Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (20): 3136-3142.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1235
Previous Articles Next Articles
Clinical application of individualized tourniquet pressure in primary total knee arthroplasty
Zhou Jianguo1, Hu Weiquan1, Bi Shengrong1, Hu Bijuan2, Liu Shiwei1, Xiong Long3, Qian Rui1
- 1Department of Joint Surgery, 2Department of Ultrasound, Ganzhou People’s Hospital, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, Jiangxi Provincial People’s Hospital, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China
-
Online:2019-07-18Published:2019-07-18 -
Contact:Qian Rui, Chief physician, Department of Joint Surgery, Ganzhou People’s Hospital, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China -
About author:Zhou Jianguo, Doctoral candidate, Attending physician, Department of Joint Surgery, Ganzhou People’s Hospital, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81560355 (to XL)| the Science and Technology Program of the Health Commission of Jiangxi Province, No. 20177236 (to ZJG)| the Science and Technology Program of Ganzhou, No. GZ2017ZSF128 (to ZJG)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Jianguo, Hu Weiquan, Bi Shengrong, Hu Bijuan, Liu Shiwei, Xiong Long, Qian Rui. Clinical application of individualized tourniquet pressure in primary total knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(20): 3136-3142.
share this article
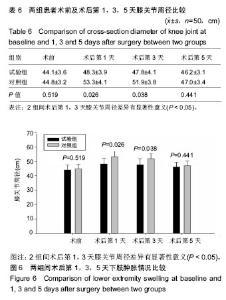
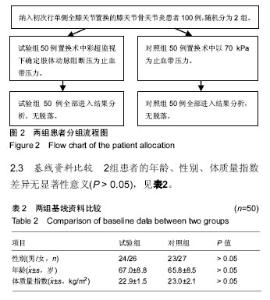
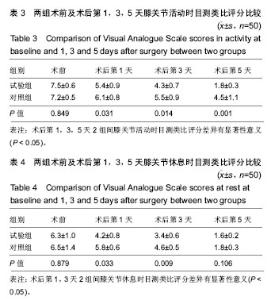
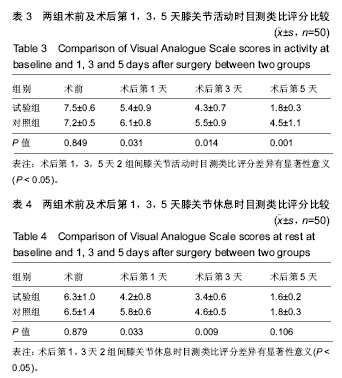
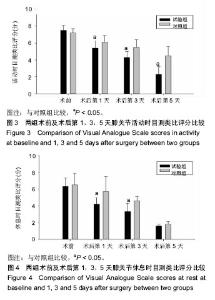
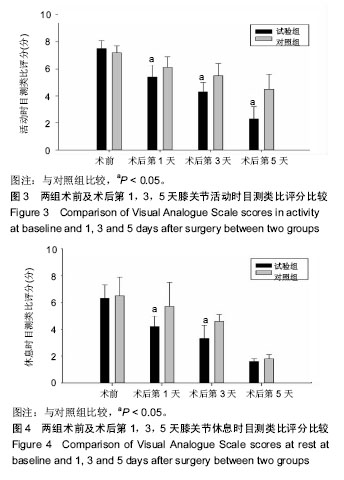
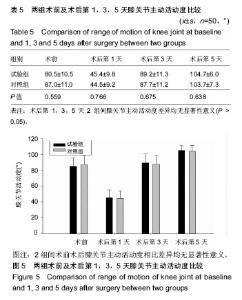
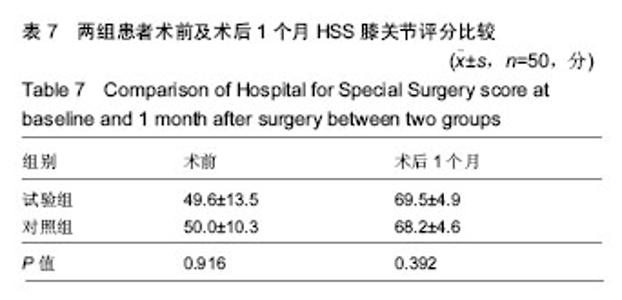
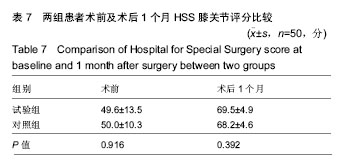
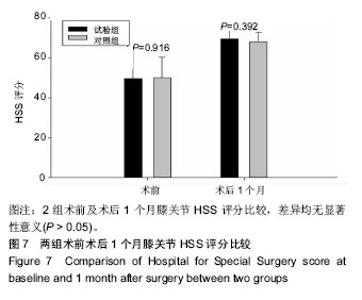
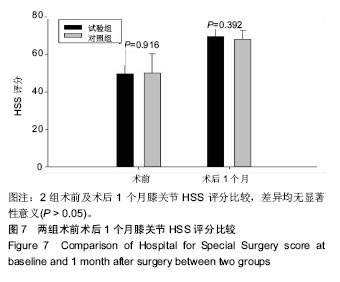
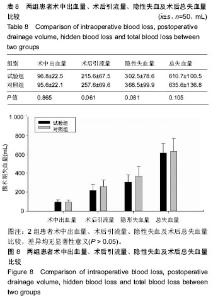
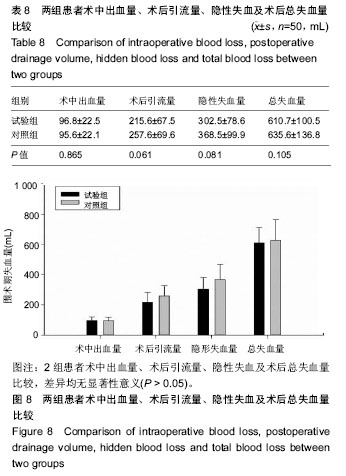
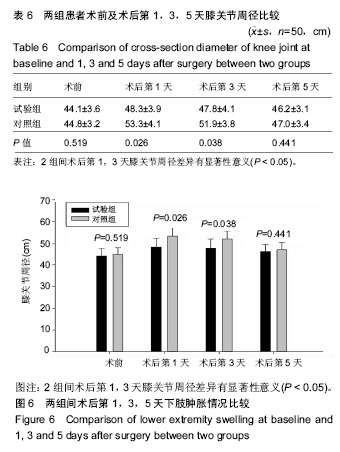
2.6 两组患者术后下肢肿胀及血栓情况比较 2组患者均未出现肺栓塞、伤口不愈合等并发症。术后第1天完善双下肢动静彩超,2组各出现2例小腿肌间静脉血栓,术后应用抗凝治疗、反复热敷、每天多次充气压力波治疗,术后1周复查均肌间血栓均消失。此次研究作者认为术后第1天发现小腿肌间静脉血栓主要因为患者功能锻炼不恰当不规范,采用抗凝同时反复多次热敷按摩,并每天多次充气压力波治疗,督促患者及时规范功能锻炼,加速血液循环等综合措施,故1周后复查肌间静脉血栓消失。 术后第1,3天对照组较试验组下肢肿胀明显,2组差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);2组术后第5天下肢肿胀差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表6及图6。"
| [1] Tai TW, Chang CW, Lai KA, et al.Effects of tourniquet use on blood loss and soft-tissue damage in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94(24): 2209-2215.[2] 蔡道章,杨杨,张曾.高凝血状态患者人群全膝关节置换术中应用止血带的对照研究[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2018, 12(4): 495-500.[3] Abbas K, Raza H, Umer M, et al. Effect of early release of tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2013;23(8): 562-565. [4] Kvederas G, Porvaneckas N, Andrijauskas A, et al. A randomized double-blind clinical trial of tourniquet application strategies for total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(12): 2790-2799.[5] Huang ZY, Pei FX, Ma J, et al. Comparison of three different tourniquet application strategies for minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty: a prospective non-randomized clinical trial. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014; 134(4): 561-570.[6] Zhang W, Liu A, Hu D, et al. Effects of the timing of tourniquet release incemented total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014;9(125): 1-11.