Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Association between SLC30A8 gene polymorphisms and diabetes mellitus after renal transplantation
Yu Ai-rong1, Fan Xing2, Liu Hui-ming1, Xin Hua-wen1, Wu Xiao-chun1
- 1Department of Clinical Pharmacology, 2Department of Nephrology, Wuhan General Hospital of Guangzhou Military Region, Wuhan 430070, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2013-01-28Revised:2013-04-24Online:2013-07-30Published:2013-07-30 -
About author:Yu Ai-rong☆, M.D., Associate chief pharmacist, Department of Clinical Pharmacology, Wuhan General Hospital of Guangzhou Military Region, Wuhan 430070, Hubei Province, China yarfwy@163.com -
Supported by:Planning Project of Hubei Natural Science Foundation, No. 2009CDB010*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yu Ai-rong, Fan Xing, Liu Hui-ming, Xin Hua-wen, Wu Xiao-chun. Association between SLC30A8 gene polymorphisms and diabetes mellitus after renal transplantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.31.006.
share this article
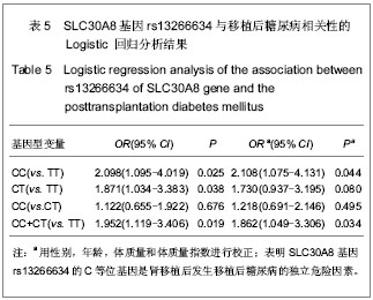
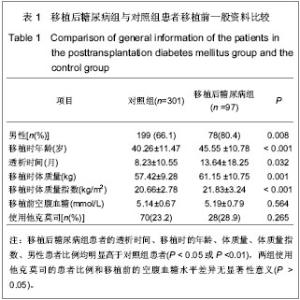
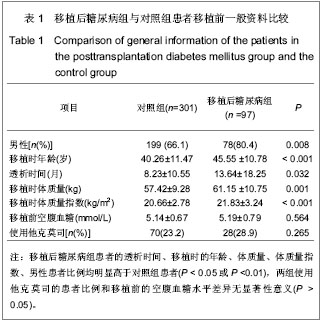
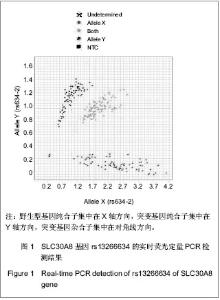
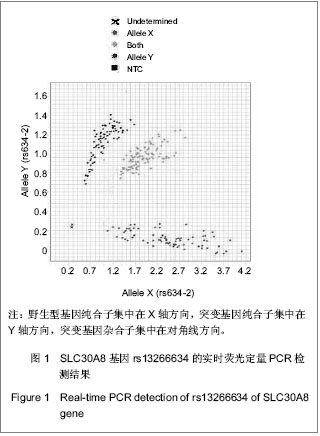
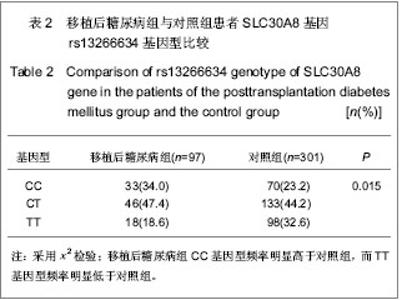
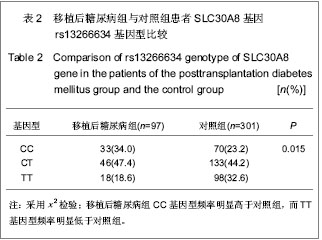
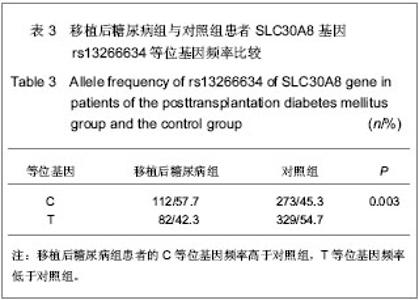
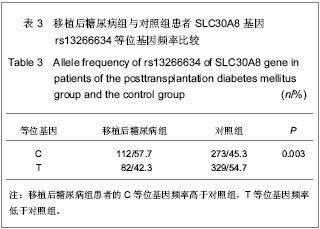
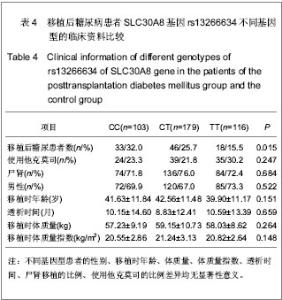
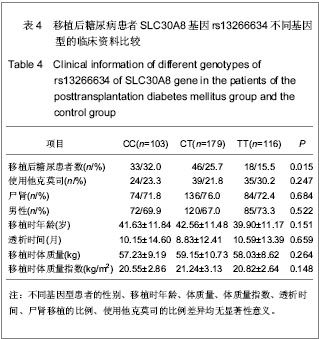
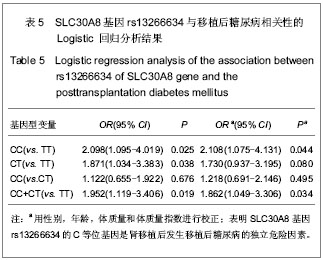
2.5 SLC30A8基因rs13266634与移植后糖尿病相关性 在单因素logistic回归中,将SLC30A8基因rs13266634基因型纳入变量分析,结果见表5。CC基因型和CT基因型患者移植后发生移植后糖尿病的风险分别是TT基因型患者的2.098倍(95%CI:1.095-4.019,P=0.025)和1.871倍(95%CI:1.034-3.383,P=0.038)。本课题的前期研究结果表明[26]:男性(OR=2.104, P=0.009)、年龄(OR=1.041,P < 0.001)、体质量(OR=1.040,P =0.001)和体质量指数(OR=1.142, P < 0.001)均是移植后糖尿病发病的危险因素,因此,在多因素logistic回归中,用性别、移植时年龄、体质量和体质量指数等危险因素进行校正后,SLC30A8基因rs13266634的CC基因型(与TT基因型相比,OR=2.108,P=0.044)仍是肾移植后发生移植后糖尿病的危险因素。CC基因型与CT基因型相比,其OR=1.218,但相关性无显著性意义(P =0.495)。 合并CC基因型和CT基因型,进行logistic回归分析,结果表明:CC+CT基因型患者移植后发生移植后糖尿病的风险是TT基因型患者的1.952倍(95%CI:1.119- 3.406,P=0.019);用性别、移植时年龄、体质量和体质量指数进行校正后,其OR=1.862(95%CI:1.049- 3.306,P=0.034),表明SLC30A8基因rs13266634的C等位基因是肾移植后发生移植后糖尿病的独立危险因素。"
| [1] Montori VM, Basu A, Erwin PJ, et al. Posttransplantation diabetes: a systematic review of the literature. Diabetes Care. 2002; 25(3): 583-592.[2] Cosio FG, Pesavento TE, Kim S,et al.Patient survival after renal transplantation: IV. Impact of post-transplant diabetes. Kidney Int. 2002; 62(4): 1440-1446. [3] Revanur VK, Jardine AG, Kingsmore DB, et al. Influence of diabetes mellitus on patient and graft survival in recipients of kidney transplantation. Clin Transplant.2001; 15(2): 89-94. [4] Shah T,Kasravi A,Huang E,et al.Risk factors for development of new-onset diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation. Transplantation. 