Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (27): 5750-5756.doi: 10.12307/2025.817
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of unilateral knee osteoarthritis on gait dynamics and muscle activation asymmetry in elderly women
Li Yongjie, Liu Mengling, Zhang Dakuan, Fu Shenyu, Liu Hongju
- Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital Guizhou Hospital, Guiyang 550014, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2024-04-04Accepted:2024-07-10Online:2025-09-28Published:2025-03-03 -
Contact:Liu Hongju, MD, Chief physician, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital Guizhou Hospital, Guiyang 550014, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Li Yongjie, MS, Rehabilitation therapist-in-charge, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital Guizhou Hospital, Guiyang 550014, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:2023 Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Support Plan, No. [2023]179 (to LHJ); 2023 Guizhou Provincial Health Commission Science and Technology Fund Project, No. gzwkj2023-124 (to FSY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Yongjie, Liu Mengling, Zhang Dakuan, Fu Shenyu, Liu Hongju. Effect of unilateral knee osteoarthritis on gait dynamics and muscle activation asymmetry in elderly women[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5750-5756.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
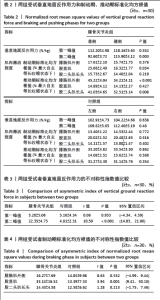
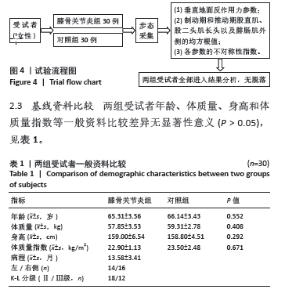
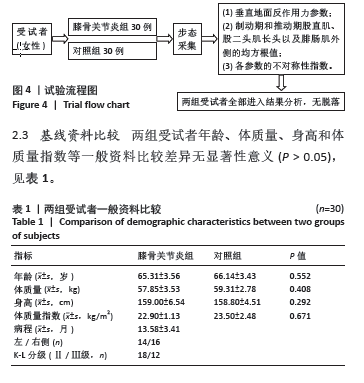
2.4 垂直地面反作用力和制动期、推动期标准化均方根值 两组受试者垂直地面反作用力和制动期、推动期标准化均方根值的数值如表2所示,均服从正态分布。其中膝骨关节炎组两侧肢体垂直地面反作用力第二峰值之间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),制动期股直肌和推动期腓肠肌外侧、股二头肌长头标准化均方根值之间差异也有显著性意义 (P < 0.05)。对照组两侧肢体所有指标之间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 2.5 两组受试者垂直地面反作用力的不对称性指数值比较 两组受试者垂直地面反作用力第一峰值和第二峰值均服从正态分布,其中第一峰值的不对称性指数值差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),而第二峰值不对称性指数值的差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表3。 2.6 两组受试者制动期、推动期标准化均方根值的不对称性指数值比较 两组受试者制动期各肌肉标准化均方根值均服从正态分布,其中股直肌标准化均方根值的不对称性指数值在两组之间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表4。"
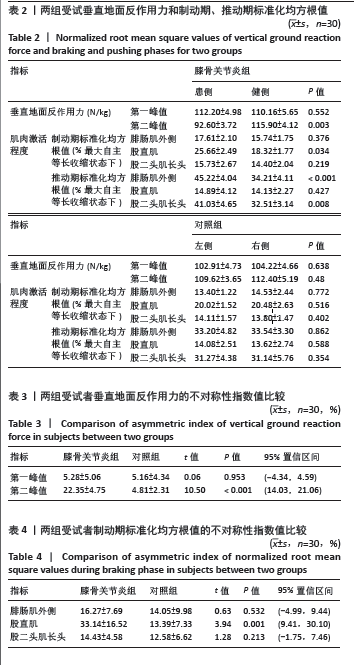
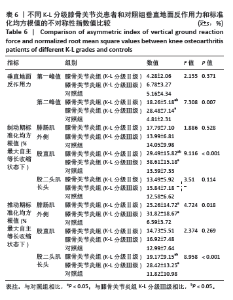
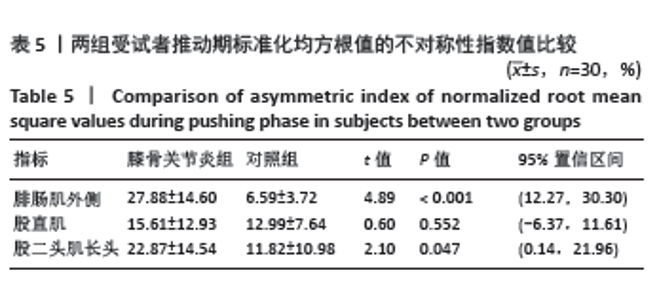
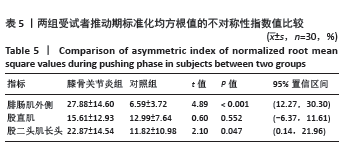
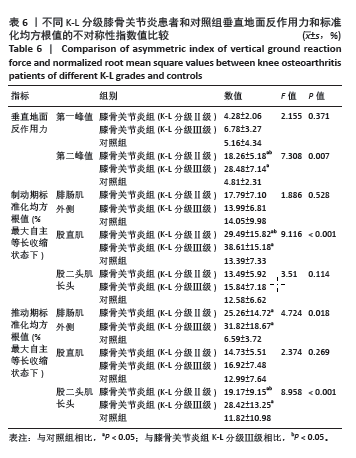
2.7 不同K-L分级膝骨关节炎患者和对照组垂直地面反作用力和标准化均方根值的不对称性指数比较 K-L分级Ⅱ,Ⅲ级膝骨关节炎患者和对照组垂直地面反作用力和标准化均方根值的不对称性指数比较如表6所示,均服从正态分布。其中在垂直地面反作用力中,方差结果显示3组受试者垂直地面反作用力第二峰值的不对称性指数值之间差异有显著性意义(F=7.308,P=0.007)。事后多重检验发现,K-L分级Ⅱ级和Ⅲ级的膝骨关节炎组患者垂直地面反作用力第二峰值的不对称性指数值均显著高于对照组 (P < 0.05),K-L分级Ⅲ级的膝骨关节炎组患者垂直地面反作用力第二峰值的不对称性指数值高于K-L分级Ⅱ级患者(P < 0.05)。 在制动期标准化均方根值中,方差结果显示3组受试者股直肌标准化均方根值的不对称性指数值之间差异有显著性意义(F=9.116,P < 0.001)。事后多重检验发现,K-L分级Ⅱ级和Ⅲ级的膝骨关节炎组患者股直肌标准化均方根值的不对称性指数值均显著高于对照组(P < 0.05),K-L分级Ⅲ级的膝骨关节炎组患者股直肌标准化均方根值的不对称性指数值高于K-L分级Ⅱ级患者(P < 0.05)。 在推动期标准化均方根值中,方差结果显示3组受试者腓肠肌外侧(F=4.724,P=0.018)和股二头肌长头(F=8.958,P < 0.001)标准化均方根值的不对称性指数值之间差异有显著性意义。事后多重检验发现,K-L分级Ⅱ级和Ⅲ级的膝骨关节炎组腓肠肌外侧和股二头肌长头标准化均方根值的不对称性指数值均显著高于对照组(P < 0.05),K-L分级Ⅲ级的膝骨关节炎组患者股二头肌长头标准化均方根值的不对称性指数值高于K-L分级Ⅱ级患者(P < 0.05)。 2.8 不良事件 所有受试者在进行步态测试过程中均未发生任何不良事件。"
