Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (4): 1058-1072.doi: 10.12307/2025.933
Effects of Guilu Erxian Glue on gut microbiota in rats with knee osteoarthritis: machine learning and 16S rDNA analysis
Gu Fucheng1, 2, Yang Meixin1, 2, Wu Weixin1, 2, Cai Weijun1, 2, Qin Yangyi1, 2, Sun Mingyi1, 2, Sun Jian1, 2, Geng Qiudong1, 2, Li Nan1, 2
- 1College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350122, Fujian Province, China; 2Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Orthopedics and Sports Rehabilitation, Ministry of Education, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350122, Fujian Province, China
-
Received:2024-10-21Accepted:2024-12-06Online:2026-02-08Published:2025-05-23 -
Contact:Li Nan, Doctoral supervisor, College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350122, Fujian Province, China; Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Orthopedics and Sports Rehabilitation, Ministry of Education, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350122, Fujian Province, China -
About author:Gu Fucheng, Master candidate, College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350122, Fujian Province, China; Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Orthopedics and Sports Rehabilitation, Ministry of Education, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350122, Fujian Province, China -
Supported by:Fujian Provincial Financial Special Project, No. X2022001, X2022002 (to LN); Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China, No. 2023J01865 (to LN); Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China, No. 2022J01364 (to GQD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gu Fucheng, Yang Meixin, Wu Weixin, Cai Weijun, Qin Yangyi, Sun Mingyi, Sun Jian, Geng Qiudong, Li Nan. Effects of Guilu Erxian Glue on gut microbiota in rats with knee osteoarthritis: machine learning and 16S rDNA analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1058-1072.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
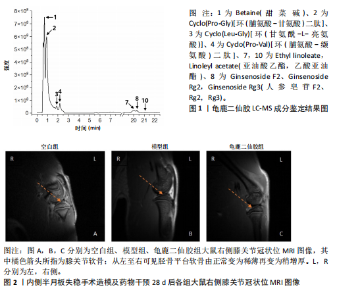
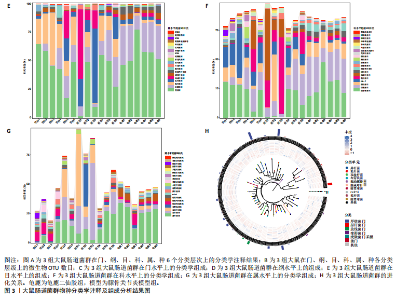
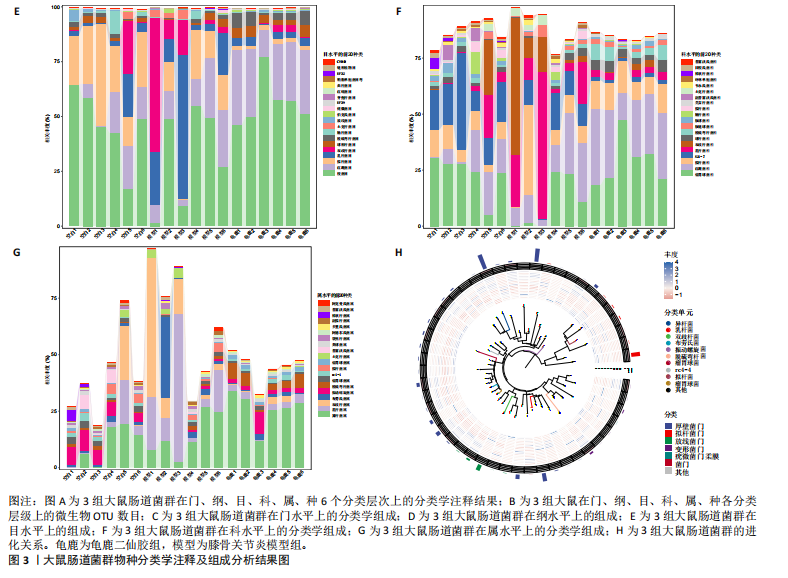
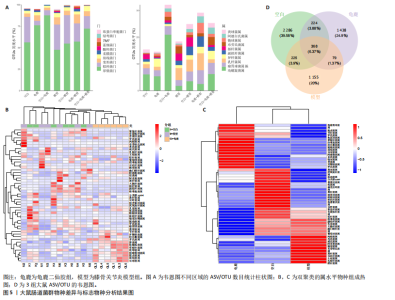
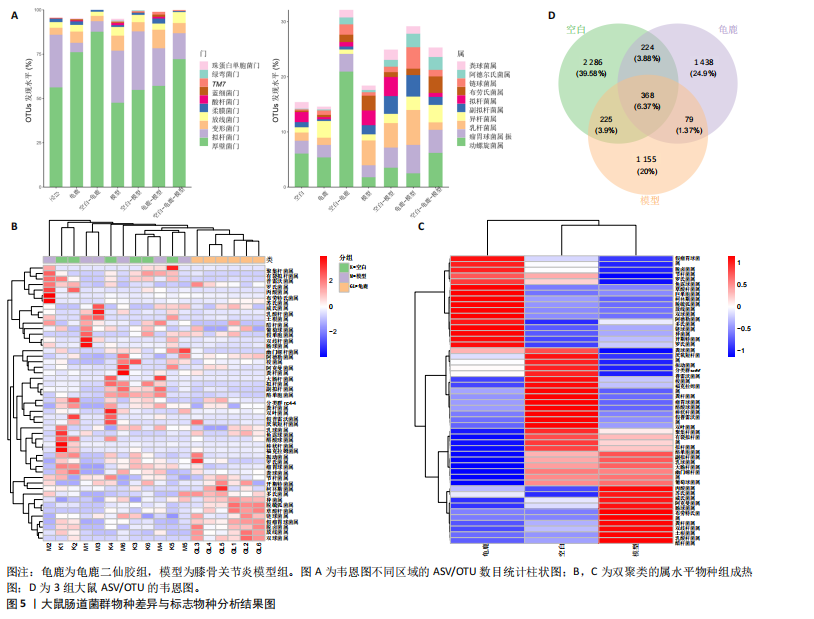
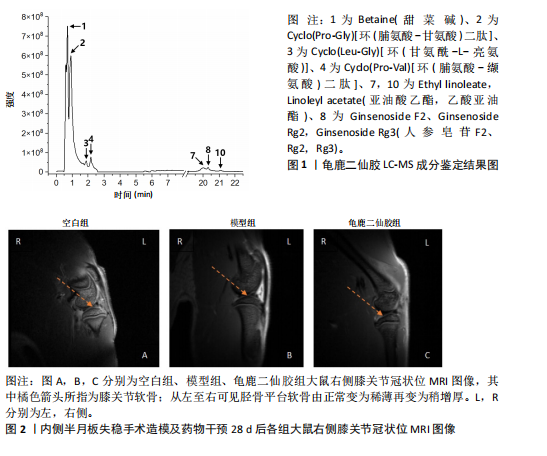
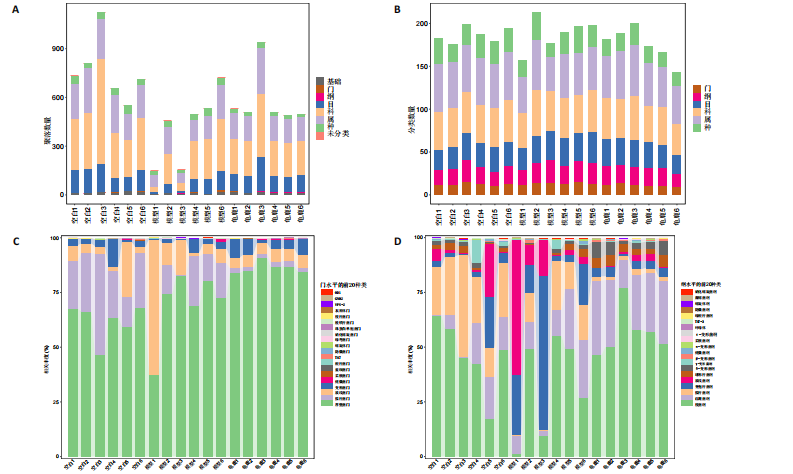
2.1 实验动物数量分析 实验共有18只SD雄性大鼠,造模及干预过程均无大鼠死亡而脱失。 2.2 龟鹿二仙胶高效液相色谱分析成分鉴定结果 对龟鹿二仙胶中药复方进行LC-MS成分鉴定,共指出7种有效成分,分别为Betaine(甜菜碱)、Cyclo(Pro-Gly)[环(脯氨酸-甘氨酸)二肽]、Cyclo(Leu-Gly)[环(甘氨酰-L-亮氨酸)]、Cyclo(Pro-Val)[环(脯氨酸-缬氨酸)二肽]、Ethyl linoleate(亚油酸乙酯),Linoleyl acetate(乙酸亚油酯)、Ginsenoside F2、Ginsenoside Rg2、Ginsenoside Rg3(人参皂苷F2,Rg2,Rg3),见图1。 2.3 膝关节软骨核磁病理评估 核磁分析结果:空白组膝关节无滑膜炎症且内侧髁及胫骨平台软骨完整均匀,关节间隙尚可;而模型组大鼠膝关节存在呈高信号影的慢性滑膜炎症,股骨内侧髁软骨层部分变薄,部分消失,关节间隙变窄;龟鹿二仙胶组大鼠高密度影的滑膜炎症范围减少,且股骨头内侧髁软骨较模型组退化较少,见图2A-C。 2.4 肠道菌群生物信息分析结果 根据16S rDNA测序数据,3组大鼠的肠道菌群在门、纲、目、科、属等多个分类层级上存在显著的差异。空白组的肠道菌群在门、纲、目、科、属、种等层级上表现出较高的多样性,富集了多种有益微生物。模型组大鼠则表现出明显的菌群失衡,主要体现在门水平上的厚壁菌门和拟杆菌门的丰度显著降低,而变形菌门的比例显著增加。龟鹿二仙胶组大鼠的肠道菌群结构有了显著改善,其厚壁菌门和拟杆菌门的比例回升,恢复了更为多样的菌群组成,接近空白组,见图3A。3组大鼠在不同分类层级(门、纲、目、科、属、种)上的微生物OTU数量结果表明,模型组大鼠的OTU数量在所有分类层级上均显著低于空白组,尤其在属和种的层次,表明膝骨关节炎模型的建立导致了肠道菌群的显著丧失和多样性下降。相比之下,龟鹿二仙胶组大鼠的OTU数量显著回升,尤其在属和种的层次,表明龟鹿二仙胶通过调节肠道菌群恢复了部分多样性,见图3B。在门水平,空白组的肠道菌群主要由厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)、"