[7] Na YG, Bamne AB, Won HH, et al. After early release of tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty, should it be reinflated or kept deflated? A randomized trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015; 25(9): 2769-2777.[8] Tie K, Hu D, Qi Y, et al. Effects of tourniquet release on total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2016;39(4): 642-650.[9] Ishii Y, Matsuda Y. Effect of tourniquet pressure on perioperative blood loss associated with cementless total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(3): 325-330.[10] Ishii Y, Noguchi H, Matsuda Y, et al. A new tourniquet system that determines pressures in synchrony with systolic blood pressure in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23(7): 1050-1056.[11] Tetro AM, Rudan JF. The effects of a pneumatic tourniquet on blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Can J Surg. 2001;44(1): 33-38.[12] Smith TO, Hing CB. Is a tourniquet beneficial in total knee replacement surgery? A meta-analysis and systematic review. Knee. 2010;17(2): 141-147.[13] 谢小伟,岳辰,黄泽宇,等.全膝关节置换术应用与不应用止血带的随机对照研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2017, 25(17): 1572-1576.[14] 张琦,董纪元,龚科,等. 应用止血带对人工全膝关节置换术的影响研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2016, 30(4): 421-425.[15] Zhang W, Li N, Chen S, et al. The effects of a tourniquet used in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surge Res. 2014; 9(13): 1-9.[16] 杜传超,邱海滨,张衡,等. 关于全膝关节置换术中使用止血带利弊随机对照性研究的系统回顾及Meta 分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2017, 32(8): 800-803.[17] Pfitzner T, von Roth P, Voerkelius N, et al. Influence of the tourniquet on tibial cement mantle thickness in primary total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(1): 96-101.[18] Tejwani NC, Immerman I, Achan P, et al. Tourniquet cuff pressure: The gulf between science and practice. J Trauma. 2006; 61(6): 1415-1418.[19] Lee OS, Lee MC, Han HS. Efficacy and safety of a new elastic tourniquet cuff in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled study. Biomed Eng Online. 2017; 16(1): 102.[20] 薛晨曦,姚运峰,荆珏华. 全膝关节置换术中使用止血带的效果与安全性分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2018, 33(6): 626-628.[21] Olivecrona C, Ponzer S, Hamberg P, et al. Lower tourniquet cuff pressure reduces postoperative wound complications after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(24): 2216-2221.[22] 谢小伟,岳辰,康鹏德,等. 加速康复模式下初次全膝关节置换术后急性疼痛的相关因素分析[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2016, 9(6): 489-492.[23] 王刚,曹晓瑞,陈晓勇,等.膝关节置换术中止血带的使用对术后加速康复的影响[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2017, 10(1): 27-32.[24] 李小磊,王琦,颜连启,等.全膝关节置换过程中止血带使用方法对患肢功能恢复的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(53): 8560-8564.[25] Unver B, Karatosun V, Tuncali B. Effects of tourniquet pressure on rehabilitation outcomes in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Nurs. 2013;32(4): 217-222.[26] Zan PF, Yang Y, Fu D, et al. Releasing of tourniquet before wound closure or not in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(1): 31-37.[27] de Souza Leão MG, Neta GP, Coutinho LI,et al. Comparative analysis of pain in patients who underwent total knee replacement regarding the tourniquet pressure. Revista Brasileira de Ortopedia (English Edition). 2016;51(6): 672-679.[28] Papalia R, Zampogna B, Franceschi F, et al. Tourniquet in knee surgery. Br Med Bull. 2014; 11(1): 63-76.[29] 黄家谷,张克,田华,等.单侧初次全膝关节置换后隐性失血的因素分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(26): 3823-3829. |
