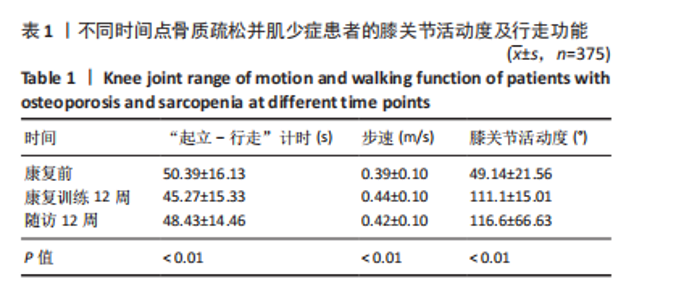
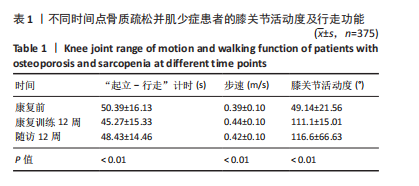
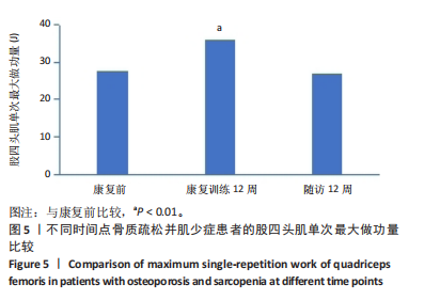
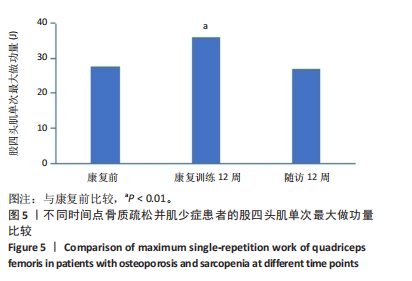
[1] HIRSCHFELD HP, KINSELLA R, DUQUE G. Osteosarcopenia: where bone, muscle, and fat collide. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(10):2781-2790.
[2] 冯婷婷,王佳贺.骨质疏松与肌少症相关性研究进展[J].实用老年医学, 2020,34(3):216-219.
[3] CEDENO-VELOZ B, LÓPEZ-DÓRIGA BONNARDEAUXA P, DUQUE G. Osteosarcopenia: A narrative review. Rev Esp Geriatr Gerontol. 2019;54(2):103-108.
[4] 李宽,王春方,孙长城,等.限弧等速肌力训练对于髌股关节炎髌骨轨迹的影响[J].中国康复,2020,35(8):413-417.
[5] 杜建平,任薇,夏能能,等.等速肌力训练对改善膝骨关节炎肌肉功能的Meta分析[J].中国康复,2020,35(11):594-599.
[6] KRISHNASAMY P, HALL M, ROBBINS SR. The role of skeletal-muscle in the pathophysiology and management of knee osteoarthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018;57(suppl_4):iv22-iv33.
[7] 马远征,王以朋,刘强,等.中国老年骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2018)[J].中国实用内科杂志,2019,39(1):38-61.
[8] 孙建琴,中华医学会老年医学分会,《中华老年医学杂志》编辑委员会,等. 中国老年肌少症诊疗专家共识(2021)[J].中华老年医学杂志,2021,40(8):943-952.
[9] 沈妍交,郝秋奎,张蒙,等.老年肌少症综合干预循证临床实践指南[J].中国循证医学杂志,2024,24(4):378-384.
[10] SHEN Y, SHI Q, NONG K, et al. Exercise for sarcopenia in older people: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023;14(3):1199-1211.
[11] 陆明,邱贵兴,翁习生.全膝关节置换围手术期应用骨关节角度测量器的价值[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(30):5861-5864.
[12] SHAFSHAK TS, ELNEMR R. The Visual Analogue Scale Versus Numerical Rating Scale in Measuring Pain Severity and Predicting Disability in Low Back Pain. J Clin Rheumatol. 2021;27(7):282-285.