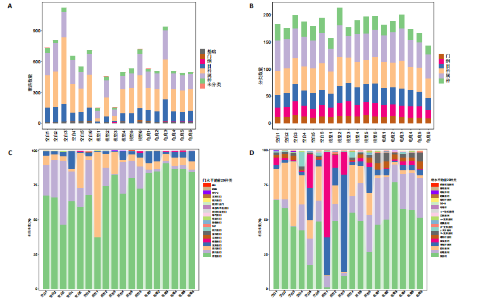
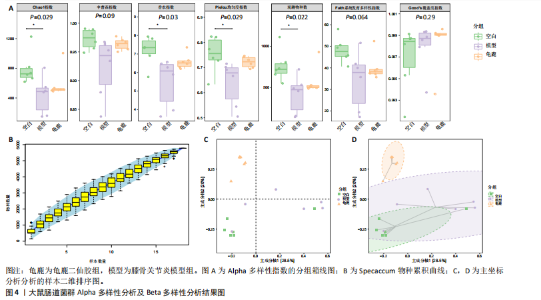
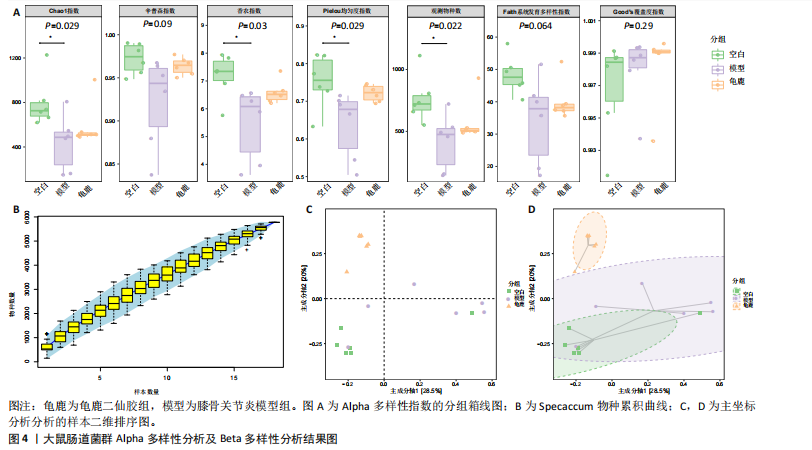
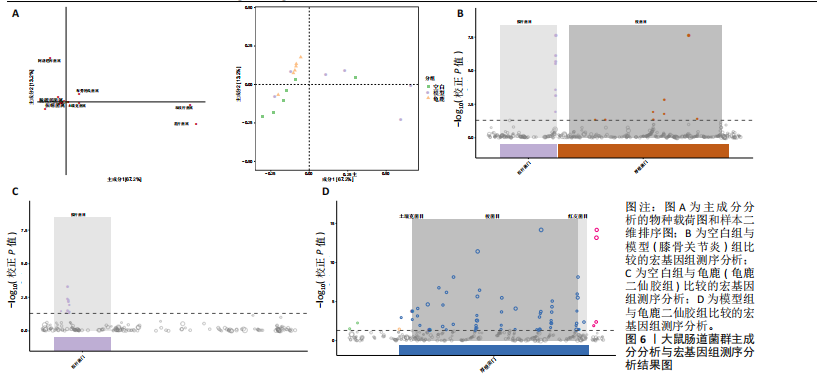
拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)和变形菌门(Proteobacteria)构成,且比例较为均衡,见图3C。模型组大鼠肠道菌群中,厚壁菌门和拟杆菌门的比例显著减少,而变形菌门的丰度显著增加。龟鹿二仙胶组大鼠的肠道菌群厚壁菌门和拟杆菌门的比例有所回升,变形菌门的丰度下降。在纲、目、科、属水平,见图3D-G,空白组和龟鹿二仙胶组的菌群组成表现出较为相似的特征,以乳酸菌属(Lactobacillus)和异杆菌属(Akkermansia)为主,而模型组大鼠则以梭菌属(Clostridium)和双歧杆菌属(Bifidobacterium)为主,且梭菌属的比例显著增加。龟鹿二仙胶组大鼠恢复了乳酸菌属和异杆菌属的丰度,同时显著减少了梭菌属的丰度。进化树显示,空白组和龟鹿二仙胶组大鼠的菌群组成较为相似,表明它们的肠道菌群结构较为接近,主要由乳酸菌属、异杆菌属等有益菌主导,见图3H。相比之下,模型组大鼠的肠道菌群表现出较大的进化距离,且在物种组成上与空白组和龟鹿二仙胶组存在显著差异。 2.5 Alpha多样性分析及Beta多样性分析 3组的总样本量为18个,纳入全部18个样本之后,物种累积曲线趋于平缓,这说明可以观察 6 000 多个物种,且物种数量不会随着样本的增加而增加,提示实验纳入的样本数量可以很好地反映微生物群落的丰富度。图4A中显示了7个指标的分析结果:①Chao1指数结果显示,空白组的Chao1指数显著高于模型组(P < 0.05),表明空白组肠道菌群具有更高的物种丰富度,龟鹿二仙胶组的大鼠Chao1指数明显高于模型组,但与空白组差异不显著。②Simpson指数分析结果显示,模型组的Simpson指数显著高于空白组和龟鹿二仙胶组(P < 0.05),提示模型组肠道菌群中某些物种的丰度过高,造成了菌群的不均衡。龟鹿二仙胶组的Simpson指数明显降低,显示出菌群的均衡得到了恢复。③Shannon指数分析结果显示,空白组的Shannon指数显著高于模型组(P < 0.01),说明空白组肠道菌群多样性较高,而模型组由于菌群失衡,Shannon指数显著下降;龟鹿二仙胶组的Shannon指数也有所回升,接近空白组。④Pielou均匀度指数分析结果显示,空白组的Pielou均匀度指数显著高于模型组,提示造模处理引起了微生物群落均匀度的显著下降。而龟鹿组的Pielou均匀度指数较模型组显著恢复,接近空白组的水平,表明龟鹿二仙胶干预对微生物群落的均匀性具有显著的改善作用,3组在Pielou均匀度指数上存在显著差异(P=0.029)。⑤观测物种数分析结果显示,空白组的观测物种数显著高于模型组,而龟鹿组的观测物种数较模型组显著增加,并趋近空白组,这表明龟鹿二仙胶干预能够在一定程度上恢复模型组因疾病造成的物种丰富度下降,差异具有显著性(P=0.022)。⑥Faith系统发育多样性指数分析结果显示,在3组间Faith系统发育多样性指数未表现出显著差异(P=0.064),但趋势上,空白组的指数最高,模型组最低,而龟鹿组表现出一定程度的恢复。尽管差异未达到显著性水平,该结果仍提示龟鹿二仙胶干预对系统发育多样性的潜在正向作用。⑦Good’s覆盖度指数分析结果显示,所有组别的Good’s覆盖度指数均接近1,表明测序深度足够,样本测序结果具有高度可靠性。虽然各组Good’s覆盖度指数无显著性差异,模型组的覆盖度指数略低于空白组和龟鹿组,提示模型组的菌群多样性仍存在一定不足,3组之间无显著性差异(P=0.29)。主坐标分析显示,图中3组大鼠的样本显著分为3类,空白组、模型组和龟鹿二仙胶组的样本在主坐标分析图中显示出明显的分离,见图4B-D。模型组的样本之间的距离较大,说明该组大鼠肠道菌群的组成差异较为显著。空白组和龟鹿二仙胶组的样本则更为集中,表明它们的菌群组成相似,并且与模型组之间存在显著差异(P < 0.01)。龟鹿二仙胶组的样本分布接近空白组;ANOSIM分析表明,空白组与模型组、龟鹿二仙胶组之间的群落差异显著(R=0.65,P < 0.01),空白组与龟鹿二仙胶组之间也显示出一定的群落差异,但该差异显著性较小(R=0.35,P < 0.05),提示龟鹿二仙胶组与空白组相比,肠道菌群的组成有所恢复。 2.6 物种差异分析与标志物种 通过韦恩图分析了3组大鼠肠道菌群的物种组成差异。其中,空白组特有的物种为2 286个,占39.58%;模型组特有的物种为1 155个,占20%;龟鹿二仙胶组特有的物种为1 438个,占24.9%。表明模型组大鼠的肠道菌群与空白组和龟鹿二仙胶组的差异较大,尤其是在模型组,许多有害菌的丰度增加,而龟鹿二仙胶组则表现出接近空白组的物种组成。在门水平,空白组和龟鹿二仙胶组的肠道菌群以厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)和拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)为主,而模型组则出现了变形菌门(Proteobacteria)丰度的明显增加,见图5A左图。在属水平,空白组和龟鹿二仙胶组的肠道菌群主要由乳酸菌属(Lactobacillus)和异杆菌属(Akkermansia)占主导地位,而模型组大鼠则以梭菌属(Clostridium)和双歧杆菌属(Bifidobacterium)为主,显示出有害菌的比例增加,见图5A右图。龟鹿二仙胶组恢复了乳酸菌属和异杆菌属的丰度,同时显著减少了梭菌属的丰度。双聚类属水平物种组成热图显示空白组呈现出以乳酸菌属(Lactobacillus)、异杆菌属(Akkermansia)等有益菌为主的特征,且这些有益菌在该组大鼠的肠道中丰度较高,显示出良好的肠道微生态状态,见图5B,C。其他常见的有益菌如双歧杆菌属(Bifidobacterium)和普雷沃氏菌属(Prevotella)也在空白组中有所丰度。3组之间共享的物种有368个,占总物种的6.37%,见图5D。模型组显示了较大的差异,梭菌属(Clostridium)和变形菌属(Proteus)表现出较高的丰度,而乳酸菌属和异杆菌属的丰度显著降低。龟鹿二仙胶组的热图与空白组相似,乳酸菌属(Lactobacillus)和异杆菌属(Akkermansia)的丰度显著回升,接近空白组的水平。此外,梭菌属(Clostridium)和其他有害菌的丰度显著下降,见图5。 2.6.1 主成分分析及宏基因组测序分析结果 实验利用主成分分析及宏基因组测序分析尝试寻找样本组间在统计上具有显著差异的ASV/OTU,再找出这些差异ASV/OTU在不同分类水平上具有富集的趋势。图6A的主成分分析显示空白组和龟鹿二仙胶组的"
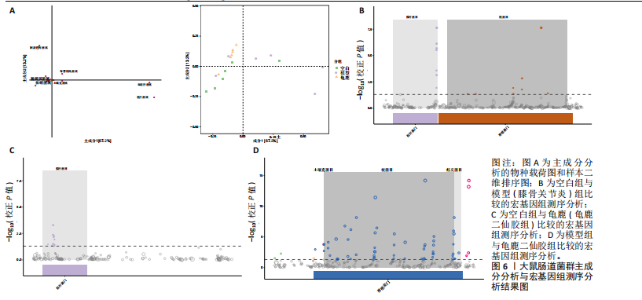
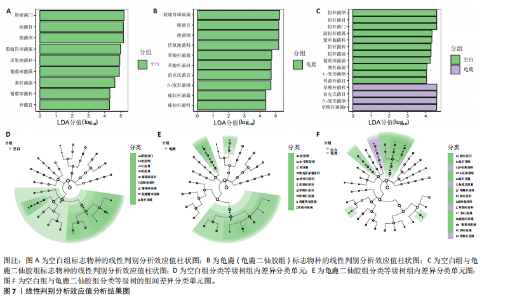
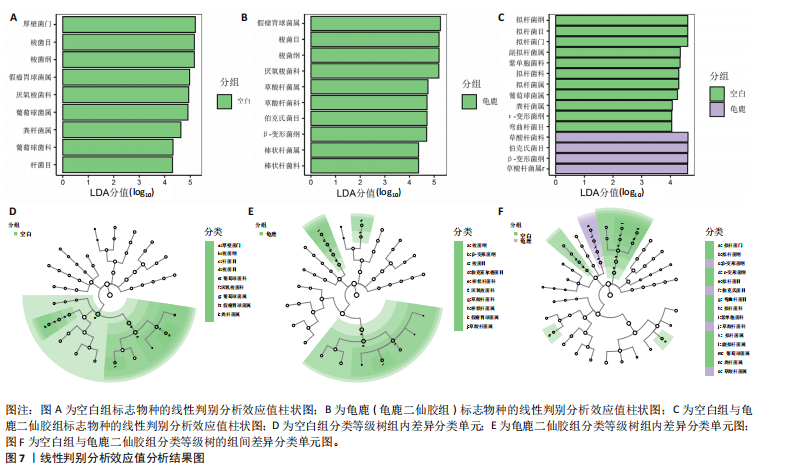
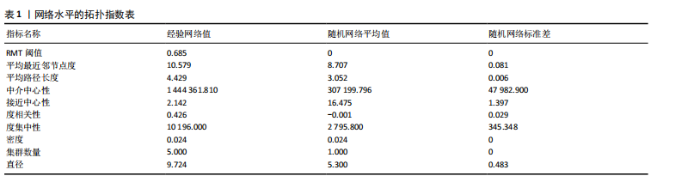
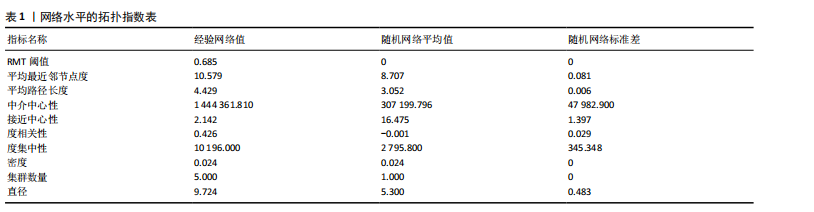
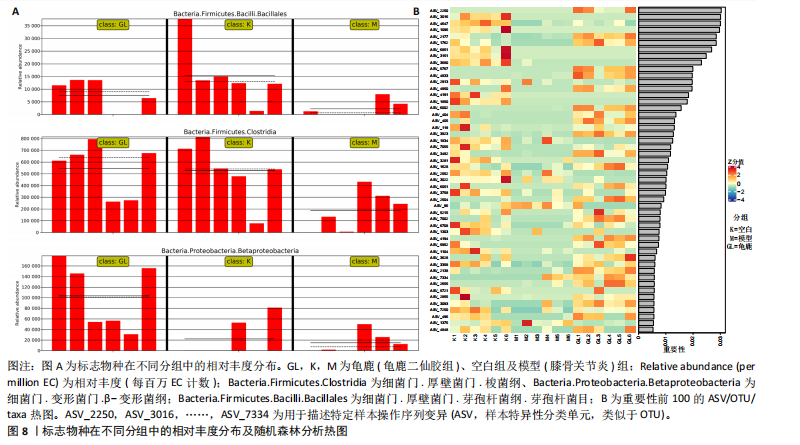
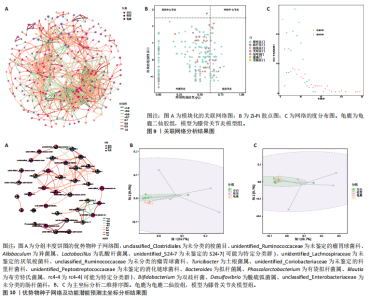
