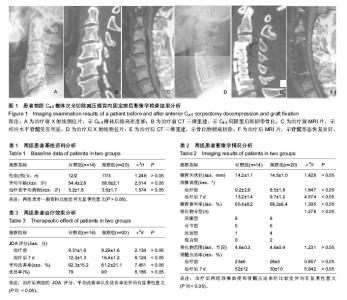
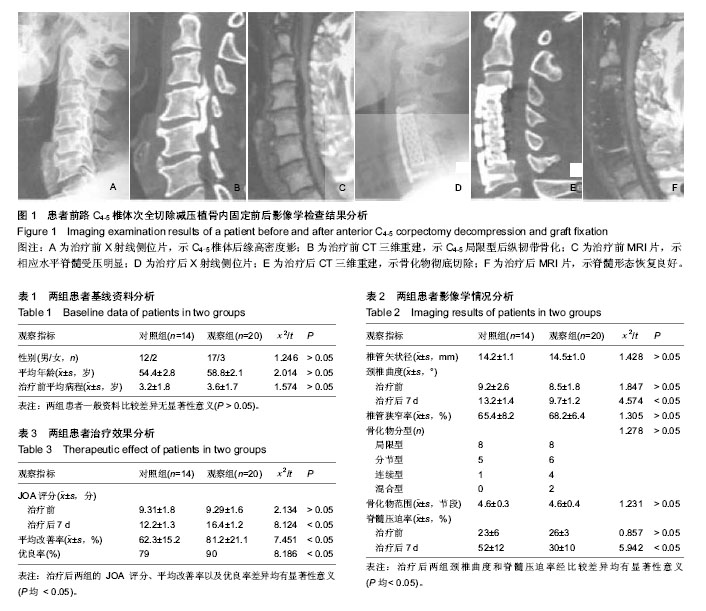
| [1] 张本,侯铁胜,沈洪兴,等.颈椎后纵韧带骨化症的手术治疗及前后路手术比较[J].实用骨科杂志,2013,19(10):865-869.
[2] 颜廷振,张晶,魏彦春,等.颈椎全椎板切除减压和植骨融合内固定术治疗地方氟骨性颈椎后纵韧带骨化症[J].广东医学,2013, 34(21):3303-3305.
[3] 苏允裕,劳贵昌.一期前后路联合手术治疗颈椎后纵韧带骨化症效果观察[J].山东医药, 2014,54(12):37-39.
[4] 焦根龙,李志忠,潘永勤,等.髓内外减压在有脊髓信号改变的颈椎后纵韧带骨化症中的疗效分析[J].南方医科大学学报,2013, 33(9):1382-1385,1389.
[5] 俞阳,范海泉,陈铭,等.ARCH钢板在颈椎后路椎管成形术中的应用治疗颈椎后纵韧带骨化症近期疗效观察[J].重庆医学, 2013,42(22):2616-2618.
[6] Yamazaki M, Okawa A, Mannoji C. Postoperative paralysis following posterior decompression with instrumented fusion for thoracic myelopathy caused by ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J Clin Neurosci. 2010;18(2): 294-296.
[7] Ikeda Y, Nakajima A, Aiba A,et al.Association between serum leptin and bone metabolic markers, and the development of heterotopic ossification of the spinal ligament in female patients with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(9):1450-1458.
[8] 雷涛,申勇,王林峰,等.节段型严重颈椎后纵韧带骨化症前路、后路手术的疗效比较与选择策略[J].中华骨科杂志,2013, 33(2):117-122.
[9] 王振宇,王强,王乾章,等.浅谈颈椎后纵韧带骨化症的手术治疗[J].医学与哲学,2013,34(22):62-64,71.
[10] 马雷,申勇,杨大龙,等.前后路手术与单纯前路或后路手术治疗颈椎孤立型后纵韧带骨化症的比较研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012,22(10):884-888.
[11] 王贤,韦敏克,梁斌,等.一期前后联合手术与单纯后路手术治疗重度颈椎后纵韧带骨化症临床疗效的差异分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2013,21(21):2138-2141.
[12] 黄凯,周盛源,唐宇军,等.单节段颈椎后纵韧带骨化症前后路手术的疗效比较[J].脊柱外科杂志,2013,11(3):164-167.
[13] Kawano O, Maeda T, Mori E. Influence of Spinal Cord Compression and Traumatic Force on the Severity of Cervical Spinal Cord Injury Associated With Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament.Spine. 2014;39(14): 1108-1112.
[14] Chin DK, Han IB, Ropper AE, et al. Association of VKORC1-1639G>A polymorphism with susceptibility to ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine: a Korean study. Acta Neurochirurgica. 2013;155(10): 1937-1942.