2006; 82(12): 1673-1676.[5] Kamar N, Mariat C, Delahousse M, et al.Diapason Study Group. Diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation: a French multicentre observational study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007; 22(7):1986-1993.[6] 余爱荣,范星,辛华雯,等.肾移植术后糖尿病发病率与危险因素[J]. 药物流行病学杂志,2011,20(4):169-172.[7] Hur KY, Kim MS, Kim YS, et al. Risk factors associated with the onset and progression of posttransplantation diabetes in renal allograft recipients. Diabetes Care. 2007; 30: 609-615.[8] Baltar J, Ortega T, Ortega F, et al. Posttransplantation diabetes mellitus: prevalence and risk factors. Transplant Proc. 2005;37(9):3817-3818.[9] 余爱荣,辛华雯,吴笑春,等.含环孢素的三联免疫治疗方案对肾移植受者糖耐量的影响[J].药物流行病学杂志,2007,16(5): 277-279.[10] Heisel O, Heisel R, Balshaw R, et al. New onset diabetes mellitus in patients receiving calcineurin inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Transplant. 2004; 4: 583-595.[11] 余爱荣,辛华雯,吴笑春,等. 环孢素和他克莫司对肾移植后发生糖尿病的影响研究[J].中国药师,2011,14(4):521-523.[12] Sumrani N, Delaney V, Ding Z, et al. Posttransplant diabetes mellitus in cyclosporine-treated renal transplant recipients. Transplant Proc. 1991; 23:1249-1250.[13] Numakura K, Satoh S, Tsuchiya N, et al. Clinical and genetic risk factors for posttransplant diabetes mellitus in adult renal transplant recipients treated with tacrolimus. Transplantation. 2005; 80:1419-1424.[14] 余爱荣,范星,刘慧明,等.中国肾移植患者钙蛋白酶10基因多态性与移植后糖尿病的相关性研究[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2012,17(8):901-906.[15] 余爱荣,辛华雯,刘慧明,等.脂联素基因多态性与移植后糖尿病的相关性研究[J].中国药师,2011,14(9):1253-1255.[16] Chimienti F, Devergnas S, Favier A, et al. Identification and cloning of a beta-cell specific zinc transporter, ZnT-8, localized in to insulin secretory granules. Diabetes. 2004; 53: 2330-2337.[17] Ng MC, Park KS, Oh B, et al. Implication of genetic variants near TCF7L2, SLC30A8, HH EX, CDKAL1, CDKN2A /B, IGF2BP2, and FTO in type 2 diabetes and obesity in 6719 Asians. Diabetes. 2008; 57: 2226-2233.[18] Zeggini E, Weedon MN, Lindgren CM, et al. Replication of genome-wide association signals in UK samples reveals risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Science. 2007; 316:1336-1341.[19] Sladek R, Rocheleau G, Rung J, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies novel risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2007; 445:881-885.[20] Steinthorsdottir V, Thorleifsson G, Reynisdottir I, et al. A variant in cdkal1 influences insulin response and risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet. 2007; 39:770-775.[21] Wu Y, Li H, Loos RJ, et al. Common variants in CDKAL1, CDKN2A/B, IGF2BP2, SLC30A8, and HHEX/IDE genes are associated with type 2 diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in a Chinese Han population. Diabetes. 2008; 57:2834-2842.