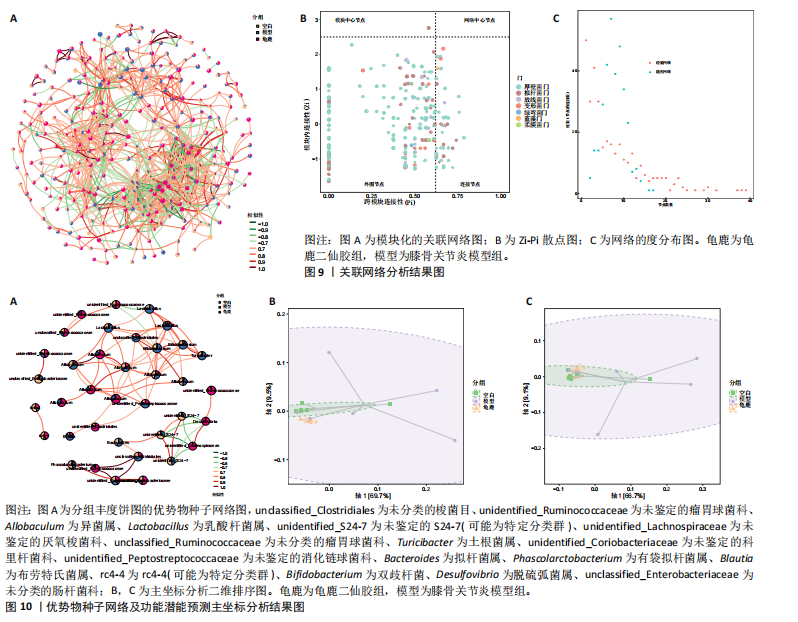
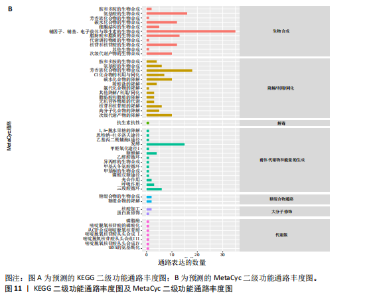
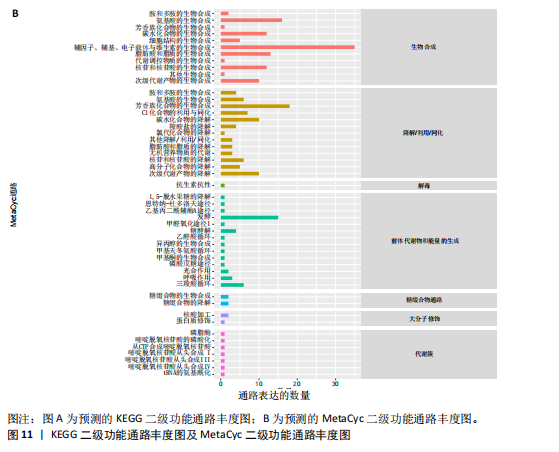
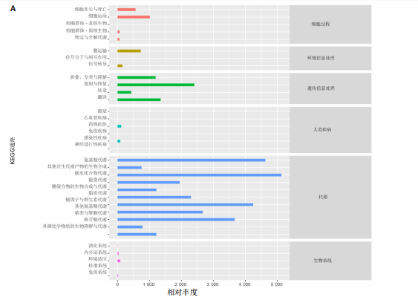
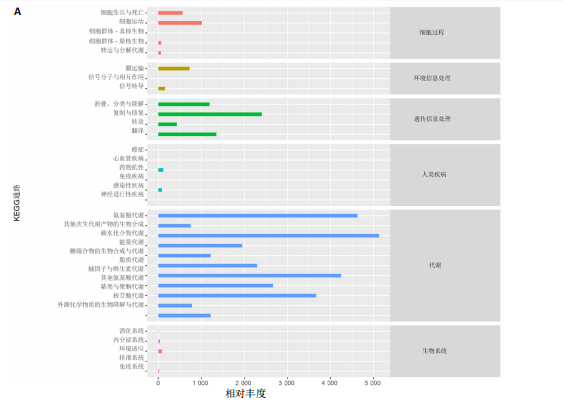
大鼠样本在图中聚集在一起,显示出较高的相似性,说明它们的肠道菌群组成较为相似。相比之下,模型组的样本在主成分分析图中与空白组和龟鹿二仙胶组有明显的分离;空白组和龟鹿二仙胶组的样本分布较为集中,组内变异较小,显示出这些组的肠道菌群组成较为一致。模型组的样本则显著分散,表现出较大的组内差异。图6B的宏基因组测序分析显示空白组和龟鹿二仙胶组的物种组成差异较小,且这些物种在组间的丰度差异较为显著。相比之下,模型组的肠道菌群与空白组和龟鹿二仙胶组在物种丰度上有更大的差异,尤其是在一些有害菌的丰度上,模型组表现出显著的上升。模型组肠道菌群的差异性比空白组和龟鹿二仙胶组大。图6C显示,空白组和龟鹿二仙胶组的标志物种主要为乳酸菌属(Lactobacillus)和异杆菌属(Akkermansia),而模型组则以梭菌属(Clostridium)为主。线性判别分析得分的柱状图显示,乳酸菌属和异杆菌属在空白组和龟鹿二仙胶组中的线性判别分析得分较高,表明这些物种在这两组中占据主导地位。图6D显示,模型组的大鼠肠道菌群中,梭菌属、双歧杆菌属和普雷沃氏菌属的丰度显著增加,而乳酸菌属和异杆菌属的丰度则显著减少。 2.6.2 线性判别分析效应值分析及随机森林分析结果 实验使用线性判别分析效应值分析和随机森林算法深入挖掘变量之间复杂的非线性相互依赖关系,寻找龟鹿二仙胶干预过后的标志物种,见图7A-F。图7A,D显示,乳酸菌属(Lactobacillus)和异杆菌属(Akkermansia)在空白组中的线性判别分析得分显著高于模型组,表明这些物种在空白组的肠道菌群中占据主导地位;模型组的肠道菌群中,梭菌属(Clostridium)和变形菌属(Proteus)的线性判别分析得分较高,表明它们在模型组中占据主导地位。图7B,E显示,与空白组和模型组相比,龟鹿二仙胶组的乳酸菌属和异杆菌属的线性判别分析得分均有显著回升。图7C,F显示,龟鹿二仙胶组的乳酸菌属和异杆菌属的线性判别分析得分与空白组相似,而模型组的差异性物种,如梭菌属的得分较低。图8A显示,模型组中梭菌属(Clostridium)和双歧杆菌属(Bifidobacterium)的丰度较高,而在空白组中,乳酸菌属和异杆菌属的丰度占主导地位。随机森林分析结果表明,梭菌属的丰度在模型组中的重要性最高,其对组间差异性贡献最大,图8B显示,龟鹿二仙胶组的大鼠肠道菌群恢复了乳酸菌属和异杆菌属的丰度,同时显著减少了梭菌属和变形菌属的丰度。分析结果显示,乳酸菌属和异杆菌属对龟鹿二仙胶组的差异贡献显著,表明龟鹿二仙胶通过促进有益菌的生长,抑制有害菌的过度生长,有助于恢复肠道菌群的平衡。 2.7 关联网络分析结果 图9A显示,在共现网络中,龟鹿二仙胶组、模型组和空白组通过颜色区分、节点的连边权重代表菌种间的相关性。龟鹿二仙胶组形成了更加紧密和中心化的网络结构,节点间相关性显著增强(相似性值集中在0.7-1.0),提示龟鹿二仙胶可能通过增强有益菌之间的协同作用,改善菌群稳态。图9B的模块内和模块间连接性分析进一步验证关键菌群的网络拓扑属性。模块连接性(Zi)和网络连接性(Pi)的散点分布显示,大部分菌种属于外围节点,而在龟鹿二仙胶组中,关键模块的核心节点显著增多,主要分布于厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)和拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes),与其对肠道菌群的调控效果密切相关。此外,图9C的网络统计特性分析表明,龟鹿二仙胶组的网络直径和节点数量显著高于随机网络,进一步证明了龟鹿二仙胶组网络结构的生物学意义和稳定性。这些结果提示,龟鹿二仙胶通过显著优化菌群网络结构,可能在调节宿主微生态平衡方面发挥重要作用,见表1。 2.8 优势物种子网络及功能潜能预测 图10A可见,在优势物种子网络中龟鹿二仙胶组的网络连接性显著增强,反映出菌群内的协同作用得到明显改善。通过饼图可以看出,龟鹿二仙胶组关键优势菌种的丰度显著高于模型组和空白组,尤其是厚壁菌门 (Firmicutes)和拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)。 图10B,C主坐标分析显示龟鹿二仙胶组样本与其他组分离度明显,主坐标分析主成分1和2分别解释了肠道菌群变异的45.3%和21.7%。结果表明,龟鹿二仙胶通过调节肠道菌群的组成和结构,显著改变了膝骨关节炎大鼠的菌群功能潜能。 2.9 代谢通路统计结果 基于KEGG数据库的代谢通路分析结果显示,龟鹿二仙胶干预后大鼠肠道菌群的代谢活动在多个主要的一级和二级代谢通路中呈现显著变化,见图11A。一级代谢通路归为6类:代谢、细胞过程、遗传信息处理、环境信息处理、生物体系统和人类疾病。代谢(Metabolism) 类别中与氨基酸代谢(Amino acid metabolism)、碳水化合物代谢(Carbohydrate metabolism) 以及脂质代谢(Lipid metabolism) 相关的通路均显著上调,这表明龟鹿二仙胶可能通过增强菌群对这些基础营养物质的代谢能力,改善宿主的整体能量利用效率与营养状况。此外,细胞过程(Cellular Processes) 类别中的通路如细胞运动(Cell motility)、细胞生长与死亡(Cell growth and death) 等,也表现出活性的增强,提示龟鹿二仙胶在调节肠道菌群的更新和代谢活性方面可能具有积极的作用,维持了菌群的动态平衡。遗传信息处理(Genetic Information Processing) 类别中的复制和修复(Replication and repair) 途径显著恢复,可能有助于受损菌群的基因稳定性,促进有益菌种的生长和维持其功能稳定。在环境信息处理(Environmental Information Processing) 方面,信号转导和膜运输相关通路也有所增强,表明龟鹿二仙胶可能通过增强菌群的环境适应能力,促进菌群之间及其与宿主之间的相互作用。此外,在人类疾病(Human Diseases) 类别中,免疫性疾病、感染性疾病等代谢途径的丰度增加,可能暗示龟鹿二仙胶对增强宿主免疫力具有一定潜在作用,从而减缓炎症反应和改善疾病状态。 MetaCyc数据库中的代谢分析进一步验证了龟鹿二仙胶对大鼠肠道菌群的广泛调节作用,见图11B。MetaCyc代谢路径主要包括生物合成(Biosynthesis)、退化/利用/同化(Degradation/Utilization/Assimilation)、解毒(Detoxification) 和前体代谢物和能量的生成(Generation of Precursor Metabolite and Energy) 等多个代谢类别。在生物合成(Biosynthesis) 方面,"
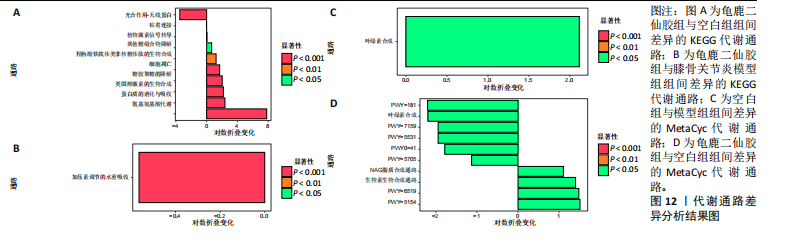
