Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (26): 5704-5712.doi: 10.12307/2025.699
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine glycosylation in neurodegenerative diseases and its clinical application prospects
Jiang Qianping1, Yang Dan2, 3, 4, Wan Shilei1, Xu Dandan2, 3, 4, 5, Cao Lu3, 6, Zhou Jing2, 3, 4, 5
- 1School of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Orthopedics, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430065, Hubei Province, China; 2Department of Tuina and Rehabilitation Medicine, Hubei Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430061, Hubei Province, China; 3Hubei Sizhen Laboratory, Wuhan 430065, Hubei Province, China; 4Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430061, Hubei Province, China; 5First Clinical Medical College, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430065, Hubei Province, China; 6School of Basic Medical Sciences, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430065, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2024-07-27Accepted:2024-09-14Online:2025-09-18Published:2025-02-28 -
Contact:Zhou Jing, MD, Doctoral supervisor, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Tuina and Rehabilitation Medicine, Hubei Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430061, Hubei Province, China; Hubei Sizhen Laboratory, Wuhan 430065, Hubei Province, China; Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430061, Hubei Province, China Co-corresponding author: Cao Lu, MD, Assistant researcher, Hubei Sizhen Laboratory, Wuhan 430065, Hubei Province, China; School of Basic Medical Sciences, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430065, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Jiang Qianping, Master’s candidate, School of Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Orthopedics, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430065, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:2023 Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (Joint Fund Project), Nos. 2023AFD128 (to ZJ) and 2023AFD143 (to CL); 2024 Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (Joint Fund Project), No. 2023AFD279 (to XDD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jiang Qianping, Yang Dan, , , Wan Shilei, Xu Dandan, , , , Cao Lu, , Zhou Jing, , , . Role of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine glycosylation in neurodegenerative diseases and its clinical application prospects[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5704-5712.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
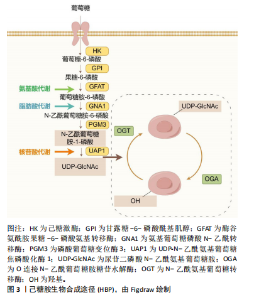
2.1 O-GlcNAc糖基化的动态调控 O-GlcNAc糖基化是一种动态且可逆的单糖修饰机制,其动态平衡受多种途径的严格调控[4]。首先,O-GlcNAc糖基化水平与葡萄糖代谢直接相关。研究表明,人体摄入的葡萄糖中,绝大部分葡萄糖进入糖酵解途径,但有3%-5%的葡萄糖通过己糖胺生物合成途径转化为尿苷二磷酸N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖。尿苷二磷酸N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖作为一个重要的糖基供体,在内质网和高尔基体内驱动多个关键的糖基化反应,见图3。 其次,与复杂的多酶磷酸化调控机制不同,O-GlcNAc糖基化仅由2种酶负责调控,分别是N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖转移酶(O-GlcNAc transferase,OGT)和O-GlcNAc糖苷水解酶(O-GlcNAcase,OGA)[5]。OGT是一种主要位于细胞核的可溶性蛋白,由N端的四肽重复序列和C端的活性结构域组成[6],负责将GlcNAc附加到蛋白质的丝氨酸或苏氨酸残基上,从而提升体内O-GlcNAc糖基化水平。OGA主要定位于细胞质,由N端的糖苷水解酶结构域、茎结构域和C端的乙酰基转移酶结构域构成,专门识别并水解O-GlcNAc修饰的蛋白质,从而降低O-GlcNAc糖基化水平[7]。 此外,O-GlcNAc糖基化还与其他翻译后修饰,如磷酸化、甲基化和乙酰化等有复杂的相互作用,共同调节"
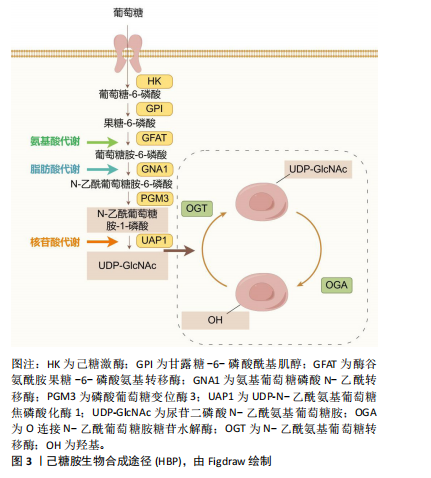
