Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (5): 705-711.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.05.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Artificial chordae transplantation and saddle ring annuloplasty in the treatment of degenerative mitral regurgitation
Han Jin-song, Wang Hui-shan, Yin Zong-tao, Han Hong-guang, Song Heng-chang
- Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Area Command, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China
-
Revised:2013-11-15Online:2014-01-29Published:2014-01-29 -
Contact:Wang Hui-shan, M.D., Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Area Command, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Han Jin-song, Studying for doctorate, Associate chief physician, Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Area Command, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Han Jin-song, Wang Hui-shan, Yin Zong-tao, Han Hong-guang, Song Heng-chang. Artificial chordae transplantation and saddle ring annuloplasty in the treatment of degenerative mitral regurgitation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(5): 705-711.
share this article
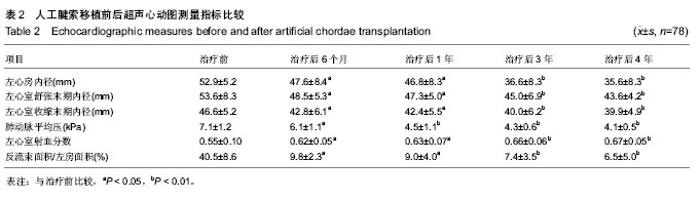
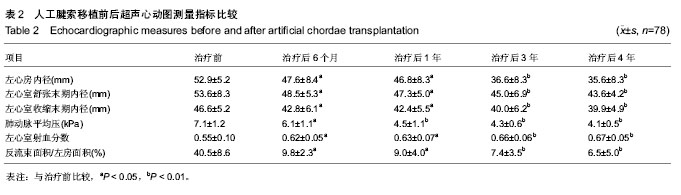
2.1 治疗早期情况 85例患者中行人工腱索移植41例、行人工腱索移植+后叶楔形切除21例、行人工腱索移植+后叶楔形切除+滑行(Sliding)技术23例。每例使用Gore-Tex人工腱索为1-4根。对85例患者均行二尖瓣人工瓣环环缩技术,均使用SJMTM刚性鞍形成形环进行环缩术。在85例患者中使用30号环64例、使用32号环21例。同期行三尖瓣成形术40例(Kay成形术5例、Edwards MC3 三尖瓣瓣环环缩术35例)。平均体外循环时间为62-105 min,平均为(72±11) min;主动脉阻断时间为39-80 min,平均为(55±8) min。住院时间为9-21 d,平均为(15±4) d。治疗后早期无死亡病例。 2.2 随访结果 出院后随访共78例,随访率为91.7% (78/85)。随访时间为6个月-4年。78例中,1例于治疗后13个月死于脑梗死,1例死于交通事故,余76例均存活。NYHA心功能分级Ⅰ级59例,Ⅱ级17例。复查超声心动图彩色多普勒血流成像测量提示二尖瓣微量反流及微量以下反流67例,二尖瓣轻度反流9例。三尖瓣无明显反流35例,微量反流1例,轻度反流4例。 2.3 人工腱索移植前后超声心动图测量指标比较 见表2。门诊复查超声心动图显示治疗后各时间点与治疗前的指标比较,左心房内径明显减少(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),左心室舒张末期内径明显减少(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),左心室收缩末期内径明显减少(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),二尖瓣反流束面积/左房面积明显减少(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),肺动脉平均压明显降低(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),射血分数明显增加(P < 0.05或P < 0.01)。所有病例均未出现二尖瓣前叶收缩期前向运动现象(SAM征)。 2.4 并发症及不良反应 并发症情况:治疗后出现窦性心动过缓12例,阵发性室上性心动过速25例。其中3例阵发性室上性心动过速患者行同步电复律后好转。1例患者治疗前有心房颤动伴快-慢综合征,术后表现为间断的短暂意识丧失,心率变化较大,最快190次/min,最慢30次/min,动态心电图示R-R间期最长7 s,安装永久起搏器后好转。1例治疗后1周出现延迟性心包填塞的表现,经心包穿刺留置置管引流后治愈。 不良反应情况:所有患者中均无成形环断裂、成形环撕脱、溶血、左室流出道梗死、人工腱索断裂或劈裂等不良事件发生。无因二尖瓣反流程度加重或避免撕裂需要再次手术行瓣膜置换术的患者。"
| [1] 高峰,孟旭.二尖瓣成形术临床应用542 例及随访[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志,2007,23(5): 301-303.[2] De Bonis M, Lorusso R, Lapenna E,et al.Similar long-term results of mitral valve repair for anterior compared with posterior leaflet prolapse.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006; 131(2):364-370. [3] 孙海宁,王巍,宋云虎,等.二尖瓣成形术治疗二尖瓣前叶脱垂的疗效分析[J].中国胸心血管外科临床杂志,2010, 17(4): 283-286.[4] Qin JX1, Shiota T, McCarthy PM,et al. Importance of mitral valve repair associated with left ventricular reconstruction for patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy: a real-time three-dimensional echocardiographic study.Circulation. 2003; 108 Suppl 1:II241-246.[5] Goldsmith IR, Lip GY, Patel RL.A prospective study of changes in the quality of life of patients following mitral valve repair and replacement.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2001;20(5): 949-955.[6] 王春生,丁文军,洪涛,等.142例二尖瓣关闭不全患者行二尖瓣修复成形术的手术经验[J].上海医学,2004,27(10):713-716.[7] Seeburger J, Kuntze T, Mohr FW.Gore-tex chordoplasty in degenerative mitral valve repair.Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;19(2):111-115.[8] 张卫,郭震,叶伟.二尖瓣成形术的临床应用及疗效分析[J].中国胸心血管外科临床杂志,2010,17(6):503-505.[9] Salvador L, Mirone S, Bianchini R,et al. A 20-year experience with mitral valve repair with artificial chordae in 608 patients.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008;135(6):1280-1287.[10] David TE.Artificial chordae.Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004;16(2):161-168.[11] Frater RW, Berghuis J, Brown AL Jr,et al.The experimental and clinical use of autogenous pericardium for the replacement and extension of mitral and tricuspid value cusps and chordae.J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 1965;6(3):214-228.[12] 赵强,朱丹,王宜青,等.Gore-Tex人工腱索在二尖瓣前叶脱垂修复术中的应用[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志,2006,22(1):12-14.