Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 2886-2895.doi: 10.12307/2026.081
Previous Articles Next Articles
Visualization analysis of piriformis syndrome: research trends and hotspots
Li Kanglin, Jiang Yongdong, Wu Yufeng
- Zhongshan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Zhongshan 528400, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2025-03-14Accepted:2025-05-14Online:2026-04-18Published:2025-09-08 -
Contact:Wu Yufeng, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, Zhongshan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Zhongshan 528400, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Li Kanglin, MS candidate, Zhongshan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Zhongshan 528400, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Kanglin, Jiang Yongdong, Wu Yufeng. Visualization analysis of piriformis syndrome: research trends and hotspots[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2886-2895.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
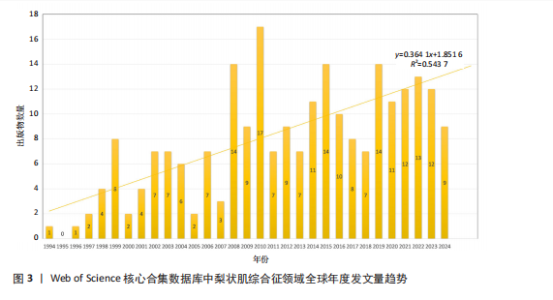
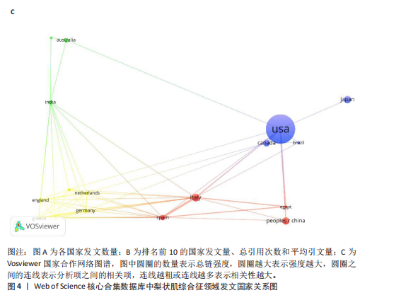
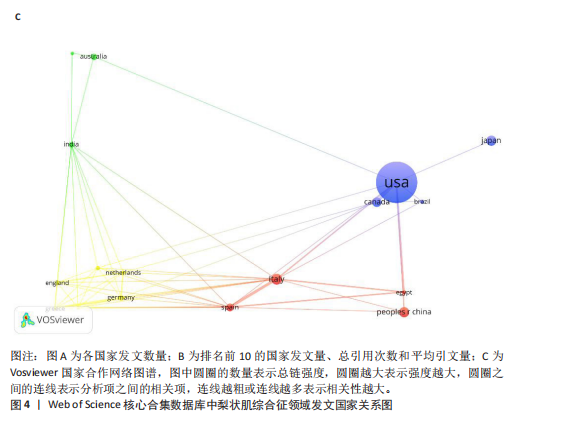
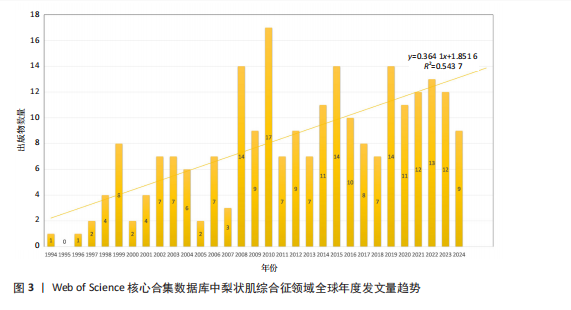
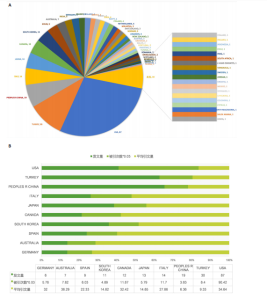
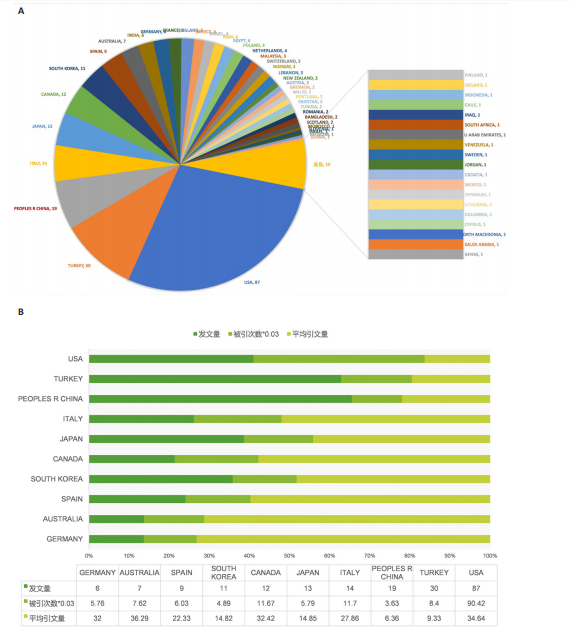
图3展示了1994-2024年梨状肌综合征领域文献的分布情况。1994年,有关梨状肌综合征的研究首次在Web of Science核心合集数据库出现。在1997年之前,这一时期该领域的相关研究尚处于起步阶段,论文发表数量寥寥无几;全球文献数量于1999年迎来首个峰值,共计8篇;2000-2007年期间,平均每年出版4.75篇文献,呈现出缓慢增长的趋势;2008-2010年,全球文献数量呈现快速增长态势,并于2010年达到第二个峰值,数量达到17篇;2011-2018年,发文量虽有所回落,总体仍保持稳定增长;2019-2024年,发文量持续增加。 综上所述,全球关于梨状肌综合征领域的发文量在增长过程中虽存在一定波动,但整体呈现向上发展的趋势。经线性分析可得方程=0.364 1x+1.851 6,R2=0.543 7,这表明梨状肌综合征领域的研究在过去呈现出增长趋势,不过在增长过程中受到多种因素的干扰而产生波动。未来该领域的研究趋势可能会持续受到各种复杂因素的综合影响,值得进一步关注和深入分析。 2.2 梨状肌综合征领域研究国家分析 1994-2024年,全球范围内总计57个国家或地区参与了梨状肌综合征领域的发文活动,各国家发表文献数量如图4A所示;由图4B得知,在发文量排名前10的国家中,除中国和土耳其外,其余大多为发达国家;从地理分布来看,亚洲地区的中国、日本和韩国位列其中。在该研究领域,美国处于绝对的领先地位,发文量高达87篇,遥遥领先其他国家,美国的发文量近乎是排名第二的土耳其的3倍,并且作为最早开展该领域研究的国家在该领域的影响力首屈一指。土耳其在发文量方面表现尚可,但在被引次数和平均引文量方面尚存在较大提升空间。中国虽发文量位居第三,但平均引文量却处于最低水平,这表示中国在该领域的研究成果在引用层面相对不足,可能在研究质量、创新性及成果传播范围等方面存在一定的改进"