脂肪酸和脂质的生物合成(Fatty Acid and Lipid Biosynthesis)、辅因子、假体基团、电子载体和维生素的生物合成(Cofactor,Prosthetic Group,Electron Carrier,and Vitamin Biosynthesis) 的通路显著上调,表明龟鹿二仙胶可能通过促进这些营养物质的合成,提高宿主对这些关键代谢产物的可利用性,进而增强其免疫调节和抗炎功能。退化/利用/同化(Degradation/Utilization/Assimilation) 类别中的芳香族化合物降解、脂肪酸降解等功能增强,提示龟鹿二仙胶有助于提高菌群对有害物质的降解与利用,从而优化肠道的微生态环境。特别是在解毒(Detoxification) 方面,通过增强代谢产物的解毒和清除能力,龟鹿二仙胶组的菌群可能更好地保护宿主免受潜在毒素的危害。前体代谢物和能量的生成(Generation of precursor metabolite and energy) 类别中的代谢途径,如三羧酸循环和糖酵解等基础代谢过程得到了显著增强,反映出龟鹿二仙胶组菌群的能量代谢活性提高。这些代谢活动的增强可能在一定程度上改善了宿主的能量平衡及其对环境压力的适应能力。此外,在大分子修饰(Macromolecule modification) 和代谢簇(Metabolic clusters) 方面,龟鹿二仙胶组的代谢途径也显示出增强,提示其可能通过促进菌群基因表达和代谢产物修饰,维持菌群的健康与稳定性。 2.9.1 代谢通路差异分析结果 获得代谢通路的丰度数据后,使用宏基因组测序分析法找出KEGG及MetaCyc组间具有显著差异代谢通路。图12A显示,KEGG中龟鹿二仙胶组与空白组差异代谢通路主要包括氰氨基酸代谢(Cyanoamino acid metabolism)、蛋白质消化和吸收(Protein digestion and absorption)、类固醇激素生物合成(Steroid hormone biosynthesis)、糖胺聚糖降解(Glycosaminoglycan degradation)、细胞凋亡(Apoptosis)、铁载体基团非核糖体肽的生物合成(Biosynthesis of siderophore group nonribosomal peptides)、其他聚糖降解(Other glycan degradation)、植物激素信号转导(Plant hormone signal transductio)。图12B显示,龟鹿二仙胶组与模型组差异代谢通路为加压素"
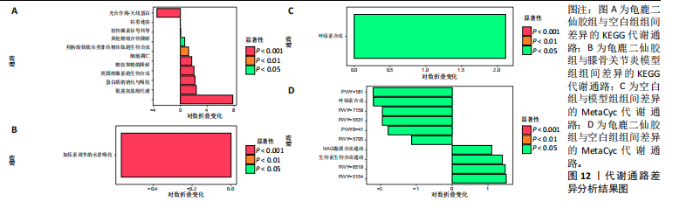
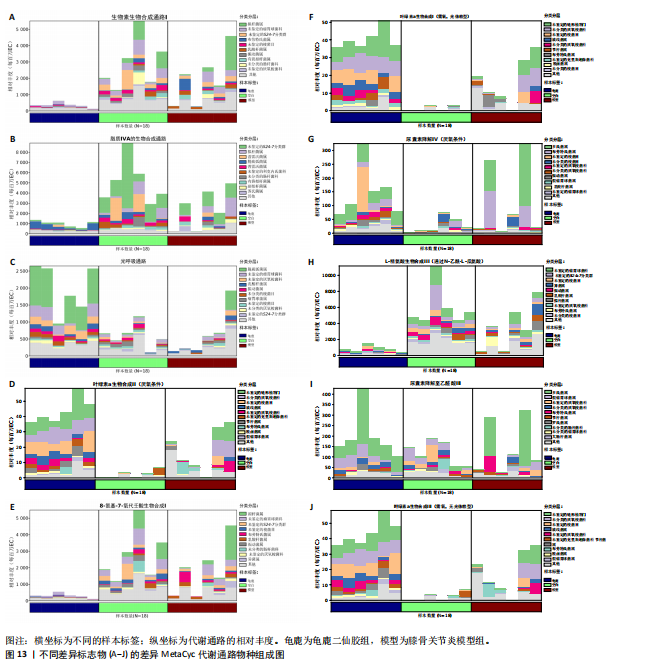
调节水重吸收(Vasopressin regulated water reabsorption)。图12C,D显示,MetaCyc中空白组与模型组差异代谢通路为叶绿素合成(Chlorophyll Syn)、龟鹿二仙胶组与空白组差异代谢通路为pwy-181,7159,5531,5705,6519,5154;叶绿素合成(Chlorophyll Syn)、生物素生物合成(Biotin Biosynthesis PWY)。 2.9.2 差异通路的物种组成结果 依据显著差异的代谢通路,使用分层的样本代谢通路丰度表进行差异通路的物种组成分析,见图13。在空白组中,生物素合成通路(Biotin biosynthesis)的物种贡献较为集中,而在模型组中该通路丰度显著降低,显示膝骨关节炎状态下相关功能的削弱。龟鹿二仙胶组显著提升了该通路的丰度,说明龟鹿二仙胶可能通过提高肠道菌群对"

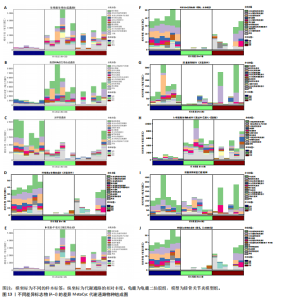
生物素的合成能力,增强宿主的代谢能力和免疫调节;模型组的叶绿素a生物合成(Chlorophyllide a biosynthesis I)通路几乎失活,而龟鹿二仙胶组的通路活性显著恢复。优势贡献物种为变形菌门(Proteobacteria);脂质代谢(Lipid IVA biosynthesis)通路在龟鹿二仙胶组中的丰度明显高于模型组和空白组;尿囊素降解(Allantoin degradation IV)功能在模型组中显著受抑,而龟鹿二仙胶组显著恢复其活性;光呼吸(Photorespiration)通路在模型组中下降显著,龟鹿二仙胶组的恢复表明其对肠道微生物能量代谢的调节作用。L-精氨酸生物合成(L-arginine biosynthesis Ⅲ)龟鹿二仙胶组在L-精氨酸合成中的活性显著高于其他两组。主要贡献菌为厚壁菌门和放线菌门;龟鹿二仙胶组在叶绿素a生物合成Ⅱ(Chlorophyllide a biosynthesis Ⅱ)通路上的活性显著增强,与模型组相比显示出强大的恢复能力。尿囊素降解至乙醛酸模型组(Allantoin degradation to glyoxylate Ⅲ)的代谢活性受损,龟鹿二仙胶组在该通路的活性显著提升。8-氨基-7-氧代壬二酸生物合成,(8-amino-7-oxononanoate biosynthesis Ⅰ),龟鹿二仙胶组在该通路上的丰度显著增加,物种贡献集中于厚壁菌门和拟杆菌门。龟鹿二仙胶组叶绿素a生物合成光依赖(Chlorophyllide a biosynthesis Ⅲ)的代谢活性大幅度提升,恢复了模型组失衡的代谢功能。"

| [1] 肖剑伟.骨关节炎中西医结合诊疗指南[J].风湿病与关节炎,2023,12(6):70-80. [2] 周荣, 廖文洁.软骨下骨在骨关节炎中的病理改变及其机制研究[J].系统医学,2021,6(24):190-193. [3] 李崇,缪季峰,林秋宁,等.外泌体非编码RNA在骨关节炎软骨损伤修复中的研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志,2021,41(3):186-194. [4] GRASSEL S, ASZODI A. Osteoarthritis and cartilage regeneration: focus on pathophysiology and molecular mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(24): 6156. [5] JANG S, LEE K, JU JH. Recent updates of diagnosis, pathophysiology, and treatment on osteoarthritis of the knee. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2619. [6] BELK JW, KRAEUTLER MJ, HOUCK DA, et al. Platelet-rich plasma versus hyaluronic acid for knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Sport Med. 2021;49(1):249-260. [7] ZEITER S, KOSCHITZKI K, ALINI M, et al. Evaluation of preclinical models for the testing of bone tissue-engineered constructs. Tissue Eng Part C-Methods. 2020;26(2):107-117. [8] 李文顺,李楠,余丹丹,等.龟鹿二仙胶汤治疗膝骨关节炎的临床研究[J].福建中医学院学报, 2005,15(6):30-32. [9] 李楠,雒焕生,赵诣,等.