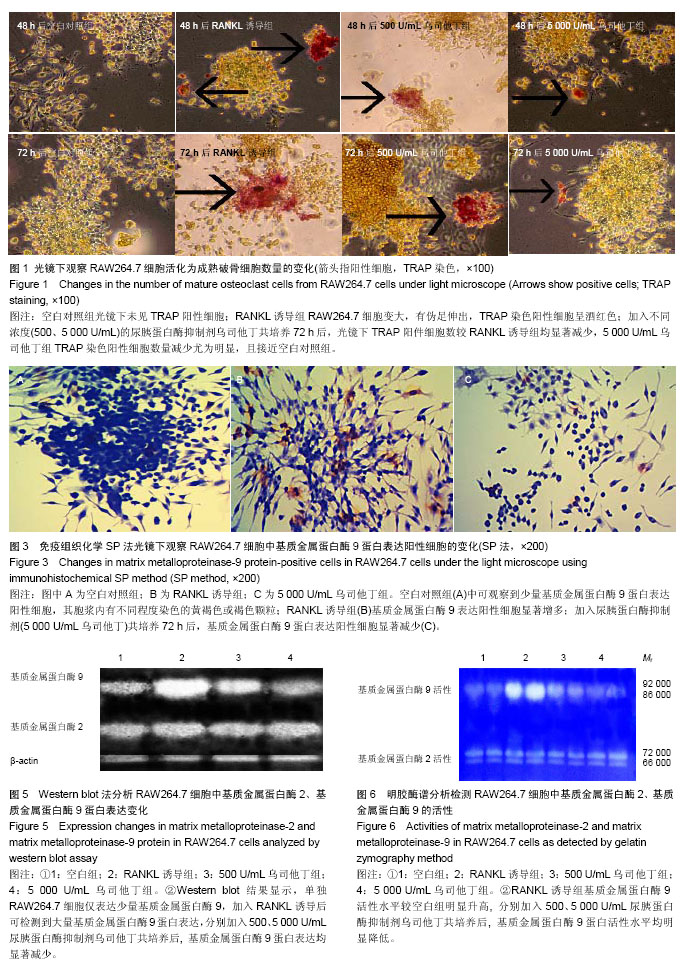
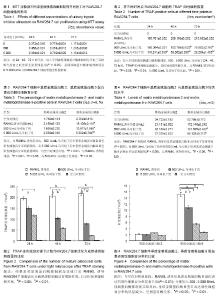
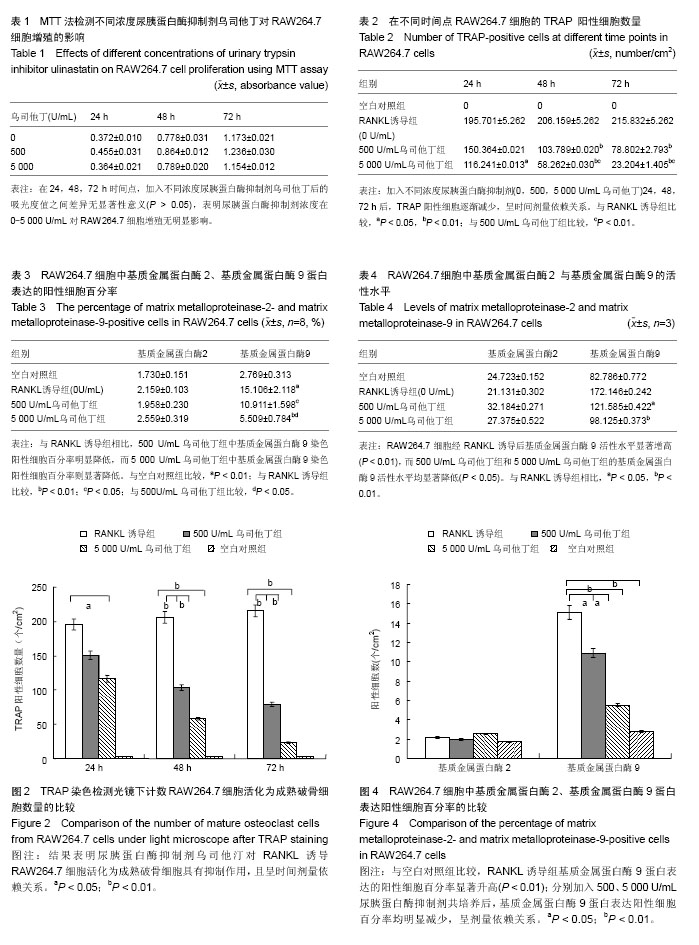
| [1] Athanasou NA,Quinn J,Bulstrode CJ.Resorption of bone byinflammatory cells derived from the joint capsules of hip arthroplasties.J Bone Joint Surg Br.1992;74(1):57-62.