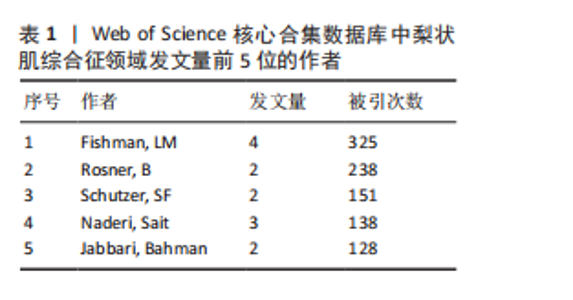
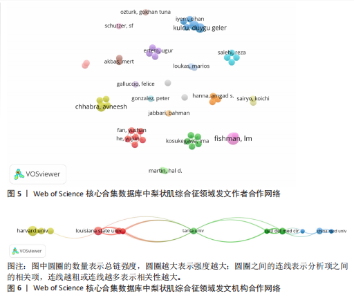
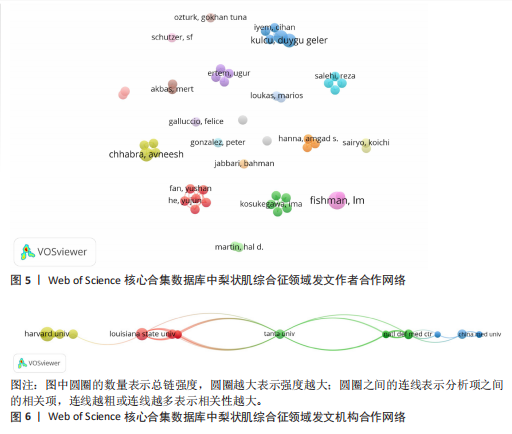
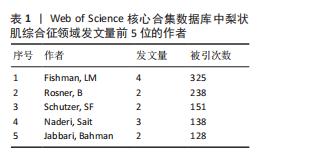
空间。意大利、日本、加拿大和韩国的发文量基本持平,然而,意大利和加拿大的被引次数相近且明显高于部分其他国家,这一现象表明其研究成果在国际学术界具有一定的认可度。澳大利亚尽管发文量较少,但其平均引文量高达36.29,为各国最高,这一数据表示虽然澳大利亚在该领域发文量有限,但成果质量颇高,获得了全球专家学者的广泛接受与认可。 如图4C所示,各节点之间的连线较少且较细,说明各个国家之间的合作发文较少。其中,与美国开展合作较多的是加拿大、澳大利亚、意大利;新西兰、德国、荷兰、希腊间的连线较多,说明这几个国家相互合作较多。结果说明梨状肌综合征领域的研究主要集中在各个国家,它们之间的合作较少,部分国家有固定的合作团队。 2.3 梨状肌综合征领域研究作者分析 通过图5可以直观了解到该领域研究的作者具有较为稳定的合作团队,但各个团队之间的合作较少,部分作者团队甚至与其他团队没有合作。表1展示了发文量最多的5位作者,其中Fishman发文量排名第一,共计发表4篇文献,第一篇文献发布于2002年,总引用325次,平均每篇文献被引用约81.25次。Fishman是来自美国哥伦比亚大学医学院的教授,在梨状肌综合征研究领域贡献卓越。"
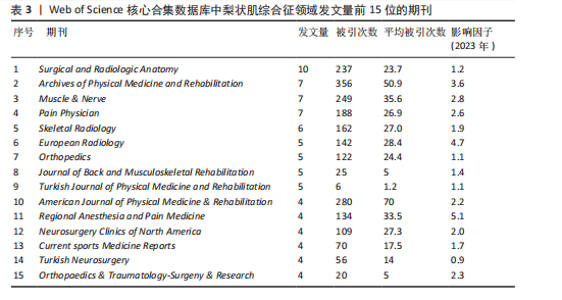
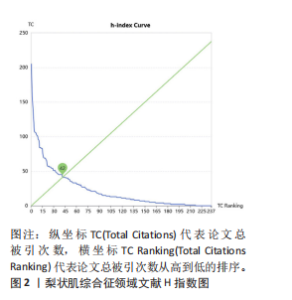
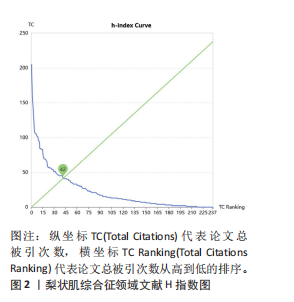
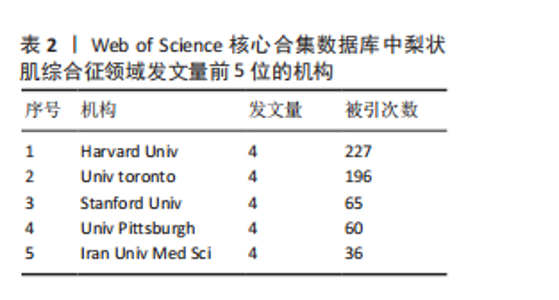
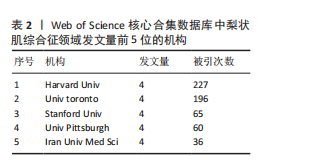
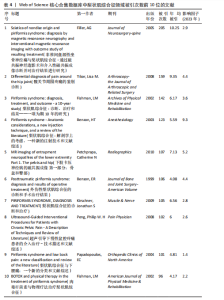
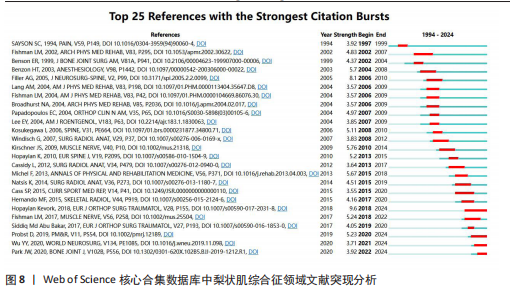
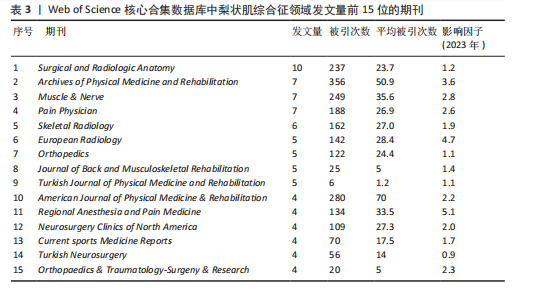
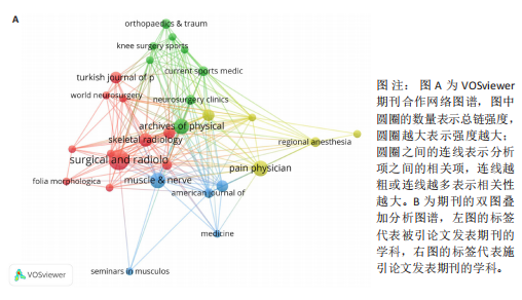
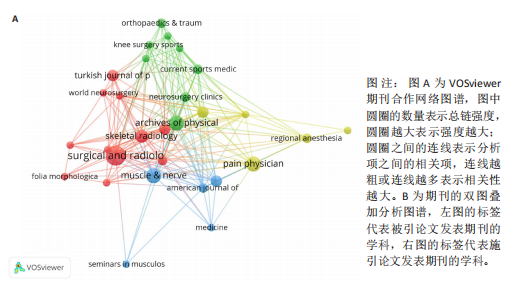
2.5 梨状肌综合征领域发文期刊分析 由图7A可以发现,《Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy》的节点最大,表明该期刊文献被引用率最高,此期刊的文章代表了该领域的研究方向,其高被引文献反映了学术影响力,说明研究成果取得了国际认可。结合表3来看,发文量最大的15个期刊中排名第一的是《Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy》,共发表了10篇文献,总被引次数为237,平均被引用23.7次;排名第10的《American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation》虽然发文量不多,但文献平均引用频次却达到了70次,明显超过了其他期刊。从2023年最新的影响因子分析,《Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine》影响因子最高,为5.1。综合来看,《Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation》 发文量排名第二,总被引次数达到了最高(356次),平均被引次数达到了50.9次,影响因子(2023年)为3.6,仅次于《Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine》和《European Radiology》,由此可见《Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation》在梨状肌综合征领域有较大的影响力。梨状肌综合征属于肌肉骨骼和康复领域相关的疾病,而《Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation》专注于物理医学与康复,所以在该领域的研究成果很可能是前沿和可靠的,能为梨状肌综合征的诊断、治疗和康复提供有价值的参考。 