[22] Xiang J, Li XY, Xu M, et al. Zinc transporter-8 gene (SLC30A8) is associated with type 2 diabetes in Chinese. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008; 93(10):4107-4112.[23] Kang ES, Kim MS, Kim YS, et al. A Polymorphism in the Zinc Transporter Gene SLC30A8 Confers Resistance Against Posttransplantation Diabetes Mellitus in Renal Allograft Recipients. Diabetes. 2008; 57(4): 1043-1047.[24] Kang ES, Kim MS, Kim CH, et al. Association of common type 2 diabetes risk gene variants and posttransplantation diabetes mellitus in renal allograft recipients in Korea. Transplantation. 2009; 88(5):693-698.[25] American Diabetes Association: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27 (Suppl. 1): S5-S10.[26] Yu AR, Xin HW, Wu XC, et al. Adiponectin gene polymorphisms are associated with posttransplantation diabetes mellitus in Chinese renal allograft recipients. Transplantation Proceeding. 2011; 43(5): 1607-1611.[27] Chimienti F, Devergnas S, Pattou F,et al . In vivo expression and functional characterzation of the zinc transporter ZnT8 in glucose induced insulin secretion. J Cell Sci. 2006; 119: 4199-4206.[28] Scott LJ, Mohlke KL, Bonnycastle LL, et al. A genome-wide association study of type 2 diabetes in Finns detects multiple susceptibility variants. Science. 2007; 316(5829): 1341-1345.[29] Gamboa-Meléndez MA, Huerta-Chagoya A, Moreno-Macías H, et al. Contribution of common genetic variation to the risk of type 2 diabetes in the Mexican Mestizo population. Diabetes. 2012; 61(12):3314-3321.[30] Potapov VA, Shamkhalova MN, Smetanina SA, et al.Polymorphic markers TCF7L2 rs12255372 and SLC30A8 rs13266634 confer susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in a Russian population. Genetika. 2010; 46(8):1123-1131.[31] Chauhan G, Spurgeon CJ, Tabassum R, et al. Impact of common variants of PPARG, KCNJ11, TCF7L2, SLC30A8, HHEX, CDKN2A, IGF2BP2, and CDKAL1 on the risk of type 2 diabetes in 5,164 Indians. Diabetes. 2010; 59(8):2068-2074.[32] Hu C, Zhang R, Wang C, et al. PPARG, KCNJ11, CDKAL1, CDKN2A-CDKN2B, IDE-KIF11-HHEX, IGF2BP2 and SLC30A8 are associated with type 2 diabetes in a Chinese population. PLoS One. 2009; 4(10):e7643.[33] Han X, Luo Y, Ren Q, et al. Implication of genetic variants near SLC30A8, HHEX, CDKAL1, CDKN2A/B, IGF2BP2, FTO, TCF2, KCNQ1, and WFS1 in type 2 diabetes in a Chinese population. BMC Med Genet. 2010; 28(11):81.[34] 李春勇,张林,毛吉扬. SLC30A8基因多态性与2型糖尿病易感性的meta分析[J]. 中国分子心脏病学杂志,2010,10(1):36-39.[35] Jing YL, Sun QM, Bi Y, et al. SLC30A8 polymorphism and type 2 diabetes risk: evidence from 27 study groups. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2011; 21(6):398-405.[36] Xu K, Zha M, Wu X, et al. Association between rs13266634 C/T polymorphisms of solute carrier family 30 member 8 (SLC30A8) and type 2 diabetes, impaired glucose tolerance, type 1 diabetes-a meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011; 91(2):195-202.