[15] 任斌,蔡林,陈志龙,等.前路手术治疗合并邻近椎间盘突出的颈椎后纵韧带骨化症[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2012,1(1):46-49.
[16] Passias PG, Wang SB, Wang SL,et al.Combined ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament at C2-3 and invagination of the posterior axis resulting in Myelopathy. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(3):478-486.
[17] Sohn S, Chung CK. Increased Bone Mineral Density and Decreased Prevalence of Osteoporosis in Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament: A Case-Control Study. Calcif Tissue Int. 2013;92(1):28-34.
[18] 郝定均,贺宝荣,许正伟,等.胸椎后纵韧带骨化症术后临床疗效及其相关因素分析[J].脊柱外科杂志, 2012,10(4):215-219.
[19] 鲁世金,潘汉升,刘汝专,等.老年重度颈椎节段型后纵韧带骨化症的手术疗效[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2013,23(4):352-358.
[20] Kudo H, Yokoyama T, Tsushima E. Interobserver and intraobserver reliability of the classification and diagnosis for ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the cervical spine. Eur Spine J. 2013;22 (1):205-210.
[21] Ito K, Yukawa Y, Machino M. Spinal cord cross-sectional area during flexion and extension in the patients with cervical ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament.Eur Spine J. 2013;22(11):2564-2568.
[22] 徐仲阳.胸椎后纵韧带骨化症的分型及治疗方法的选择[J].中国卫生产业,2014,11(6):153-154.
[23] 王振宇,孙元,王强,等.经后路椎管扩大减压术治疗多节段颈椎后纵韧带骨化症[J].医学与哲学,2012,33(22):21-23.
[24] 张本,侯铁胜,沈洪兴,等.颈椎后纵韧带骨化症的手术疗效及影响因素分析[J].广东医学, 2013,34(23):3564-3568.
[25] 王新伟,袁文,陈德玉,等.颈椎后纵韧带骨化症的手术方式选择及疗效[J].中华外科杂志, 2012,50(7):596-600.
[26] 王占朝,陆骅,史建刚,等.前后路联合手术治疗多节段颈椎后纵韧带骨化症[J].实用骨科杂志,2012,18(5):427-430.
[27] 刘俊英,张一,赵金彩,等.后路手术治疗颈椎后纵韧带骨化症患者术后并发症的观察及护理[J].河北医药, 2012,34(4):610-611.
[28] 周珂,祁磊,李牧,等.颈椎后纵韧带骨化症的临床分型及手术方式的选择[J].医学与哲学,2012,33(10):24-26.
[29] 王丽燕.前后路联合手术治疗重症脊髓型颈椎病32例围手术期护理[J].中国药物与临床,2014,14(6):857-858,859.
[30] 刘春雨,金丽,彭宝淦,等.颈椎前路或前后路联合植入物内固定治疗严重后纵韧带骨化症[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(4): 535-540.
[31] 刘长征,马雪海,郑进.后路间接减压植入物内固定与后路椎板切除直视下减压内固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(52):9863-9868.
[32] 徐宏兵.老年腰椎管狭窄症手术治疗的临床研究[D].华中科技大学,2013.
[33] 任斌,蔡林,王建平.后路椎板切除入路手术治疗椎管内神经鞘瘤的疗效[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012,22(8):688-692.
[34] 吴洁石,包聚良,徐瑞生.颈椎后路椎板切除侧块螺钉植骨内固定治疗颈椎管狭窄症[J].江苏医药, 2011,37(5):579-581.
[35] 孟萍,高姗.腰椎后路、椎板切除减压、间盘切除、椎间植骨融合内固定术术后三天功能锻炼指导[J].沈阳医学院学报, 2012, 4(2):103-104.
[36] 胡孔和.颈椎单开门OsteoMed M3钉板内固定椎管扩大成形术生物力学及临床研究[D].南方医科大学, 2011.
[37] 姚广清.非连续椎体次全切除术与单开门手术治疗多节段颈椎病的疗效对比分析[D].华中科技大学,2011.
[38] 陈晓庆,杨惠林,王根林.局麻后路椎板切除减压治疗胸椎黄韧带骨化症[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2009,17(7):544-546.
[39] 刘法敬.胸椎黄韧带骨化症髓内高信号的临床研究与手术治疗策略[D].河北医科大学,2013.
[40] 刘潮坚,蔡拉加,石昭宏.腰椎间盘突出症四种不同术式的疗效比较[J].现代医院, 2011,11(3):46-48. |