Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (8): 1248-1257.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1087
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hip function after total hip arthroplasty through different approaches: a network meta-analysis
Zhang Chi1, Lü Haoyuan2, Zhang Xiaoyun3, Lin Zonghan3, Chen Yueping3, Dong Panfeng3, Feng Yang1
- 1Graduate School, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2First Clinical College, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430061, Hubei Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2019-03-18Published:2019-03-18 -
Contact:Lin Zonghan, Chief physician, Master supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhang Chi, Master candidate, Graduate School, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81760796 (to CYP); the Key Project of Guangxi Health Department, No. S201419-05 (to CYP); the Discipline Training Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine-Orthopedics Construction Project, No. 04B2017082 (to CYP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Chi, Lü Haoyuan, Zhang Xiaoyun, Lin Zonghan, Chen Yueping, Dong Panfeng, Feng Yang. Hip function after total hip arthroplasty through different approaches: a network meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1248-1257.
share this article

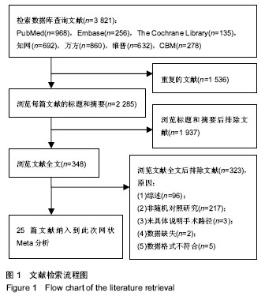
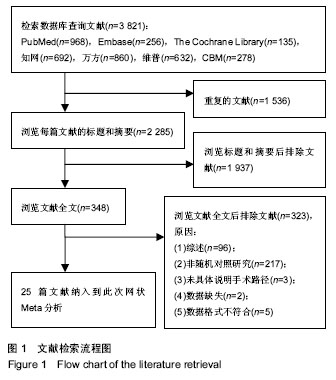
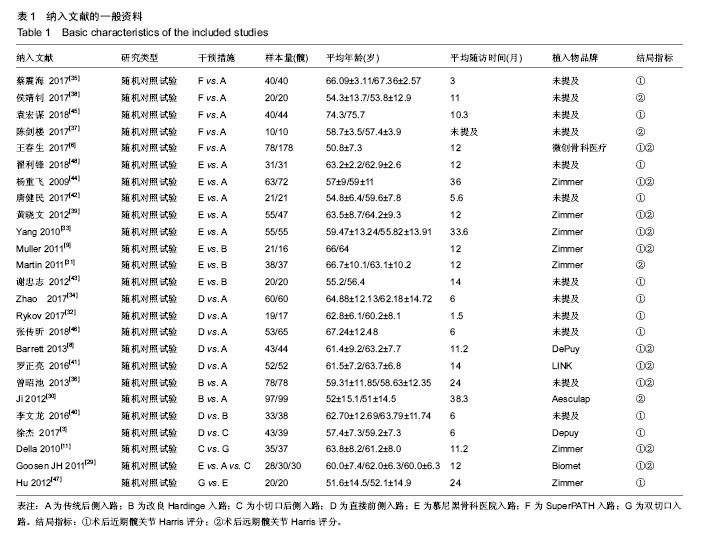
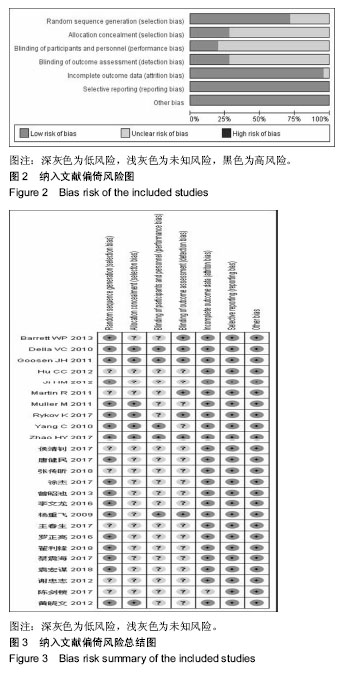
2.2 纳入研究的基本特征 25篇文献共研究2 253髋,所有患者均接受全髋关节置换术,手术入路中传统后侧入路963髋,改良Hardinge入路286髋,小切口后侧入路104髋,直接前侧入路303髋,慕尼黑骨科医院入路352髋,SuperPATH入路188髋,双切口入路57髋,纳入文献的一般资料见表1。 2.3 纳入文献的方法学质量评价 18篇文献描述了正确的随机分配序列产生方法[3,8-9,11,29-30,32-36,39-42,44-45,48],7篇文献论述了详细的分配隐藏方案[9,11,29,32-34,39],8篇文献描述了盲法[8,11,29,31-34,44],除了1篇文献的随访情况描述不完整外[37],其他所有文献均有论述详细的失访与退访情况,并完整汇报了预先设定的所有结果,所有纳入文献基线一致,数据真实有效,所有研究不涉及利益关系。纳入文献的偏倚风险图见图2,偏倚风险总结图见图3。"
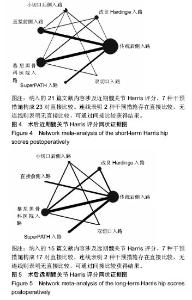
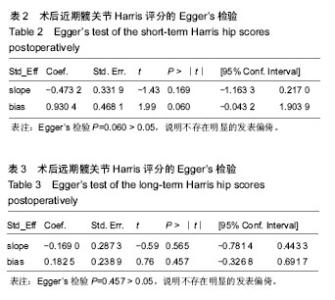
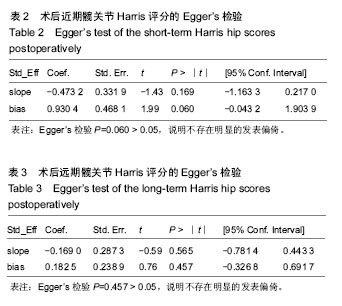
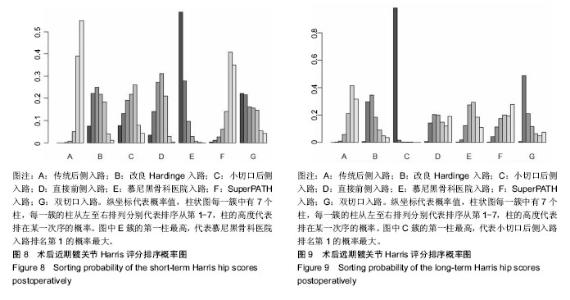
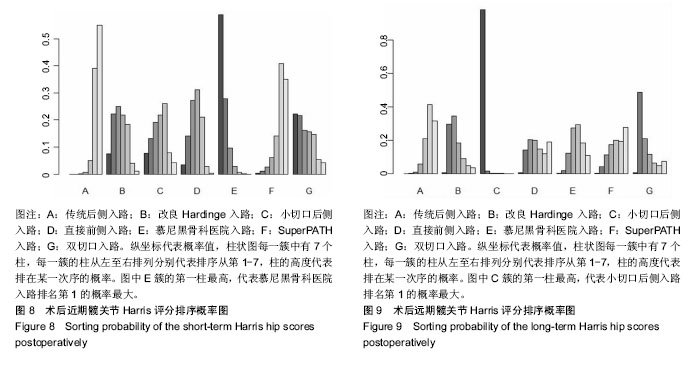