[37] Huang Q, Yin JY, Dai XP, et al. Association analysis of SLC30A8 rs13266634 and rs16889462 polymorphisms with type 2 diabetes mellitus and repaglinide response in Chinese patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2010; 66(12): 1207-1215.[38] 马聪. SLC30A8,TCF7L2单核苷酸多态性与南方人2型糖尿病的相关性研究.江苏大学硕士学位论文. 2010 [39] 汪志红. TCF7L2及SLC30A8基因多态性与2型糖尿病的关联研究.重庆医科大学博士学位论文.2008[40] Tabara Y, Osawa H, Kawamoto R, et al. Replication study of candidate genes associated with type 2 diabetes based on genome-wide screening. Diabetes. 2009; 58:493-498.[41] Emdin SO, Dodson GG, Cutfield JM, et al. Role of zinc in insulin biosynthesis: some possible zinc-insulin interactions in the pancreatic B-cell. Diabetologia. 1980; 19:174-182.[42] Dodson G, Steiner D. The role of assembly in insulin’s biosynthesis. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998; 8:189-194.[43] Fu Y, Tian W, Pratt EB, et al. Down-regulation of Znt8 expression in ins-1 rat pancreatic beta cells reduces insulin content and glucose-inducible insulin secretion. PLoS ONE. 2009; 4:e5679.[44] Lefebvre B, Vandewalle B, Balavoine AS, et al. Regulation and functional effects of ZNT8 in human pancreatic islets. J Endocrinol. 2012; 214(2):225-232.[45] Zheng X, Ren W, Zhang S, et al. Association of type 2 diabetes susceptibility genes (TCF7L2, SLC30A8, PCSK1 and PCSK2) and proinsulin conversion in a Chinese population. Mol Biol Rep. 2012; 39(1):17-23.[46] Boesgaard TW, Zilinskaite J, Vanttinen M, et al. The common SLC30A8 arg325trp variant is associated with reduced first-phase insulin release in 846 non-diabetic offspring of type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetologia. 2008; 51:816-820.[47] Patel CJ, Chen R, Kodama K, et al. Systematic identification of interaction effects between genome- and environment-wide associations in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Hum Genet. 2013. [Epub ahead of print][48] 张红梅.糖尿病新基因SLC30A8的生物信息学分析[J].中国老年学杂志,2010,30(8):2286-2289.[49] Kirchhoff K, Machicao F, Haupt A, et al. Polymorphisms in the TCF7L2, CDKAL1 and SLC30A8 genes are associated with impaired proinsulin conversion. Diabetologia. 2008; 51: 597-601.[50] Kim I, Kang ES, Yim YS, et al. A low-risk ZnT-8 allele (W325) for post-transplantation diabetes mellitus is protective against cyclosporin A-induced impairment of insulin secretion. Pharmacogenomics J. 2011; 11(3):191-198.[51] Lee HC. Post-renal transplant diabetes mellitus in Korean subjects: superimposition of transplant-related immunosuppressant factors on genetic and type 2 diabetic risk factors. Diabetes Metab J. 2012; 36(3):199-206.[52] Xu J, Wang J, Chen B. SLC30A8 (ZnT8) variations and type 2 diabetes in the Chinese Han population. Genet Mol Res. 2012; 11(2):1592-1598. [53] Kurzawski M, Dziewanowski K, ?apczuk J, et al. Analysis of common type 2 diabetes mellitus genetic risk factors in new-onset diabetes after transplantation in kidney transplant patients medicated with tacrolimus. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2012; 68(12):1587-1594. |