龟鹿二仙胶汤及其拆方对大鼠软骨细胞凋亡基因表达的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2011,19(7):1-3. [10] 李楠,杜江,黄远鹏,等.龟鹿二仙胶及其拆方对SD大鼠膝骨关节炎的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2013,28(6):1677-1680. [11] 耿秋东,葛海雅,王和鸣,等.基于网络药理学探讨龟鹿二仙胶治疗骨关节炎的作用及机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(8):1229-1236. [12] SENGPRASERT P, WAITAYANGKONN P, KAMENKIT O, et al. Catabolic mediators from TLR2-mediated proteoglycan aggrecan peptide-stimulated chondrocytes are reduced by Lactobacillus-conditioned media. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):18043. [13] STEVENS C, NORRIS S, ARBEEVA L, et al. Gut microbiome and osteoarthritis: insights from the naturally occurring canine model of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024;76(12):1758-1763. [14] WANG Y, MA M, DAI W, et al. Bacteroides salyersiae is a potent chondroitin sulfate-degrading species in the human gut microbiota. Microbiome. 2024;12(1):41. [15] LUO S, CHEN Z, DENG L, et al. Causal link between gut microbiota, neurophysiological states, and bone diseases: a comprehensive mendelian randomization study. Nutrients. 2023;15(18):3934. [16] LIU L, TIAN F, LI G, et al. The effects and significance of gut microbiota and its metabolites on the regulation of osteoarthritis: close coordination of gut-bone axis. Front Nutr. 2022;9: 1012087. [17] HAO X, SHANG X, LIU J, et al. The gut microbiota in osteoarthritis: where do we stand and what can we do? Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):42. [18] ARORA V, SINGH G, O-SULLIVAN I, et al. Gut-microbiota modulation: the impact of thegut-microbiotaon osteoarthritis. Gene. 2021;785: 145619. [19] ELSAWY NA, IBRAHIEM AH, YOUNIS GA, et al. Microbiome and femoral cartilage thickness in knee osteoarthritis: is there a link? Cartilage. 2024. doi: 10.1177/19476035241276852. [20] CHEN LC, LIN YY, TSAI YS, et al. Live and dead clostridium butyricum gkb7 diminish osteoarthritis pain and progression in preclinical animal model. Environ Toxicol. 2024;39(11):4927-4935. [21] 易南星,米倚林,许晓彤,等.加味独活寄生合剂缓解小鼠膝骨关节炎过程中肠道菌群的参与机制[J].中国药理学通报,2022,38(4):625-632. [22] BIAN M, ZHU C, NIE A, et al. Guizhi Shaoyao Zhimu Decoction ameliorates gouty arthritis in rats via altering gut microbiota and improving metabolic profile. Phytomedicine. 2024;131:155800. [23] CUEVAS-SIERRA A, RAMOS-LOPEZ O, RIEZU-BOJ JI, et al. Diet, gut microbiota, and obesity: links with host genetics and epigenetics and potential applications. Adv Nutr. 2019;10(suppl_1):S17-S30. [24] KARIM A. Unveiling the potential of probiotics in osteoarthritis management. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2024;27(1):2. [25] 刘晓辰,付维力.骨关节炎动物模型的选择[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(11):1769-1776. [26] 李仪奎.中药药理实验方法学[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,2006. [27] LIU Q, HAO H, LI J, et al. Oral administration of bovine milk-derived extracellular vesicles attenuates cartilage degeneration via modulating gut microbiota in dmm-induced mice. Nutrients. 2023;15(3):747. [28] NAKAHATA A, ITO A, NAKAHARA R, et al. Meniscus injury induces patellofemoral osteoarthritis development mediated by synovitis and gait kinematics: a preclinical study. Cartilage. 