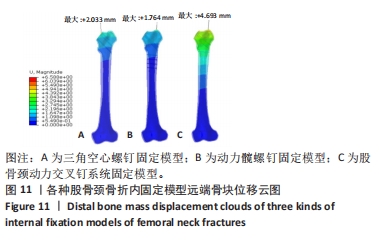
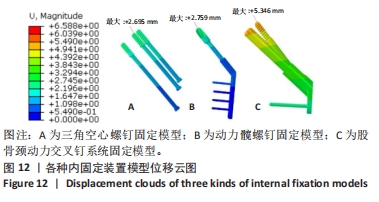
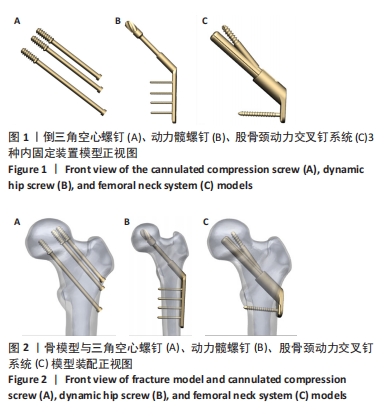
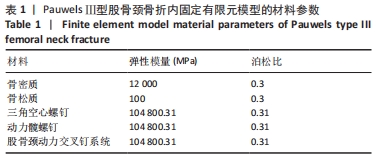
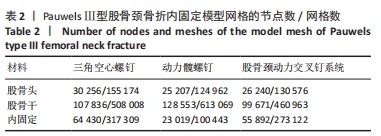
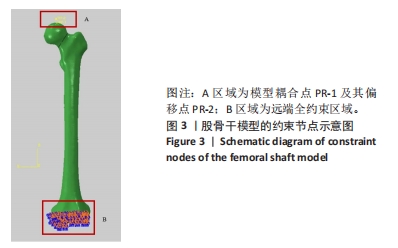
[1] DENNISON E, MOHAMED MA, COOPER C. Epidemiology of Osteoporosis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2006;32(4):617-629.
[2] 张英泽. 临床创伤骨科流行病学[M]. 3版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社,2018: 223-225.
[3] HUANG B, WANG Y, WANG H, et al. Epidemiology and the economic burden of traumatic fractures in China: A population-based study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1104202.
[4] PAUWELS F. Der Schenkelhalsbruch//PAUWELS F. Gesammelte Abhandlungen zur funktionellen Anatomie des Bewegungsapparates. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1965:1-138.
[5] SHEN M, WANG C, CHEN H, et al. An update on the Pauwels classification. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11(1):161.
[6] COLLINGE CA, FINLAY A, RODRIGUEZ-BUITRAGO A, et al. Treatment Failure in Femoral Neck Fractures in Adults Less Than 50 Years of Age: Analysis of 492 Patients Repaired at 26 North American Trauma Centers. J Orthop Trauma. 2022;36(6): 271-279.
[7] 张长青, 张英泽, 余斌, 等. 成人股骨颈骨折诊治指南[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2018,20(11):921-928.
[8] Fixation using Alternative Implants for the Treatment of Hip fractures (FAITH) Investigators. Fracture fixation in the operative management of hip fractures (FAITH): an international, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;389(10078):1519-1527.
[9] QIU L, HUANG Y, LI G, et al. Essential role of reliable reduction quality in internal fixation of femoral neck fractures in the non-elderly patients-a propensity score matching analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):346.
[10] EBERLE S, GERBER C, VON OLDENBURG G, et al. A Biomechanical Evaluation of Orthopaedic Implants for Hip Fractures by Finite Element Analysis andIn-Vitro Tests. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2010;224(10):1141-1152.
[11] CHEN W, TAI C, SHIH C, et al. Selection of fixation devices in proximal femur rotational osteotomy: clinical complications and finite element analysis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2004;19(3):255-262.
[12] DAMANY DS, PARKER MJ, CHOJNOWSKI A. Complications after intracapsular hip fractures in young adults. Injury. 2005;36(1):131-141.
[13] SLOBOGEAN GP, SPRAGUE SA, SCOTT T, et al. Management of young femoral neck fractures: Is there a consensus? Injury. 2015;46(3):435-440.
[14] PANTELI M, RODHAM P, GIANNOUDIS PV. Biomechanical rationale for implant choices in femoral neck fracture fixation in the non-elderly. Injury. 2015;46(3): 445-452.
[15] LIPORACE F, GAINES R, COLLINGE C, et al. Results of Internal Fixation of Pauwels Type-3 Vertical Femoral Neck Fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(8):1654-1659.
[16] GUIMARAES J, ROCHA LR, NORONHA RT, et al. Vertical femoral neck fractures in young adults: a closed fixation strategy using a transverse cancellous lag screw. Injury. 2017;48 Suppl 4:S10-S16.
[17] ZHOU L, LIN J, HUANG A, et al. Modified cannulated screw fixation in the treatment of Pauwels type Ⅲ femoral neck fractures: A biomechanical study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2020;74:103-110.
