Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (31): 6743-6752.doi: 10.12307/2025.539
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects and mechanisms of exosomal miRNA in treatment of multiple myeloma
Zhao Yihan1, 2, Sun Xuhang2, Zhao Lin3, Jiang Shiqing1
- 1Department of Hematology and Oncology, First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 2School of First Clinical Medicine, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 3Department of Hematology, Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200000, China
-
Received:2024-07-16Accepted:2024-08-22Online:2025-11-08Published:2025-02-26 -
Contact:Jiang Shiqing, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Hematology and Oncology, First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Zhao Yihan, Doctoral candidate, Department of Hematology and Oncology, First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; School of First Clinical Medicine, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Joint Open Project of the State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine “Zhang Zhongjing Inheritance and Innovation Special Project”, No. GZY-KJS-2022-038-2 (to JSQ); Natural Science Foundation (General Project) of Henan Province, No. 202300420055 (to JSQ); Major Special Project of Scientific Research on Traditional Chinese Medicine in Henan Province, No. 2024ZYZD03 (to JSQ); Graduate Student Research and Innovation Program of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2023KYCX003 (to ZYH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Yihan, Sun Xuhang, Zhao Lin, Jiang Shiqing. Effects and mechanisms of exosomal miRNA in treatment of multiple myeloma[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6743-6752.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
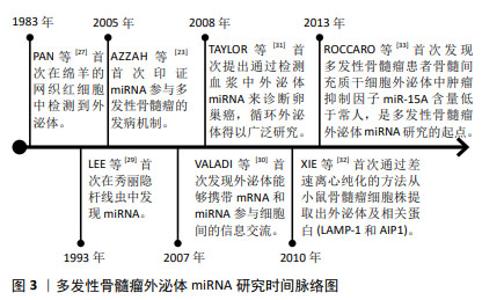
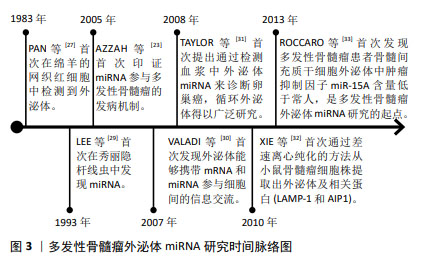
2.1 外泌体miRNA概要 细胞能够分泌各种类型的细胞外囊泡,根据细胞外囊泡的大小、内容物和形成机制,它们可分为不同的亚群,包括外泌体(30-150 nm)、微泡(200-1 000 nm)和凋亡小体(50-5 000 nm),ESCRT蛋白及辅助蛋白Alix,TSG101,HSC70,HSP90β,抗原CD86,CD63,CD9,CD81可作为外泌体的标记物,用以区别和鉴定不同类型的细胞外囊泡[10-11]。细胞膜连续内陷导致细胞多囊体的产生,多囊体与细胞内囊泡和细胞器相互影响,造成外泌体成分的异质性和多样性,所有细胞类型均可分泌外泌体,其结构类似于脂质体,由脂质双层膜组成,表面和内部存在多种生物分子,如蛋白质、核酸和脂质等;作为纳米级别的有膜结构小囊泡,外泌体可有效地在细胞间传递生理、病理信息,深入了解外泌体的科学结构和功能对于探索细胞间通讯、器官稳态与疾病的分子机制具有重要意义[12-13]。 