2024. doi: 10.1177/19476035241299769. [29] MILLER KA, BAIER MANWELL LM, BARTELS CM, et al. Implementing an osteoarthritis management program to deliver guideline-driven care for knee and hip osteoarthritis in a U.S. academic health system. Osteoarthr Cartilage. 2024;6(2):100452. [30] PAN H, GUO R, JU Y, et al. A single bacterium restores the microbiome dysbiosis to protect bones from destruction in a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis. Microbiome. 2019;7(1):107. [31] LYU J, WANG T, CHEN Y, et al. Oral intake of streptococcus thermophilus improves knee osteoarthritis degeneration: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study. Heliyon. 2020;6(4):e3757. [32] TAYE I, BRADBURY J, GRACE S, et al. Probiotics for pain of osteoarthritis; An N-of-1 trial of individual effects. Complement Ther Med. 2020;54:102548. [33] BIVER E, BERENBAUM F, VALDES AM, et al. Gut microbiota and osteoarthritis management: An expert consensus of the European society for clinical and economic aspects of osteoporosis, osteoarthritis and musculoskeletal diseases (ESCEO). Ageing Res Rev. 2019;55:100946. [34] BONANZINGA T, CONTE P, ANZILLOTTI G, et al. Native intra-articular knee microbiome is a matter of facts: a systematic review of clinical evidence. EFORT Open Rev. 2024;9(10):969-979. [35] 叶敏兰,唐晓颇,高阳鹭,等.基于16S rDNA测序技术的膝骨关节炎湿热痹阻证、寒湿痹阻证患者肠道菌群差异性研究[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2024,31(1):152-158. [36] 吴霜,袁立霞,廖晴,等.基于16S rDNA测序研究当归拈痛汤对膝骨关节炎小鼠肠道菌群的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2024,30(11):9-17. [37] HUANG Z, CHEN J, LI B, et al. Faecal microbiota transplantation from metabolically compromised human donors accelerates osteoarthritis in mice. ARD. 2020;79(5):646-656. [38] YUAN X, CHEN R, ZHANG Y, et al. Gut microbiota: effect of pubertal status. BMC Microbiol. 2020; 20(1):334. [39] FAVAZZO LJ, HENDESI H, VILLANI DA, et al. The gut microbiome-joint connection: implications in osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2020; 32(1):92-101. [40] LI J, LIANG J, LIU Y, et al. Corrigendum: Basal metabolic rate mediates the causal relationship between gut microbiota and osteoarthritis: a two-step bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Front Microbiol. 2024;15:1510272. [41] ZHU D, WANG X, XI Z, et al. Diet influences knee osteoarthritis osteophyte formation via gut microbiota and serum metabolites. iScience. 2024;27(6):110111. [42] WANG J, WANG Y, CHEN Z, et al. Study on the mechanism of Shugan Lidan Xiaoshi granule in preventing acute pancreatitis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. Heliyon. 2024;10(5):e27365. [43] ZHANG X, KHAKISAHNEH S, HAN S, et al. Ginseng extracts improve circadian clock gene expression and reduce inflammation directly and indirectly through gut microbiota and PI3K signaling pathway. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024;10(1):24. [44] ZHOU X, LI W, ZHUANG C, et al. Lei’s formula attenuates osteoarthritis mediated by suppression of chondrocyte senescence via the mTOR axis: in vitro and in vivo experiments. Aging. 2024;16(5):4250. [45] FAN Y, BIAN X, MENG X, et al. Unveiling inflammatory and prehypertrophic cell populations as key contributors to knee cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis using multi-omics data integration. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024;83(7):926-944. [46] 陈景涛,陈有,李玉静,等.