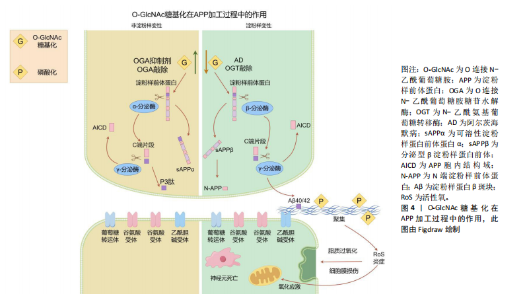
蛋白质功能。其中,O-GlcNAc糖基化与磷酸化之间的相互作用研究最为深入。两种修饰均作用于蛋白质的丝氨酸或苏氨酸残基,其相互作用模式可分为以下4种[8]:①相同位点的竞争性修饰;②不同位点的交替性修饰;③不同位点的同时修饰;④位点依赖性的交替性修饰与同时修饰并存。 2.2 大脑中的O-GlcNAc糖基化的作用 O-GlcNAc糖基化广泛分布于体内几乎所有类型的细胞与组织之中,尤其在大脑中高度表达[9-10]。与外周器官相比,大脑中的OGT与OGA高度活跃,大多数蛋白质都被O-GlcNAc糖基化修饰。在神经发育过程中,O-GlcNAc糖基化通过修饰转录因子和转录共激活因子[例如cAMP反应元件结合蛋白(cyclic-AMP response binding protein,CREB)][11],参与基因表达调控,影响神经元生成和分化。此外,它还调控重要的信号通路如Wnt[12]、Notch[13]、Hedgehog[14],这些通路在神经元的生成和分化中发挥关键作用。在轴突生长和引导方面,O-GlcNAc修饰微管相关蛋白(如tau蛋白)及肌动蛋白等,调控细胞骨架的稳定性和动态性,同时通过修饰GTP酶Rac1调节其活性,进一步影响轴突导向。神经营养因子如脑源性神经营养因子的信号传导也受到O-GlcNAc修饰的调控,影响其受体TrkB的活性,进而影响神经元的存活和生长。 O-GlcNAc糖基化还参与了突触前和突触后膜上多种蛋白质的修饰[15],如突触泡相关蛋白和突触后密度蛋白(如PSD-95),这些修饰有助于突触形成和成熟[16]。同时,O-GlcNAc通过修饰谷氨酸受体(如AMPA[17]、NMDA受体)和相关信号蛋白,调节突触强度变化,参与突触可塑性的调节[18]。在神经保护和应激反应中,O-GlcNAc通过升高应激相关蛋白(如NRF2)水平,激活抗氧化基因表达,减轻神经细胞损伤。此外,O-GlcNAc通过修饰热休克蛋白,能够促进错误折叠蛋白的修复或清除,维持细胞蛋白质稳态。因此,O-GlcNAc糖基化在神经发育与成熟的各个环节中发挥着至关重要的调控作用。 2.3 O-GlcNAc糖基化与神经退行性疾病的关联 2.3.1 O-GlcNAc糖基化与阿尔茨海默病 阿尔茨海默病是一种由于大脑海马区及皮质神经元功能受到损害所引发的神经退行性疾病。阿尔茨海默病患者在发病后会表现出认知功能、记忆和学习能力的显著减退。其主要病理特征包括神经元胞体内淀粉样β蛋白聚集形成的斑块,以及细胞内tau蛋白形成的神经纤维缠结[19]。 淀粉样β蛋白斑块的形成过程始于淀粉样前体蛋白(amyloid precursor protein,APP)的逐步蛋白酶切割。APP可通过2种途径进行处理[20]:非淀粉样变性途径和淀粉样变性途径。在生理条件下,APP通常被α-分泌酶(ADAM10或ADAM17)优先切割,生成具有神经保护作用的可溶性片段sAPPα,从而避免了淀粉样β蛋白的产生。sAPPα在促进突触功能和神经修复方面具有重要作用。另一方面,如果APP被β位点APP切割酶1(BACE1)切割,则会生成片段sAPPβ,随后经γ-分泌酶(包括PSEN1或PSEN2)进一步切割,产生长链淀粉样β蛋白肽(淀粉样蛋白β40和淀粉样蛋白β42)。这些淀粉样β蛋白肽易于聚集,形成可溶性寡聚体和不溶性纤维状结构,最终沉积在脑组织中形成淀粉样β蛋白斑块,见图4。 淀粉样β蛋白的积累和形成斑块被认为是神经毒性的主要原因,导致神经元损伤和死亡[21]。因此,清除或抑制淀粉样β蛋白的产生被认为是阿尔茨海默病治疗的重要策略。研究发现O-GlcNAc糖基化可以通过抑制淀粉样β蛋白聚集来减少神经元死亡[22]。在阿尔茨海默病患者与小鼠模型中[23],通过抑制小鼠体内OGA水平,使其受体连接丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶3的O-GlcNAc糖基化水平升高[24],丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶3的O-GlcNAc糖基化修饰可以抑制自身磷酸化及与丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶1的相互作用,减少淀粉样β蛋白聚集、神经炎症与坏死。同样,在阿尔茨海默病转基因小鼠模型中,OGA抑制剂的应用显著抑制了γ-分泌酶活性与星形胶质细胞的活化[25],降低了淀粉样蛋白β40与淀粉样蛋白β42的生成,有效改善了记忆障碍、炎症反应和神经元死亡等阿尔茨海默病相关病理。 tau蛋白在正常情况下与微管相互作用,促进微管的组装,维护微管网络的稳定,并在轴突运输、细胞骨架组织以及神经突起生长等神经细胞基本功能中发挥着关键作用。然而,在病理条件下[26],tau蛋白过度磷酸化,导致tau蛋白从微管上脱离,增加细胞质中游离tau蛋白的含量,加剧了神经纤维缠结的形成,这是阿尔茨海默病病理进程中的一个重要环节。研究发现,tau蛋白上存在多个O-GlcNAc糖基化修饰位点。在人类脑组织中,与正常tau蛋白相比,高磷酸化的tau蛋白O-GlcNAc糖基化水平显著降低[27]。在动物模型中,通过使用OGA抑制剂[28-29],可以显著降低tau蛋白的磷酸化水平,改善认知障碍和神经炎症,同时减少神经元纤维缠结的数量[30]。相反,使用OGT抑制剂后,tau蛋白的磷酸化水平上升,导致tau蛋白的聚集。这些研究结果表明tau蛋白上可能存在O-GlcNAc糖基化与磷酸化之间的竞争性修饰机制。后续研究进一步发现,O-GlcNAc糖基化在tau蛋白的Ser400位点上可以直接抑制tau蛋白在体外的聚集[31]。"
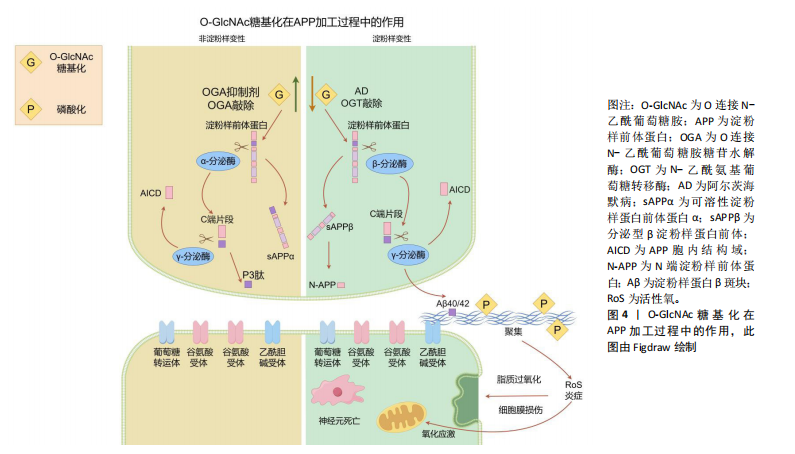
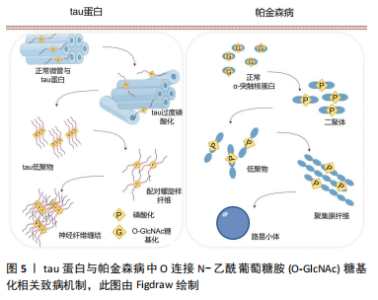
O-GlcNAc糖基化不仅通过抑制tau蛋白的磷酸化来影响其功能,而且存在一种直接阻碍tau蛋白形成寡聚物的机制,从而消除其潜在的神经毒性。这一发现为理解tau蛋白在阿尔茨海默病中的作用提供了新的视角,并为开发针对tau蛋白糖基化修饰的治疗策略提供了理论基础。 此外,tau蛋白过度磷酸化也介导了突触功能障碍与记忆缺陷。CREB是一种在学习与记忆过程中发挥重要作用的细胞转录因子[9],沉默信息调节因子2相关酶1 (sirtuin 1,SIRT1)是一种去乙酰化酶,它能够使CREB去乙酰化,并抑制CREB在Ser133位点的磷酸化,导致CREB失活[32]。失活的CREB会抑制OGT的表达,导致O-GlcNAc糖基化水平降低并增加特定位点的磷酸化。Yin等[18]构建了一种脑特异性SIRT1缺乏的小鼠模型(SIRT1 flox/Cre+),从中观察到了OGA表达的降低,引起了tau蛋白O-GlcNAc糖基化水平的升高,改善了突触功能障碍与学习记忆的缺陷。这一发现揭示了SIRT1-OGT轴在调节tau蛋白过度磷酸化中的作用,为治疗阿尔茨海默病中tau蛋白过度磷酸化提供了一个潜在的靶点。 2.3.2 O-GlcNAc糖基化与帕金森病 帕金森病的临床表现包括静息性震颤、运动迟缓、肌肉僵硬、姿势不稳和步态障碍[33],这些运动功能障碍主要源于黑质-纹状体路径中多巴胺能神经元的丢失以及基底神经节功能的失衡。除了运动障碍,帕金森病患者还常常表现出非运动症状,如睡眠障碍、情绪变化和认知下降,这表明帕金森病不仅影响中枢神经系统,还可能波及外周神经系统。 帕金森病的主要病理标志是路易小体和路易神经纤维在神经细胞中的积聚,其中α-突触核蛋白是其关键成分。α-突触核蛋白主要位于突触前末梢和突触囊泡中,在调节突触囊泡的迁移、释放和维持中起关键作用[34],见图5。"
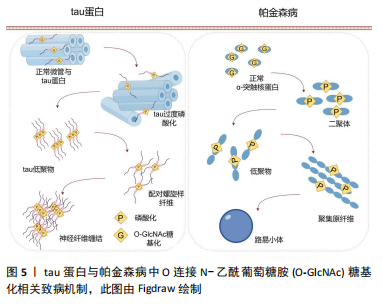