外泌体介导的生物反应可以加重或抑制疾病,在各种疾病中,外泌体提供了一个观察细胞或组织状态改变的平台,循环体液外泌体的研究突出了它们在疾病诊断、进展和预后判断、疗效评估方面的重要价值[14]。外泌体中包含了mRNA,tRNA,miRNA,lncRNA和circRNA等多种类型的核酸分子,包括miRNA,lncRNA和circRNA在内的非编码RNA,被认为是多发性骨髓瘤发生和进展的关键因素[15]。miRNA作为一种长度为19-25个碱基的小型非编码RNA,可与Argonaute (Ago)蛋白和RNA诱导沉默的复合物(RNA-induced silencing complex,RISC)中的其他关键因子相互作用,通过破坏mRNA或抑制其翻译来调控基因表达,参与多种生物过程,包括细胞增殖、细胞死亡[16-19]、细胞谱系的分化、干细胞维持和发育阶段的调控等,可作为癌抑制基因或癌基因发挥作用,影响肿瘤患者的生存[20-22]。尽管miRNA数量众多且种类庞杂,但大部分miRNA在进化过程中高度保守。miRNA参与多发性骨髓瘤发病机制的第一个证据由AZZAH等[23]提出,研究表明miR-125b,miR-133a,miR-1,miR-124a,miR-15及miR-16等在多发性骨髓瘤中低表达,考虑白血病抑制因子作为miR-125b靶标、Stat3和血管生成素1前体作为miR-124a的靶点分别发挥作用。 外泌体具有在细胞间转移miRNA的能力,现已有研究证实外泌体miRNA作为细胞间信息通讯的重要载体在多种恶性肿瘤的生理、病理过程中发挥了关键作用[24-26]。文章通过总结发现,多发性骨髓瘤外泌体miRNA的作用机制涉及促进多发性骨髓瘤细胞恶性增殖迁移和血管生成、抑制多发性骨髓瘤细胞衰老凋亡、诱导肾间质纤维化、塑造抑制性免疫微环境、提高耐药相关蛋白的表达或者增强多发性骨髓瘤细胞对蛋白酶抑制剂的敏感性、增强化疗药物治疗效果等。 2.2 多发性骨髓瘤外泌体miRNA研究历史概要 在1983年,PAN和JOHNSTONE[27]在绵羊的网织红细胞中首次检测到外泌体,1987年,JOHNSTONE等[28]正式提出“外泌体”一词并将其命名为“Exosome”,当时被认为是参与细胞废物排泄的囊泡;1993年,LEE等[29]首次在秀丽隐杆线虫lin4位点发现了miRNA;在2005年,AZZAH等[23]首次印证了miRNA参与多发性骨髓瘤的发病机制;在2007年,VALADI等[30]首次发现外泌体能够携带mRNA和miRNA参与细胞间的信息交流;在2008年,TAYLOR等[31]首次提出通过检测血浆中外泌体miRNA来诊断卵巢癌,循环外泌体得以广泛研究,近年来在肿瘤诊疗的相关研究中逐渐细化。在2010年,XIE等[32]首次通过差速离心纯化的方法从小鼠骨髓瘤细胞株提取出外泌体及相关蛋白(LAMP-1和AIP1)。在2013年,ROCCARO等[33]首次发现多发性骨髓瘤患者骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体中肿瘤抑制因子miR-15a含量低于常人水平,是多发性骨髓瘤外泌体miRNA研究的起点。具体见时间脉络图,见图3。"
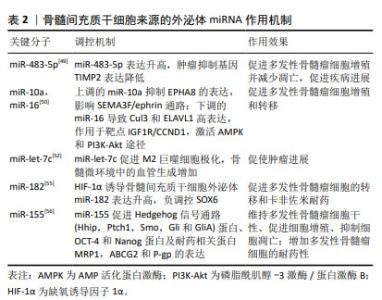
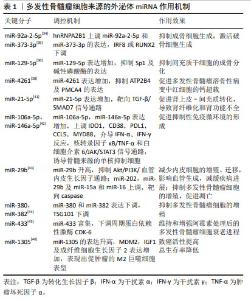
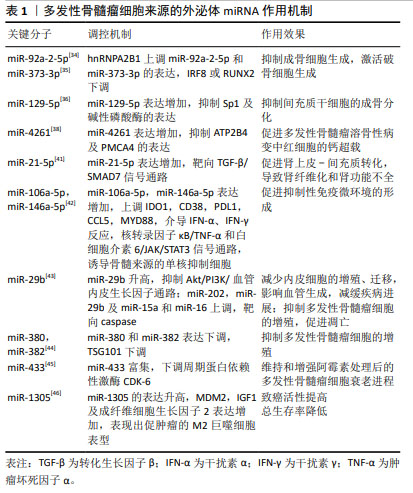
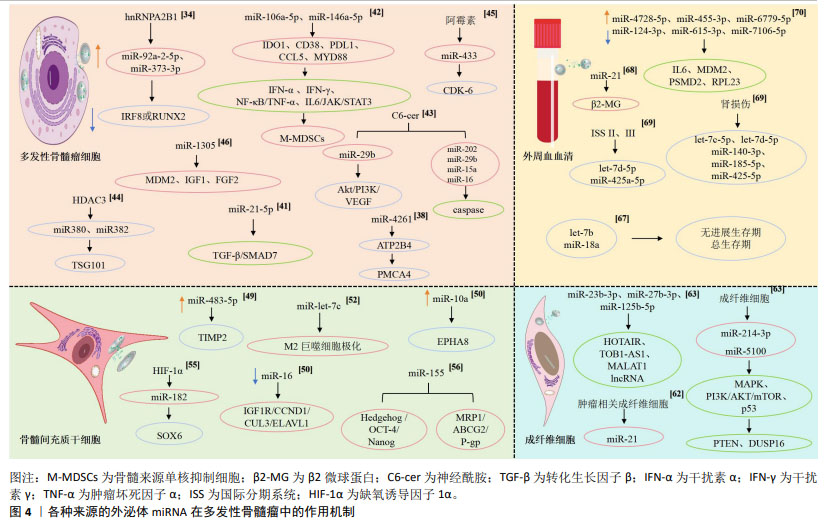
多发性骨髓瘤细胞的N6-甲基腺苷(N6-methyladenosine,m6A)阅读器hnRNPA2B1水平与多发性骨髓瘤患者溶骨性病变的数量呈高度正相关,hnRNPA2B1可以介导上调多发性骨髓瘤细胞miR-92a-2-5p和miR-373-3p的表达,通过外泌体转运到受体单核细胞或间充质干细胞,激活破骨细胞生成并且下调IRF8或RUNX2以抑制成骨细胞生成,研究阐明了多发性骨髓瘤细胞外泌体miRNA通过介导hnRNPA2B1参与骨病变的关键机制,提示hnRNPA2B1可能是多发性骨髓瘤骨病变的靶点[34]。RAIMONDO等[35-36]发现多发性骨髓瘤细胞外泌体可以将miR-129-5p转运至人间充质干细胞,高表达的人间充质干细胞miR-129-5p可以抑制具有促进成骨分化作用的转录因子Sp1及其靶标碱性磷酸酶的表达,证实了多发性骨髓瘤细胞外泌体miRNA可抑制间充质干细胞的成骨分化。高钙血症是多发性骨髓瘤最常见的并发症之一,通常是由于破骨细胞活性增加引起溶骨性病变,破骨细胞和成骨细胞失衡,导致血液中钙、磷水平升高[37]。BIAN等[38]发现多发性骨髓瘤溶骨性病变中红细胞存在钙超载现象,其机制为多发性骨髓瘤CD138+细胞的外泌体可以将miR-4261递送到红细胞,下调ATP2B4的表达,最终引起红细胞钙离子外排通道主要依赖的细胞膜PMCA4蛋白表达的降低,进而导致钙超载。 