2.4 直接Meta分析 2.4.1 术后近期髋关节Harris评分 21篇文献报道了近期髋关节Harris评分[3,6,8- 9,11,29,32-36,39-48],合计样本量1 922髋,其中手术入路传统后侧入路834髋,改良Hardinge入路152髋,小切口后侧入路104髋,直接前侧入路303髋,慕尼黑骨科医院入路314髋,SuperPATH入路158髋,双切口入路57髋。3篇文献报道了SuperPATH入路与传统后侧入路的近期髋关节Harris评分[6,35,45],异质性小(P=0.904,I2=0.0%),固定效应模型合并结果显示SuperPATH入路的近期髋关节Harris评分高于传统后侧入路(MD=0.43,95%CI[0.04,0.82]);6篇文献报道了慕尼黑骨科医院入路与传统后侧入路的近期髋关节Harris评分[29,33,39,42,44,48],异质性小(P=0.490,I2=0.0%),固定效应模型合并结果显示慕尼黑骨科医院入路的近期髋关节Harris评分高于传统后侧入路(MD=7.17,95%CI[6.51,7.84]);2篇文献报道了慕尼黑骨科医院入路与改良Hardinge入路的近期髋关节Harris评分[9,43],异质性小(P=0.597,I2=0.0%),固定效应模型合并结果显示慕尼黑骨科医院入路的近期髋关节Harris评分高于改良Hardinge入路(MD=1.33,95%CI [0.30,2.36]);5篇文献报道了直接前侧入路与传统后侧入路的近期髋关节Harris评分[8,32,34,41,46],异质性小(P=0.223,I2=29.8%),固定效应模型合并结果显示直接前侧入路的近期髋关节Harris评分高于传统后侧入路(MD= 1.13,95%CI[0.18,2.08]);1篇文献报道了改良Hardinge入路与传统后侧入路的近期髋关节Harris评分[36],结果显示改良Hardinge入路的近期髋关节Harris评分高于传统后侧入路(MD=5.28,95%CI[3.24,7.32]);1篇文献报道了直接前侧入路与改良Hardinge入路的近期髋关节Harris评分[40],结果显示2组的近期髋关节Harris评分相当(MD=1.29,95%CI[-0.39,2.97]);1篇文献报道了直接前侧入路与小切口后侧入路的近期髋关节Harris评分[3],结果显示直接前侧入路的近期髋关节Harris评分高于小切口后侧入路(MD=6.50,95%CI[4.65,8.35]);1篇文献报道了小切口后侧入路与双切口入路的近期髋关节Harris评分[11],结果显示2组近期髋关节Harris评分相当(MD=0.00,95%CI-5.08,5.08]);1篇文献报道了慕尼黑骨科医院入路与小切口后侧入路的近期髋关节Harris评分[29],结果显示2组近期髋关节Harris评分相当(MD=-7.00,95%CI [-15.48,1.48]);1篇文献报道了传统后侧入路与小切口后侧入路的近期髋关节Harris评分[29],结果显示传统后侧入路的近期髋关节Harris评分低于小切口后侧入路(MD=-10.00,95%CI [-19.12,-0.88]);1篇文献报道了双切口入路与慕尼黑骨科医院入路的近期髋关节Harris评分[47],结果显示2组近期髋关节Harris评分相当(MD=-1.00,95%CI[-4.72,2.72])。 2.4.2 术后远期髋关节Harris评分 15篇文献报道了远期髋关节Harris评分[6,8-9,11,29-31,33,36-39,41,44,47],合计样本量1 512髋,其中传统后侧入路684髋,改良Hardinge入路 228髋,小切口后侧入路64髋,直接前侧入路95髋,慕尼黑骨科医院入路276髋,SuperPATH入路108髋,双切口入路57髋。4篇文献报道了慕尼黑骨科医院入路与传统后侧入路的远期髋关节Harris评分[29,33,39,44],异质性小(P=0.576,I2=0.0%),固定效应模型合并结果显示2组的远期髋关节Harris评分相当(MD=0.23,95%CI[-0.68,1.14]);3篇文献报道了SuperPATH入路与传统后侧入路的远期髋关节Harris评分[6,37-38],异质性小(P=0.423,I2=0.0%),固定效应模型合并结果显示2组远期髋关节Harris评分相当(MD=0.16,95%CI[-1.07,1.40]);2篇文献报道了慕尼黑骨科医院入路与改良Hardinge入路的远期髋关节Harris评分[9,31],异质性较小(P=0.168,I2=47.3%),固定效应模型合并结果显示2组远期髋关节Harris评分相当(MD=1.81,95%CI[-3.28,6.90]);1篇文献报道了小切口后侧入路与双切口入路的远期髋关节Harris评分[11],结果显示2组远期髋关节Harris评分相当(MD=2.00,95%CI[-1.06,5.06]);2篇文献报道了改良Hardinge入路与传统后侧入路的远期髋关节Harris评分[30,36],异质性小(P=0.608,I2=0.0%),固定效应模型合并结果显示改良Hardinge入路的远期髋关节Harris评分高于传统后侧入路(MD=1.57,95%CI[0.21,2.94]);2篇文献报道了直接前侧入路与传统后侧入路的远期髋关节Harris评分[8,41],异质性小(P=0.558