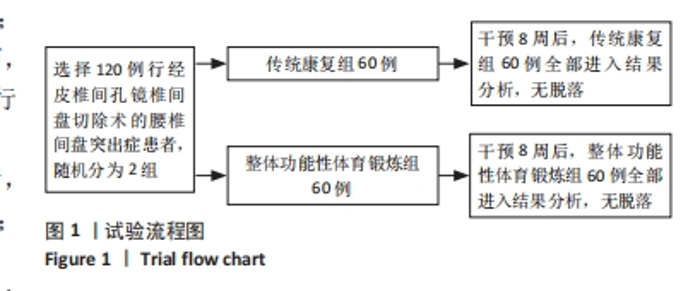
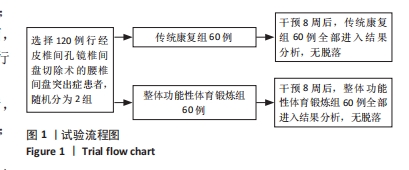
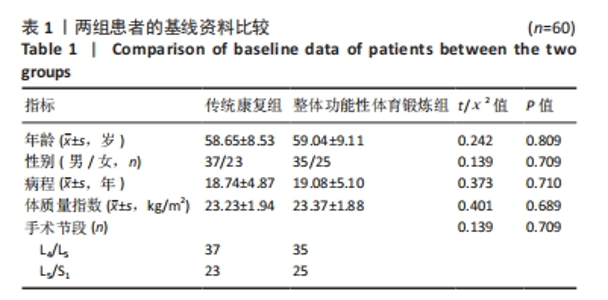
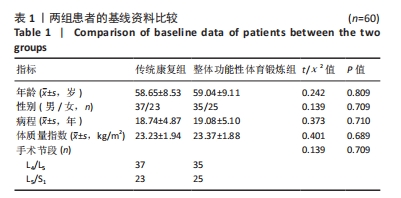
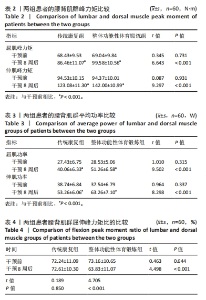
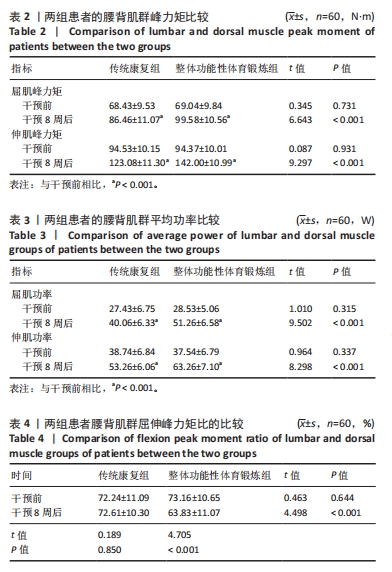
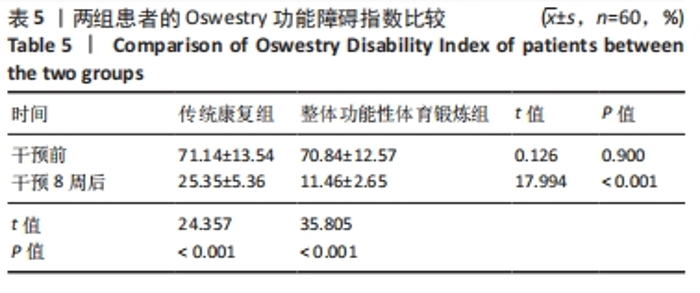
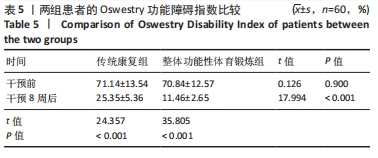
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (33): 7096-7101.doi: 10.12307/2025.815
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of overall functional physical exercise on lumbar biomechanics in patients with lumbar disc herniation after surgery
Yang Yu1, Li Yinghao1, Duo Zhuangzhi2, Zhou Dingrong3
- 1Zhengzhou Shengda College of Economics and Trade, Zhengzhou 451191, Henan Province, China; 2Department of Physical Education, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, Henan Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics of Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou 454002, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2024-04-01Accepted:2024-07-05Online:2025-11-28Published:2025-04-12 -
Contact:Duo Zhuangzhi, MS, Associate professor, Department of Physical Education, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, Henan Province, China -
About author:Yang Yu, MS, Lecturer, Zhengzhou Shengda College of Economics and Trade, Zhengzhou 451191, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Henan Province Education Curriculum Reform Research Project, No. 2024-JSJYYB-133 (to LYH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Yu, Li Yinghao, Duo Zhuangzhi, Zhou Dingrong. Effect of overall functional physical exercise on lumbar biomechanics in patients with lumbar disc herniation after surgery[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7096-7101.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] HORNUNG AL, BARAJAS JN, RUDISILL SS, et al. Prediction of lumbar disc herniation resorption in symptomatic patients: a prospective, multi-imaging and clinical phenotype study. Spine J. 2023;23(2):247-260. [2] MA Z, YU P, JIANG H, et al. Conservative Treatment for Giant Lumbar Disc Herniation: Clinical Study in 409 Cases. Pain Physician. 2021;24(5): E639-E648. [3] RICKERS KW, PEDERSEN PH, TVEDEBRINK T, et al. Comparison of interventions for lumbar disc herniation: a systematic review with network meta-analysis. Spine J. 2021;21(10):1750-1762. [4] TAŞPINAR G, ANGIN E, OKSÜZ S. The effects of Pilates on pain, functionality, quality of life, flexibility and endurance in lumbar disc herniation. J Comp Eff Res. 2023;12(1):e220144. [5] WANG W, LONG F, WU X, et al. Clinical Efficacy of Mechanical Traction as Physical Therapy for Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Meta-Analysis. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022;2022:5670303. [6] ZHANG AS, XU A, ANSARI K, et al. Lumbar Disc Herniation: Diagnosis and Management. Am J Med. 2023;136(7):645-651. [7] KAMPER SJ, OSTELO RW, RUBINSTEIN SM, et al. Minimally invasive surgery for lumbar disc herniation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2014;23(5):1021-1043. [8] KANNO H, AIZAWA T, HAHIMOTO K, et al. Minimally invasive discectomy for lumbar disc herniation: current concepts, surgical techniques, and outcomes. Int Orthop. 2019;43(4):917-922. [9] LEROY HA, GORWOOD W, HÄRTL R, et al. Minimally invasive tubular approach for lumbar extraforaminal disc herniation: how I do it. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2023;165(3):761-765. [10] CHEN Z, ZHANG L, DONG J, et al. Percutaneous Transforaminal Endoscopic Discectomy Versus Microendoscopic Discectomy for Lumbar Disk Herniation: Five-year Results of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2023;48(2):79-88. [11] GADJRADJ PS, HARHANGI BS, AMELINK J, et al. Percutaneous Transforaminal Endoscopic Discectomy Versus Open Microdiscectomy for Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2021;46(8):538-549. [12] MAAYAN O, PAJAK A, SHAHI P, et al. Percutaneous Transforaminal Endoscopic Discectomy Learning Curve: A CuSum Analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2023;48(21):1508-1516. [13] YIN S, DU H, YANG W, et al. Prevalence of Recurrent Herniation Following Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy: A Meta-Analysis. Pain Physician. 2018;21(4):337-350. [14] SOUSA O, DOS SANTOS COELHO F, PEREIRA P. Postoperative recommendations for single-level lumbar disc herniation: a cross-section survey. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023;143(9):5467-5473. [15] ZHANG R, ZHANG SJ, WANG XJ. Postoperative functional exercise for patients who underwent percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy for lumbar disc herniation. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018; 22(1 Suppl):15-22. [16] ZHU Y, XIA S, YANG W, et al. Early efficacy of postoperative rehabilitation training for lumbar disc herniation. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2023; 15(1):97. [17] MACNAB I. Negative disc exploration. An analysis of the causes of nerve-root involvement in sixty-eight patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971;53(5):891-903. [18] KIM YK, KANG D, LEE I, et al. Differences in the Incidence of Symptomatic Cervical and Lumbar Disc Herniation According to Age, Sex and National Health Insurance Eligibility: A Pilot Study on the Disease’s Association with Work. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018; 15(10):2094. [19] SHEN SC, CHEN HC, TSOU HK, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy for L5-S1 disc herniation based on image analysis and clinical findings: A retrospective review of 345 cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023;102(5):e32832. [20] WANG L, HE T, LIU J, et al. Revealing the Immune Infiltration Landscape and Identifying Diagnostic Biomarkers for Lumbar Disc Herniation. Front Immunol. 2021;12:666355. [21] ABDULLAH F, BAI A, SAHIL F, et al. Lumbar Disc Herniation: Comparing Pain Relief After Medical and Surgical Intervention. Cureus. 2021;13(6): e15885. [22] SUN K, HUANG F, QI B, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis for Chinese herbal medicine Duhuo Jisheng decoction in treatment of lumbar disc herniation: A protocol for a systematic review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(9):e19310. [23] LI J, CHU X, WAN W, et al. Radiographic characteristics-based classification system for percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy surgical approach selection in patients with L5-S1 disc herniation: a hierarchical clustering analysis. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023;13(12):8204-8217. [24] WANG R, LIANG ZY, CHEN XY, et al. Technical Tips for Percutaneous Transforaminal Endoscopic Discectomy: A Three-step Maneuver for Puncture and Early Clinical Experience. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(1):104-110. [25] WANG W, TANG L, ZHANG G, et al. Postoperative Upper-limb Palsy After Posterior Percutaneous Endoscopic Cervical Foraminotomy and Discectomy. Pain Physician. 