多达50%多发性骨髓瘤患者存在肾功能不全的症状,作为多发性骨髓瘤的主要特征之一,肾功能不全与患者总生存期缩短和早期死亡风险升高相关,轻链沉积、铸型肾病、淀粉样变和肾纤维化是多发性骨髓瘤患者肾功能不全的主要病理机制[39-40],来自多发性骨髓瘤细胞的外泌体高表达的miR-21-5p能够通过靶向转化生长因子β/SMAD7信号通路促进肾上皮-间充质转化,导致肾纤维化和肾功能不全[41]。多发性骨髓瘤细胞来源的外泌体miRNA不仅参与了溶骨性病变、高钙血症、肾功能不全的病理过程,还参与了多发性骨髓瘤免疫微环境的抑制、免疫治疗耐药的发生和发展。多发性骨髓瘤细胞外泌体递送的miR-106a-5p和miR-146a-5p可以上调外周血单核细胞中各种免疫抑制/炎症分子如IDO1,CD38,PDL1,CCL5及MYD88,这些分子通过介导干扰素α、干扰素γ反应,核转录因子κB/肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6/JAK/STAT3信号通路诱导外周血中骨髓来源的单核抑制细胞(monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells,M-MDSCs),包括诱导抑制性免疫细胞在内的多种骨髓细胞群,促进抑制性免疫微环境的形成[42]。 近年来,血管生成已经成为肿瘤治疗的重要靶点之一,抗血管生成在多发性骨髓瘤的治疗中具有很好的应用前景。C6-ceramide(C6-cer)是一种具有细胞通透性的短链神经酰胺,常用于模拟内源性神经酰胺。研究发现,经C6-cer处理的多发性骨髓瘤细胞外泌体miR-29b升高,Akt通路是miR-29b在内皮细胞中的直接靶标,miR-29b转录后通过抑制Akt/PI3K/血管内皮生长因子通路以减少内皮细胞的增殖、迁移,进而影响血管生成,减缓疾病进展;此外,C6-cer还可以增加多发性骨髓瘤细胞外泌体miR-202,miR-29b,miR-15a和miR-16水平以抑制多发性骨髓瘤细胞的增殖,促进其凋亡,此过程可能与caspase相关[43]。组蛋白去乙酰化酶(HDAC3)是多发性骨髓瘤的一个重要的治疗靶点,HDAC3敲低的HS5-多发性骨髓瘤细胞通过降低外泌体miR-380和miR-382的表达,下调TSG101,从而抑制多发性骨髓瘤细胞的增殖[44]。除了外泌体miRNA在多发性骨髓瘤细胞的增殖中的调控作用已经得到研究证实,其在多发性骨髓瘤细胞衰老中的调控作用也得到关注,VULPIS等[45]研究发现,经阿霉素干预后的多发性骨髓瘤细胞外泌体miR-433富集,富集的miR-433可以独立于由p53和p21介导的经典衰老程序诱导衰老,下调周期蛋白依赖性激酶CDK-6以维持和增强阿霉素处理后的多发性骨髓瘤细胞衰老进程。 LEE等[46]证实了多发性骨髓瘤细胞外泌体miRNA的预后作用,研究表明,在低氧环境中多发性骨髓瘤细胞外泌体miR-1305的表达升高,其靶基因MDM2、胰岛素生长因子1、成纤维细胞生长因子2表达增加,提高了致癌活性;此外,外泌体miR-1305从多发性骨髓瘤细胞转移到巨噬细胞,表现出促肿瘤的M2巨噬细胞表型,高外泌体miR-1305患者的总生存率低于低外泌体miR-1305患者。 2.4 骨髓间充质干细胞来源的外泌体miRNA 骨髓微环境对多发性骨髓瘤细胞的存活和恶性增殖十分重要,骨髓间充质干细胞作为骨髓基质细胞的前体细胞,是骨髓造血微环境的重要组成部分,具有多向分化潜能和自我更新能力,可以通过介导造血干细胞黏附、分泌多种细胞因子发挥造血支持作用,还具有旁分泌和免疫调节等功能[47-48]。多发性骨髓瘤细胞与骨髓基质细胞的相互作用是多发性骨髓瘤进展的重要机制[49-57],骨髓间充质干细胞是否通过外泌体介导疾病的发生发展引起了广泛的关注,见表2。 "

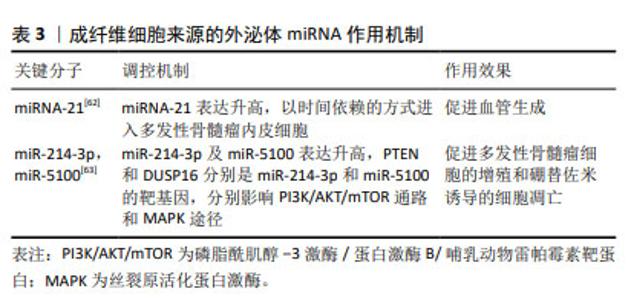
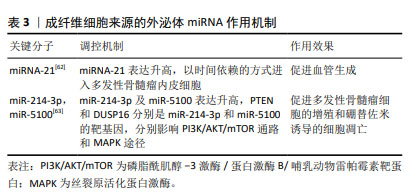
有研究通过对良性疾病和多发性骨髓瘤患者骨髓间充质干细胞进行微阵列分析,筛选出差异表达的miR-483-5p,研究发现其可通过外泌体从骨髓间充质干细胞转运到多发性骨髓瘤细胞以增加表达,促进多发性骨髓瘤细胞增殖并减少凋亡,肿瘤抑制基因TIMP2是miR-483-5p的下游靶点,研究阐释了骨髓间充质干细胞通过释放外泌体调节miR-483-5p/TIMP2轴,促进多发性骨髓瘤恶性进展的病理过程[49]。PENG等[50]通过微阵列数据集和生信工具分析了15例多发性骨髓瘤患者和10名健康供者的生物标本信息,发现骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体中miR-10a的上调和miR-16的下调可能是导致多发性骨髓瘤进展的潜在机制,上调的miR-10a转移到多发性骨髓瘤细胞并抑制EPHA8的表达,与下游SEMA3F相互作用,影响ephrin受体信号传导途径和轴突引导,而下调的外泌体miR-16导致Cul3和ELAVL1的高表达,与靶点IGF1R/CCND1相互作用,激活AMP活化蛋白激酶(AMP-activated protein kinase,AMPK)和磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶(phosphatidylinositol‐3kinase,PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B,Akt)途径,最终促进多发性骨髓瘤细胞增殖和转移。