α-突触核蛋白的异常聚集和过度磷酸化是帕金森病发病过程中的关键事件,导致神经元功能受损和细胞死亡。研究发现,α-突触核蛋白上存在的O-GlcNAc糖基化位点能够显著减少其异常聚集和致病性自组装,从而降低神经元毒性[35]。LEE等[36]通过全原子分子动力学模拟研究发现,O-GlcNAc糖基化可以通过破坏α-突触核蛋白单体间的氢键抑制其异常聚集。他们提出了一个捕捉α-突触核蛋白聚合的物理机制模型,揭示了在没有O-GlcNAc糖基化修饰的条件下α-突触核蛋白寡聚化的分子机制。 在帕金森病中,多巴胺能神经元除了参与运动调节,还涉及情绪、认知、学习和记忆等多个方面,O-GlcNAc糖基化在这一过程中起重要作用[37]。研究人员发现,在多巴胺能神经元中特异性敲除OGT的小鼠表现出多巴胺能神经元的显著缺失和过早死亡[38],这表明O-GlcNAc糖基化在维持多巴胺能神经元的生存和功能中至关重要。在帕金森病小鼠模型中,通过条件敲除OGA以提高O-GlcNAc糖基化水平,显著减轻了帕金森病的病理特征,恢复了受损的多巴胺释放和运动行为,并且这种选择性的增强不会对神经元的结构或生存产生负面影响。 综上所述,O-GlcNAc糖基化修饰通过减少α-突触核蛋白的异常聚集和多巴胺能神经元的丢失来减缓帕金森病的病理进程。鉴于O-GlcNAc水平的提高不会对多巴胺能神经元的生存产生负面影响,开发靶向O-GlcNAc糖基化的治疗策略具有潜在的临床意义和价值。 2.3.3 O-GlcNAc糖基化与肌萎缩侧索硬化症 肌萎缩侧索硬化以上下运动神经元的退化为主要特征,临床表现包括骨骼肌的进行性无力与萎缩,最终通常因呼吸衰竭而死亡。大约90%的肌萎缩侧索硬化病例为散发型,与过度的神经元刺激、环境因素、氧化应激和炎症等相关;剩余10%为家族型,主要由显性遗传常染色体上的突变引起,涉及超氧化物歧化酶1(superoxide dismutase 1,SOD1)、TAR DNA结合蛋白43(43 kDa TARDNA binding protein,TDP-43)、肉瘤融合和9号染色体开放阅读框72(C-hromosome 9 open reading frame 72,C9orf72)[39]。在组织层面,肌萎缩侧索硬化病理特征包括神经丝在神经元细胞内的异常聚集以及TDP-43蛋白的异常积累和形成包涵体。 神经丝是神经元细胞骨架的重要组成部分,在维持神经元形态、支持细胞结构和信号传递方面发挥关键作用。研究表明,神经丝上存在O-GlcNAc糖基化修饰位点。在超氧化物歧化酶1过表达的小鼠和大鼠模型中,神经丝的O-GlcNAc糖基化水平显著降低,这表明O-GlcNAc糖基化可能在神经丝的稳定性和功能调节中起重要作用。进一步研究显示,使用OGA抑制剂可以显著减轻致病性神经丝的异常聚集[40],这表明O-GlcNAc糖基化可能通过抑制神经丝的过度磷酸化来缓解肌萎缩侧索硬化的病理特征。这一发现对理解肌萎缩侧索硬化的发病机制和寻找潜在治疗方法具有重要意义。 TDP-43蛋白的异常积累和形成包涵体是肌萎缩侧索硬化症的另一病理标志。TDP-43是一种RNA/DNA结合蛋白,在RNA转录、选择性剪接和mRNA稳定性调节中发挥作用。研究发现,在人体SH-SY5Y神经母细胞瘤细胞中,TDP-43存在内源性的O-GlcNAc糖基化位点[41],这些位点位于T199和T233,提升O-GlcNAc糖基化水平能够减少TDP-43的聚集和过度磷酸化,降低细胞毒性,并增强其剪接功能。在果蝇模型中,选择性增强TDP-43的O-GlcNAc糖基化改善了幼虫和成虫的运动缺陷,并延长了成虫的寿命,进一步支持了O-GlcNAc糖基化在调节TDP-43功能中的重要性。 氧化应激和细胞损伤也被认为是肌萎缩侧索硬化的危险因素。HSIEH等[42]发现,缺失NPGPx(一种氧化应激传感器)的小鼠表现出肌萎缩侧索硬化样表型,包括瘫痪、肌肉去神经支配和运动神经元丢失,并伴随着O-GlcNAc糖基化和活性氧水平紊乱。而使用OGA抑制剂进行干预,可以显著改善其运动神经元损伤和瘫痪状况。这些研究结果共同表明,O-GlcNAc糖基化可以通过多种途径改善肌萎缩侧索硬化的病理状态。 2.3.4 O-GlcNAc糖基化与亨廷顿舞蹈病 亨廷顿舞蹈病主要临床表现为运动和认知功能障碍[43],其病理学特征包括由突变型亨廷顿蛋白引起的细胞内蛋白质包涵体的形成和神经元的丢失。正常的亨廷顿蛋白在细胞信号传导、细胞凋亡调节、囊泡运输和细胞核内运输等生理过程中发挥关键作用。然而,突变型亨廷顿蛋白具有显著的聚集倾向[44],这种聚集可以引发细胞毒性,损害线粒体的轴突运输和突触传递功能,进而导致相关脑区神经元的损伤。研究显示,亨廷顿蛋白及其相互作用蛋白1相关蛋白(huntingtin interacting protein 1-related,HIP1R)均受到O-GlcNAc糖基化的修饰。在神经母细胞瘤细胞和亨廷顿舞蹈病苍蝇模型中,降低O-GlcNAc糖基化水平可以通过增强自噬小体-溶酶小体的功能,增加基础自噬通量,减少亨廷顿蛋白聚集和细胞毒性,从而促进亨廷顿蛋白聚集物的清除[45]。类似的结果在秀丽隐杆线虫的亨廷顿舞蹈病模型中得到了验证,研究者发现OGA失活显著提高了亨廷顿舞蹈病的毒性,而删除OGT则可以减轻这种毒性[46]。 核胞质运输的中断是亨廷顿舞蹈病病理特征中的另一重要方面,这一过程涉及由核孔蛋白构成的核孔复合体对大分子在细胞核与细胞质之间的运输进行严格调控。在亨廷顿舞蹈病患者和小鼠模型中,都观察到了核孔蛋白的异常定位现象[47]。研究表明,使用OGA抑制剂Thiamet-G处理原代培养的过表达突变型亨廷顿蛋白神经元,可以减少突变基因引起的核胞质转运中断,有效提升细胞活力并显著降低细胞死亡率[48]。此外,核孔蛋白同样被发现存在O-GlcNAc糖基化修饰位点,这种修饰对于维持核孔的完整性和选择性过滤功能至关重要。 总的来说,关于O-GlcNAc糖基化在亨廷顿舞蹈病病理过程中的作用仍存在争议。O-GlcNAc糖基化在不同疾病和蛋白中的作用可能存在差异。因此,深入研究O-GlcNAc糖基化在亨廷顿舞蹈病中的具体作用机制,对于理解疾病的发展和探索新的治疗策略具有重要意义。 2.4 OGA抑制剂的研发及临床应用潜力 根据O-GlcNAc 糖基化在神经退行性疾病中的作用,已开发和正在开发中的主要生物制剂主要集中在以下几类:首先,OGA抑制剂是最为成熟的一类[49],包括PUGNAc[50]、streptozotocin(STZ)[51]、NAG-Thiazoline[52]、NButGT[53]、GlcNAcstatin C[54]、Thiamet G[55]、iminocyclitol derivative[56]以及新合成的化合物5i[57]、13[58]、39[59],见图6。其中,STZ作为一种温和的体外抑制剂,由于其结构性毒性,临床适用性十分受限。相比之下,PUGNAc在体外显示出比STZ更高的抑制效果,但由于其对溶酶体己糖苷酶的选择性较低,未能广泛应用。NAG-Thiazoline作为第一个融合噻唑啉核心的OGA抑制剂,同样因为对溶酶体缺乏足够的选择性而受到限制。NButGT通过在噻唑啉核心上引入较大的取代基,显著提高了其对溶酶体的选择性。在这些OGA抑制剂中,Thiamet G作为一种高效的OGA抑制剂,具有良好的血脑屏障穿透能力,广泛用于细胞培养和动物实验,成为目前应用最广泛的OGA抑制剂。而最新合成的化合物5i、13和39在抑制OGA活性方面表现出更为优异的效果,并且具有更好的血脑屏障穿透性,显示出比Thiamet G更大的潜力,其中化合物13能够显著减少tau蛋白的过度磷酸化,并改善小鼠的认知障碍。这些研究进展突出显示了OGA抑制剂在神经退行性疾病治疗中的巨大潜力,并为未来开发更加有效和特异性的治疗方法打下了坚实的基础。"

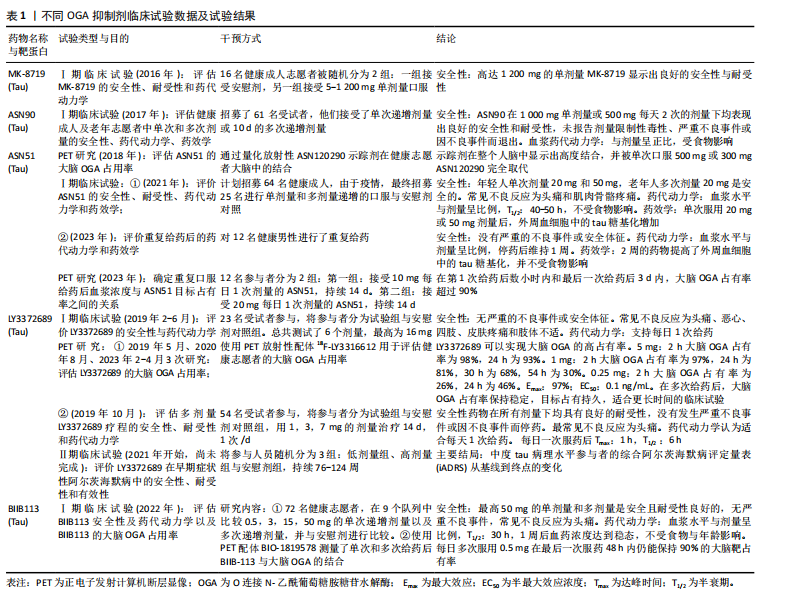
