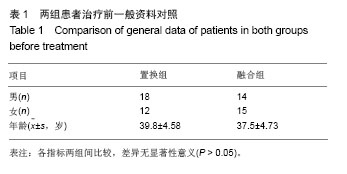
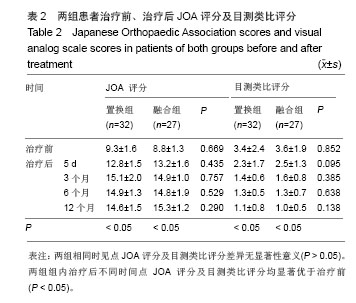
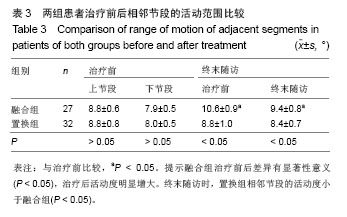
| [1]Verhagen AP,van Middelkoop M,Rubinstein SM,et al.Effect of various kinds of cervical spinal surgery on clinical outcomes:A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain. 2013;154(11): 2388-2396.
[2]Skeppholm M, Olerud C. Comparison of Dysphagia Between Cervical Artificial Disc Replacement and Fusion: Data From a Randomized Controlled Study With Two Years of Follow-up. Spine. 2013;38(24):E1507-1510.
[3]张雪松,张永刚,肖嵩华,等.单节段人工椎间盘置换治疗颈椎病的中长期疗效[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012,22(10):879-883.
[4]Goffin J,van Loon J,Van Calenbergh F,et al. A clinical analysis of 4 and 6 year follow-up results after cervical disc replacement surgery using the Bryan Cervical Disc Prosthesis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2010;12(3):261-269.
[5]Hilibrand AS,Carlson GD,Palumbo MA. Radiculopathy andmyelopathy at segments adjacent to the site of a previous anterior cervical arthrodesis. Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;(4): 519-528.
[6]Park JJ,Quirno M,Cunningham MR,et al.Analysis of segmental cervical spine vertebral motion after prodisc-C cervical disc replacement.Spine. 2010;35(8):E285-289.
[7]Heller JG, Sasso RC, Papadopoulos SM, et al. Comparison of Bryan cervical disc arthroplasty with anterior cervical decompression and fusion. Spine. 2009;34(2):101-107.
[8]田伟,阎凯,于杰,等. Bryan人工间盘置换与前路减压融合治疗颈椎退行性疾病的中期随访[J].中华骨科杂志,2013,33(2):97-104.
[9]Grupp TM,Meisel HJ,Cotton JA,et al. Alternative bearing malerials for intervertebral disc arthruplasty. Biomaterials. 2009;31(3):523-531.
[10]孙宇,刘忠军.颈椎病外科治疗的回顾[J].北京大学学报, 2002, 34(5):627-629.
[11]王振国.颈椎病发病机制与外科治疗[J].中外健康文摘, 2010, 7(10):166-167.
[12]楼永坚,陈红卫.颈椎病手术治疗进展[J].医学综述, 2012,18(20): 3419-3422.
[13]Bryan VE Jr. Cervical motion segment replacement. Eur Spine. 2002;11(Suppl 2):S92-S97.
[14]胥少汀,葛宝丰.实用骨科学[M]. 4版.北京:人民军医出版社, 2012.
[15]Zhang X,Zhang X,Chen C, et al. Randomized, controlled, multicenter, clinical trial comparing Bryan cervical discarthroplasty with anterior cervical decompression and fusion in china.Spine. 2012;37(6): 433-438.
[16]Park DH,Ramakrishnan P,Cho TH,et al. Effect of lower two level anterior cervical fusion on the superior adjacent level. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;7(3):336-340.
[17]Lu Y, McAnany SJ, Hecht AC, et al. Utilization Trends of Cervical Artificial Disc Replacement After FDA Approval Compared With Anterior Cervical Fusion: Adoption of New Technology. Spine. 2014;39(3):249-255.
[18]王自洲,柳达,付勤.人工颈椎间盘置换术与颈椎前路减压植骨融合术治疗颈椎病的效果比较[J].中国当代医药,2013,20(15):4-6.
[19]戚小忠,徐宏光.颈椎间盘置换术治疗颈椎病的短期疗效观察[J]. 皖南医学院学报,2013,32(2):107-109.
[20]Heller JG, Sasso RC, Papadopoulos SM, et al. Comparison of Bryan cervical disc arthroplasty with anterior cervical decompression and fusion. Spine. 2009;34(2):101-107.
[21]孙宇,赵衍斌,周菲菲,等.颈椎人工椎间盘置换后对邻近节段退变的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(6):474-479.
[22]蒋涛,任先军,王卫东, 等.人工颈椎间盘置换对邻近节段椎间盘的保护作用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(7):529-533.
[23]Yang B, Li H, Zhang T, et al.The incidence of adjacent segment degeneration after cervical disc arthroplasty (CDA):a meta analysis of randomized controlled trials. PloS One. 2012; 7(4):e35032.
[24]Lehmberg J,Meyer B. Anterior cervical discectomy and implantation of an artificial disc (Prestige,Medtronic).Eur Spine. 2013;22(3):675-677.
[25]Coric D, Nunley PD, Guyer RD, et al. Prospective, randomized,multicenter study of cervical arthroplasty: 269 patients from the Kineflex/C artificial disc investigational device exemption study with a minimum 2-year follow-up: clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine. 2011;15(4):348-358.
[26]薛翔.颈椎人工椎间盘置换术研究进展[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2014,28(3):217-219.
[27]Du J,Li M,Liu H,et al.Early follow-up outcomes after treatment of degenerative disc disease with the discover cervical disc prosthesis. Spine. 2011;11(4):281-289.
[28]Wang Q, Cheng H, Mao Z, et al. Clinical and radiographic results after treatment of cervical degenerative disc disease with the bryan disc prosthesis :a prospective study with 2-year follow-up. Acta Orthop Belgica. 2011;77(6):809-815.
[29]叶凯山,王栓科.人工颈椎间盘置换术治疗脊髓型颈椎病的疗效观察[J].临床骨科杂志,2013,16(6):608-610.
[30]Lee JH, Kim JS, Lee JH, et al. Comparison of cervical kinematics between patients with cervical artificial disc replacement and anterior cervical discectomy and fusion for cervical disc herniation. Spine J. 2014;14(7):1199-1204. |