骨髓间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体对多发性骨髓瘤细胞增殖的影响以及在远距离归巢作用中的意义已逐步得到证实[51]。血管生成是由骨髓微环境分泌的细胞因子和生长因子调控的复杂过程,影响肿瘤的发生、发展、侵袭和转移,骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体miR-let-7c能够促进M2巨噬细胞极化,促进骨髓微环境中的血管生成,促使肿瘤进展,miR-let-7c可以作为多发性骨髓瘤血管生成的生物标志物和新的治疗靶点[52]。 耐药性目前是多发性骨髓瘤治疗中的一个主要临床挑战,外泌体作为一种信号传导介质,可以改变肿瘤对化疗药物的敏感性,参与肿瘤的进展,骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体RNAs是否在多发性骨髓瘤耐药过程中的发挥作用引起了关注。研究发现骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体中miR-182富集[53-54],在SRY-Box转录因子6(SOX6)的3’-UTR中存在miR-182的结合位点,缺氧诱导因子1α作为关键转录因子,诱导多发性骨髓瘤患者骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体miR-182表达升高,通过负调控SOX6这一外泌体来源miR-182的直接靶标,靶向SOX6下调,促进多发性骨髓瘤细胞的转移和卡非佐米耐药[55];此外,骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体miR-155能够通过增加Hedgehog信号通路(Hhip,Ptch1,Smo、Gli和GliA)蛋白、OCT-4和Nanog的蛋白表达,维持多发性骨髓瘤细胞干性、促进多发性骨髓瘤细胞的增殖、抑制多发性骨髓瘤细胞凋亡,骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体miR-155同时还能促进耐药相关蛋白MRP1、ABCG2和P-gp的表达,增加多发性骨髓瘤细胞的耐药性[56]。 由于在治疗过程中耐药性的演变,多发性骨髓瘤的治疗反应是不可预测的,因此需要一个系统性的临床工具,以评估多药耐药性的演变,预测复发风险,并在临床治疗中定期监测疾病进展。现有的临床工具大多数是通过肿瘤负荷的间接测量来判断疗效,不能直接常规测量或者无创检测耐药蛋白表达,并且不能捕获与多发性骨髓瘤相关的多位点克隆浸润,外泌体作为耐药蛋白转移的有效载体,可用以判断多发性骨髓瘤耐药发展的预后[57]。 2.5 成纤维细胞来源的外泌体miRNA 肿瘤相关成纤维细胞(cancer-associated fibroblasts,CAF)是肿瘤微环境的主要参与者,可以产生和重塑细胞外基质,分泌趋化因子、细胞因子和生长因子,调节肿瘤干细胞的可塑性,介导耐药过程[58],已被证实在胰腺癌、乳腺癌及多发性骨髓瘤等肿瘤的发生发展过程中起重要作用[59-61]。 SUN等[62]将CAF外泌体与多发性骨髓瘤内皮细胞共培养发现,CAF中外泌体miRNA-21含量丰富,并且能够以时间依赖的方式进入多发性骨髓瘤内皮细胞,并通过促进增殖、迁移和微管生成来刺激血管生成,CAF来源的外泌体miR-21可以作为多发性骨髓瘤的一种新的诊断性生物标志物和治疗靶点;多发性骨髓瘤细胞与骨髓成纤维细胞之间的相互作用在多发性骨髓瘤的发展和耐药中有着重要意义,在意义未明单克隆免疫球蛋白血症(MGUS)向多发性骨髓瘤过渡的期间,多发性骨髓瘤细胞过表达miR-23b-3p,miR-27b-3p,miR-125b-5p,miR-214-3p和miR-5100,与多发性骨髓瘤成纤维细胞外泌体共培养的受体多发性骨髓瘤细胞仅选择性地过表达miR-214-3p,miR-5100,而不是miR-23b-3p,miR-27b-3p和miR-125b-5p,多发性骨髓瘤细胞表达的HOTAIR、TOB1-AS1和MALAT1 lncRNA是miR-23b-3p,miR-27b-3p和miR-125b-5p的分子海绵,多发性骨髓瘤细胞通过表达HOTAIR,TOB1-AS1和MALAT1 lncRNA来平衡来自成纤维细胞外泌体的miRNA的摄取,受体多发性骨髓瘤细胞选择性地表达miR-214-3p和miR-5100,PTEN和DUSP16分别是miR-214-3p和miR-5100的靶基因,PTEN是PI3K/AKT/mTOR通路的主要负调节因子,DUSP16的抑制可以增加MAPK途径的活性,选择性表达的外泌体miRNAs通过调节多发性骨髓瘤细胞中的MAPK,PI3K/AKT/mTOR和p53通路促进多发性骨髓瘤细胞的增殖和硼替佐米诱导的细胞凋亡,研究证实了多发性骨髓瘤细胞具有摄取多发性骨髓瘤成纤维细胞衍生的外泌体和通过lncRNA选择性过表达外泌体miRNA的能力[63],见表3。 "
