Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (18): 2933-2938.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.18.025
Previous Articles Next Articles
The treatment of wounds caused by rejection after allogeneic bone transplantation: traditional wound dressing and vacuum sealing drainage
Zhang Nu, Zhang Chun, Liu Shi-qing
- Third Department of Orthopedics, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430060, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2014-04-02Online:2014-04-30Published:2014-04-30 -
About author:Zhang Nu, M.D., Associate chief physician, Third Department of Orthopedics, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430060, Hubei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Nu, Zhang Chun, Liu Shi-qing. The treatment of wounds caused by rejection after allogeneic bone transplantation: traditional wound dressing and vacuum sealing drainage[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(18): 2933-2938.
share this article

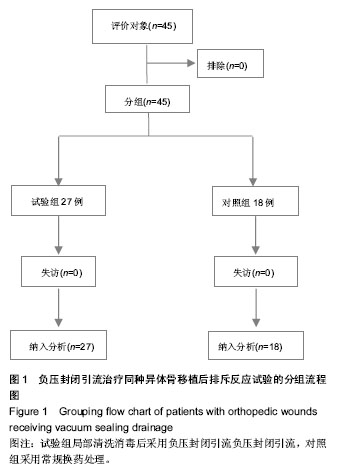
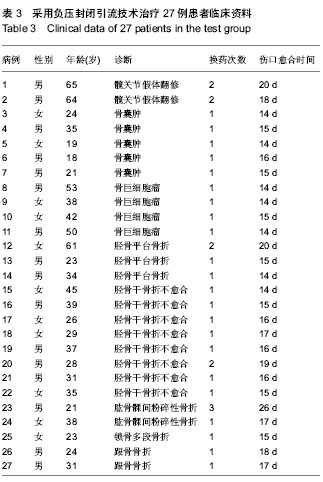
2.3 基线资料比较 两组性别比例、年龄、术后排斥反应出现的时间及持续时间等基线资料比较差异无显著性意义,具有可比性。 2.4 两组治疗效果比较 两组患者在同种异体骨移植后7-14 d出现排斥反应,表现为伤口渗液,渗出淡红色清亮液体,伤口周围无红肿,无压痛,皮温不高,全身无发热,渗出液涂片未发现脓球,细菌培养无细菌生长。两组均行抗生素预防感染及口服醋酸泼尼松治疗。 试验组27例患者应用负压封闭引流治疗,由于排斥反应延续时间一般为5-7 d,故22例使用负压封闭引流1次后伤口愈合,4例由于排斥反应延续时间较长,故在7 d后更换负压封闭引流,1例患者出现发热,患肢肿痛加剧,闻到异味,看到泡沫内出现黄绿色、灰褐色等污点,考虑为感染,遂拆除负压封闭引流,伤口分泌物作涂片及细菌培养,伤口行清创去除同种异体骨和内固定材料,改为持续灌注冲洗引流,期间行传统换药2次,伤口愈合。总之试验组平均换药次数为1.22次,伤口平均愈合时间为16.26 d,伤口感染率为4%,取得了较好的治疗效果。 对照组18例应用传统换药治疗,根据伤口渗液量,每日换药更换无菌敷料一二次,渗液量减少后改为隔日换药1次,每次换药尽量挤出伤口内的积液,一般7-14 d后伤口愈合,伤口平均愈合时间为21.06 d,其中有5例出现了伤口感染,感染率为28%,表现为患者出现发热,患肢肿痛加剧,伤口分泌物黏稠,黄绿色,闻到异味,遂行伤口清创去除同种异体骨,改为持续灌注冲洗引流治疗后伤口愈合。 比较两组间伤口换药次数、愈合时间及伤口感染率数据差异均有显著性意义,见表1-3,试验组较对照组创面愈合时间明显缩短,换药次数明显减少,极大地减轻了临床医生的工作强度。"

| [1] Czitrom AA,Axelrod T,Fernandes B.Antigen presenting cells and bone allotransplantation.Clin Orthop.1985;197:27-31. [2] Horawitz MC,Friedlaender GE.Induction of specific T-cell responsivenes to allogemeic bone.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991;73(8):1157-1168. [3] 陈实.移植免疫学[M].武汉:湖北科学技术出版社,1998:89-92. [4] Phiatanakul WP,Vande Vord PJ,Teitge RA,et al.Immune resonse in patients receiving fresh osteochondral allografts. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ).2004;33(7):345-488. [5] 封兴华,丁鸿才,刘斌.深低温冷冻对降低异体骨抗原性作用的实验研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,1995,11(4):248-251. [6] 陆军,吴苏稼,施鑫.同种异体骨移植的免疫反应[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2002,9(4):388-391. [7] Wingenfeld C,Egli RJ,Hemfing A,et al.Cryoreservation of osteochondral allografts: direthyl sulfoxide romotes angiogenesis and immune tolerance in mice. J Bone Joint Surg.2002;84:1420-1429. [8] Guo S,Feng W,Jia Y.Lyophilized small-segment allogeneic bone in repairing bone defect due to benign bone tumor and tumor-like lesions after resection and curettage. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2007;21(8):789-792. [9] Buecker PJ Gebhardt MC.Are fibula strut allografts a reliable alternative for periarticular reconstruction after curettage for bone tumors. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007; 461:170-174. [10] Smrke D,Gubina B,Domanoviç D,et al.Allogeneic platelet gel with autologous cancellous bone graft for the treatment of a large bone defect.Eur Surg Res. 2007;39(3):170-174. [11] Preston RD,Meinberg TA,Payne JB,et al.Inflammatory mediator release following bone grafting in humans: a pilot study.J Clin Periodontol.2007;34(9):797-804. [12] Constantinos K,Stephanie B,Christopher SA,et al. Bacterial Colonization of Bone Allografts: Establishment and Effects of Antibiotics. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2010; 468:2113-2121. [13] 张旗,建强,罗乐宣,等.冷冻干燥60 钴灭菌表面脱钙异体骨移植的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,1999,16(4):313-314. [14] 张春喜.大量同种异体骨(段)应用于大块骨缺损后激素的应用[J].