[13] Chiappini B, Sanchez A, Noirhomme P,et al. Replacement of chordae tendineae with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) sutures in mitral valve repair: early and long-term results.J Heart Valve Dis. 2006;15(5):657-663.[14] Lawrie GM, Earle EA, Earle NR. Feasibility and intermediate term outcome of repair of prolapsing anterior mitral leaflets with artificial chordal replacement in 152 patients.Ann Thorac Surg. 2006;81(3):849-856.[15] Murala JS, Wolfenden HD, Youssef GS,et al. Finger fracture mitral valvuloplasty: a tribute to the pioneers of cardiac surgery. Med J Aust. 2007;186(11):605.[16] Suri RM, Schaff HV, Dearani JA,et al. Survival advantage and improved durability of mitral repair for leaflet prolapse subsets in the current era.Ann Thorac Surg. 2006;82(3):819-826. [17] Maisano F, Caldarola A, Blasio A,et al. Midterm results of edge-to-edge mitral valve repair without annuloplasty.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003;126(6):1987-1997.[18] Chang BC, Youn YN, Ha JW,et al. Long-term clinical results of mitral valvuloplasty using flexible and rigid rings: a prospective and randomized study. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;133(4):995-1003.[19] Matsunaga A, Tahta SA, Duran CM. Failure of reduction annuloplasty for functional ischemic mitral regurgitation.J Heart Valve Dis. 2004;13(3):390-397. [20] 黄焕雷,谢旭晶,费洪文,等.实时三维超声在人工腱索二尖瓣成形术中的应用[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志,2010,26(6):361-364.[21] Okada Y, Nasu M, Takahashi Y,et al. Late results of mitral valve repair for mitral regurgitation.Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003;51(7):282-288.[22] Braunberger E, Deloche A, Berrebi A,et al. Very long-term results (more than 20 years) of valve repair with carpentier's techniques in nonrheumatic mitral valve insufficiency. Circulation. 2001;104(12 Suppl 1):I8-11.[23] Gazoni LM, Fedoruk LM, Kern JA,et al. A simplified approach to degenerative disease: triangular resections of the mitral valve.Ann Thorac Surg. 2007;83(5):1658-64.[24] Gillinov AM, Cosgrove DM. Mitral valve repair for degenerative disease.J Heart Valve Dis. 2002;11 Suppl 1:S15-20.[25] Gillinov AM, Cosgrove DM.Chordal transfer for repair of anterior leaflet prolapse.Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004;16(2):169-173.[26] Calafiore AM. Longitudinal plication of the posterior leaflet in myxomatous disease of the mitral valve.Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;87(6):2004-2005. [27] Sternik L, Zehr KJ.Systolic anterior motion of the mitral valve after mitral valve repair: a method of prevention.Tex Heart Inst J. 2005;32(1):47-49.[28] Pereda D, Topilsky Y, Nishimura RA,et al. Asymmetric Alfieri's stitch to correct systolic anterior motion after mitral valve repair.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011;39(5):779-781. [29] Quill JL, Bateman MG, St Louis JL,et al. Edge-to-edge repairs of P2 prolapsed mitral valves in isolated swine hearts.J Heart Valve Dis. 2011;20(1):5-12.[30] Mascagni R, Al Attar N, Lamarra M,et al. Edge-to-edge technique to treat post-mitral valve repair systolic anterior motion and left ventricular outflow tract obstruction.Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;79(2):471-473.[31] Lange R, Guenther T, Noebauer C,et al. Chordal replacement versus quadrangular resection for repair of isolated posterior mitral leaflet prolapse.Ann Thorac Surg. 2010;89(4):1163- 1170.[32] Kobayashi J, Sasako Y, Bando K,et al.Ten-year experience of chordal replacement with expanded polytetrafluoroethylene in mitral valve repair.Circulation. 2000;102(19 Suppl 3):III30-34.[33] Perier P, Hohenberger W, Lakew F,et al.Toward a new paradigm for the reconstruction of posterior leaflet prolapse: midterm results of the "respect rather than resect" approach.Ann Thorac Surg. 2008;86(3):718-725.[34] Salvador L, Mirone S, Bianchini R,et al. A 20-year experience with mitral valve repair with artificial chordae in 608 patients.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008;135(6):1280-1287.[35] Kasegawa H, Shimokawa T, Shibazaki I,et al. Mitral valve repair for anterior leaflet prolapse with expanded polytetrafluoroethylene sutures.Ann Thorac Surg. 2006;81(5): 1625-1631.[36] Rodriguez E, Nifong LW, Chu MW, et al. Robotic mitral valve repair for anterior leaflet and bileaflet prolapse.Ann Thorac Surg. 2008;85(2):438-444. [37] Carpentier A.Cardiac valve surgery--the "French correction".J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1983;86(3):323-337.