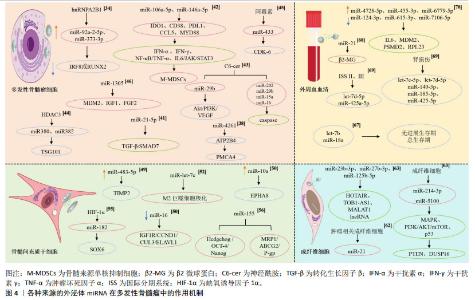
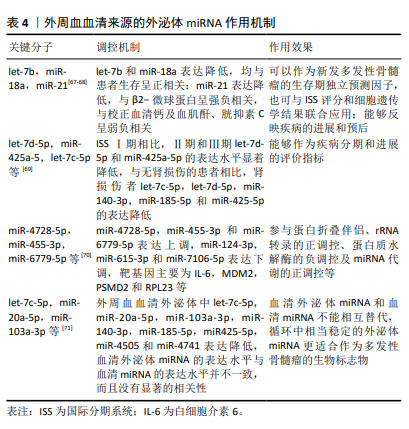
MANIER等[67]通过TaqMan低密度miRNA阵列检测了156份多发性骨髓瘤患者外周血血清中22个miRNA表达情况,发现let-7b和miR-18a可以作为新发多发性骨髓瘤的无进展生存期和总生存期独立预测因子,二者可与国际分期系统(International Staging System,ISS)评分和多发性骨髓瘤细胞遗传学结果联合应用,提高多发性骨髓瘤预后的评估价值。另有研究发现,多发性骨髓瘤患者血清外泌体来源的miR-21的表达水平明显低于健康对照组,miR-21与反映多发性骨髓瘤肿瘤负荷的β2-微球蛋白呈强负相关,与校正血清钙及反映多发性骨髓瘤患者肾功能损伤严重程度的血肌酐、胱抑素C呈弱负相关,提示外泌体来源miR-21能够反映多发性骨髓瘤的进展和预后。此外,血清外泌体来源的Let-7b和miR-18a在多发性骨髓瘤患者中显著低表达,两种miRNA均与β2-微球蛋白、胱抑素C、校正血清钙呈弱相关,提示其反映多发性骨髓瘤患者疾病进展的效用有限,但Let-7b和miR-18a的表达水平与多发性骨髓瘤患者的生存呈正相关,两种miRNA的低表达预示着患者生存期缩短[68]。在疾病的不同阶段,血清外泌体miRNA的表达水平不同:与ISS Ⅰ期相比,Ⅱ期和Ⅲ期的患者let-7d-5p和miR-425a-5p表达水平显著降低,与无肾损伤的患者相比,肾损伤患者的let-7c-5p,let-7d-5p,miR-140-3p,miR-185-5p和miR-425-5p的表达降低,表明外泌体miRNA表达水平的变化可以用来判断疾病病程分期和进展情况[69]; 关于多发性骨髓瘤外周血来源的外泌体miRNA的研究,目前仍处于探索阶段,面对数量庞大的、种类繁杂的外泌体miRNA,如何找出高敏且准确的miRNA是一个值得关注的问题。FANG等[70]从9名健康供者和19例新诊断多发性骨髓瘤患者的外周血中收集血清外泌体进行miRNA测序,共发现了多发性骨髓瘤患者313个血清外泌体差异表达miRNA,158种呈上调趋势,155例呈下调趋势。其中,排名前3位的上调差异表达miRNA包括miR-4728-5p,miR-455-3p和miR-6779-5p,排名前3位的下调差异表达miRNA包括miR-124-3p,miR-615-3p和miR-7106-5p,相关的靶基因主要为白细胞介素6,MDM2,PSMD2和RPL23等,涉及蛋白折叠伴侣,rRNA转录的正调控,蛋白质水解酶的负调控,miRNA代谢的正调控等通路。ZHANG等[71]发现,多发性骨髓瘤患者外周血外泌体中let-7c-5p,miR-20a-5p,miR-103a-3p,miR-140-3p,miR-185-5p,miR425-5p,miR-4505和miR-4741表达降低,血清外泌体miRNA的表达水平与血清miRNA的表达水平并不一致,而且没有显著的相关性,因此建议这两种不同的检测方法不能相互替代,由于RNA酶的存在,血清miRNA测定相对不稳定,外泌体因其特定结构可以保护RNA免于降解,在循环中相当稳定的外泌体miRNA更适合作为多发性骨髓瘤的生物标志物。 2.7 不同种类细胞来源的外泌体miRNA在多发性骨髓瘤中的作用机制复杂多样 上述内容总结了多发性骨髓瘤细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞、肿瘤相关成纤维细胞、外周血细胞外泌体miRNA在多发性骨髓瘤中的各种作用机制,涉及骨病变、高钙血症及肾功能不全等多种并发症的发生以及免疫微环境的抑制、免疫药物耐药、新生血管生成、细胞增殖凋亡及细胞衰老等多类病理过程,其分子机制复杂多样,具体见图4。 "
| [1] MALARD F, NERI P, BAHLIS N, et al. Multiple myeloma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2024;10(1):45. [2] VAN DE DONK N, PAWLYN C, YONG KL. Multiple myeloma. Lancet. 2021;397(10272):410-427. [3] ZHANG N, WU J, WANG Q, et al. Global burden of hematologic malignancies and evolution patterns over the past 30 years. Blood Cancer J. 2023;13(1):82. [4] GENG J, ZHAO J, FAN R, et al. Global, regional, and national burden and quality of care of multiple myeloma, 1990-2019. J Glob Health. 