Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (9): 2370-2379.doi: 10.12307/2026.651
Previous Articles Next Articles
Efficacy of different nonsurgical treatments for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Liu Jinlong1, Abuduwupuer·Haibier2, Bai Zhen1, Su Danyang1, Miao Xin1, Li Fei1, Yang Xiaopeng1
- 1First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China; 2Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2025-03-04Accepted:2025-05-07Online:2026-03-28Published:2025-09-29 -
Contact:Yang Xiaopeng, PhD, Master’s supervisor, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
About author:Liu Jinlong, Master candidate, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Jinlong, Abuduwupuer·Haibier, Bai Zhen, Su Danyang, Miao Xin, Li Fei, Yang Xiaopeng. Efficacy of different nonsurgical treatments for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2370-2379.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
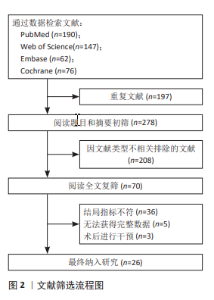
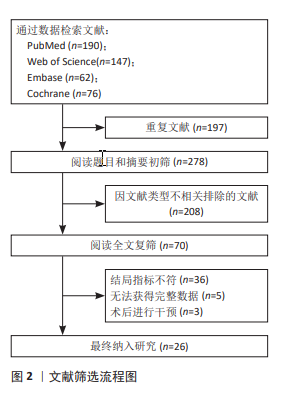
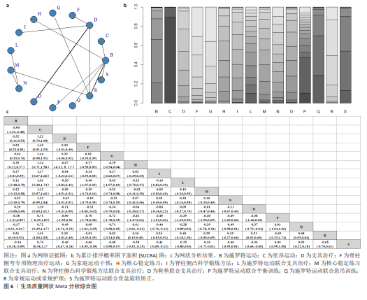
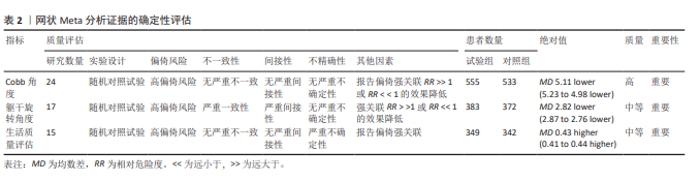
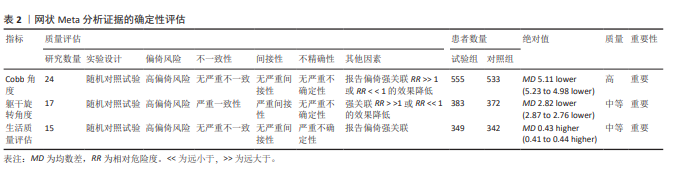
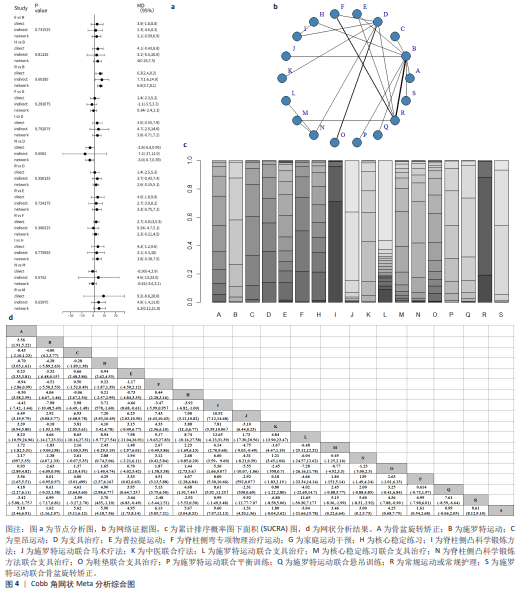
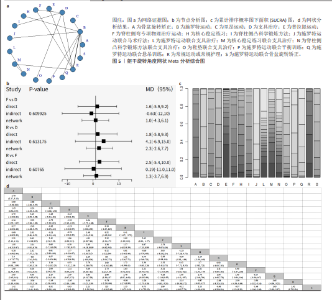
2.4 网状分析结果 2.4.1 Cobb角网状分析结果 见图4。 网络证据图:24项随机对照试验报道了Cobb角变化值[20-25,27,29-45], 包括干预措施18项,不同圆圈表示不同非手术疗法,两圆圈直线连接表示存在直接比较,连线的粗细表示纳入文献的数量不同。其中Schroth运动与常规护理的研究对比最多,网络证据关系见图4b。可知其包含闭合环,直接与间接比较结果差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),节点分析见图4a。 网状Meta分析结果:结果显示共产生两两对比153项,Cobb角网状分析结果见图4d。 功效排名:SUCRA概率排序显示,Schroth运动联合马术治疗(5.5%) > Schroth运动联合骨盆旋转矫正(9.1%) > Schroth运动联合悬吊训练(19.3%),概率越小说明对AIS患者干预效果越好,见图4c。"
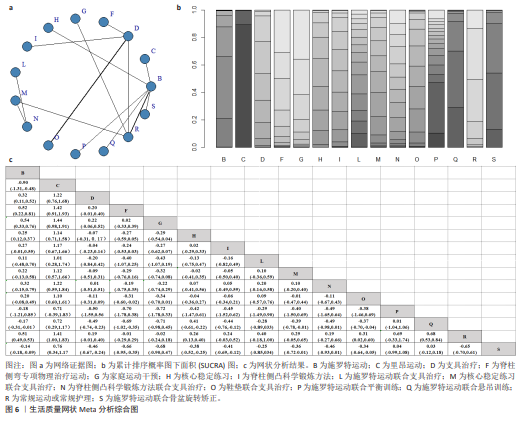
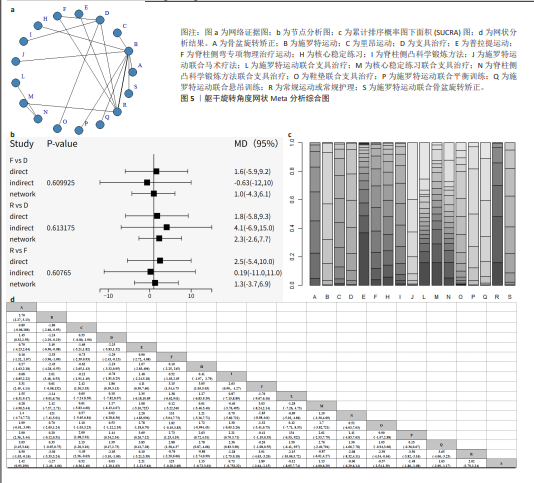
2.4.2 躯干旋转角度网状分析结果 见图5。 网络证据图:17项随机对照试验报道了躯干旋转角度变化值[20-23,25-27,29-31,33-34,36,38-39,44-45],其中包括17项干预措施,网络关系见图5a。存在闭合环,通过节点分析可知,直接与间接比较结果差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图5b。 网状Meta分析结果:结果显示共产生两两对比136项,躯干旋转角度网状分析结果见图5d。 功效排名:SUCRA概率排序显示,Schroth运动联合马术治疗(8.1%) > Schroth运动联合悬吊训练(12.7%) > Schroth运动联合平衡训练(17.1%),概率越小说明与基线值相比躯干旋转角度减小越多,见图5c。"
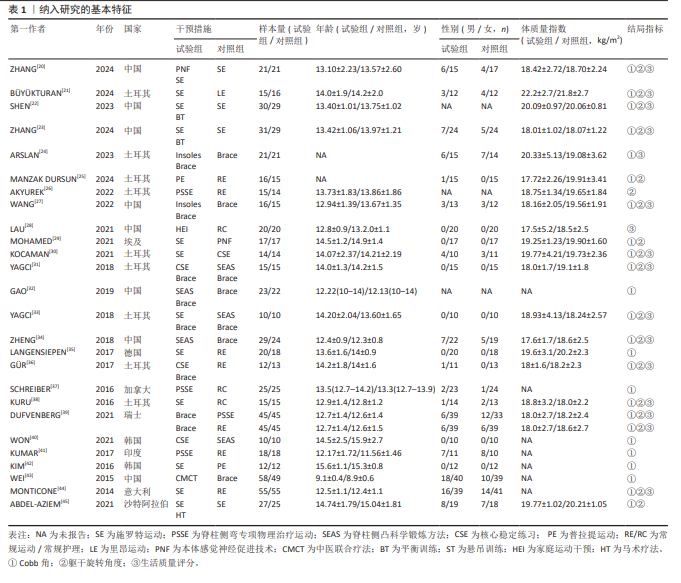
| [1] ALMANSOUR H, PEPKE W, BRUCKNER T, et al. Three-Dimensional Analysis of Initial Brace Correction in the Setting of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. J Clin Med. 2019;8(11):1804. [2] MARYA S, TAMBE AD, MILLNER PA, et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis : a review of aetiological theories of a multifactorial disease. Bone Joint J. 2022;104-B(8):915-921. [3] 徐帅, 苏永佳, 王振波, 等. 中国大陆中小学生脊柱侧凸的患病特点:关于72项研究的Meta分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2021,31(10):901-910. [4] PEREZ-MACHADO G, BERENGUER-PASCUAL E, BOVEA-MARCO M, et al. From genetics to epigenetics to unravel the etiology of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Bone. 2020; 140:115563. [5] WEINSTEIN SL. The Natural History of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop. 2019; 39(Issue 6, Supplement 1 Suppl 1):S44-S46. [6] ASHER MA, BURTON DC. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: natural history and long term treatment effects. Scoliosis. 