,I2=0.0%),固定效应模型合并结果显示2组的远期髋关节Harris评分相当(MD=0.65,95%CI[-1.16,2.46]);1篇文献报道了慕尼黑骨科医院入路与小切口后侧入路的远期髋关节Harris评分[29],结果显示2组远期髋关节Harris评分相当(MD= -6.00,95%CI[-12.01,0.01]);1篇文献报道了传统后侧入路与小切口后侧入路的远期髋关节Harris评分[29],结果显示传统后侧入路的远期髋关节Harris评分低于小切口后侧入路(MD=-7.00,95%CI[-12.64,-1.36]);1篇文献报道了双切口入路与慕尼黑骨科医院入路的远期髋关节Harris评分[47],结果显示2组远期髋关节Harris评分相当(MD=0.00,95%CI[-2.56,2.56])。 2.5 网状Meta分析 2.5.1 网状证据图 纳入的21篇文献内容涉及近期髋关节Harris评分,7种干预措施构成23对直接比较,纳入的15篇文献内容涉及远期髋关节Harris评分,7种干预措施构成17对直接比较,连线表明2种干预措施存在直接比较,无连线则表明无直接比较,可通过间接比较获得结果,见图4,5。 "
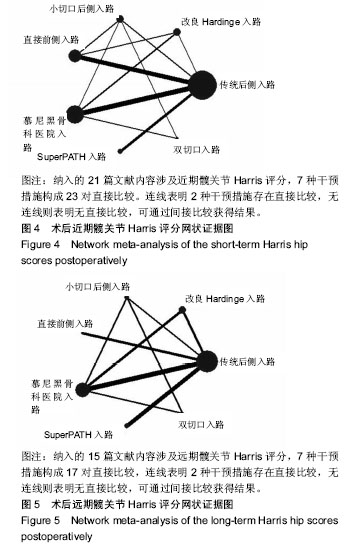
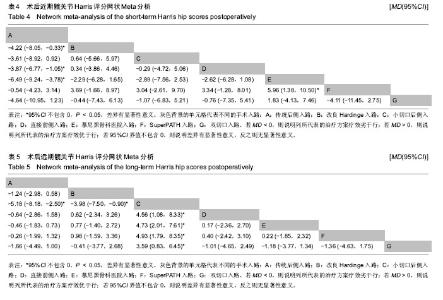
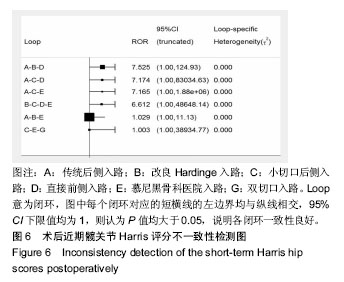
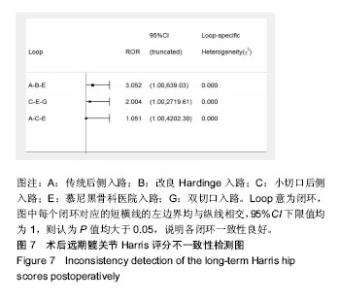
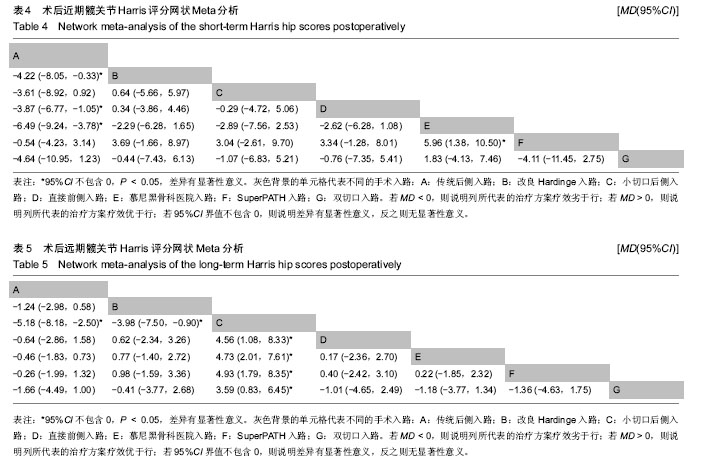
2.5.4 网状Meta分析结果 各干预措施对比潜在规模缩减因子值均为1,说明模型收敛性良好。传统后侧入路的近期髋关节Harris评分低于改良Hardinge入路、直接前侧入路、慕尼黑骨科医院入路,差异有显著性意义;慕尼黑骨科医院入路的近期髋关节Harris评分高于SuperPATH入路,差异有显著性意义。小切口后侧入路的远期髋关节Harris评分高于传统后侧入路、改良Hardinge入路、小切口后侧入路、直接前侧入路、SuperPATH入路、慕尼黑骨科医院入路、双切口入路,差异有显著性意义。 近期髋关节Harris评分、远期髋关节Harris评分其他两两比较的网状Meta分析结果差异均无显著性意义,见表4,5。 "
| [1] 彭伟秋,张祥洪,李富明,等. 侧卧位直接前方入路与直接外侧入路初次全髋关节置换术的比较[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2018, 26(11):999-1004.[2] Hoppenfeld S, Boer PD, Buckley R. Surgical exposures in orthopaedics: the anatomic approach. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 1984:363.[3] 徐杰,庄伟达,李新炜,等. 直接前入路和后外侧保留梨状肌入路全髋关节置换术的疗效对比[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(2):214-220.[4] Hardinge K. The direct lateral approach to the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1982;64-B(1):17-19.[5] Post ZD, Orozco F, Diaz-Ledezma C, et al. Direct anterior approach for total hip arthroplasty: indications, technique, and results. J Am Acad Orthop Surg.2014;22(9):595-603.[6] 王春生,蒋武强,马瑞,等. 经皮穿刺辅助全髋入路在全髋关节置换的早期应用[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2017,11(6): 565-568.[7] Harris WH. Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. an end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg. 1969;51(4):737-755.[8] Barrett WP, Turner SE, Leopold JP. Prospective randomized study of direct anterior vs postero-lateral approach for total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(9):1634-1638.