2024;14:04033. [5] SURVEILLANCE, EPIDEMIOLOGY, AND END RESULTS PROGRAM. Cancer stat facts: myeloma. national cancer institute (2024). https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/mulmy.html [6] MINA R, MUSTO P, ROTA S, et al. Carfilzomib induction, consolidation, and maintenance with or without autologous stem-cell transplantation in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: pre-planned cytogenetic subgroup analysis of the randomised, phase 2 FORTE trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023;24(1):64-76. [7] BIRD S, PAWLYN C. IMiD resistance in multiple myeloma: current understanding of the underpinning biology and clinical impact. Blood. 2023;142(2):131-140. [8] ALIPOOR SD, CHANG H. Exosomal miRNAs in the tumor microenvironment of multiple myeloma. Cells. 2023;12(7):1030. [9] CHEN M, XU R, ZHANG J, et al. Editorial: understanding the rna species in the extracellular vesicles of multiple myeloma. Front Oncol. 2022;12:946160. [10] DOYLE LM, WANG MZ. Overview of extracellular vesicles, their origin, composition, purpose, and methods for exosome isolation and analysis. Cells. 2019;8(7):727. [11] ALLEGRA A, DI G, TONACCI A, et al. Multiple myeloma cell-derived exosomes: implications on tumorigenesis, diagnosis, prognosis and therapeutic strategies. Cells. 2021;10(11):2865. [12] WANG X, HE L, HUANG X, et al. Recent progress of exosomes in multiple myeloma: pathogenesis, diagnosis, prognosis and therapeutic strategies. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(7):1635. [13] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977. [14] ARYA SB, COLLIE SP, PARENT CA. The ins-and-outs of exosome biogenesis, secretion, and internalization. Trends Cell Biol. 2024;34(2):90-108. [15] HASHEMI M, ROSHANZAMIR SM, PASKEH MDA, et al. Non-coding RNAs and exosomal ncRNAs in multiple myeloma: an emphasis on molecular pathways. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023;941:175380. [16] HAMILTON AJ, BAULCOMBE DC. A species of small antisense RNA in posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science. 1999;286(5441): 950-952. [17] KIM VN, NAM JW. Genomics of microRNA. Trends Genet. 2006;22: 165-173. [18] MORI MA, LUDWIG RG, GARCIA-MARTIN R, et al. Extracellular miRNAs: from biomarkers to mediators of physiology and disease. Cell Metab. 