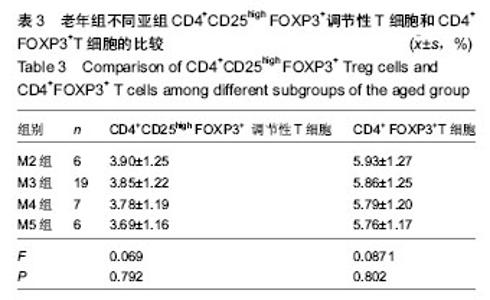
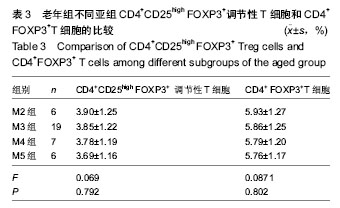
| [1] Rooney CM.Can Treg elimination enhance NK cell therapy for AML? Blood. 2014;123(25):3848-3849.
[2] 崔俊杰.脐带间充质干细胞对阿糖胞苷诱导的HL-60细胞凋亡影响的研究[D].北京协和医学院中国医学科学院,2013.
[3] 周华,周倩兰,唐晓文,等. allo-HSCT治疗进展期难治性急性髓系白血病的长期随访结果[J].浙江临床医学,2014,16(7): 1017- 1018, 1021.
[4] 刘会兰,孙自敏,杨会志,等.自体外周血干细胞移植治疗急性髓细胞白血病[J].临床输血与检验,2007,9(4):313-315.
[5] Sriskanthadevan S,Jeyaraju DV,Chung TE,et al.AML cells have low spare reserve capacity in their respiratory chain that renders them susceptible to oxidative metabolic stress.Blood. 2015 Jan 28. pii: blood-2014-08-594408. [Epub ahead of print]
[6] Govindaraj C, Madondo M,Kong YY,et al.Lenalidomide-based maintenance therapy reduces TNF receptor 2 on CD4 T cells and enhances immune effector function in acute myeloid leukemia patients.Am J Hematol.2014;89(8):795-802.
[7] Govindaraj C,Tan P,Walker P,et al.Reducing TNF receptor 2+ regulatory T cells via the combined action of azacitidine and the HDAC inhibitor, panobinostat for clinical benefit in acute myeloid leukemia patients.Clin Cancer Res.2014;20(3): 724-735.
[8] Zhou Q,Hu Y,Howard OM,et al.In vitro generated Th17 cells support the expansion and phenotypic stability of CD4(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells in vivo.Cytokine. 2014; 65(1):56-64.
[9] Goodyear OC,Dennis M,Jilani NY,et al.Azacitidine augments expansion of regulatory T cells after allogeneic stem cell transplantation in patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML).Blood.2012;119(14):3361-3369.
[10] 杜晓辉,刘利利,宁宁,等.胃癌患者血清调节性T细胞、细胞毒性T淋巴细胞的检测及意义[J].中华实验外科杂志,2013,30(12): 2704-2706.
[11] 李晶晶,牛倩,唐笛娇,等.多发性骨髓瘤患者外周血Th17和Treg细胞比率的平衡关系研究[J].中华血液学杂志,2013,34(11): 936-940.
[12] Bachanova V,Cooley S,Defor TE, et al.Clearance of acute myeloid leukemia by haploidentical natural killer cells is improved using IL-2 diphtheria toxin fusion protein.Blood. 2014;123(25):3855-3863.
[13] Sun YX,Kong HL,Liu CF,et al.The imbalanced profile and clinical significance of T helper associated cytokines in bone marrow microenvironment of the patients with acute myeloid leukemia.Hum Immunol.2014;75(2):113-118.
[14] Salagianni M,Lekka E,Moustaki A,et al.NK cell adoptive transfer combined with Ontak-mediated regulatory T cell elimination induces effective adaptive antitumor immune responses.J Immunol.2011;186(6):3327-3335.
[15] Curti A,Ruggeri L,D'Addio A,et al.Successful transfer of alloreactive haploidentical KIR ligand-mismatched natural killer cells after infusion in elderly high risk acute myeloid leukemia patients.Blood.2011;118(12):3273-3279.
[16] Rubnitz JE,Inaba H,Ribeiro RC, et al.NKAML: a pilot study to determine the safety and feasibility of haploidentical natural killer cell transplantation in childhood acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol.2010;28(6):955-959.
[17] 王远,吴昌平,卢斌峰,等.调节性T细胞在肿瘤免疫逃逸中的机制[J].中华实验外科杂志,2013,30(11):2466-2469.
[18] 王会平,沈元元,熊术道,等.老年急性髓细胞白血病患者调节性T细胞的表达及临床意义[J].中华老年医学杂志,2013,32(7): 754-756.
[19] 牟冠男,徐雯.调节性T细胞在急性髓细胞白血病中的作用[J].国际免疫学杂志,2013,36(2):106-111.
[20] Mato AR,Morgans A,Luger SM.Novel strategies for relapsed and refractory acute myeloid leukemia.Curr Opin Hematol. 2008;15(2):108-114.
[21] Fontenot JD,Gavin MA,Rudensky AY.Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cells.Nat Immunol.2003;4(4):330-336.
[22] Hartigan-O'Connor DJ,Poon C,Sinclair E.Human CD4 + regulatory T cells express lower levels of the IL-7 receptor alpha chain (CD127),allowing consistent identification and sorting of live cells.J Immunol Methods.2007;319(1-2):41-52.
[23] Kanakry CG,Hess AD,Gocke CD.Early lymphocyte recovery after intensive timed sequential chemotherapy for acute myelogenous leukemia:peripheral oligoclonal expansion of regulatory T cells.Blood.2011;(2):608-611.
[24] Prabhala RH,Neri P,Bae JE.Dysfunctional T regulatory cells in multiple myeloma.Blood.2006;(1):301-304.
[25] Zhang N,Schr(o)ppel B,Lal G.Regulatory T cells sequentially migrate from inflamed tissues to draining lymph nodes to suppress the alloimmune response.Immunity.2009; (3): 458-469.
[26] Yang W,Xu Y.Clinical significance of Treg cell frequency in acute myeloid leukemia.Int J Hematol.2013;98(5):558-562.
[27] Yang XW,Wang P,Liu JQ,et al.Coordinated regulation of the immunoproteasome subunits by PML/RARα and PU.1 in acute promyelocytic leukemia.Oncogene. 2014;33(21): 2700-2708.
[28] Iachininoto MG,Nuzzolo ER,Bonanno G,et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibition constrains indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) activity in acute myeloid leukaemia cells. Molecules.2013;18(9):10132-10145.
[29] Martino M,Fedele R,Moscato T,et al.Optimizing outcomes following allogeneic hematopoietic progenitor cell transplantation in AML: the role of hypomethylating agents. Curr Cancer Drug Targets.2013;13(6):661-669. |