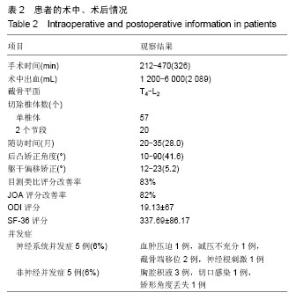
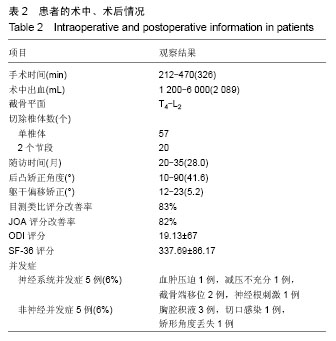
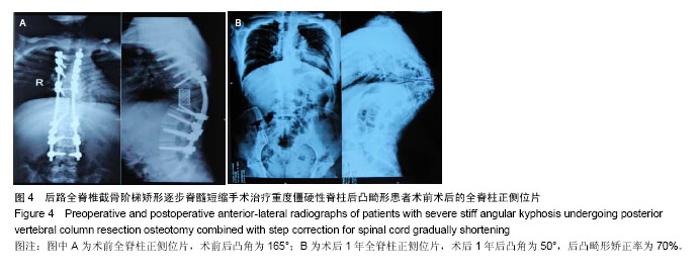
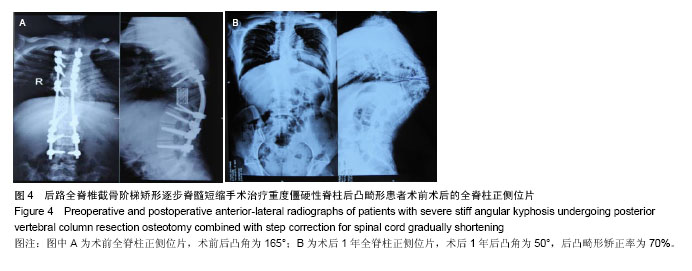
| [1] 仉建国,张新华,邱贵兴,等.特发性脊柱侧凸远端融合椎的选择[J].中华骨科杂志,2010,30(4):321-324.
[2] 陆明, Fischenko VY, Vleschenko VA,等. 脊柱侧凸患者椎间盘结构特点的相关病因学研究[J].临床医学工程杂志,2010, 17(3): 1-4.
[3] 陆明, Fischenko VY, Vleschenko VA,等. 在分子生物学水平对脊柱侧凸患者椎旁肌结构特点进行相关的病因学研究[J].临床医学工程杂志,2010, 17(5): 1-3.
[4] 陆明, Fischenko VY, Vleschenko VA,等. 脊柱侧弯患者椎旁肌组织单体的放射性核素衍射研究和肌短缩蛋白的生物化学特性观察[J].临床医学工程杂志, 2010,17(7):1-4.
[5] 陆明,Fischenko VY, Vleschenko VA,等. 特发性脊柱侧凸患者髓核结构特点及相关病因学[J].中国组织工程与临床康复,2010, 14(37): 7008.
[6] 孙永生,梁朝,温建民.腰椎融合及其临床应用策略[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2011,5(16):4621-4626.
[7] 颜连启,宦诚,孙钰,等. 腰椎融合固定和非融合固定生物力学分析[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2011,5(16):4432-4437.
[8] 石洋,常楚,杨璐,等.后外侧植骨融合与后路椎间植骨融合治疗腰椎退行性疾病的疗效评价[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2011, 5(8): 2394-2398.
[9] 王岩,张永刚,郑国权,等.脊柱去松质骨截骨治疗僵硬性脊柱侧后凸的有效性及安全性分析[J]. 中华外科杂志,2010,48(22): 1701-1704.
[10] 范建平,王传锋,朱晓东,等.Ponte截骨治疗成年人特发性脊柱侧后凸疗效分析[J].临床骨科杂志,2013,16(2):121-124.
[11] Hamzaoglu A,Alanay A,Ozturk C,et al.Posterior vertebral column resection in severe spinal deformities: a total 102cases. Spine(Phla Pa1976). 2011;36(5):E340-344.
[12] 姚子明,仉建国,邱贵兴,等.一期后路全脊椎切除治疗重度脊柱畸形围手术期并发症及相关危险因素分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2013, 33(5):440-446.
[13] Lenke LG,Sides BA,Koester LA,et al. Vertebral column resection for the treatment of severe spinal deformity. Clin Orthop Res. 2010;(468):687-699.
[14] Lenke LG,O’Leary PT,Bridwell KH,et al. Posterior vertebral column resection for severe pediatric deformity minimum two year follow-up of thirty-five consecutive patients. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(20):2213-2221.
[15] Xie J, Wang Y, Zhao Z, et al. Posterior vertebral column resection for correction of rigid spinal deformity curves greater than 100°. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;17(6):540-551.
[16] Lenke LG, Newton PO, Sucato DJ, et al. Complications after 147 consecutive vertebral column resections for severe pediatric spinal deformity: a multicenter analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(2):119-132.
[17] Ma HS, Chen ZM, Yang B, et al. [Analysis of neurological deficits complications in the treatment of spinal deformity with posterior spinal osteotomy]. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012; 50(4):328-332.
[18] Schairer WW, Carrer A, Lu M, et al. The Increased Prevalence of Cervical Spondylosis in Patients with Adult Thoracolumbar Spinal Deformity. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014.
[19] Kanter AS, Shaffrey CI, Mummaneni P, et al.Introduction: Adult spinal deformity: pathophysiology and corrective measures. Neurosurg Focus. 2014;36(5): doi: 10.3171/2014.3.FOCUS14112.
[20] Fujimori T, Inoue S, Le H, et al. Long fusion from sacrum to thoracic spine for adult spinal deformity with sagittal imbalance: upper versus lower thoracic spine as site of upper instrumented vertebra. Neurosurg Focus. 2014;36(5):E9.
[21] Fu J, Liu C, Zhang G, et al. Pulmonary Function Improvement in Patients With Ankylosing Spondylitis Kyphosis Following Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014. [Epub ahead of print].
[22] Clement JL, Chau E, Geoffray A, et al. Restoration of thoracic kyphosis by simultaneous translation on two rods for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2014. [Epub ahead of print]. |