| [1] 中华医学会物理医学与康复学分会, 四川大学华西医院. 中国膝骨关节炎康复治疗指南(2023版)[J]. 中国循证医学杂志,2024,24(1): 1-14. [2] ÖZüDOğRU A, GELECEK N. Effects of closed and open kinetic chain exercises on pain, muscle strength, function, and quality of life in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Rev Assoc Med Bras. 2023;69(7): e20230164. [3] DE ROOIJ M, VAN DER LEEDEN M, HEYMANS MW, et al. Prognosis of Pain and Physical Functioning in Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2016;68(4):481-492. [4] 冯晓晴, 蔡道章, 余星磊,等. 基于GBD大数据中国膝骨关节炎疾病负担现状与趋势分析[J]. 现代预防医学,2022,49(10):1753-1760. [5] BLACK AL, CLARK AL. Sexual dimorphism in knee osteoarthritis: Biomechanical variances and biological influences. J Orthop. 2022;32: 104-108. [6] LIU S, AMIRI P, MCGREGOR AH, et al. Bilateral Asymmetry in Knee and Hip Musculoskeletal Loading During Stair Ascending/Descending in Individuals with Unilateral Mild-to-Moderate Medial Knee Osteoarthritis. Ann Biomed Eng. 2023;51(11):2490-2503. [7] SAXBY DJ, BRYANT AL, VAN GINCKEL A, et al. Greater magnitude tibiofemoral contact forces are associated with reduced prevalence of osteochondral pathologies 2-3 years following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019; 27(3):707-715. [8] SHIMIZU H, SHIMOURA K, IIJIMA H, et al. Functional manifestations of early knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rheumatol. 2022;41(9):2625-2634. [9] MILLS K, HUNT MA, FERBER R. Biomechanical deviations during level walking associated with knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2013;65(10):1643-1665. [10] MILLS K, HUNT MA, LEIGH R, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of lower limb neuromuscular alterations associated with knee osteoarthritis during level walking. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2013;28(7):713-724. [11] TAJDINI H, LETAFATKAR A, BREWER BW, et al. Association between Kinesiophobia and Gait Asymmetry after ACL Reconstruction: Implications for Prevention of Reinjury. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(6):3264. [12] 刘鑫玥, 刘鹏波, 霍洪峰. 双任务介入对社区脑卒中患者步态参数及其对称性的影响[J]. 医用生物力学,2023,38(6):1114-1119. [13] GIANNAKOU E, FOTIADOU S, GOURGOULIS V, et al. A Comparative Analysis of Symmetry Indices for Spatiotemporal Gait Features in Early Parkinson’s Disease. Neurol Int. 2023;15(3):1129-1139. [14] MANTASHLOO Z, LETAFATKAR A, MORADI M. Vertical ground reaction force and knee muscle activation asymmetries in patients with ACL reconstruction compared to healthy individuals. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(6):2009-2014. [15] 中华中医药学会. 膝骨关节炎中西医结合诊疗指南(2023年版)[J]. 中医正骨,2023,35(6):1-10. [16] YU HB, TAI WH, LI J, et al. Effects of Shoe Midsole Hardness on Lower Extremity Biomechanics during Jump Rope in Healthy Males. Healthcare (Basel). 2021;9(10):1394. [17] 张嘉源, 马小远, 周志鹏,等. 非预期条件下前交叉韧带重建术后运动员侧切动作下肢运动生物力学特征[J]. 