[13] QIAO YJ, LI F, ZHANG LD, et al. Analysis of the clinical efficacy of two-stage revision surgery in the treatment of periprosthetic joint infection in the knee: A retrospective study. World J Clin Cases. 2022; 10(36):13239-13249.
[14] LI F, WEI C, HUO S, et al. Predictors of deep-vein thrombosis for acute stroke at admission to a rehabilitation unit: A retrospective study. Front Neurol. 2023;14:1137485.
[15] 孙振晓,刘化学,焦林瑛,等.医院焦虑抑郁量表的信度及效度研究[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2017,11(2):198-201.
[16] DE ALMEIDA MACÊDO E, APPENZELLER S, LAVRAS COSTALLAT LT. Assessment of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) performance for the diagnosis of anxiety in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int. 2017;37(12):1999-2004.
[17] GIELEN E, DUPONT J, DEJAEGER M, et al. Sarcopenia, osteoporosis and frailty. Metabolism. 2023;145:155638.
[18] 王浩越,李国华.肌少症与骨质疏松症的相关性的研究进展[J].联勤军事医学,2023,37(11):984-988.
[19] 张婷婷.老年慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者骨质疏松与肌少症的相关性研究[D].西宁:青海大学,2023.
[20] DAS C, DAS PP, KAMBHAMPATI SBS. Sarcopenia and Osteoporosis. Indian J Orthop. 2023;57(Suppl 1):33-41.
[21] FAGUNDES BELCHIOR G, KIRK B, PEREIRA DA SILVA EA, et al. Osteosarcopenia: beyond age-related muscle and bone loss. Eur Geriatr Med. 2020;11(5): 715-724.
[22] PALMIERI-SMITH RM, BROWN SR, WOJTYS EM, et al. Functional Resistance Training Improves Thigh Muscle Strength after ACL Reconstruction: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2022;54(10):1729-1737.
[23] 刘强,杨曼,熊小云,等. 本体感觉训练对膝关节骨性关节炎患者全膝关节置换术后本体感觉及膝关节功能的影响[J].新乡医学院学报,2021,38(2):180-183.
[24] COHEN D, BACKSTEIN D. Nerve Injuries in Total Knee Arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 2022;53(2):123-127.
[25] HAFFAR A, GOH GS, FILLINGHAM YA, et al. Treatment of arthrofibrosis and stiffness after total knee arthroplasty: an updated review of the literature. Int Orthop. 2022;46(6):1253-1279.
[26] LINDSTROM M, STRANDBERG S, WREDMARK T, et al. Functional andmuscle morphometric effects of ACL reconstruction. A prospectiveCT study with 1 year follow-up. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2013;23(4):431-442.
[27] WILLIAMS GN, SNYDER-MACKLER L, BARRANCE PJ, et al. Quadricepsfemoris muscle morphology and function after ACL injury: A differential response in copers versus non-copers. J Biomech. 2005;38(4):685-693.
[28] YOUNG A, STOKES M, CROWE M. The size and strength of the quadriceps muscles of old and young men. Clin Physiol. 1985;5(5):
145-154.
[29] BIRCHMEIER T, LISEE C, KANE K, et al. Quadriceps muscle size following ACL injury and reconstruction: A systematic review. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(3):598-608.
[30] FASSBENDER HG, WEGNER K. Morphology andpathogenesis of soft tissue rheumatism. Z Rheumaforsch. 1973;32(9):355-374.
[31] LUND N, BENGTSSON A, THORBORG P. Muscletissue oxygen pressure in primary fibromyalgia. Scand J Rheumatol. 1986;15(2):165-173.
[32] O’ MAHONY SM, DINAN TG, CRYAN JF. The gut microbiota as a key regulator of visceral pain. Pain. 2017;158 Suppl 1:S19-S28.
|