[9] Muller M, Tohtz S, Springer I, et al. Randomized controlled trial of abductor muscle damage in relation to the surgical approach for primary total hip replacement: minimally invasive anterolateral versus modified direct lateral approach. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(2):179-189.[10] 冯尔宥,林飞太,林丽琼,等.改良后侧入路小切口人工全髋关节置换的初步临床应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2016,31(6): 627-628.[11] Della VC, Dittle E, Moric M, et al. A prospective randomized trial of mini-incision posterior and two-incision total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(12): 3348-3354.[12] 吴婷婷,刘丹璐,黄娇,等. 偏倚风险评估工具在针刺Cochrane系统评价中的应用[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2014,14(3):361-364.[13] 张天嵩,钟文昭,李博. 实用循证医学方法学.2版[M].长沙:中南大学出版社, 2014.[14] 赵坤,陈凌霄,田金徽,等.使用R、GeMTC和STATA软件实现连续变量的网状Meta分析[J].中国循证医学杂志, 2015,15(7): 861-868.[15] 汪徐林,秦正积,陆益花,等. Stata软件在网状Meta分析中的应用[J]. 现代预防医学, 2016,43(19):3461-3464.[16] 田金徽,李伦. 网状Mate分析方法与实践[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社, 2017.[17] 石修权,王增珍. Egger’s Test与Begg’s Test的功效差异比较与原因分析[J]. 华中科技大学学报(医学版), 2009,38(1):91-93.[18] 易跃雄,张蔚,刘小媛,等. 网状Meta分析图形结果解读[J].中国循证医学杂志, 2015,15(1):103-109.[19] Chimento GF, Pavone V, Sharrock N, et al. Minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty: a prospective randomized study. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(2):139-144.[20] Ogonda L, Wilson R, Archbold P, et al. A minimal-incision technique in total hip arthroplasty does not improve early postoperative outcomes. a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg. 2005,87(4):701-710.[21] Shitama T, Kiyama T, Naito M, et al. Which is More Invasive-Mini Versus Standard Incisions in Total Hip Arthroplasty? Int Orthop. 2009;33(6):1543.[22] Parvizi J, Restrepo C, Maltenfort MG. Total hip arthroplasty performed through direct anterior approach provides superior early outcome: results of a randomized, prospective study. Orthop Clin North Am. 2016;47(3):497-504.[23] Meneghini RM, Smits SA. Early discharge and recovery with three minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty approaches: a preliminary study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(6): 1431-1437.