利用CiteSpace对238篇文献进行期刊双图叠加分析,如图7B所示,左图的标签代表被引用论文发表期刊的学科,其中主要来自数学、毒理学、生态学、分子生物学、物理学、心理学、运动康复学等学科相关的期刊;右图的标签代表施引论文发表期刊的学科,大部分发表于计算机、毒理学、心理学、护理学、运动康复学、医学、神经学相关学科的期刊上。 2.6 梨状肌综合征领域高影响力论文 图8描绘了梨状肌综合征领域前25篇最强爆发的文献。表4描绘了梨状肌综合征领域前10篇引用次数最多的文献。结合来看,梨状肌综合征领域中最有影响力的论文最近出现在2018年,Hopayian Kevork、Probst D、Wu "
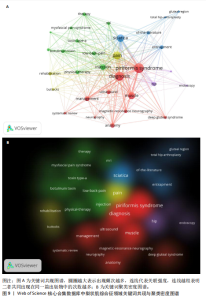
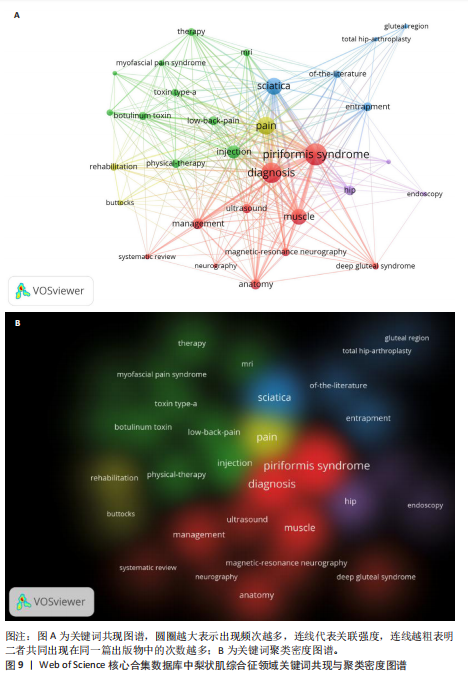
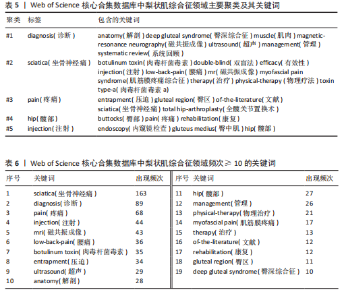
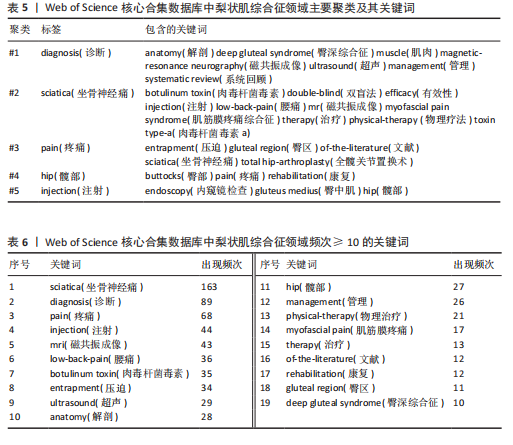
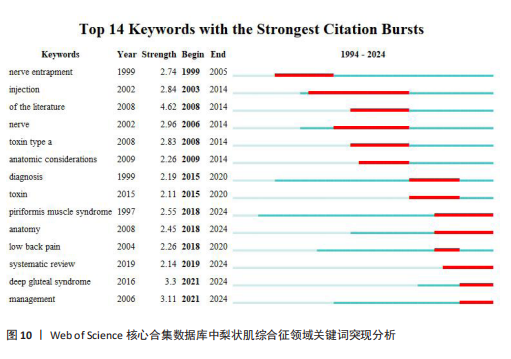
YY、Park JW发表的的文献在2024年仍旧具有影响力;最强的爆发引用由 Hopayian Kevork在2018年发表在《Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol》上,爆发强度为9.6;Filler AG于2005年发表在《J Neurosurg-Spine》上的“Sciatica of nondise origin and piriformis syndrome: diagnosis by magnetic resonance neurography and interventional magnetic resonance imaging with outcome study of resulting treatment”爆发强度是8.1,在前25篇引用次数最多的文献中排名第二,被引用次数到达了205,是纳入文献中被引次数最高的,年均被引10.25次。 2.7 梨状肌综合征领域关键词分析 2.7.1 关键词共现分析 使用VOSviewer对238篇文献绘制关键词共现网络图谱,见图9。在梨状肌综合征领域中共有780 个关键词,选择其中频次≥5的54个重点关键词进行可视化,关键词共现生成的网络分为5个聚类,分别是 #1 诊断(红色)、#2 坐骨神经痛(蓝色)、#3疼痛(黄色)、#4 髋部(紫色)、#5 注射(绿色)。主要聚类及其包含的关键词如表5所示。 为了更清晰地了解关键词具体情况,在去除与检索策略相关的检索词并合并同义关键词后,根据普莱斯定律计算得出高频关键词出现次数为9.56次,故将频次≥10的关键词制作成表6,可以看出sciatica(坐骨神经痛)、diagnosis(诊断)、pain(疼痛)、injection(注射)、mri(磁共振成像)、low-back-pain(腰痛)、botulinum toxin (肉毒杆菌毒素)、entrapment(压迫)、ultrasound(超声)、physical-therapy (物理治疗)、rehabilitation(康复)、deep gluteal syndrome(臀深综合征)等高频关键词构成了该领域的代表性术语。 2.7.2 关键词突现分析 结合CiteSpace软件的突发性探测功能对关键词突现强度进行排序,形成关键词爆发图谱,通过分析关键词爆发强度和持续时间可以掌握该领域在不同时间段的研究热点,预测未来的研究方向和发展趋势。1994-2024年期间梨状肌综合征"
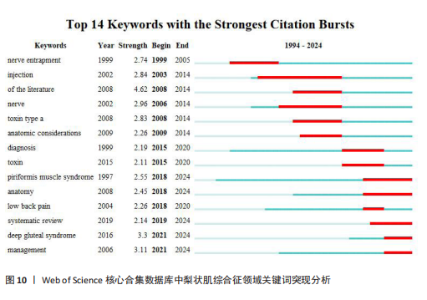
领域中引用爆发最强的前14个关键词,见图10。1994-2024 年,引用爆发强度最强的关键词是“文献”,强度值为4.62,从2008年一直持续到2014年,与图2分析结果相对应,即2008-2014年间梨状肌综合征领域领域相关的文献迎来发表高峰。其他的高爆发强度关键词包括“deep gluteal syndrome(臀深综合征)”“management (管理)”“nerve(神经)”“injection(注射)”“toxin type a(肉毒杆菌毒素a)”“nerve entrapment(神经压迫)”“anatomy (解剖)”“low back pain(腰痛)”“diagnosis(诊断)”和“systematic review(系统回顾)”,这些关键词一直是持续的热点词,与图9和表5分析结果一致。同时可以看出,“anatomy (解剖)” “deep gluteal syndrome (臀深综合征)”“management (管理)”是近年来的突发关键词,表明了梨状肌综合征该领域未来有可能会围绕以上 3个方向进行。"