中国医疗前沿,2008,3(20):7-9. [15] Fleischmann W,Strecker W,Bombelli M. Vacuum sealing as treatment of soft damage in open fractures. Unfallchirurg. 1993;96(9):488-492. [16] 裘华德,王彦峰.负压封闭引流技术介绍[J].中国实用外科杂志, 1998,18(4):233-234. [17] 李钊伟,杨杰山.负压封闭引流技术在治疗骨科复杂创面的治疗进展[J].青海医药杂志,2011,41(5):92-94. [18] 王虔.负压封闭引流术在骨科的应用进展[J].辽宁医学院学报, 2012,33(1):91-93. [19] 张一,田晓滨,韩伟,等.负压封闭引流技术在四肢开放性骨折并皮肤软组织缺损中的应用[J].贵州医药,2008,32(12):1086-1088. [20] 陈林.负压封闭引流技术在四肢开放性骨折并皮肤软组织缺损中的应用[J].临床医学, 2010,30(8):27-28. [21] 蒋国群,胡永才,周海洋,等.负压封闭引流技术辅助下游离植皮修复骶尾部压疮疗效观察[J].现代医药卫生,2013,29(12): 1861- 1862. [22] 曲家富,闫荣亮,王良,等.负压封闭引流技术结合肌瓣转移游离植皮治疗小腿及足踝部软组织缺损伴骨外露[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2013,15(4):316-319. [23] Deijkers RL,Bouma GJ,van der Meer-Prins EM,et al.Human bone allografts can induce T cells with high affinity for donor antigens. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1999;81:538-544. [24] 张培琴,谭家华,王松,等.醋酸强的松龙在同种异体骨移植中的应用[J].山东医药,2010,50(19):53-54. [25] 王昌建,姚元章.负压封闭引流治疗肢体远端慢性感染及溃疡创面[J].创伤外科杂志, 2005,7(4):306. [26] Liao Q,Xu J,Weng XJ,et al.Effectiveness of vacuum sealing drainage combined with anti-taken skin graft for primary closing of open amputation wound.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2012;26(5):558-562. [27] Ren GH,Li JW,Li RG,et al.Treatment of large circular soft tissue defect in lower extremities with a combination of bridge flaps and free skin graft covered by vacuum sealing drainage.Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi.2012;50(1):39-44. [28] Li RG,Ren GH,Tan XJ,et al.Free flap transplantation combined with skin grafting and vacuum sealing drainage for repair of circumferential or sub-circumferential soft-tissue wounds of the lower leg.Med Sci Monit.2013;19:510-517. [29] Cen S,Huang F,Yang T,et al. Early use of vacuum sealing drainage to repair the wound of the injured in Wenchuan earthquake.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009;23(6):657-659. [30] Stannard JP,Singanamala N,Volgas DA.Fix and flap in the era of vacuum suction devices: What do we know in terms of evidence based medicine?Injury.2010;41(8):780-786. [31] Zhang L,Quan C,Jiang J,et al.The combined application of dissociate skin flap and vacuum sealing drainage on the defect of the large neck neoplasms after surgical procedures. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi.2012; 26(24): 1113-1135. [32] Lei J,Li HS,Hao ZM,et al.Mode of debridement, negative-pressure therapy combined with tissue transplantation for treatment of complicated and refractory wounds.Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi.2011;27(6):456-460. [33] Li RG,Yu B,Wang G,et al.Sequential therapy of vacuum sealing drainage and free-flap transplantation for children with extensive soft-tissue defects below the knee in the extremities.Injury. 2012;43(6):822-828. [34] Dosluoglu HH,Loghmanee C,Lall P,et al.Management of early (<30 day) vascular groin infections using vacuum-assisted closure alone without muscle flap coverage in a consecutive patient series.J Vasc Surg. 2010;51(5):1160-1166. [35] Wei D,Wang Y,Yuan J,et al.One-stage operation for pelvis and acetabular fractures combined with Morel-Lavallée injury by internal fixation associated with vacuum sealing drainage.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014; 28(1):38-42. [36] Zhang WK,Zhang WK,Wang HB,et al.Vacuum sealing drainage and free coupling chain-link posterior tibial artery flap in the reconstruction of degloving injury of propodium. Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi.2013;29(4): 258-260. [37] Qu J,Yan R,Wang L,et al.Free dermatoplasty combined with vacuum sealing drainage for the treatment of large-area soft tissue defects accompanied by bone exposure in the lower leg.Exp Ther Med.2013;5(5):1375-1380. [38] Liu G,Pan SP,Chen XP.Vacuum sealing drainage for the treatment of in postoperative wound disunion after calcaneal fracture.Zhongguo Gu Shang.2012;25(9):782-784. [39] Guo XB,Li JS,Zhang JF,et al.Application of the vacuum sealing drainage technique combined with skin flap in chronic ulcerative wounds.Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi.2012; 28(4):270-273. |