其次,OGT激动剂,如GlcNAc或其衍生物,可以通过增加细胞内的尿苷二磷酸N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖水平,从底物供应的角度促进OGT增加O-GlcNAc修饰。此外,一些研究对特定糖苷类化合物进行了探索,期望通过分子干预来影响O-GlcNAc水平。基因疗法和基因编辑工具也是重要的方向,siRNA介导的OGA减弱技术,通过RNA干扰减少OGA表达,从而间接提高O-GlcNAc水平,而CRISPR/Cas9基因编辑则用于精确调控OGA或OGT基因表达,以研究其在神经退行性疾病中的具体作用及治疗潜力。最后,一些天然化合物及其衍生物如类黄酮和其他植物提取物,也被发现在一定程度上能够影响O-GlcNAc糖基化水平,但具体机制和效果仍在研究中。 上述生物制剂主要停留在动物和细胞等实验层面,目前已有多种OGA抑制剂进入临床试验阶段,主要被运用于阿尔茨海默病的治疗,包括Alectos Therapeutics与默沙东公司推出的MK-8719[60-61],Asceneuron公司的ASN90[62]、ASN51,Eli Lilly公司的LY3372689与Biogen公司的BIIB113。它们都经过了详尽的临床前试验,以评估在动物模型中的安全性和有效性。MK-8719在携带人tau蛋白的rTg4510小鼠模型中应用时,能显著提升脑内O-GlcNAc糖基化水平,减少病理性tau蛋白。正电子发射断层成像研究也证实MK-8719在大鼠和rTG4510小鼠脑中实现了稳定的靶向结合。ASN90的临床前研究显示,在P301S tau转基因小鼠中,每日口服ASN90能显著提升脑内tau蛋白的糖基化水平,阻止tau缠结的发展,并改善小鼠的运动和行为,延长生存期。ASN90还能增强α-突触核蛋白的O-GlcNAc糖基化,减缓帕金森小鼠模型的运动障碍。ASN51是ASN90的第2版,以胶囊形式服用,作用时间更长,适合每日1次。BIIB113的临床前研究显示在rTG4510小鼠系中,BIIB113能实现85%的大脑OGA占有率,使tau病理减少43%,最终MK-8719被确立为首个临床候选药物,并进入Ⅰ期临床试验。其他OGA抑制剂也相继开展Ⅰ期临床试验,其中LY3372689应用于一项针对病程前期阿尔茨海默病患者的大型Ⅱ期临床试验,治疗时间超过1年。 以上临床试验结果表明,OGA抑制剂在人体内具有良好的耐受性和足够的安全性,所有Ⅰ期临床试验均未报告严重的不良事件或安全体征,见表1,OGA抑制剂在其中表现出优秀的药代动力学与药效学。这些结果将进一步支持OGA抑制剂的开发与更多Ⅱ期临床试验的开展。 未来应该集中验证O-GlcNAc糖基化对底物蛋白的影响,对有毒蛋白质的抑制作用可能取决于蛋白质的靶点、疾病的不同阶段、体内糖代谢的水平[63]。OGA抑制剂产生的保护作用可能不仅仅通过提高O-GlcNAc糖基化水平,还可能涉及OGA的其他保护性下游分子作用,确切的分子机制有待进一步研究。同时,应积极推进OGA抑制剂Ⅱ期临床试验,检验在更大样本中的有效性与安全性。"
| [1] ONOHUEAN H, AKIYODE AO, AKIYODE O, et al. Epidemiology of neurodegenerative diseases in the East African region: A meta-analysis. Front Neurol. 2022;13:1024004. [2] BALANA AT, PRATT MR. Mechanistic roles for altered O-GlcNAcylation in neurodegenerative disorders. Biochem J. 2021;478(14):2733-2758. [3] YIN R, WANG X, LI C, et al. Mass Spectrometry for O-GlcNAcylation. Front Chem. 2021;9:737093. [4] CZAJEWSKI I, VAN AALTEN DMF. The role of O-GlcNAcylation in development. Development. 2023;150(6):dev201370. [5] WU C, LI J, LU L, et al. OGT and OGA: Sweet guardians of the genome. J Biol Chem. 2024;300(4):107141. [6] LAZARUS BD, LOVE DC, HANOVER JA. Recombinant O-GlcNAc transferase isoforms: identification of O-GlcNAcase, yes tyrosine kinase, and tau as isoform-specific substrates. Glycobiology. 2006;16(5):415-421. [7] XIONG J, XU D. Mechanistic Insights into the Hydrolysis of O-GlcNAcylation Catalyzed by Human O-GlcNAcase. J Phys Chem B. 2020;124(42):9310-9322. [8] ZEIDAN Q, HART GW. The intersections between O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation: implications for multiple signaling pathways. J Cell Sci. 2010; 123(Pt 1):13-22. [9] MERGENTHALER P, LINDAUER U, DIENEL GA, et al. Sugar for the brain: the role of glucose in physiological and pathological brain function. Trends Neurosci. 2013;36(10):587-597. [10] MUHA V, FENCKOVA M, FERENBACH AT, et al. O-GlcNAcase contributes to cognitive function in Drosophila. J Biol Chem. 2020;295(26):8636-8646. [11] REXACH JE, CLARK PM, MASON DE, et al. Dynamic O-GlcNAc modification regulates CREB-mediated gene expression and memory formation. Nat Chem Biol. 2012;8(3):253-261. [12] SHEN H, ZHAO X, CHEN J, et al. O-GlcNAc transferase Ogt regulates embryonic neuronal development through modulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Hum Mol Genet. 2021;31(1):57-68. [13] TANWAR A, STANLEY P. Synergistic regulation of Notch signaling by different O-glycans promotes hematopoiesis. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1097332. [14] DAS S, BAILEY SK, METGE BJ, et al. O-GlcNAcylation of GLI transcription factors in hyperglycemic conditions augments Hedgehog activity. Lab Invest. 2019;99(2):260-270. [15] HAN S, KIM JN, PARK CH, et al. Modulation of synaptic transmission through O-GlcNAcylation. Mol Brain. 2024;17(1):1. [16] LAGERLÖF O, HART GW, HUGANIR RL. O-GlcNAc transferase regulates excitatory synapse maturity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017; 114(7):1684-1689. [17] CORTI E, DUARTE CB. The role of post-translational modifications in synaptic AMPA receptor activity. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023;51(1):315-330. [18] YIN X, LI Y, FAN X, et al. SIRT1 deficiency increases O-GlcNAcylation of tau, mediating synaptic tauopathy. Mol Psychiatry. 2022;27(10):4323-4334. [19] KNOPMAN DS, AMIEVA H, PETERSEN RC, et al. Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7(1):33. [20] LAO K, ZHANG R, LUAN J, et al. Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Amyloid-β Receptors and Transporters in Alzheimer’s Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;79(4): 1429-1442. [21] HUANG CW, RUST NC, WU HF, et al. Low glucose induced Alzheimer’s disease-like biochemical changes in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons is due to dysregulated O-GlcNAcylation. Alzheimers Dement. 2023;19(11):4872-4885. [22] AHMAD W. Glucose enrichment impair neurotransmission and induce Aβ oligomerization that cannot be reversed by manipulating O-β-GlcNAcylation in the C. elegans model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Nutr Biochem. 2022;108:109100. [23] NEHRA G, PROMSAN S, YUBOLPHAN R, et al. Cognitive decline, Aβ pathology, and blood-brain barrier function in aged 5xFAD mice. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2024; 21(1):29. [24] LI S, QU L, WANG X, et al. Novel insights into RIPK1 as a promising target for future Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Pharmacol Ther. 2022; 231:107979. [25] DONG X, SHU L, ZHANG J, et al. Ogt-mediated O-GlcNAcylation inhibits astrocytes activation through modulating NF-κB signaling pathway.J Neuroinflammation.2023;20(1):146. [26] RANI L, MALLAJOSYULA SS. Phosphorylation-Induced Structural Reorganization in Tau-Paired Helical Filaments. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021;12(9):1621-1631. [27] OTERO-GARCIA M, MAHAJANI SU, WAKHLOO D, et al. Molecular signatures underlying neurofibrillary tangle susceptibility in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron. 2022;110(18):2929-2948.e8. [28] PAN D, GU JH, ZHANG J, et al. Thiamme2-G, a Novel O-GlcNAcase Inhibitor, Reduces Tau Hyperphosphorylation and Rescues Cognitive Impairment in Mice. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;81(1):273-286. [29] ROSTGAARD N, JUL PH, GARMER M, et al. Increasing O-GlcNAcylation Attenuates tau Hyperphosphorylation and Behavioral Impairment in rTg4510 Tauopathy Mice. J Integr Neurosci. 2023;22(5):135. [30] CANTRELLE FX, LOYENS A, TRIVELLI X, et al. Phosphorylation and O-GlcNAcylation of the PHF-1 Epitope of Tau Protein Induce Local Conformational Changes of the C-Terminus and Modulate Tau Self-Assembly Into Fibrillar Aggregates. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021;14:661368. [31] YUZWA SA, CHEUNG AH, OKON M, et al. O-GlcNAc modification of tau directly inhibits its aggregation without perturbing the conformational properties of tau monomers. J Mol Biol. 2014;426(8):1736-1752. [32] LU S, YIN X, WANG J, et al. SIRT1 regulates O-GlcNAcylation of tau through OGT. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(8):7042-7055. [33] LO RY. Epidemiology of atypical parkinsonian syndromes. Tzu Chi Med J. 2021; 34(2):169-181. [34] 齐雪,李家慧,朱远峰,等.α-突触核蛋白的异常修饰及在帕金森病中的作用机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(8):1301-1306. [35] TAVASSOLY O, YUE J, VOCADLO DJ. Pharmacological inhibition and knockdown of O-GlcNAcase reduces cellular internalization of α-synuclein preformed fibrils. FEBS J. 2021;288(2):452-470. [36] LEE BE, KIM HY, KIM HJ, et al. O-GlcNAcylation regulates dopamine neuron function, survival and degeneration in Parkinson disease. Brain. 2020;143(12): 3699-3716. [37] RADEMACHER K, NAKAMURA K. Role of dopamine neuron activity in Parkinson’s disease pathophysiology. Exp Neurol. 2024;373:114645. [38] LEE BE, SUH PG, KIM JI. O-GlcNAcylation in health and neurodegenerative diseases. Exp Mol Med. 2021;53(11):1674-1682. [39] MEJZINI R, FLYNN LL, PITOUT IL, et al. ALS Genetics, Mechanisms, and Therapeutics: Where Are We Now? Front Neurosci. 2019;13:1310. [40] LOBSIGER CS, GARCIA ML, WARD CM, et al. Altered axonal architecture by removal of the heavily phosphorylated neurofilament tail domains strongly slows superoxide dismutase 1 mutant-mediated ALS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(29):10351-10356. [41] ZHAO MJ, YAO X, WEI P, et al. O-GlcNAcylation of TDP-43 suppresses proteinopathies and promotes TDP-43’s mRNA splicing activity. EMBO Rep. 2021;22(6):e51649. [42] HSIEH YL, SU FY, TSAI LK, et al. NPGPx-Mediated Adaptation to Oxidative Stress Protects Motor Neurons from Degeneration in Aging by Directly Modulating O-GlcNAcase. Cell Rep. 2019;29(8):2134-2143.e7. [43] MCCOLGAN P, TABRIZI SJ. Huntington’s disease: a clinical review. Eur J Neurol. 2018;25(1):24-34. [44] HO LW, BROWN R, MAXWELL M, et al. Wild type Huntingtin reduces the cellular toxicity of mutant Huntingtin in mammalian cell models of Huntington’s disease. J Med Genet. 2001;38(7):450-452. [45] KUMAR A, SINGH PK, PARIHAR R, et al. Decreased O-linked GlcNAcylation protects from cytotoxicity mediated by huntingtin exon1 protein fragment. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(19):13543-13553. [46] WANG P, LAZARUS BD, FORSYTHE ME, et al. O-GlcNAc cycling mutants modulate proteotoxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans models of human neurodegenerative diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(43):17669-17674. [47] GRIMA JC, DAIGLE JG, ARBEZ N, et al. Mutant Huntingtin Disrupts the Nuclear Pore Complex. Neuron. 2017;94(1):93-107.e6. [48] ZHU Y, LIU TW, MADDEN Z, et al. Post-translational O-GlcNAcylation is essential for nuclear pore integrity and maintenance of the pore selectivity filter. J Mol Cell Biol. 2016;8(1):2-16. [49] LOI EM, TOMAŠIČ T, BALSOLLIER C, et al. Discovery of a New Drug-like Series of OGT Inhibitors by Virtual Screening. Molecules. 2022;27(6):1996. [50] HALTIWANGER RS, GROVE K, PHILIPSBERG GA. Modulation of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine levels on nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins in vivo using the peptide O-GlcNAc-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase inhibitor O-(2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucopyranosylidene)amino-N-phenylcarbamate. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273(6):3611-3617. [51] HERR RR, JAHNKE JK, ARGOUDELIS AD. The structure of streptozotocin. J Am Chem Soc. 1967;89(18):4808-4809. [52] CETINBAŞ N, MACAULEY MS, STUBBS KA, et al. Identification of Asp174 and Asp175 as the key catalytic residues of human O-GlcNAcase by functional analysis of site-directed mutants. Biochemistry. 2006;45(11):3835-3844. [53] WHITWORTH GE, MACAULEY MS, STUBBS KA, et al. Analysis of PUGNAc and NAG-thiazoline as transition state analogues for human O-GlcNAcase: mechanistic and structural insights into inhibitor selectivity and transition state poise. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129(3):635-644. [54] DORFMUELLER HC, BORODKIN VS, SCHIMPL M, et al. GlcNAcstatin: a picomolar, selective O-GlcNAcase inhibitor that modulates intracellular O-glcNAcylation levels. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128(51):16484-16485. [55] YUZWA SA, MACAULEY MS, HEINONEN JE, et al. A potent mechanism-inspired O-GlcNAcase inhibitor that blocks phosphorylation of tau in vivo. Nat Chem Biol. 2008;4(8):483-490. [56] BERGERON-BRLEK M, GOODWIN-TINDALL J, CEKIC N, et al. A Convenient Approach to Stereoisomeric Iminocyclitols: Generation of Potent Brain-Permeable OGA Inhibitors. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015;54(51):15429-15433. [57] TAWADA M, FUSHIMI M, MASUDA K, et al. Discovery of a Novel and Brain-Penetrant O-GlcNAcase Inhibitor via Virtual Screening, Structure-Based Analysis, and Rational Lead Optimization. J Med Chem. 2021;64(2):1103-1115. [58] WEBER P, MÉSZÁROS Z, JAGEČIĆ D, et al. Diaminocyclopentane-derived O-GlcNAcase inhibitors for combating tau hyperphosphorylation in Alzheimer’s disease. Chem Commun (Camb). 2022;58(63):8838-8841. [59] LI X, HAN J, BUJARANIPALLI S, et al. Structure-based discovery and development of novel O-GlcNAcase inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Med Chem. 2022;238:114444. [60] SELNICK HG, HESS JF, TANG C, et al. Discovery of MK-8719, a Potent O-GlcNAcase Inhibitor as a Potential Treatment for Tauopathies. J Med Chem. 2019;62(22): 10062-10097. [61] WANG X, LI W, MARCUS J, et al. MK-8719, a Novel and Selective O-GlcNAcase Inhibitor That Reduces the Formation of Pathological Tau and Ameliorates Neurodegeneration in a Mouse Model of Tauopathy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2020;374(2):252-263. [62] PERMANNE B, SAND A, OUSSON S, et al. O-GlcNAcase Inhibitor ASN90 is a Multimodal Drug Candidate for Tau and α-Synuclein Proteinopathies. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2022;13(8):1296-1314. [63] DU P, ZHANG X, LIAN X, et al. O-GlcNAcylation and Its Roles in Neurodegenerative Diseases. J Alzheimers Dis. 2024;97(3):1051-1068. [64] PRATT MR, VOCADLO DJ. Understanding and exploiting the roles of O-GlcNAc in neurodegenerative diseases. J Biol Chem. 2023;299(12): 105411. [65] MA X, LI H, HE Y, et al. The emerging link between O-GlcNAcylation and neurological disorders. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017;74(20):3667-3686. [66] ALTEEN MG, TAN HY, VOCADLO DJ. Monitoring and modulating O-GlcNAcylation: assays and inhibitors of O-GlcNAc processing enzymes. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2021;68:157-165. |
