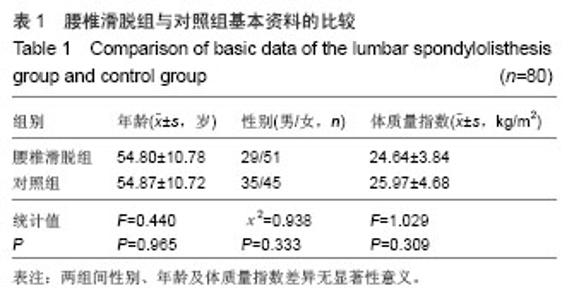
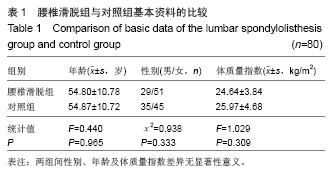
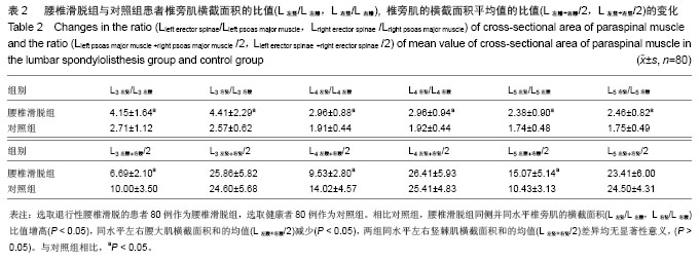
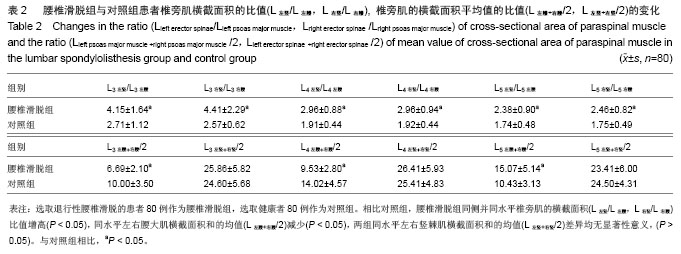
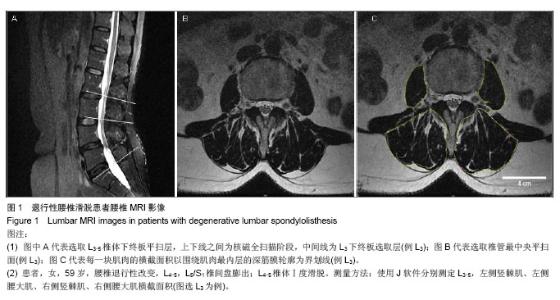
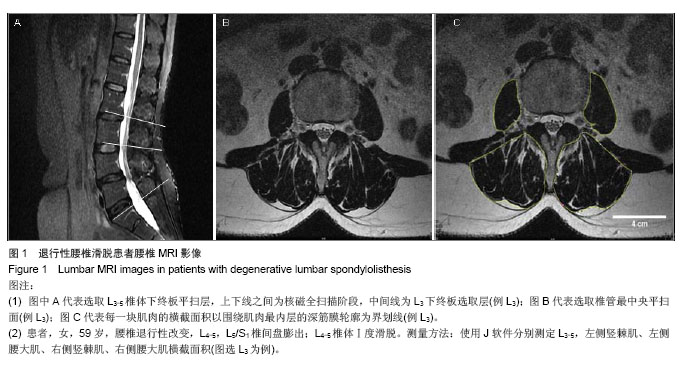
| [1]马超,吴继彬,赵猛,等.不同手术方法治疗老年退变性腰椎滑脱合并腰椎管狭窄症疗效的比较[J].中华医学杂志,2012,92(9): 620-623. [2]谢冬晓,丁文元,申勇,等.退变性腰椎侧凸两侧椎旁肌的影像学差异及其临床意义[J].中华外科杂志,2012,50(11):975-980. [3]Berlemann U, Jeszenszky DJ, Buhler DW. Facet joint remodeling indegenerative spondylolisthesis:an investigation of joint orientation and tropism. Eur Spine J. 1998;7(5):376-380. [4]Love TW, Fagen AB, Fraster RD. Degenerative spondylolisthesis development or acquired. J Bone Joint Surg. 1999;81:670-674. [5]Fujiwara A, Tamai K, An HS, et al. Orientation and osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joint. Clin Orthop. 2001;385: 88-94. [6]Goni V, Gopinathan NR, Saini YC, et al. Traumatic L5 over S1 spondyloptosis without neurological involvementmanaged nonoperatively: a case report. Chin J Traumatol. 2013;16(3): 178-181. [7]Huang KY, Lin RM, Lee YL, et al. Factors affecting disability and physical function in degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis of L4-5: evaluation with axially loaded MRI. Eur Spine J. 2009;18:1851-1857. [8]Masharawi Y, Rothschild B, Dar G, et aI. Facet orientation in the thoracolumbar spine: three dimensional anatomic and biomechanical analysi. Spine. 2004;29(16):1755-1763. [9]Cohen SP, Raja S. Pathogenesis,diagnosis,and treatment of lumbar zygapophysial(facet)joint pain. Anesthesiology. 2007; 106(3):591-614. [10]Carrera GF, Haughton VM, Syvertsen A, et al.Computed tomography of the lumbar facet joints. Radiology. 1980; 134(1):145-158. [11]周承涛,刘红,李守旭,等.腰椎关节突关节的X线基础研究及临床意义[J].中华骨科杂志,1996,16(7):438-440.[12]Fujiwara A, Tamai K, An HS, et al. Orientation and osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joint. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(385):88-94.[13]Regev GJ, Kim CW, Tomiya A, et al. Psoas muscle architectural design,in vivo sarcomere length range, and passive tensile properties support its role as a lumbar spine stabilizer. Spine. 2011;36(26):E1666-E1674.[14]Lattig F, Fekete TF, Grob D, et al. Lumbar facet joint effusion in MRI: a sign of instability in degenerative spondylolisthesis? Eur Spine J. 2012;21:276-281. [15]Logroscino CA, Tanburrelli FC, Scaramuzzo L, et al. Transdiscal L5-S1 screws for the treatment of adult spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(1):S128-S133. [16]Périé D, Curnier D. Effect of pathology type and severity on the distribution of MRI signal intensities within the degenerated nucleus pulposus: application to idiopathic scoliosis and spondylolisthesis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010;11:189. [17]张路,蔡玉新,张立明.腰椎滑脱影像学分析及诊断[J].新疆医学, 2012,42:113-114.[18]宋玉鸿,孙敏,刘庆鸿.腰椎峡部裂并脊柱滑脱的矢状位MRI表现[J].临床辅助检查,2011,13(28):206-207. [19]Michele C, Riikka N, Laura E. Is level- and side-specific multifidus asymmetry a marker for lumbar disc pathology? The Spine Journal. 