医用生物力学,2023, 38(6):1127-1133. [18] KONDO M, IWAMOTO Y, KITO N. Relationship between forward propulsion and foot motion during gait in healthy young adults. J Biomech. 2021;121:110431. [19] 刘鑫玥, 霍洪峰. 不同类型和负荷双任务对健康人动态姿势控制的影响[J]. 医用生物力学,2023,38(4):791-796+843. [20] GIRARD O, MILLET GP, MICALLEF JP. Constant low-to-moderate mechanical asymmetries during 800-m track running. Front Sports Act Living. 2024;6:1278454. [21] 卢泽惠. 单侧负重状态下行走的生物力学特征分析[D]. 呼和浩特:内蒙古师范大学,2022. [22] WIIK AV, AQIL A, BREVADT M, et al. Abnormal ground reaction forces lead to a general decline in gait speed in knee osteoarthritis patients. World J Orthop. 2017;8(4):322-328. [23] HODT-BILLINGTON C, HELBOSTAD JL, VERVAAT W, et al. Criteria of gait asymmetry in patients with hip osteoarthritis. Physiother Theory Pract. 2012;28(2):134-141. [24] BALASUBRAMANIAN CK, BOWDEN MG, NEPTUNE RR, et al. Relationship between step length asymmetry and walking performance in subjects with chronic hemiparesis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007;88(1):43-49. [25] 傅升星, 侯美金, 李镇辉,等. 电针对膝骨性关节炎患者登梯垂直地面反作用力及冲量对称性的影响[J]. 医用生物力学,2020,35(4): 467-473. [26] 安丙辰, 郑洁皎, 沈利岩. 膝骨关节炎与膝关节伸、屈肌群肌力的相关性研究[J]. 医用生物力学,2015,30(2):174-178. [27] ALSHAHRANI MS, REDDY RS, TEDLA JS, et al. Association between Kinesiophobia and Knee Pain Intensity, Joint Position Sense, and Functional Performance in Individuals with Bilateral Knee Osteoarthritis. Healthcare (Basel). 2022;10(1):120. [28] 陈博, 王芗斌, 熊凤,等. 膝骨关节炎患者登梯活动中下肢肌群肌电特征的研究进展[J]. 风湿病与关节炎,2019,8(6):68-71. [29] HUBLEY-KOZEY CL, HATFIELD GL, ASTEPHEN WILSON JL, et al. Alterations in neuromuscular patterns between pre and one-year post-total knee arthroplasty. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2010;25(10): 995-1002. [30] SANCHEZ-RAMIREZ DC, MALFAIT B, BAERT I, et al. Biomechanical and neuromuscular adaptations during the landing phase of a stepping-down task in patients with early or established knee osteoarthritis. Knee. 2016;23(3):367-375. [31] 李捷婷, 陈耿钊, 方倩颖,等. 基于多通道表面肌电探讨不同角速度下膝骨关节炎患者生物力学基础的研究[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2024,39(2):218-225. [32] HURWITZ DE, RYALS AB, CASE JP, et al. The knee adduction moment during gait in subjects with knee osteoarthritis is more closely correlated with static alignment than radiographic disease severity, toe out angle and pain. J Orthop Res. 2002;20(1):101-107. |
| [1] | Cao Xinyan, Yu Zifu, Leng Xiaoxuan, Gao Shiai, Chen Jinhui, Liu Xihua. Effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and transcranial direct current stimulation on motor function and gait in children with cerebral palsy: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1539-1548. |
| [2] | Li Linzhen, Jiao Hongzhuo, Chen Weinan, Zhang Mingzhe, Wang Jianlong, Zhang Juntao. Effect of icariin-containing serum on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory damage in human chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1368-1374. |
| [3] | Gu Fucheng, Yang Meixin, Wu Weixin, Cai Weijun, Qin Yangyi, Sun Mingyi, Sun Jian, Geng Qiudong, Li Nan. Effects of Guilu Erxian Glue on gut microbiota in rats with knee osteoarthritis: machine learning and 16S rDNA analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1058-1072. |