[38] Fundarò P, Tartara PM, Villa E,et al. Mitral valve repair: is there still a place for suture annuloplasty?Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2007;15(4):351-358.[39] Calafiore AM, Scandura S, Iacò AL,et al. A simple method to obtain the correct length of the artificial chordae in complex chordal replacement.J Card Surg. 2008;23(3):204-206. [40] Brunsting LA 3rd, Rankin JS, Braly KC,et al. Robotic artificial chordal replacement for repair of mitral valve prolapse. Innovations (Phila). 2009;4(4):229-232.[41] Poffo R, Toschi AP, Pope RB,et al. Robotic surgery in cardiology: a safe and effective procedure.Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2013;11(3):296-302. [42] Ward AF, Grossi EA, Galloway AC. Minimally invasive mitral surgery through right mini-thoracotomy under direct vision.J Thorac Dis. 2013;5(Suppl 6):S673-S679.[43] Feldman T, Cilingiroglu M.Percutaneous leaflet repair and annuloplasty for mitral regurgitation.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011; 57(5):529-537.[44] Hetzer R, Delmo Walter E.Folding or plication technique in mitral valve repair: New or renamed. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2013;145(6):1686-1687.[45] MacArthur JW Jr, Cohen JE, Goldstone AB,et al. Nonresectional single-suture leaflet remodeling for degenerative mitral regurgitation facilitates minimally invasive mitral valve repair.Ann Thorac Surg. 2013;96(5):1603-1606.[46] Mandegar MH, Yousefnia MA, Roshanali F. Preoperative determination of artificial chordae length.Ann Thorac Surg. 2007;84(2):680-682.[47] Matsui Y, Kubota S, Sugiki H,et al. Measured tube technique for ensuring the correct length of slippery artificial chordae in mitral valvuloplasty.Ann Thorac Surg. 2011;92(3):1132-1134. [48] Scorsin M, Al-Attar N, Lessana A. A novel technique of utilizing artificial chordae for repair of mitral valve prolapse.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;134(4):1072-1073.[49] von Oppell UO, Mohr FW. Chordal replacement for both minimally invasive and conventional mitral valve surgery using premeasured Gore-Tex loops.Ann Thorac Surg. 2000; 70(6):2166-2168.[50] Matsui Y, Fukada Y, Naito Y, et al. A new device for ensuring the correct length of artificial chordae in mitral valvuloplasty. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;79(3):1064-1065.[51] Rankin JS, Orozco RE, Rodgers TL,et al."Adjustable" artificial chordal replacement for repair of mitral valve prolapse.Ann Thorac Surg. 2006;81(4):1526-1528.[52] Ruyra-Baliarda X.Preliminary experience with the no prolapse system. A new device for ensuring the proper length of artificial chordae in mitral valve repair.Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2010;10(2):165-167.[53] Iida H, Sunazawa T, Doi A,et al. A device for ensuring the neochordae replacement in mitral valve repair.Ann Thorac Surg. 2010;90(6):2071-2072. [54] Shudo Y, Taniguchi K, Takahashi T,et al.Simple and easy method for chordal reconstruction during mitral valve repair. Ann Thorac Surg. 2006;82(1):348-349.[55] Chocron S.Removable clips for mitral valve repair.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;133(6):1682-1683.[56] Maselli D, De Paulis R, Weltert L,et al. A new method for artificial chordae length "tuning" in mitral valve repair: preliminary experience.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007; 134(2):454-459.[57] Smith JM, Stein H. Endoscopic placement of multiple artificial chordae with robotic assistance and nitinol clip fixation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008;135(3):610-614. [58] Chan DT, Chiu CS, Cheng LC,et al. Artificial chordae: a simple clip and tie technique.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008;136(6):1597-1599.[59] Seeburger J, Leontjev S, Neumuth M,et al. Trans-apical beating-heart implantation of neo-chordae to mitral valve leaflets: results of an acute animal study.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2012;41(1):173-176.[60] Maisano F, Cioni M, Seeburger J,et al. Beating-heart implantation of adjustable length mitral valve chordae: acute and chronic experience in an animal model.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011;40(4):840-847. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||