黄芪多糖抑制Toll样受体4/核因子κB p65通路治疗大鼠膝骨关节炎[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(31):5002-5008. [47] 韩铁玲.益生菌辅助治疗膝关节骨关节炎的临床研究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古医科大学,2023. [48] LEE YC, CHANG YT, CHENGY H, et al. Pterostilbene protects against osteoarthritis through NLRP3 inflammasome inactivation and improves gut microbiota as evidenced by in vivo and in vitro studies. J Agric Food Chem. 2024;72(16):9150-9163. [49] ZHENG YZ, CHEN QR, YANG HM, et al. Modulation of gut microbiota by crude mulberry polysaccharide attenuates knee osteoarthritis progression in rats. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024; 262(Pt 2):129936. [50] LIU M, MATUSZEK G, AZCARATE-PERIL MA, et al. An exploratory case-control study on the associations of bacterially-derived vitamin K forms with the intestinal microbiome and obesity-related osteoarthritis. Curr Dev Nutr. 2023;7(3):100049. [51] SONG X, LIU Y, CHEN S, et al. Knee osteoarthritis: a review of animal models and intervention of traditional Chinese medicine. Amem. 2024;7(2):114-126. [52] Delfino DV, Hu W, Hung Y, et al. Editorial: herbal medicines in pain management, volume II. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1364073. [53] BOER CG, RADJABZADEH D, MEDINA-GOMEZ C, et al. Intestinal microbiome composition and its relation to joint pain and inflammation. Nat Common. 2019;10(1):4881. [54] OLIPHANT K, ALLEN-VERCOE E. Macronutrient metabolism by the human gut microbiome: major fermentation by-products and their impact on host health. Microbiome. 2019;7(1):91. [55] LIU Y, DING W, WANG HL, et al. Gut microbiota and obesity-associated osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(9):1257-1265. [56] WU X, WANG Y, XIAO Y, et al. Extracellular vesicles: potential role in osteoarthritis regenerative medicine. J Orthop Translat. 2020;21:73-80. [57] ASGHAR S, LITHERLAND GJ, LOCKHART JC, et al. Exosomes in intercellular communication and implications for osteoarthritis. Rheumatology. 2020;59(1):57-68. [58] DENG Z, YANG C, XIANG T, et al. Gold nanoparticles exhibit anti-osteoarthritic effects via modulating interaction of the “microbiota-gut-joint” axis. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):157. [59] YANG F, XIONG W, LI C, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells mediate extracellular matrix remodeling in osteoarthritis through the transport of microRNA-29a. World J Stem Cells. 2024;16(2):191-206. [60] HRIDAYANKA K, DUTTAROY AK, BASAK S. Bioactive compounds and their chondroprotective effects for osteoarthritis amelioration: a focus on nanotherapeutic strategies, epigenetic modifications, and gut microbiota. Nutrients. 2024;16(21):3587. [61] MA K, PHAM T, WANG J, et al. Nanoparticle-based inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors alleviates osteoarthritis pain and cartilage damage. Sci Adv. 2024;10(7):i5501. [62] ABUGHAZALEH N, SMITH H, SEERATTAN RA, et al. Development of shoulder osteoarthritis and bone lesions in female and male rats subjected to a high fat/sucrose diet. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):25871. |