[24] Restrepo C, Parvizi J, Pour AE, et al. Prospective randomized study of two surgical approaches for total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2010;25(5):671-679.[25] Kim YH. Comparison of primary total hip arthroplasties performed with a minimally invasive technique or a standard technique: a prospective and randomized study. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21(8):1092-1098.[26] [Christensen CP, Jacobs CA. Comparison of patient function during the first six weeks after direct anterior or posterior total hip arthroplasty (tha): a randomized study. J Arthroplasty, 2015;30(9 Suppl):94-97.[27] Sculco TP, Jordan LC, Walter WL. Minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty: the hospital for special surgery experience. J Arthroplasty. 2004;35(2):137-42.[28] Taunton MJ, Mason JB, Odum SM, et al. Direct anterior total hip arthroplasty yields more rapid voluntary cessation of all walking aids: a prospective, randomized clinical trial. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(9 Suppl):169-172.[29] Goosen JH, Kollen BJ, Castelein RM, et al. Minimally invasive versus classic procedures in total hip arthroplasty: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(1):200-208.[30] Ji HM, Kim KC, Lee YK, et al. Dislocation after total hip arthroplasty: a randomized clinical trial of a posterior approach and a modified lateral approach. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(3):378-385.[31] Martin R, Clayson PE, Troussel S, et al. Anterolateral minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled study with a follow-up of 1 year. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(8):1362-1372.[32] Rykov K, Reininga I, Sietsma M, et al. Posterolateral versus direct anterior approach in total hip arthroplasty (polada trial). a randomised controlled trial to assess differences in serum markers. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(12):3652-3658.[33] Yang C, Zhu Q, Han Y, et al. Minimally-invasive total hip arthroplasty will improve early postoperative outcomes: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Ir J Med Sci. 2010;179(2):285-290.[34] Zhao HY, Kang PD, Xia YY, et al. Comparison of early functional recovery after total hip arthroplasty using a direct anterior or posterolateral approach: a randomized controlled trial. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(11):3421-3428.[35] 蔡震海,潘界恩,黄成龙,等. SuperPath微创与常规全髋关节置换术治疗股骨颈骨折的临床疗效比较研究[J]. 浙江创伤外科, 2017,22(2):343-345.[36] 曾昭池,郭中凯,朱志勇,等. 微创与常规全髋关节置换术的临床疗效比较[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2013,21(12):1173-1176.[37] 陈剑楼. SuperPATH技术行全髋关节置换的早期效果分析[J]. 中国卫生标准管理, 2017,8(17):36-37.[38] 侯靖钊,包洪卫,程彦晓. 应用SuperPATH技术行全髋关节置换的早期疗效观察[J]. 临床骨科杂志, 2017,20(1):50-53.[39] 黄晓文,程力,何天达,等. 前外侧小切口与常规后外侧切口全髋关节置换的疗效对比[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(9): 1538-1542.[40] 李文龙,范亚楠,张蕾蕾,等. 微创全髋关节置换术直接前侧入路与外侧小切口入路的对比研究[J].中医正骨, 2016,28(3):24-29.[41] 罗正亮,陈敏,尚希福,等. 侧卧位直接前方入路与后外侧入路全髋关节置换临床疗效比较[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2016,96(35): 2807-2812.[42] 唐健民,陆晟,李祥,等. 不同手术入路全髋关节置换术对患者的疗效及对Harris评分的影响分析[J]. 中国继续医学教育, 2017, 9(13):129-130.[43] 谢忠志,梁斌,尹东,等. 外侧小切口髋关节前入路初次人工全髋关节置换术疗效分析[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2012,28(4):603-605.[44] 杨重飞,朱庆生,韩一生,等. 前外侧微创全髋关节置换的临床研究[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2009,89(1):2-6.[45] 袁宏谋,朱佳俊,孙振国,等. SuperPATH入路与后外侧入路行人工全髋关节置换术的疗效比较[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2018,32(1):14-19.[46] 张传昕,王波,周义钦,等. 直接前方入路和后外侧入路在初次全髋关节置换术中的应用效果比较[J]. 山东医药, 2018,58(16): 76-78.[47] Hu CC, Chern JS, Hsieh PH, et al. Two-incision versus modified watson-jones total hip arthroplasty in the same patients-- a prospective study of clinical outcomes and patient preferences. Chang Gung Med J. 2012;35(1):54-61.[48] 翟利锋, 马苟平. 前外侧微创入路对全髋置换手术效果及预后的影响分析[J]. 浙江创伤外科, 2018,23(2):293-295.[49] Inaba Y, Kobayashi N, Yukizawa Y, et al. Little clinical advantage of modified watson-jones approach over modified mini-incision direct lateral approach in primary total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(7):1117-1122.[50] Kemp JL, MacDonald D, Collins NJ, et al. Hip arthroscopy in the setting of hip osteoarthritis: systematic review of outcomes and progression to hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(3):1055-1073.[51] Mardones R, Pagnano MW, Nemanich JP, et al. The frank stinchfield award: muscle damage after total hip arthroplasty done with the two-incision and mini-posterior techniques. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;441:63-67.[52] Meneghini RM, Pagnano MW, Trousdale RT, et al. Muscle damage during mis total hip arthroplasty: smith-petersen versus posterior approach. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006; 453:293-298.[53] Putananon C, Tuchinda H, Arirachakaran A, et al. Comparison of direct anterior, lateral, posterior and posterior-2 approaches in total hip arthroplasty: network meta-analysis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2018;28(2): 255-267.[54] 谢小波,杨智坚,林荔军,等. 微创与传统手术入路在人工全髋关节置换术后临床疗效的Meta分析[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2017,11(6):629-640.[55] 夏韶襁,刘世清,周炎,等. 微创前外侧与常规后外侧入路对全髋置换术的系统评价[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2016,22(5):393-398.[56] 李建,邱冰,甄东. SuperPATH入路与传统入路髋关节置换临床疗效的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(15): 2453-2460.[57] 李子荣,史振才,郭万首,等. 后外侧入路小切口人工全髋关节置换术[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2005,25(5):263-267.[58] 张先龙,何耀华,王琦,等. 后路小切口人工全髋关节置换术[J]. 中华创伤杂志, 2005,21(8):591-594.[59] Berger RA. Total hip arthroplasty using the minimally invasive two-incision approach. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(417) : 232-241.[60] 廖立祥,刘芳,章喆,等. 微创双切口与常规入路全髋置换的比较研究[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2009,25(16):2694-2695. |
| [1] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [2] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [3] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [4] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [5] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [6] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [7] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [8] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [9] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [10] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [11] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [12] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [13] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [14] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [15] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||