2006; 1(1):2. [7] AULIA TN, DJUFRI D, GATAM L, et al. Etiopathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS): Role of genetic and environmental factors. Narra J. 2023;3(3): e217. [8] LIANG ZT, GUO CF, LI J, et al. The role of endocrine hormones in the pathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. FASEB J. 2021;35(9):e21839. [9] 李洺, 杨一卓, 宋哈楠, 等. 基于多组学技术的青少年特发性脊柱侧凸病因学研究进展[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2024, 34(5):540-547. [10] PENG Y, WANG SR, QIU GX, et al. Research progress on the etiology and pathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020;133(4):483-493. [11] PENG C, LI D, GUO T, et al. Efficacy of Different Exercises on Mild to Moderate Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2024;103(6):494-501. [12] PLASZEWSKI M, KOTWICKI T, CHWALA W, et al. Study protocol and overview of the literature on long-term health and quality of life outcomes in patients treated in adolescence for scoliosis with therapeutic exercises. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2015;28(3):453-462. [13] SELEVICIENE V, CESNAVICIUTE A, STRUKCINSKIENE B, et al. Physiotherapeutic Scoliosis-Specific Exercise Methodologies Used for Conservative Treatment of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis, and Their Effectiveness: An Extended Literature Review of Current Research and Practice. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(15): 9240. [14] NEGRINI S, MINOZZI S, BETTANY-SALTIKOV J, et al. Braces for idiopathic scoliosis in adolescents. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;2015(6):CD6850. [15] 石茂彪, 马亚萍, 季文军, 等. 青少年特发性脊柱侧弯非手术治疗的现状[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2023,31(13):1189-1193. [16] 张浩阳, 潘英森, 叶鑫, 等. 牵引干预治疗青少年特发性脊柱侧弯的应用现状[J]. 中医儿科杂志,2024,20(4):92-95. [17] 朱博文, 姚重界, 孔令军, 等. 手法治疗青少年特发性脊柱侧弯的研究进展[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2024,39(3):1383-1386. [18] NEGRINI S, DONZELLI S, AULISA AG, et al. 2016 SOSORT guidelines: orthopaedic and rehabilitation treatment of idiopathic scoliosis during growth. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2018;13:3. [19] PAGE MJ, MOHER D, BOSSUYT PM, et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021; 372:n160. [20] ZHANG Y, CHAI T, WENG H, et al. Pelvic rotation correction combined with Schroth exercises for pelvic and spinal deformities in mild adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A randomized controlled trial. PLoS One. 2024;19(7):e307955. [21] BÜYUKTÜRAN O, KAYA MH, ALKAN H, et al. Comparison of the efficacy of Schroth and Lyon exercise treatment techniques in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A randomized controlled, assessor and statistician blinded study. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2024;72:102952. [22] SHEN X, YANG Z, ZHANG P, et al. Effects of balance training combined with Schroth therapy on adolescents with mild idiopathic scoliosis: A six-week randomized controlled trial. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2023; 36(6):1365-1373. [23] ZHANG P, SHEN X, ZHANG L, et al. Effect of sling exercise combined with Schroth therapy on adolescents with mild idiopathic scoliosis: A twelve-week randomized controlled trial. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2024;37(2):379-388. [24] ARSLAN M, GORGU SO. Effect of short-term spinal orthosis and insoles application on cobb angle, plantar pressure and balance in individuals with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2023; 110:106121. [25] MANZAK DURSUN A, OZYILMAZ S, UCGUN H, et al. The effect of Pilates-based exercise applied with hybrid telerehabilitation method in children with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A randomized clinical trial. Eur J Pediatr. 2024;183(2):759-767. [26] AKYUREK E, ZENGIN AA, AKGUL T. The preliminary results of physiotherapy scoliosis-specific exercises on spine joint position sense in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A randomized controlled trial. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2022;46(5):510-517. [27] WANG B, SUN Y, GUO X, et al. The efficacy of 3D personalized insoles in moderate adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):983. [28] LAU RW, CHEUK KY, NG BK, et al. Effects of a Home-Based Exercise Intervention (E-Fit) on Bone Density, Muscle Function, and Quality of Life in Girls with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (AIS): A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(20):10899. [29] MOHAMED RA, YOUSEF AM. Impact of Schroth three-dimensional vs. proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation techniques in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a randomized controlled study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021;25(24): 7717-7725. [30] KOCAMAN H, BEK N, KAYA MH, et al. The effectiveness of two different exercise approaches in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A single-blind, randomized-controlled trial. PLoS One. 2021;16(4): e249492. [31] YAGCI G, YAKUT Y, SIMSEK E. The effects of exercise on perception of verticality in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Physiother Theory Pract. 2018;34(8):579-588. [32] GAO C, ZHENG Y, FAN C, et al. Could the Clinical Effectiveness Be Improved Under the Integration of Orthotic Intervention and Scoliosis-Specific Exercise in Managing Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis? A Randomized Controlled Trial Study. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2019;98(8):642-648. [33] YAGCI G, AYHAN C, YAKUT Y. Effectiveness of basic body awareness therapy in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis: A randomized controlled study1. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2018;31(4):693-701. [34] ZHENG Y, DANG Y, YANG Y, et al. Whether Orthotic Management and Exercise are Equally Effective to the Patients With Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis in Mainland China?: A Randomized Controlled Trial Study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018;43(9): E494-E503. [35] LANGENSIEPEN S, STARK C, SOBOTTKE R, et al. Home-based vibration assisted exercise as a new treatment option for scoliosis - A randomised controlled trial. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2017;17(4):259-267. [36] GÜR G, AYHAN C, YAKUT Y. The effectiveness of core stabilization exercise in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A randomized controlled trial. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2017;41(3):303-310. [37] SCHREIBER S, PARENT EC, KHODAYARI ME, et al. Schroth Physiotherapeutic Scoliosis-Specific Exercises Added to the Standard of Care Lead to Better Cobb Angle Outcomes in Adolescents with Idiopathic Scoliosis - an Assessor and Statistician Blinded Randomized Controlled Trial. PLoS One. 2016;11(12):e168746. [38] KURU T, YELDAN I, DERELI EE, et al. The efficacy of three-dimensional Schroth exercises in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a randomised controlled clinical trial. Clin Rehabil. 2016;30(2):181-190. [39] DUFVENBERG M, DIARBAKERLI E, CHARALAMPIDIS A, et al. Six-Month Results on Treatment Adherence, Physical Activity, Spinal Appearance, Spinal Deformity, and Quality of Life in an Ongoing Randomised Trial on Conservative Treatment for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (CONTRAIS). J Clin Med. 2021;10(21):4967. [40] WON SH, OH DW, SHEN M. An 18-month follow-up study on the effect of a neuromuscular stabilization technique on Cobb’s angle in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A single-blind, age-matched controlled trial. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2021;34(1):87-93. [41] KUMAR A, KUMAR S, SHARMA V, et al. Efficacy of Task Oriented Exercise Program Based on Ergonomics on Cobb’s Angle and Pulmonary Function Improvement in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis- A Randomized Control Trial. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11(8):YC1-YC4. [42] KIM G, HWANGBO PN. Effects of Schroth and Pilates exercises on the Cobb angle and weight distribution of patients with scoliosis. J Phys Ther Sci. 2016;28(3): 1012-1015. [43] WEI H, XU J, JIANG Z, et al. Effect of a Traditional Chinese Medicine combined therapy on adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a randomized controlled trial. J Tradit Chin Med. 2015;35(5):514-519. [44] MONTICONE M, AMBROSINI E, CAZZANIGA D, et al. Active self-correction and task-oriented exercises reduce spinal deformity and improve quality of life in subjects with mild adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Results of a randomised controlled trial. Eur Spine J. 2014;23(6):1204-1214. [45] ABDEL-AZIEM AA, ABDELRAOUF OR, GHALLY SA, et al. A 10-Week Program of Combined Hippotherapy and Scroth’s Exercises Improves Balance and Postural Asymmetries in Adolescence Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Randomized Controlled Study. Children (Basel). 2021;9(1):23. [46] 王航平, 孙振武. 特异性训练法对青少年特发性脊柱侧凸效果的Meta分析[J]. 中国学校卫生,2020,41(9):1335-1338. [47] CHEN Y, ZHANG Z, ZHU Q. The effect of an exercise intervention on adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a network meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):655. [48] 廖粤生, 白莉莉. 青少年特发性脊柱侧弯发病机制及运动干预研究进展[J]. 