| [1] CASSIDY L, WALTERS A, BUBB K, et al. Piriformis syndrome: implications of anatomical variations, diagnostic techniques, and treatment options. Surg Radiol Anat. 2012;34:479-486. [2] HALLIN RP. Sciatic pain and the piriformis muscle. Postgrad Med. 1983;74(2):69-72. [3] HOPAYIAN K, DANIELYAN A. Four symptoms define the piriformis syndrome: an updated systematic review of its clinical features. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2018;28:155-164. [4] HERNANDO MF, CEREZAL L, PÉREZ-CARRO L, et al. Deep gluteal syndrome: anatomy, imaging, and management of sciatic nerve entrapments in the subgluteal space. Skeletal Radiol. 2015;44(7):919-934. [5] LIU C, YU R, ZHANG J, et al. Research hotspot and trend analysis in the diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease: a machine learning bibliometric analysis from 2012 to 2021. Front Immunol. 2022;13:972079. [6] PAN X, YAN E, CUI M, et al. Examining the usage, citation, and diffusion patterns of bibliometric mapping software: A comparative study of three tools. J Informetr. 2018;12(2):481-493. [7] FISHMAN LM, DOMBI GW, MICHAELSEN C, et al. Piriformis syndrome: diagnosis, treatment, and outcome—a 10-year study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2002;83(3):295-301. [8] FILLER AG, HAYNES J, JORDAN SE, et al. Sciatica of nondisc origin and piriformis syndrome: diagnosis by magnetic resonance neurography and interventional magnetic resonance imaging with outcome study of resulting treatment. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005;2(2):99-115. [9] TIBOR LM, SEKIYA JK. Differential diagnosis of pain around the hip joint. Arthroscopy. 2008;24(12):1407-1421. [10] YOEMANS W. The relation of arthritis of the sacroiliac joint to sciatica. Lancet. 