| [1] | Yu Jingbang, Wu Yayun. Regulatory effect of non-coding RNA in pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1659-1666. |
| [2] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [3] | Yuan Weibo, Liu Chan, Yu Limei. Potential application of liver organoids in liver disease models and transplantation therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [4] | Xie Liugang, Cui Shuke, Guo Nannan, Li Aoyu, Zhang Jingrui. Research hotspots and frontiers of stem cells for Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1475-1485. |
| [5] |
Li Tian, Ren Yuhua, Gao Yanping, Su Qiang.
Mechanism of agomelatine alleviating anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in APP/PS1 transgenic mice #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1176-1182.
|
| [6] | Lu Ranran, Zhou Xu, Zhang Lijie, Yang Xinling. Dimethyl fumarate alleviates nerve damage in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 989-994. |
| [7] | Huang Haina, Yu Yanrong, Bi Jian, Huang Miao, Peng Weijie. Epigenetic characteristics of hepatogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in three-dimensional culture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7848-7855. |
| [8] | Guo Zhao, Zhuang Haoyan, Shi Xuewen. Role of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of colorectal cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7872-7879. |
| [9] | Zhang Pulian, Liu Baoru, Yang Min . Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of aplastic anemia: inhibiting or activating relevant targets in its pathological evolution [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6800-6810. |
| [10] | Su Qin, Jia Siwei, Guo Minfang, Meng Tao, Li Yanbing, Mu Bingtao, Song Lijuan, Ma Cungen, Yu Jiezhong. Lycium barbarum polysaccharide intervenes in SH-SY5Y cell injury induced by beta-amyloid protein 1-42: protective effect of mitochondrial autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6688-6696. |
| [11] | Zhang Xin, Guo Baojuan, Xu Huixin, Shen Yuzhen, Yang Xiaofan, Yang Xufang, Chen Pei. Protective effects and mechanisms of 3-N-butylphthalide in Parkinson’s disease cell models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6466-6473. |
| [12] | Yu Bingbing, Wang Tingting, Fang Junlin, Guo Yun, Huang Yingru. Acupuncture for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis: meta-analysis, systematic evaluation and trial sequential analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6305-6316. |
| [13] | Wang Jiaru, Zhang Ying, Yang Yong, Qi Wen, Xiao Huaye, Ma Qiuping, Yang Lianzhao, Luo Ziwei, He Yaqing, Zhang Jiangyin, Wei Jiawen, Meng Yuan, Tan Silian. Systematic review of machine learning models for predicting functional recovery and prognosis in stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6317-6325. |
| [14] | He Ningjuan, Li Li, Wang Su, Yang Jianshe, Lei Siyun, Wang Yang. Effects of aerobic or resistance exercise on hippocampal ras/Drebrin dendritic spine plasticity in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5528-5535. |
| [15] | Shen Zilong, Wu Mingjie, Chen Xiaojing, Zhou Xibin, Zhou Chunxiang. An experimental method for simultaneously extracting the dura mater and deep cervical lymph nodes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5543-5548. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||