2012;12(10):932-939. [20]Klessinger S. Radiofrequency neurotomy for treatment of low back pain in patients with minor degenerative spondylolisthesis. Pain Physician. 2012;15(1):E71-E78. [21]Caterini R, Mancini F, Bisicchia S, et al. The correlation between exaggerated fluid in lumbar facet joints and degenerative spondylolisthesis: prospective study of 52 patients. J Orthopaed Traumatol. 2011;12:87-91. [22]Tarantino U, Fanucci E, Iundusi R, et al. Lumbar spine MRI in upright position for diagnosing acute and chronic low back pain: statistical analysis of morphological changes. J Orthopaed Traumatol. 2013;14:15-22. [23]范顺武,赵兴.腰椎不稳和腰椎滑脱的相关问题[J].中国骨伤, 2010,23(4):241-244. [24]Jeong HY, You JW, Sohn HM, et al. Radiologic Evaluation of Degeneration in Isthmic and Degenerative Spondylolisthesis. Asian Spine J. 2013;7(1):25-33. [25]周海燕.腰椎退行性变586例X线表现[J].蚌埠医学院学报,2010, 35(11):1157-1158. [26]张宝海.腰椎退变性滑脱在CT影像上的表现与临床治疗意义[J].中国实用医药,2010,5(34):53-54. [27]Remes VM, Lamberg TS, Tervahartiala PO, et al. No correlation between patient outcome and abnormal lumbar MRI findings 21 years after posterior or posterolateral fusion for isthmic spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. Eur Spine J. 2005;14:833-842. [28]王志钢,王沛,马信龙,等.骨性结构参数在退行性腰椎滑脱发病机制中的作用[J].中华骨科杂志,2003;23(9):518-522.[29]杨贤玉,王吉兴.腰椎关节突关节的方向和退变程度对退行性腰椎滑脱的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2009, 19(1):52-55.[30]李永新.关节突关节形态与退行性腰椎滑脱的关系[D].天津:天津医科大学.2010.[31]荆慧田.关节突关节角改变与退行性腰椎滑脱关系的研究[D].天津:天津医科大学.2011.[32]张建湘,荆珏华,申才良,等.脊柱后方结构在腰椎退变疾患中的作用[J].临床骨科杂志,2001,4(1):15-16.[33]Kjaer P, Bendix T, Sorensen JS, et al. Are MRI-defined fat infiltra-tions in the multifidus muscles associated with low back pain? BMC Med. 2007;5:2. [34]Marras WS, Jorgensen MJ, Granata KP, et al. Female and male trunk geometry: size and prediction of the spine loading trunk muscles derived from MRI. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2001;16:38-46. [35]李昊祯,周学儒,白瑞霞.医学影像在诊疗脊椎滑脱中的临床价值[J].当代医学,2011,17(19):84-85. [36]王宏超.中老年退变性腰椎滑脱230例CT分析[J].中国伤残医学, 2013,21(5): 281-282. [37]陈志刚.崩裂性与退行性腰椎滑脱的MRI诊断价值[J].南华大学学报,2010,38(5):681-683. [38]李振文.腰椎滑脱的影像学表现及临床分析[J].北方药学,2013, 10(10): 105. [39]Bròdano GB, Lolli F, Martikos K, et al. Fueling the debate: Are outcomes better after posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) or after posterolateral fusion (PLF) in adult patients with low-grade adult isthmic spondylolisthesis? Evid Based Spine Care J. 2010;1(1):29-34. [40]Lattig F, Fekete TF, Grob D, et al. Lumbar facet joint effusion in MRI: a sign of instability in degenerative spondylolisthesis? Eur Spine J. 2012;21(2):276-281. [41]Niemeläinen R, Briand MM, Battié MC. Substantial asymmetry in paraspinal muscle cross-sectional area in healthy adults questions its value as a marker of low back pain and pathology. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(25):2152- 2157. |