1928; 2:1119-122. [11] ROBINSON DR. Pyriformis syndrome in relation to sciatic pain. Am J Surg. 1947; 73(3):355-358. [12] PROBST D, STOUT A, HUNT D. Piriformis syndrome: a narrative review of the anatomy, diagnosis, and treatment. PM R. 2019;11 (Suppl 1):S54-63. [13] STEWART JD. The piriformis syndrome is overdiagnosed. Muscle Nerve. 2003;28(5): 644-646. [14] DURRANI Z, WINNIE AP. Piriformis muscle syndrome: an underdiagnosed cause of sciatica. J Pain Symptom Manage. 1991; 6(6):374-379. [15] FISHMAN LM, SCHAEFER MP. The Piriformis syndrome is underdiagnosed. Muscle Nerve. 2003;28(5):646-649. [16] CAMPBELL WW, LANDAU ME. Controversial entrapment neuropathies. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2008;19(4):597-608. [17] PORTA M. A comparative trial of botulinum toxin type A and methylprednisolone for the treatment of myofascial pain syndrome and pain from chronic muscle spasm. Pain. 2000;85(1):101-105. [18] KULCU DG, NADERI S. Differential diagnosis of intraspinal and extraspinal non-discogenic sciatica. J Clin Neurosci. 2008;15(11):1246-1252. [19] FISHMAN LM, ZYBERT PA. Electrophysiologic evidence of piriformis syndrome. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1992;73(4):359-364. [20] MILLER TA, WHITE K, ROSS D. The diagnosis and management of Piriformis Syndrome: myths and facts. Can J Neurol Sci. 2012;39(5):577-583. [21] LEE EY, MARGHERITA AJ, GIERADA DS, et al. MRI of piriformis syndrome. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;183(1):63-64. [22] FILLER AG, KLIOT M, HOWE FA, et al. Application of magnetic resonance neurography in the evaluation of patients with peripheral nerve pathology. J Neurosurg. 1996;85(2):299-309. [23] WADA K, GOTO T, TAKASAGO T, et al. Piriformis muscle syndrome with assessment of sciatic nerve using diffusion tensor imaging and tractography: a case report. Skeletal Radiol. 2017;46:1399-1404. [24] WADA K, HASHIMOTO T, MIYAGI R, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging and tractography of the sciatic nerve: assessment of fractional anisotropy and apparent diffusion coefficient values relative to the piriformis muscle, a preliminary study. Skeletal Radiol. 