| [1] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [2] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [3] | Zhao Zhongyi, Li Yongzhen, Chen Feng, Ji Aiyu. Comparison of total knee arthroplasty and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of traumatic osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 854-859. |
| [4] | Yuan Jun, Yang Jiafu. Hemostatic effect of topical tranexamic acid infiltration in cementless total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 873-877. |
| [5] | Lü Zexiang, Wu Jutai, Jiang Jian, Feng Xiao, Li Tengfei, Wang Yehua. Effect of tranexamic acid combined with carbazochrome sodium sulfonate on blood loss and safety after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 386-390. |
| [6] | Mieralimu•Muertizha, Ainiwaerjiang•Damaola, Lin Haishan, Wang Li . Relationship between tibio-femoral mechanical axis deviation on coronal plane and early joint function recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3300-3304. |
| [7] | Wang Hao, Wang Yitao, Lü Zexiang, Li Tengfei, Wang Shaolong, Wang Yehua. Effect of repeated intravenous tranexamic acid in the perioperative period of proximal femoral nail antirotation for femoral intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3319-3323. |
| [8] | Deng Zhibo, Li Zhi, Wu Yahong, Mu Yuan, Mu Yuexi, Yin Liangjun. Local infiltration anesthesia versus femoral nerve block for pain control and safety after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3401-3408. |
| [9] | Fu Panfeng, Shang Wei, Kang Zhe, Deng Yu, Zhu Shaobo. Efficacy of anterolateral minimally invasive approach versus traditional posterolateral approach in total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3409-3415. |
| [10] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Buyang Huanwu Decoction in prevention of deep venous thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3267-3274. |
| [11] | Huang Chenyu, Tang Cheng, Wei Bo, Li Jiayi, Li Xuxiang, Zhang Huikang, Xu Yan, Yao Qingqiang, Wang Liming. Application of three-dimensional printing guide plate in total knee arthroplasty for patients with varus and valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2789-2793. |
| [12] | Li Shangzhi, Zheng Dezhi, Liu Jun. Early analgesia of cocktail therapy after total knee arthroplasty with enhanced recovery after surgery program [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2794-2798. |
| [13] | Liu Jinlei, Yin Li, Zhang Yi, Wang Haitao, Li Zhuangyan, Xia Peige, Qiao Renqiu. Effects of intravenous tranexamic acid combined with periarticular multipoint injection of tranexamic acid cocktail on blood loss and pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2833-2839. |
| [14] | Xu Hui, Kang Bingxin, Gao Chenxin, Zhao Chi, Xu Xirui, Sun Songtao, Xie Jun, Xiao Lianbo, Shi Qi. Effectiveness of Tuina in the treatment of pain after total knee arthroplasty in patients with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2840-2845. |
| [15] | Deng Bo, Hong Hainan, Fan Yongyong, Cai Guoping, Feng Xingbing, Hong Zhenghua. Efficacy and safety of tourniquet application in total knee arthroplasty and only at the time of cementing: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2908-2914. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||