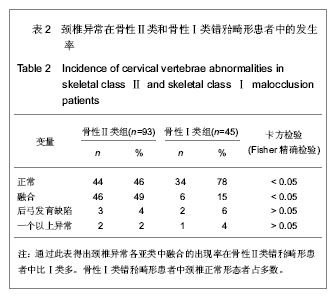
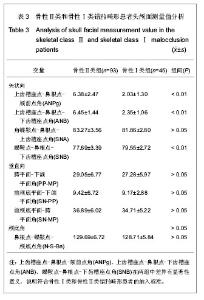
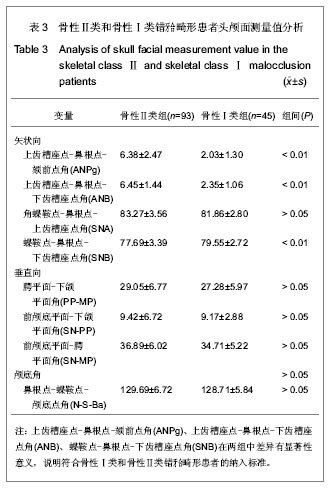
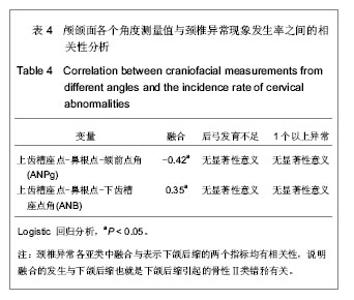
| [1] Sonnesen L, Pedersen CE, Kjaer I. Cervical column morphology related to head posture, cranial base angle, and condylar malformation. Eur J Orthod. 2007;29(4):398-403.[2] Solow B, Tallgren A. Head posture and craniofacial morphology. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1976;44(3):417-435.[3] Farman AG, Escobar V. Radiographic appearance of the cervical vertebrae in normal and abnormal development. Br J Oral Surg. 1982;20(4):264-274.[4] Poznanski AK. Cervical Spine [A]//Bailey RW, ed. Philadelphia, Lea & Febiger, 1974:47-90.[5] Cohney BC.The association of cleft palate with the Klippel-Feil syndrome. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1963;31: 179-817.[6] Yoshihara T, Suzuki J, Yawaka Y. Anomaly of cervical vertebrae found on orthodontic examination: 8-year-old boy with cleft lip and palate diagnosed with Klippel-Feil syndrome. Angle Orthod. 2010;80(5):975-980.[7] Osborne GS, Pruzansky S, Koepp-Baker H. Upper cervical spine anomalies and osseous nasopharyngeal depth. J Speech Hear Res. 1971;14(1):14-22.[8] Sandham A. Cervical vertebral anomalies in cleft lip and palate.Cleft Palate J. 1986;23(3):206-214.[9] Horswell BB.The incidence and relationship of cervical spine anomalies in patients with cleft lip and/or palate. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1991;49(7):693-697.[10] U?ar DA, Semb G.The prevalence of anomalies of the upper cervical vertebrae in subjects with cleft lip, cleft palate, or both. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2001;38(5):498-503.[11] Rajion ZA, Townsend GC, Netherway DJ,et al. A three-dimensional computed tomographic analysis of the cervical spine in unoperated infants with cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2006;43(5):513-518.[12] Lima MC, Franco EJ, Janson G,et al. Prevalence of upper cervical vertebrae anomalies in patients with cleft lip and/or palate and noncleft patients.Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2009; 46(5):481-486.[13] Gray SW, Romaine CB, Skandalakis JE. Congenital fusion of the cervical vertebrae.Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1964;118: 373-385.[14] Hensinger RN. Congenital anomalies of the cervical spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;(264):16-38.[15] Guille JT, Sherk HH. Congenital osseous anomalies of the upper and lower cervical spine in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84-A(2):277-288.[16] Tracy MR, Dormans JP, Kusumi K. Klippel-Feil syndrome: clinical features and current understanding of etiology. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(424):183-190.[17] Kaplan KM, Spivak JM, Bendo JA. Embryology of the spine and associated congenital abnormalities. Spine J. 2005; 5(5): 564-576.[18] Sonnesen L, Petri N, Kjaer I,et al. Cervical column morphology in adult patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur J Orthod. 2008;30(5):521-526.[19] Sonnesen L, Kjaer I. Cervical column morphology in patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and mandibular overjet. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2007;132(4):427.e7-12.[20] Sonnesen L, Kjaer I. Cervical vertebral body fusions in patients with skeletal deep bite. Eur J Orthod. 2007;29(5): 464-470.[21] Sonnesen L, Kjaer I. Anomalies of the cervical vertebrae in patients with skeletal Class II malocclusion and horizontal maxillary overjet. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2008; 133(2): 188.e15-20.[22] Sonnesen L, Kjaer I. Cervical column morphology in patients with skeletal open bite. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2008;11(1): 17-23.[23] 杨文静,张秦,齐武刚,等.自然头位下X线头影测量49例分析[J].口腔医学研究,2004,20(1):77-79.[24] Peng L, Cooke MS. Fifteen-year reproducibility of natural head posture: A longitudinal study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1999;116(1):82-85.[25] Bebnowski D, Hänggi MP, Markic G, et al. Cervical vertebrae anomalies in subjects with Class II malocclusion assessed by lateral cephalogram and cone beam computed tomography. Eur J Orthod. 2012;34(2):226-231.[26] Vastardis H, Evans CA. Evaluation of cervical spine abnormalities on cephalometric radiographs. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1996;109(6):581-588.[27] 曹喆,贾绮林.唇腭裂患者颈椎异常影像学表现[J].口腔正畸学, 2008,15(4):169-172.[28] McNamara JA Jr, Peterson JE Jr, Alexander RG. Three-dimensional diagnosis and management of Class II malocclusion in the mixed dentition. Semin Orthod. 1996; 2(2):114-137.[29] Kjaer I, Keeling JW, Graem N. Midline maxillofacial skeleton in human anencephalic fetuses. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 1994;31(4):250-256.[30] Kjaer I. Human prenatal craniofacial development related to brain development under normal and pathologic conditions. Acta Odontol Scand. 1995;53(3):135-143.[31] Kjaer I. Neuro-osteology. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1998;9(2): 224-244.[32] Kjaer I, Fischer-Hansen B.The adenohypophysis and the cranial base in early human development. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol. 1995;15(3):157-161.[33] Massengill AD, Huynh SL, Harris JH Jr. C2-3 facet joint "pseudo-fusion": anatomic basis of a normal variant.Skeletal Radiol. 1997;26(1):27-30.[34] Yochum TR, Rowe LJ. Essentials of skeletal radiology. Baltimore: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2005. |