中国学校卫生,2022,43(9):1436-1440. [49] 张娟娟, 蒋楠楠, 吴亚军, 等. Schroth疗法联合核心力量训练改善轻度青少年特发性脊柱侧凸患者的侧凸角度[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2025,29(27):5876-5882. [50] GAO A, LI JY, SHAO R, et al. Schroth exercises improve health-related quality of life and radiographic parameters in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients. Chin Med J (Engl). 2021;134(21):2589-2596. [51] WOOD WH, FIELDS BE. Hippotherapy: a systematic mapping review of peer-reviewed research, 1980 to 2018. Disabil Rehabil. 2021;43(10):1463-1487. [52] AMADO-FUENTES M, DENCHE-ZAMORANO A, BARRIOS-FERNANDEZ S, et al. Bibliometric Analysis on Equine-Assisted Interventions. Animals (Basel). 2024;14(12):1776. [53] STERGIOU A, TZOUFI M, NTZANI E, et al. Therapeutic Effects of Horseback Riding Interventions: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2017;96(10):717-725. [54] POTVIN-BÉLANGER A, FREEMAN A, VINCENT C. Hippotherapy and life habits with children with motor deficit and neurodevelopmental impairment: A pilot survey of parents. J Pediatr Rehabil Med. 2021;14(1):41-49. [55] FUNAKOSHI R, MASUDA K, UCHIYAMA H, et al. A possible mechanism of horseback riding on dynamic trunk alignment. Heliyon. 2018;4(9):e777. [56] SALBAŞ E, KARAHAN AY. Effects of hippotherapy simulation exercise vs. conventional home exercises on muscle strength and balance in people with multiple sclerosis: A randomized controlled trial. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2022;68: 104111. [57] RRECAJ-MALAJ S, BEQAJ S, KRASNIQI V, et al. Outcome of 24 Weeks of Combined Schroth and Pilates Exercises on Cobb Angle, Angle of Trunk Rotation, Chest Expansion, Flexibility and Quality of Life in Adolescents with Idiopathic Scoliosis. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2020;26:e920449. [58] 张威, 卜淑敏, 王涛, 等. 运动干预对青少年轻、中度特发性脊柱侧弯患者疗效的Meta分析[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2022,22(8):896-900. [59] CEBALLOS-LAITA L, CARRASCO-URIBARREN A, CABANILLAS-BAREA S, et al. The effectiveness of Schroth method in Cobb angle, quality of life and trunk rotation angle in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2023;59(2):228-236. [60] BERDISHEVSKY H, LEBEL VA, BETTANY-SALTIKOV J, et al. Physiotherapy scoliosis-specific exercises - a comprehensive review of seven major schools. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2016;11:20. [61] BETTANY-SALTIKOV J, PARENT E, ROMANO M, et al. Physiotherapeutic scoliosis-specific exercises for adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2014; 50(1):111-121. |
| [1] | Yang Qiongqiong, Liu Wei. Comparison of performance and clinical effects of zirconia and titanium implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2063-2071. |
| [2] | Wang Zhenze, Liu Fende, Zhang Rui, Li Wujun. Mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of arteriosclerosis obliterans of lower extremities: systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1869-1876. |
| [3] | Zheng Yin, Wu Zhenhua, Zhang Cheng, Ruan Kexin, Gang Xiaolin, Ji Hong. Safety and efficacy of immunoadsorption therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: a network meta-analysis and systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1260-1268. |