| [1] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [2] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [3] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [4] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [5] | Wang Hanyue, Li Furong, Yang Xiaofei, Hu Chaofeng. Direct reprogramming hepatocytes into islet-like cells by efficiently targeting and activating the endogenous genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1056-1063. |
| [6] | Jiang Xin, Qiao Liangwei, Sun Dong, Li Ming, Fang Jun, Qu Qingshan. Expression of long chain non-coding RNA PGM5-AS1 in serum of renal transplant patients and its regulation of human glomerular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 741-745. |
| [7] | Yang Xin, Jin Zhe, Feng Xu, Lu Bing. The current situation of knowledge and attitudes towards organ, eye tissue, body donation of residents in Shenyang [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 779-784. |
| [8] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [9] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [10] | Tian Lin, Shi Xiaoqing, Duan Zhenglan, Wang Kuan, Zhang Li, Wang Peimin. Efficacy and safety of transverse tibial bone transport technique in the treatment of diabetic foot:a meta-analysis#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3275-3280. |
| [11] | Xia Wenshen, He Renjiao, Ai Jinwei, Wang Jun, Li Desheng, Pei Bin. Stem cell transplantation for diabetic patients with lower-extremity arterial disease: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3110-3116. |
| [12] | Zhang Mingyan, Liu Xiangyang, Chang Lei, Chen Jing, Shen Xiongjie, Liu Bin, Peng Shuai, Zhang Chao, Wu Huanyu, Zhu Feng, Mou Haipin . Relationship between the intraoperative endplate injury and cage retropulsion after lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2856-2862. |
| [13] | Luo Yicai, Li Hao. Effect of enhanced aryl hydrocarbon receptor expression on inflammatory response and healing of alveolar bone defects in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2166-2171. |
| [14] | Zhang Tengfei, Wang Kun, Zhu Yanyu, Mei Wei, Wang Qingde. Meta-analysis of risk factors associated with adjacent segment degeneration after lumbar posterior fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1936-1943. |
| [15] | Hu Sheng, Yuan Haiyan, Hu Meng, Jin Shanhu. Effects of moderate treadmill exercise on alpha-smooth muscle actin and type IV collagen in the liver of type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1723-1727. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||