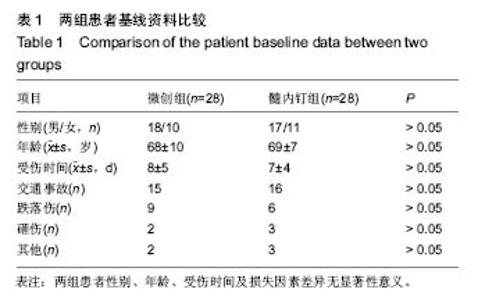
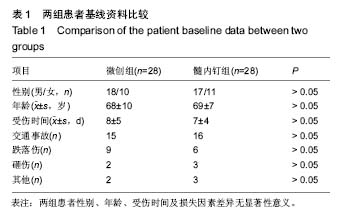
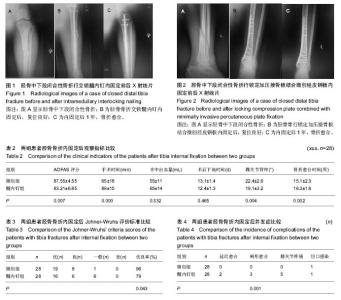
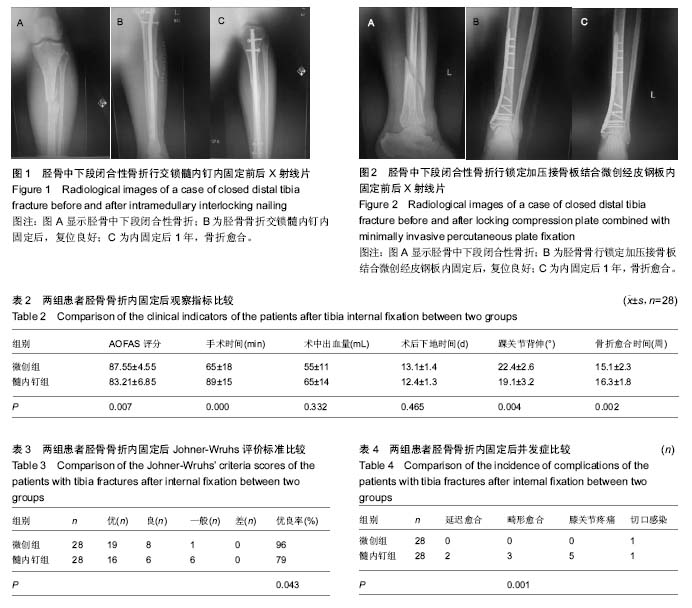
| [1] 陈仲,杨洪昌,赵学凌.骨折内固定治疗精要[M].昆明: 云南科技出版社,2012: 203.[2] Krettek C, Mller M, Miclau T. Evolution of minimally invasive plate ostesynthesis (MIPO) in the femur.Injury.2001; 32 (Suppl 3):14-23.[3] Zou J, Zhang W, Zhang CQ.Comparison of minimally invasive percutaneous plateosteosynthesis with open reduction and internal fixation for treatment of extra-articular distal tibia fractures.Injury.2013;44(8):1102-1106.[4] Richard RD, Kubiak E, Horwitz DS,et al.Techniques for the surgical treatment ofdistal tibia fractures.Orthop Clin North Am.2014;45(3):295-312.[5] ScheerlinckT, Ng CS, Handelberg F, et al. Medium term results of percutaneous, arthroscopically Assited osteosynthesis of fratures of the tibial plateau. Jbone Joint Surg(Br).2013;16(80): 959-964.[6] 范志航,熊雁,杜全印,等.新型点式接触锁定加压接骨板在治疗四肢长骨骨折中的临床应用[J].创伤外科杂志, 2014,16(3):240-243.[7] 曹前来,王安,杨海涛,等.微创锁定钢板内固定治疗胫骨多段骨折的疗效[J].武警医学. 2014;25(5):472-474.[8] Mauffrey C, Mc Guinness K, Parsons N, et al.A randomised pilot trial of “locking plate” fixation versus intramedullary nailing for extra-articular fractures of the distaltibia.Bone Joint Surg Br.2012;94(5):704-708.[9] Farouk O, Kreetk C, Miclau T, et al.Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis: does percutaneous plating disrupt femoral blood supply less than traditional technique.J Orthop Trauma.1999;13(6):401-406.[10] Ueller CA, Eingartner C, Schreitmueller E, et al. Primary stability ofvarious forms of osteosynthesis in the treatment of fractures of the Proxim al tibia.J Bone Joint Surg(Br). 2005; 7(3):26-432.[11] 任一,胡春宁,陈其宽,等.两种微创内固定治疗胫骨干中下段骨折疗效分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2014,20(8):715-719.[12] 马敏,蔡俊丰,尹峰,等.两种术式治疗胫骨中段闭合性骨折的疗效比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(18):1661-1664.[13] Liporace FA, Stadler CM, Yoon RS. Problems,tricks,and pearls in intramedullary nailing of proximal third tibial fractures. J Orthop Trauma.2013;27(1): 56-62.[14] Hess F, Sommer C. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of the distal fibula with the locking compression plate: first experience of 20 cases. Orthop Trauma.2011;25(2):110–115.[15] Janssen KW, Biert J, van Kampen A.Treatment of distal tibial fractures: plate versus nail: a retrospective outcome analysis of matched pairs of patients.Int Orthop.2007;31(5):709-714.[16] Collinge C,Protzman R.Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures.Orthop Trauma.2010;24:24-29.[17] 胡喜春,黄长明.MIPPO 技术结合 LCP 内固定治疗胫骨远端骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2012,18(3):211-212.[18] Kucukdurmaz F, Akpinar F, Saka G ,et al.A newly designed intramedullary nail with distal interlocking system for tibia fractures in adults-the clinical results. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg.2012;18: 243-249.[19] 彭磊.扩髓与不扩髓带锁髓内钉治疗长管骨骨折临床探析 [J].吉林医学, 2015(07):140-141.[20] 林成寿,刘寿坤,吴锦清,等.解剖型腔骨髓内钉微创治疗腔骨远端骨折创伤外科杂志[J],2010,12(6):520-522.[21] Richard RD, Kubiak E, Horwitz DS.Techniques for the surgical treatment of distal tibia fractures.Orthop Clin North Am.2014;45(3):295-312. [22] Heather VA,Ann BS.Randomized prospective comparison of plate versus intramedullary nail fixation for distal tibia shaft fractures.Orthop Trauma.2011;12:736-741.[23] El Attal R,Hansen M,Rosenberger R,et al.Intramedullary nailing of the distal tibia illustrated with the Expert(TM) tibia nail.Oper Orthop Traumatol.2011;23(5):397-410.[24] Casstevens C,Le T,Archdeacon MT,et al.Management of extraarticular fractures of the distal tibia:intramedullary nailing ve Isus plate fixation.Am Acad Orthop Surg.2012;20:675-683.[25] Katsoulis E, Court-Brown C, Giannoudis PV. Incidence and aetiology of anterior knee pain after intramedullary nailing of the femur and tibia.Bone Joint Surg Br.2006;88(5):576–580. |