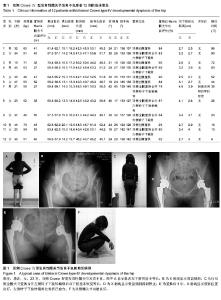
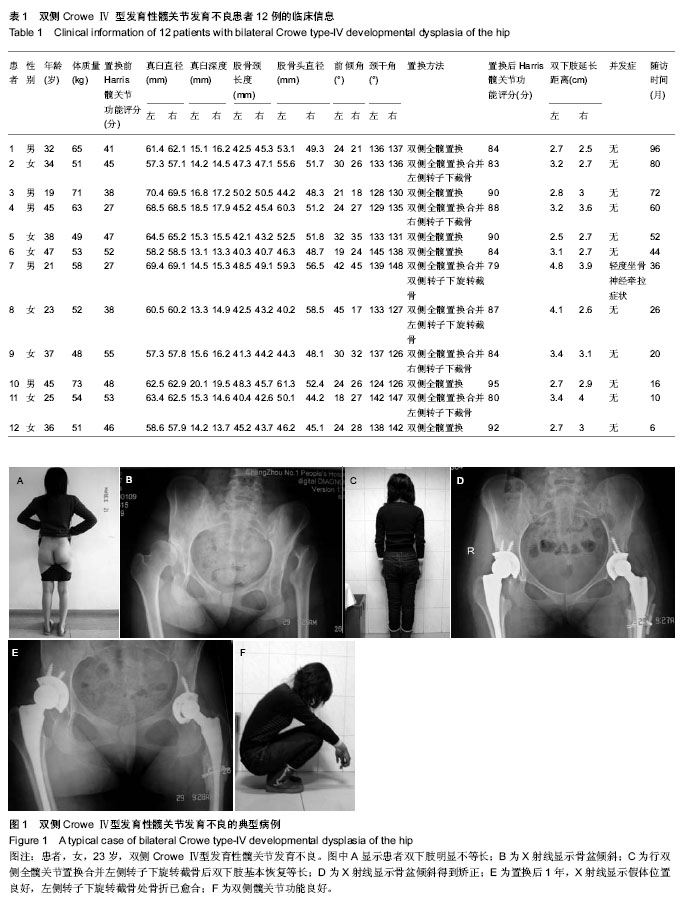
| [1] Sochart DH, Porter ML. The long-term results of Charnley low-friction arthroplasty in young patients who have congenital dislocation, degenerative osteoarthrosis, or rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79(11): 1599-1617.
[2] 李文波,张文明,白国昌,等.人工全髋关节置换术治疗成人Crowe IV 型先天性髋关节发育不良伴脱位[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2013,27(10):1153-1156.
[3] 孙启才,王祥华,宋柏杉,等.S-ROM假体全髋关节置换治疗Crowe IV 型髋关节发育不良[J].中国骨伤,2013,26(2):153- 157.
[4] Charity JA, Tsiridis E, Sheeraz A, et al. Treatment of Crowe IV high hip dysplasia with total hip replacement using the Exeter stem and shortening derotational subtrochanteric osteotomy. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(1):34-38.
[5] 刘兴炎,葛宝丰,甄平,等.全髋关节置换治疗伴有股骨头坏死的成人先天性髋关节脱位[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008,23: 462-464.
[6] Lund KH, Termansen NB. Hip replacement for congenital dislocation and dysplasia. Acta Orthop Scand. 1985;56(6): 464-468.
[7] 朱振安,戴尅戎,王友,等.全髋关节置换术治疗成人Crowe IV 型先天性髋关节脱位的临床研究[J].中华外科杂志,2006,44:1403- 1406.
[8] 雷鹏飞,胡懿郃,蔡碰德,等.大转子截骨非骨水泥全髋置换治疗成人髋关节发育不良[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(44):8191- 8195.
[9] Neumann D, Thaler C, Dorn U. Femoral shortening and cementless arthroplasty in Crowe type 4 congenital dislocation of the hip. Int Orthop. 2012;36(3):499-503.
[10] Farrell CM, Berry DJ, Cabanela ME. Autogenous femoral head bone grafts for acetabular deficiency in total-hip arthroplasty for developmental dysplasia of the hip: long-term effect on pelvic bone stock. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(6): 698-702.
[11] 赵文杰,郑连杰,何盛为,等.全髋关节置换术治疗成人高位先天性髋关节脱位[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2007,22:491-492.
[12] Chougle A, Hemmady MV, Hodgkinson JP. Severity of hip dysplasia and loosening of the socket in cemented total hip replacement. A long-term follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(1):16-20.
[13] Sanchez-Sotelo J, Berry DJ, Trousdale RT, et al. Surgical treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip in adults: II. Arthroplasty options. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2002;10(5): 334-344.
[14] Edwards BN, Tullos HS, Noble PC. Contributory factors and etiology of sciatic nerve palsy in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987;(218):136-141.
[15] Eggli S, Hankemayer S, Müller ME. Nerve palsy after leg lengthening in total replacement arthroplasty for developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999;81(5):843-845. |