| [1] | Lai Jiaming, , Song Yuling, Chen Zixi, Wei Jinghuan, Cai Hao, , Li Guoquan, . Screening of diagnostic markers for endothelial cell Senescence in mice with radiation-induced heart disease and analysis of immune infiltration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1450-1463. |
| [2] | Li Linzhen, Jiao Hongzhuo, Chen Weinan, Zhang Mingzhe, Wang Jianlong, Zhang Juntao. Effect of icariin-containing serum on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory damage in human chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1368-1374. |
| [3] | Zhang Qian, Huang Dongfeng. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis combined with machine learning to screen and validate biomarkers for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1096-1105. |
| [4] | Guan Yujie, Zhao Bin. Application and prospect of artificial intelligence in screening and diagnosis of scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 721-730. |
| [5] | Wang Zhipeng, Zhang Xiaogang, Zhang Hongwei, Zhao Xiyun, Li Yuanzhen, Guo Chenglong, Qin Daping, Ren Zhen. A systematic review of application value of machine learning to prognostic prediction models for patients with lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 740-748. |
| [6] | Zhao Feifan, Cao Yujing. An artificial neural network model of ankylosing spondylitis and psoriasis shared genes and machine learning-based mining and validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 770-784. |
| [7] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Wang Chaolu. High tibial osteotomy on a single plane: femorofibular angle as a reference marker for mechanical axis correction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 570-576. |
| [8] | Guo Jingwen, Wang Qingwei, He Zijun, Hu Zihang, Chen Zhi, Zhu Rong, Wang Yuming, Liu Wenfei, Luo Qinglu. Intra-articular injection of different concentrations of silicon-based bioceramics in treatment of knee osteoarthritis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 288-295. |
| [9] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [10] | Ma Chi, Wang Ning, Chen Yong, Wei Zhihan, Liu Fengji, Piao Chengzhe. Application of 3D-printing patient-specific instruments combined with customized locking plate in opening wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1863-1869. |
| [11] | Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Wan Haili, Chang Ying, Xiong Wenjuan, Xia Yuan. Effect of neuromuscular exercise for knee osteoarthritis pain and function: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [12] | Wang Peiguang, Zhang Xiaowen, Mai Meisi, Li Luqian, Huang Hao. Generalized equation estimation of the therapeutic effect of floating needle therapy combined with acupoint embedding on different stages of human knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1565-1571. |
| [13] | Wang Mi, Ma Shujie, Liu Yang, Qi Rui. Identification and validation of characterized gene NFE2L2 for ferroptosis in ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1466-1474. |
| [14] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [15] |
Zhao Wensheng, Li Xiaolin, Peng Changhua, Deng Jia, Sheng Hao, Chen Hongwei, Zhang Chaoju, He Chuan.
Gut microbiota and osteoporotic fractures #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1296-1304.
|
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||