| [1] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [2] | Jiang Xin, Qiao Liangwei, Sun Dong, Li Ming, Fang Jun, Qu Qingshan. Expression of long chain non-coding RNA PGM5-AS1 in serum of renal transplant patients and its regulation of human glomerular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 741-745. |
| [3] | Mu Yufeng, Wei Lina, Wu Yong, Shao Anliang, Chen Liang, Qu Shuxin, Xu Liming. Development and evaluation of alpha-galactosyl antigen-deficient rabbit model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 281-285. |
| [4] | Tian Lin, Shi Xiaoqing, Mao Jun, Zhang Nongshan, Zhang Li, Xing Runlin, Wang Peimin. Meta-analysis of vacuum-sealing drainage combined with antibiotic bone cement in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2618-2624. |
| [5] | Cai Hongmei, Wang Wei, Wang Wenjuan, Zhou Xiaohong. Kinesiology taping combined with manual lymph drainage reduces postoperative lymphedema related to breast cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2247-2251. |
| [6] | Li Liqiang, Jiao Longxing, Zhang Wu, Yan Wentao, Li Jian, Li Minghao. Effect of immature dendritic cells derived from bone marrow on rejection of orthotopic liver transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2025-2029. |
| [7] | Hua Hong, Xie Tongling, Hao Guiliang. Immunomodulatory effect of human adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells on skin transplantation between different mouse strains [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 73-77. |
| [8] | Wang Jing, Xu Shuai, Liu Haiying. Hidden blood loss during posterior lumbar interbody fusion in lumbar spinal stenosis patients with and without rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(33): 5307-5314. |
| [9] | Hou Senrong, Yang Weiyi, Luo Minghui, Pan Jianke, Huang Hetao, Zeng Lingfeng, Liu Jun, Liang Guihong. Perioperative management strategy without drainage tube after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(33): 5371-5378. |
| [10] | Zhao Xin, Shi Xin, Chen Bei, Cao Yanpeng, Chen Yaowu, Liu Xiaoren, He Yusheng, He Liyun, Li Xiying, Liu Jun. Vacuum sealing drainage enhances wound healing by up-regulating collagen type I/III ratio in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5122-5127. |
| [11] |
Gu Yingxuan, Huang Linfeng, Hu Xiaohui, Quan Xiaoming, Kang Liangqi, Zhou Linghan, Wang Xiaojun.
Platelet-rich plasma combined with negative pressure for chronic refractory wounds: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4257-4264. |
| [12] | Liu Ting, Yang Tingting, Ma Xiaona, Ma Haibin, Jin Yiran, Liang Xueyun. Immunoregulation of allograft rejection: a role played by human CD200+ sub-population from human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(13): 2068-2073. |
| [13] | Liu Zhiling, Gao Minghong, Chen Yingxin. Bio-engineering cornea versus human donor cornea in the treatment of fungal corneal ulcer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(10): 1563-1569. |
| [14] | Yuan Bo, Wang Zhiwei, Tang Yifan, Zhou Shengyuan, Chen Xiongsheng, Jia Lianshun. Construction of polycaprolactone-tricalcium phosphate with different mixture ratios using three-dimensional printing technology and its osteoinductivity in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 821-826. |
| [15] | Lu Chao, Liu Wengang, Wu Huai, Ye Guozhu, Chen Guocai, Chen Jin. Sealing of intramedullar femoral canal for blood loss after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 636-642. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||