2017;46:309-314. [25] KANAKIS D, LAZARIS A, PAPADOPOULOS E, et al. Piriformis syndrome--an attempt to understand its pathology. Clin Neuropathol. 2010;29(2):65-70. [26] SIKDAR S, SHAH JP, GEBREAB T, et al. Novel applications of ultrasound technology to visualize and characterize myofascial trigger points and surrounding soft tissue. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2009;90(11):1829-1838. [27] CHEN J, LIU J, ZENG J, et al. Ultrasonographic reference values for assessing normal sciatic nerve ultrasonography in the normal population. J Med Ultrasound. 2018;26(2): 85-89. [28] SIDDIQ MAB, KHASRU MR, RASKER JJ. Piriformis syndrome in fibromyalgia: clinical diagnosis and successful treatment. Case Rep Rheumatol. 2014;2014(1):893836. [29] SMOLL NR. Variations of the piriformis and sciatic nerve with clinical consequence: a review. Clin Anat. 2010;23(1):8-17. [30] BARTRET AL, BEAULIEU CF, LUTZ AM. Is it painful to be different? Sciatic nerve anatomical variants on MRI and their relationship to piriformis syndrome. Eur Radiol. 2018;28:4681-4686. [31] WINDISCH G, BRAUN EM, ANDERHUBER F. Piriformis muscle: clinical anatomy and consideration of the piriformis syndrome. Surg Radiol Anat. 2007;29:37-45. [32] FISHMAN LM, ANDERSON C, ROSNER B. BOTOX and physical therapy in the treatment of piriformis syndrome. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2002;81(12):936-942. [33] MISIRLIOGLU TO, AKGUN K, PALAMAR D, et al. Piriformis syndrome: comparison of the effectiveness of local anesthetic and corticosteroid injections: a double-blinded, randomized controlled study. Pain Physician. 2015;18(2):163. [34] FISHMAN LM, KONNOTH C, ROZNER B. Botulinum neurotoxin type B and physical therapy in the treatment of piriformis syndrome: a dose-finding study. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;83(1):42-50. [35] MICHEL F, DECAVEL P, TOUSSIROT E, et al. Piriformis muscle syndrome: diagnostic criteria and treatment of a monocentric series of 250 patients. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2013;56(5):371-383. [36] ÖZTÜRK GT, ERDEN E, ERDEN E, et al. Effects of ultrasound-guided platelet rich plasma injection in patients with piriformis syndrome. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2022;35(3):633-639. |
| [1] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Yuping, Ba Yinying, Chi Li, Wang Wenjuan, Wang Jiajia. Research context and trend of TBK1 in autoimmunity, signaling pathways, gene expression, tumor prevention and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11. |
| [2] | Huang Jie, Zeng Hao, Wang Wenchi, Lyu Zhucheng, Cui Wei. Visualization analysis of literature on the effect of lipid metabolism on osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1558-1568. |
| [3] | Yang Zeyu, Zhi Liang, Wang Jia, Zhang Jingyi, Zhang Qingfang, Wang Yulong, Long Jianjun. A visualized analysis of research hotspots in high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation from the macroscopic perspective [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1320-1330. |
| [4] | Guan Yujie, Zhao Bin. Application and prospect of artificial intelligence in screening and diagnosis of scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 721-730. |
| [5] | Zhang Qian, Wang Fuxia, Wang Wen, Zhang Kun. Characteristic analysis of nanogel composite system and its application strategies in visualization of diagnostic imaging and therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 480-488. |
| [6] | Jiang Kan, Alimujiang·Abudourousuli, Shalayiding·Aierxiding, Aikebaierjiang·Aisaiti, Kutiluke·Shoukeer, Aikeremujiang·Muheremu. Biomaterials and bone regeneration: research hotspots and analysis of 500 influential papers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 528-536. |
| [7] | Wang Jiaying, Xu Chun, Mayila · Abudukelimu. Global research status, trends and hotspots of anxiety/depression in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2920-2932. |