2022;25(8):E1289-E1296. [26] ZHANG J, WANG X, CAI Z, et al. Analgesic effect of epidural anesthesia via the intervertebral foramen approach in percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy: a retrospective study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022; 22(1):397. [27] ZHAO Y, YUAN S, TIAN Y, et al. Necessity of routinely performing foraminoplasty during percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal discectomy (PETD) for lumbar disc herniation. Br J Neurosurg. 2023;37(3):277-283. [28] COULOMBE BJ, GAMES KE, NEIL ER, et al. Core Stability Exercise Versus General Exercise for Chronic Low Back Pain. J Athl Train. 2017; 52(1): 71-72. [29] ATSIDAKOU N, MATSI AE, CHRISTAKOU A. The effectiveness of exercise program after lumbar discectomy surgery. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021; 16:99-105. [30] LIU SK, SONG YL, DING WY, et al. The effect of systematic lower-limb rehabilitation training in elderly patients undergoing lumbar fusion surgery: a retrospective study. Oncotarget. 2017;8(68):112720-112726. [31] WU T, YE Y. The Effect of Lower-Limb Exercise on Pain Management of the Patients Undergoing Posterior Lumbar Fusion Surgery: A Retrospective Case-Control Study. Pain Res Manag. 2021;2021:3716696. [32] KIM BJ, KIM T, AHN J, et al. Manipulative rehabilitation applied soon after lumbar disc surgery improves late post-operative functional disability: A preliminary 2-year follow-up study. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2017;30(5):999-1004. [33] WANG H, HUO Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Clinical Rehabilitation Effect of Postoperative Lower-Limb Training on the Patients Undergoing OLIF Surgery: A Retrospective Study. Pain Res Manag. 2020;2020:1065202. [34] 李珂珂, 李艳, 汤莉, 等. 运用表面肌电分析悬吊治疗老年腰椎间盘突出症患者双侧肌肉失衡的疗效[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2020, 40(23):4987-4990. [35] HAGIYAMA A, YAMAMOTO N, KATAOKA Y. Comment on ‘effectiveness of a 12-month home-based exercise program on trunk muscle strength and spine function after lumbar spine fusion surgery: a randomized controlled trial’. Disabil Rehabil. 2022;44(17):4946. [36] ILVES O, NEVA MH, HÄKKINEN K, et al. Effectiveness of a 12-month home-based exercise program on trunk muscle strength and spine function after lumbar spine fusion surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Disabil Rehabil. 2022;44(4):549-557. [37] 宋爱晶, 邓京捷, 吕晓红, 等. 等速肌力测试膝、踝关节及腰背肌力量的评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015,19(46):7425-7429. [38] 史珊怡, 关睿骞, 于志国. 五段拔伸推拿法联合中药热敷治疗腰椎间盘突出症[J]. 贵州医科大学学报,2020,45(2):228-232. [39] 李飞舟, 黄锡婷, 张海, 等. 以ODI为指导的中西医结合康复疗法在老年腰椎间盘突出症中的作用[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2020,40(23): 5004-5007. [40] 占飞, 吴毅, 胡永善, 等. 腰椎间盘突出症患者腰屈伸肌的功能变化[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,1998,13(4):156-158. |
| [1] | Lu Qi, Sun Maji, Wang Xuezhi, Song Ting, Ma Yiming, Yuan Feng, Chen Hongliang. Two visual arthroplasty techniques for L5-S1 disc herniation: a half-year follow-up evaluation of clinical outcomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1841-1847. |
| [2] | Feng Zhimeng, Sun Ning, Sun Zhaozhong, Li Yuefei, Liu Changzhen, Li Sa. Three-dimensional image reconstruction can safely assist one-hole split endoscope in treatment of #br# L5/S1 far lateral lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1876-1882. |