| [4] | Leng Xiaoxuan, Zhao Yuxin, Liu Xihua. Effects of different neuromodulatory stimulation modalities on non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s patients: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1282-1293. |
| [5] | Yang Yuanyuan, Zhou Shanshan, Cheng Xiaofei, Feng Luye, Tang Jiqin. Network meta-analysis of non-invasive brain stimulation in the treatment of lower limb motor dysfunction after stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1008-1018. |
| [6] | Wang Yalei, Wang Xuezhi, Zhou Tao, Shen Xinxin, Fang Ding, Chen Hongliang. Effect of sacroiliac joint ankylosis on outcomes of L5/S1 transforminal lumbar interbody fusion and lumbar sagittal parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 634-641. |
| [7] | Liao Guangtao, Feng Ziyu, Fu Xiaoyong, Zhao Qinglan, Chen Chao, Hong Jinsong. Subtalar arthroereisis for treatment of pediatric flexible flatfoot: relationship between radiographic indicators and clinical efficacy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 661-670. |
| [8] | Chen Ping, Du Jinchao, Wang Hongying, Zhang Hui, Wang Haixia. Different inspiratory muscle training methods improve exercise and cardiopulmonary function of patients after cardiac surgery: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 3134-3144. |
| [9] | Li Jie, Zhao Xiaofeng, Zeng Qi, Zhou Runtian, Chen Rong, Hu Xijian, Zhao Bin. Influencing factors of spine deformity progression in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and construction of a joint prediction model and nomogram [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2727-2735. |
| [10] | Gao Shiai, Yu Zifu, Chen Jinhui, Cao Xinyan, Leng Xiaoxuan, Liu Xihua. Efficacy of non-invasive neuromodulation techniques on autism spectrum disorder: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2550-2559. |
| [11] | Hu Yujie, Xie Ping, , Lu Weijie, Yang Kang, Deng Yaoting, Liu Mengyang. Meta-analysis of the clinical efficacy of high-intensity interval exercise and middle-intensity continuous training in patients with coronary heart disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2584-2593. |
| [12] | Zhang Xinxin, Gao Ke, Xie Shidong, Tuo Haowen, Jing Feiyue, Liu Weiguo. Network meta-analysis of non-surgical treatments for foot and ankle ability and dynamic balance in patients with chronic ankle instability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1931-1944. |
| [13] | Wang Juan, Wang Guanglan, Zuo Huiwu. Efficacy of exercise therapy in the treatment of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients: #br# a network meta-analysis #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1714-1726. |
| [14] | Li Zhe, Li Ping, Zhang Chao, Guo Guangling. A network meta-analysis of efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells from different sources in treatment of premature ovarian failure animal models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7898-7908. |
| [15] | Tian Jinxin, Zhao Yuxin, Hu Tong, Cui Tiantian, Ma Lihong. Effects of different transcranial magnetic stimulation modes on refractory depression in adults: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7639-7648. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||