| [8] | Liu Tongyan, Li Yuan, Sun Wei, Yao Bing, Fang Shanshan, Zhou Lingyun. Current status and hotspot analysis of experimental research on electroacupuncture intervention for peripheral nerve regeneration: electroacupuncture parameters, acupuncture effects and molecular mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2608-2617. |
| [9] | Huang Hailun, Wei Yatao, Liu Yongai, Wu Junzhe, Gao Heng, Sun Kui, Cao Zhenwen. Visualization analysis of lumbar spondylolisthesis treatment research from a bibliometric perspective [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2618-2628. |
| [10] | Jiao Jingya, Zhang Yeting. Analysis of thematic evolution pathways in the field of physical activity and neurogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2653-2661. |
| [11] | Zhao Qianwei, Sun Guangyuan . Intestinal organoids: a bibliometric analysis of the latest trends in tissue/organ biology, disease modeling, and clinical applications [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 238-247. |
| [12] | Yu Daiyao, Shi Ping, Yang Lan, Li Zhishu, Lu Yongping. Advances and application of neutrophil extracellular traps and activated platelets in lung cancer research [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 229-237. |
| [13] | Liang Haobo, Wang Zeyu, Ma Wenlong, Liu Hao, Liu Youwen. Hot issues in the field of joint revision: infection, rehabilitation nursing, bone defect, and prosthesis loosening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1963-1971. |
| [14] | Xie Liugang, Cui Shuke, Guo Nannan, Li Aoyu, Zhang Jingrui. Research hotspots and frontiers of stem cells for Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1475-1485. |
| [15] | Chang Jinxia, Liu Yufei, Niu Shaohui, Wang Chang, Cao Jianchun. Visualization analysis of macrophage polarization in tissue repair process [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1486-1496. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||