[2] Ulrich SD,Seyler TM,Bennett D,et al.Total hip arthroplasties: What are the reasons for revision? Int Orthop.2008;32(5): 597-604.
[3] Gallo J,Slouf M,Goodman SB.The relationship of polyethylene wear to particle size, distribution, and number: A possible factor explaining the risk of osteolysis after hip arthroplasty.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2010;94(1):171-177.
[4] Abdelmoula LC,Ben M'barek R,Ben Hadj Yahia C,et al. Bisphosphonates: indications in bone diseases other than osteoporosis.Tunis Med. 2011;89(6):511-516.
[5] Wilkinson JM,Little DG.Bisphosphonates in orthopedic applications. Bone.2011;49(1):95-102.
[6] Ren W,Markel DC.Emerging ideas: can erythromycin reduce the risk of aseptic loosening?Clin Orthop Relat Res.2011; 469(8):2399-2403.
[7] Ren W,Zhang R,Hawkins M,et al.Efficacy of periprosthetic erythromycin delivery for wear debris-induced inflammation and osteolysis.Inflamm Res.2010;59(12):1091-1097.
[8] 余剑,赵建宁.破骨细胞活化过程中免疫内酯LY267108对核因子κB的抑制[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(15):2309-2313.
[9] Gu Y,Lee HM,Sorsa T,et al.Doxycyline inhibits mononuclear cell-mediated connective tissue breakdown.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol.2010;58(2):218-225.
[10] Ong SM,Taylor GJ.Doxycycline inhibits bone resorption by human interface membrane cells from aseptically loose hip replacements.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2003;85(3):456-461.
[11] Wu YJ,Ling Q,Zhou XH,et al.Urinary trypsin inhibitor attenuates Heptic ischemia-reperfusion injury by reducing nuclear factor-kappa B activation.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int.2009;8(1):53-58.
[12] Inoue K,Takano H,Yanagisawa R, et al.Protective effects of urinary trypsin inhibitor on systemic inflammatory response induced by lipopolysaccharide.J Clin Biochem Nutr,2008; 43(3):139-142.
[13] Inoue K, Takano H. Urinary trypsin inhibitor as a therapeutic option for endotoxin related inflammatory disorders. Expert Opin Investig Drugs,2010,19(4):513-520.
[14] 葛叶盈,徐云,成建庆,等.乌司他丁对老年髋关节置换患者术后并发症影响的病例对照研究[J].中国骨伤,2011,24(6):459-462.
[15] Lee JY,Lee JY,Chon JY,et al.The effect of ulinastatin on hemostasis in major orthopedic surgery.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2010;58(1):25-30.
[16] Hua G,Haiping Z,Baorong H,et al.Effect of Ulinastatin on the Expression of iNOS, MMP-2, and MMP-3 in degenerated nucleus pulposus cells of rabbits.Connective Tissue Res. 2013;54(1):29-33.
[17] Jiang Y,Jia T,Gong W,et al.Titanium particle-challenged osteoblasts promote osteoclastogenesis and osteolysis in a murine model of periprosthestic osteolysis.Acta Biomater. 2013;9(7):7564-7572.
[18] Krane SM,Inada M.Matrix metalloproteinases and bone.Bone. 2008; 43(1):7-18.
[19] Chen D,Zhang X,Guo Y,et al.MMP-9 inhibition suppresses wear debris-induced inflammatory osteolysis through downregulation of RANK/RANKL in a murine osteolysis model.Int J Mol Med.2012;30(6):1417-1423.
[20] Gallo J,Goodman SB,Konttinen YT,et al.Particle disease: biologic mechanisms of periprosthetic osteolysis in total hip arthroplasty. Innate Immun.2013;19(2):213-224.
[21] Yamanaka Y,Clohisy JC,Ito H,et al.Blockade of JNK and NFAT pathways attenuates orthopedic particle-stimulated osteoclastogenesis of human osteoclast precursors and murine calvarial osteolysis. J Orthop Res.2013;31(1):67-72.
[22] Okada Y,Naka K,Kawamura K,et al.Localization of matrix metallo-proteinase 9 (92-kilodalton gelatinase/type IV collagenase = gelatinase B) in osteoclasts: implications for bone resorption.Lab Invest.1995;72(3):311-322.
[23] Engsig MT,Chen QJ,Vu TH,et al.Matrix metalloproteinase 9 and vescular endothelial growth factor are essential for osteoclast recruitment into developing long bones.J Cell Biol. 2000;151(4):879-889. |