| [4] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Wang Chaolu. High tibial osteotomy on a single plane: femorofibular angle as a reference marker for mechanical axis correction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 570-576. |
| [5] | Guo Jingwen, Wang Qingwei, He Zijun, Hu Zihang, Chen Zhi, Zhu Rong, Wang Yuming, Liu Wenfei, Luo Qinglu. Intra-articular injection of different concentrations of silicon-based bioceramics in treatment of knee osteoarthritis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 288-295. |
| [6] | Ma Chi, Wang Ning, Chen Yong, Wei Zhihan, Liu Fengji, Piao Chengzhe. Application of 3D-printing patient-specific instruments combined with customized locking plate in opening wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1863-1869. |
| [7] | Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Wan Haili, Chang Ying, Xiong Wenjuan, Xia Yuan. Effect of neuromuscular exercise for knee osteoarthritis pain and function: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [8] | Fu Enhong, Yang Hang, Liang Cheng, Zhang Xiaogang, Zhang Yali, Jin Zhongmin. OpenSim-based prediction of lower-limb biomechanical behavior in adolescents with plantarflexor weakness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1789-1795. |
| [9] | Chen Yueping, Chen Feng, Peng Qinglin, Chen Huiyi, Dong Panfeng . Based on UHPLC-QE-MS, network pharmacology, and molecular dynamics simulation to explore the mechanism of Panax notoginseng in treating osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1751-1760. |
| [10] | Wang Peiguang, Zhang Xiaowen, Mai Meisi, Li Luqian, Huang Hao. Generalized equation estimation of the therapeutic effect of floating needle therapy combined with acupoint embedding on different stages of human knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1565-1571. |
| [11] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [12] | Ma Haoyu, Qiao Hongchao, Hao Qianqian, Shi Dongbo. Causal effects of different exercise intensities on the risk of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1305-1311. |
| [13] | Wu Guangtao, Qin Gang, He Kaiyi, Fan Yidong, Li Weicai, Zhu Baogang, Cao Ying . Causal relationship between immune cells and knee osteoarthritis: a two-sample bi-directional Mendelian randomization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1081-1090. |
| [14] | Wang Tong, Zheng Yu, Jia Chengming, Yang Hu, Zhang Guangfei, Ji Yaoyao. Action mechanism of Gegenmaqi prescription in treatment of periarthritis of shoulder combined with type 2 diabetes based on TCMSP database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7669-7678. |
| [15] | Fang Ying, Zhang Yanwei, Li Xi, Yan Peidong, Bi Miao. Improvements in automatic diagnosis methods for knee osteoarthritis based on deep learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7511-7518. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||