[18] JOHNSON JP, BORENSTEIN TR, WARYASZ GR, et al. Vertically Oriented Femoral Neck Fractures: A Biomechanical Comparison of 3 Fixation Constructs. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(7):363-368.
[19] FILIPOV O. Biplane double-supported screw fixation (F-technique): a method of screw fixation at osteoporotic fractures of the femoral neck. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2011;21(7):539-543.
[20] FILIPOV O, GUEORGUIEV B. Unique stability of femoral neck fractures treated with the novel biplane double-supported screw fixation method: A biomechanical cadaver study. Injury. 2015;46(2):218-226.
[21] FILIPOV O, STOFFEL K, GUEORGUIEV B, et al. Femoral neck fracture osteosynthesis by the biplane double-supported screw fixation method (BDSF) reduces the risk of fixation failure: clinical outcomes in 207 patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017;137(6):779-788.
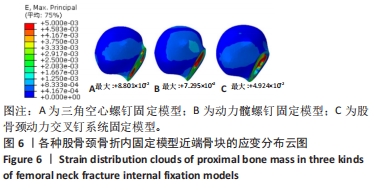
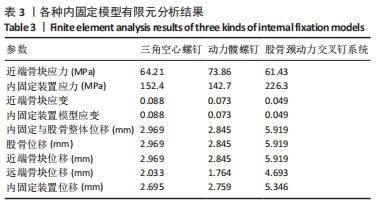
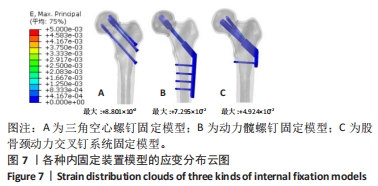
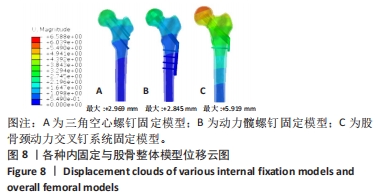
[22] 严坤, 牟利民, 杨晓辉, 等. 三种空心钉构型固定Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(18):2807-2811.
[23] ZHANG LL, ZHANG Y, MA X, et al. Multiple cannulated screws vs. dynamic hip screws for femoral neck fractures. Orthopade. 2017;46(11):954-962.
[24] 王青, 姜达君, 贾伟涛. Pauwels三型股骨颈骨折不同内固定方式的meta分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2018,38(9):1046-1052.
[25] CHA Y, SONG JU, YOO JI, et al. Improved control over implant anchorage under the use of the femoral neck system for fixation of femoral neck fractures: a technical note. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1): 621.
[26] COMPANIES DS. Femoral Neck System | Trauma & Extremities| DePuy Synthes. [2023/07/12]. https://www.jnjmedtech.com/en-US/product/femoral-neck-system.
[27] KARL STOFFEL CS. Femoral Neck System. [2023/07/12]. https://www.aofoundation.org/approved/approvedsolutionsfolder/2017/femoral-neck-system?searchurl=%2Fsearchresults#tab=details.
[28] STOFFEL K, ZDERIC I, GRAS F, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of the Femoral Neck System in Unstable Pauwels Ⅲ Femoral Neck Fractures: A Comparison with the Dynamic Hip Screw and Cannulated Screws. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(3):131-137.
[29] JIANG J, CHEN J, XING F, et al. Comparison of femoral neck system versus cannulated screws for treatment of femoral neck fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):285.
[30] 杨家赵, 周雪锋, 朱万博, 等. FNS与空心螺钉固定治疗青壮年股骨颈骨折的近期疗效比较[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2021,23(9):761-768.
[31] 许翔宇, 周方, 田耘, 等. FNS与DHS固定治疗股骨颈骨折的早期疗效比较[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2021,23(9):754-760.
[32] XIA Y, ZHANG W, HU H, et al. Biomechanical study of two alternative methods for the treatment of vertical femoral neck fractures – A finite element analysis. Comput Meth Prog Bio. 2021;211:106409.
[33] TENG Y, ZHANG Y, GUO C. Finite element analysis of femoral neck system in the treatment of Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(28):e29450.
[34] JUNG CH, CHA Y, YOON HS, et al. Mechanical effects of surgical variations in the femoral neck system on Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture : a finite element analysis. Bone Joint Res. 2022;11(2):102-111.
[35] CHA Y, SONG JU, YOO JI, et al. Improved control over implant anchorage under the use of the femoral neck system for fixation of femoral neck fractures: a technical note. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):621.
[36] 范智荣, 苏海涛, 周霖, 等. 新型股骨颈内固定系统治疗不稳定性股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(15):2321-2328.
[37] 杜兵, 马腾, 路遥, 等. 新型股骨颈内固定系统与3枚空心钉加内侧钢板固定青壮年Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2021,7(6):333-338.
[38] HUANG S, ZHANG Y, ZHANG X, et al. Comparison of femoral neck system and three cannulated cancellous screws in the treatment of vertical femoral neck fractures: clinical observation and finite element analysis. Biomed Eng Online. 2023;22(1):20.
|