| [3] | Zhang Chunlin, Hou Zhaohua, Yan Xu, Jiang Yan, Fu Su, Ning Yongming, Li Dongzhe, Dong Chao, Liu Xiaokang, Wang Yongkui, Cao Zhengming, Yang Tengyue. Decompression mechanism of symmetrically adduction of lumbar decompression induced resorption of herniated nucleus pulpous [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1810-1819. |
| [4] | Zhi Fang, Zhu Manhua, Xiong Wei, Lin Xingzhen. Analgesic effect of acupuncture in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 936-941. |
| [5] | Zhang Ziyu, Chen Longhao, Sheng Wei, Lyu Hanzhe, Shen Ying, Wang Binghao, Lyu Zhizhen, Lyu Lijiang. Application of artificial intelligence in the diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation: evolution towards standardization, efficiency, and precision of diagnosis and treatment methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6269-6276. |
| [6] | Bai Liang, Fu Su, Yan Xu, Zhang Chunlin, Li Ying . Measurement of intervertebral disc height and analysis of strength after induced resorption of herniated nucleus pulpous [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5785-5794. |
| [7] |
Wang Qianliang, Zhang Qianzhongyi, Peng Yujian, Yan Jun.
Effects of unilateral biportal endoscopic transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion on paraspinal muscles
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5862-5868.
|
| [8] | Zhang Ruofan, Guan Huanhuan, He Zhuoqun, Zhang Yunfeng, Jin Feng, Wang Zhiqiang, Wang Jianzhong, Li Xiaohe, Zhu Yong, Wang Haiyan, Zhang Kai. Effect of minimally invasive interbody fusion device height on lumbar biomechanics in patients with adolescent lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(21): 4421-4429. |
| [9] | Gu Jiangpeng, Chen Xujing, Liu Yikang, Guo Wei, Liu Xiaomin, Wang Fei, Feng Wei. Short-term effect of manipulation therapy for lumbar disc herniation quantitatively evaluated by three-dimensional scoliosis angle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(21): 4552-4559. |
| [10] | Wang Qianliang, Chen Jianpeng, Wang Yuanbin, Yan Jun. Mechanism of circ05188 targeting miR-199a-5p involved in nociceptive hypersensitivity in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4230-4238. |
| [11] | Gao Haoran, Zhang Heling, Jia Fanglin, Guo Di, Jing Li, Shi Yaozhou, Song Hanlin, Gao Xiao, Feng Hu. Risk factors related to intradural lumbar disc herniation analyzed by propensity score matching [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(15): 3199-3205. |
| [12] | Yin Hao, Ji Meiqi, Hu Zhixiang, Wu Han, Lyu Heng, Li Shengyun, Li Lei, Zhai Chuntao, Lyu Yue. Comparison and evaluation of three different methods for preparing rat models of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(14): 2930-2936. |
| [13] | Cao Zhengpei, Lu Shengsheng, Zhang Jiahuan, Wang Xiaoying. Effects of silver needle comprehensive therapy on the ultrasonographic morphology of multifidus muscles in patients with lumbar disc herniation: an ultrasound morphologic assessment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2261-2267. |
| [14] | Yu Weijie, Liu Aifeng, Chen Jixin, Guo Tianci, Jia Yizhen, Feng Huichuan, Yang Jialin. Advantages and application strategies of machine learning in diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1426-1435. |
| [15] | He Xinyu, Zhou Honghai, Jiang Hong, Ma Zhijia, Su Shaoting, Lin Zehong, Tian Junming, Chen Longhao, Liu Baijie. Changes in lumbosacral sagittal plane parameters of L5/S1 disc herniation reabsorption [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1330-1335. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||