2019;30(4):656-673. [19] BEREZIKOV E, PLASTERK RH. Camels and zebrafish, viruses and cancer: a microRNA update. Hum Mol Genet. 2005;14(Suppl 2):R183-R190. [20] MATTICK JS, MAKUNIN IV. Small regulatory RNAs in mammals. Hum Mol Genet. 2005;14(Suppl 1):R121-R132. [21] ZHANG B, PAN X, COBB GP, et al. Micro RNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 2007;302(1):1-12 [22] LIN H, XING Y, LEE P, et al. A microRNA component of the p53 tumor suppressor network. Nature. 2007;447:1130-1134. [23] AZZAH A, TAMMY P, MARTA C, et al. MicroRNA expression analysis in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2005;106:1554. [24] WANG Y, LI S, HU M, et al. Universal STING mimic boosts antitumour immunity via preferential activation of tumour control signalling pathways. Nat Nanotechnol. 2024;19(6):856-866. [25] HE Z, ZHONG Y, REGMI P, et al. Exosomal long non-coding RNA TRPM2-AS promotes angiogenesis in gallbladder cancer through interacting with PABPC1 to activate NOTCH1 signaling pathway. Mol Cancer. 2024;23(1):65. [26] WANG L, SHEN K, GAO Z, et al. Melanoma derived exosomes amplify radiotherapy induced abscopal effect via IRF7/I-IFN axis in macrophages. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(13):e2304991. [27] PAN B, JOHNSTONE R . Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: selective externalization of the receptor. Cell. 1983;33(3):967-978. [28] JOHNSTONE R, ADAM M, HAMMOND J, et al.Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation.Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem, 1987;262(19):9412-9420. [29] LEE RC, FEINBAUM R, AMBROS V.The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75(5):843-854. [30] VALADI H, EKSTRÖM K, BOSSIOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nature Cell Biology. 2007;9(6):654-659. [31] TAYLOR D, GERCEL-TAYLOR C. MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2008;110(1):13-21. [32] XIE Y, BAI O, ZHANG H, et al. Tumor necrosis factor gene-engineered J558 tumor cell-released exosomes stimulate tumor antigen P1A-specific CD8+ CTL responses and antitumor immunity. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2010;25(1):21-28. [33] ROCCARO AM, SACCO A, MAISO P, et al. BM mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes facilitate multiple myeloma progression. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(4):1542-1555. [34] LIU R, ZHONG Y, CHEN R, et al. m(6)A reader hnRNPA2B1 drives multiple myeloma osteolytic bone disease. Theranostics. 2022;12(18): 7760-7774. [35] RAIMONDO S, SAIEVA L, VICARIO E, et al. Multiple myeloma-derived exosomes are enriched of amphiregulin (AREG) and activate the epidermal growth factor pathway in the bone microenvironment leading to osteoclastogenesis. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12(1):2. [36] AIMONDO S, URZÌ O, CONIGLIARO A, et al. Extracellular vesicle microRNAs contribute to the osteogenic inhibition of mesenchymal stem cells in multiple myeloma. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(2):449. [37] GHUMMAN GM, HAIDER M, RAFFAY EA, et al. Hypercalcemia-induced hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis with hypophosphatemia in a multiple myeloma patient: lessons for the clinical nephrologist. J Nephrol. 2023;36(2):315-317. [38] BIAN S, ZHANG X, LIN L, et al. Exosomal MiR-4261 mediates calcium overload in RBCs by downregulating the expression of ATP2B4 in multiple myeloma. Front Oncol. 2022;12:978755. [39] DIMOPOULOS MA, MERLINI G, BRIDOUX F, et al. Management of multiple myeloma-related renal impairment: recommendations from the International Myeloma Working Group. Lancet Oncol. 2023; 24(7):e293-e311. [40] SALAHUDDIN AZ, ALAM MR, HOSSAIN RM, et al. Renal involvement as a presenting feature of multiple myeloma. Mymensingh Med J. 2019;28(3):527-535. [41] LIU L, LIU L, LIU R, et al. Exosomal miR-21-5p derived from multiple myeloma cells promote renal epithelial-mesenchymal transition through targeting TGF-β/SMAD7 signalling pathway. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2023;50(9):711-718. [42] MIZUHARA K, SHIMURA Y, TSUKAMOTO T, et al. Tumour-derived exosomes promote the induction of monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells from peripheral blood mononuclear cells by delivering miR-106a-5p and miR-146a-5p in multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol. 2023;203(3):426-438. [43] LIU L, YE Q, LIU L, et al. C6-ceramide treatment inhibits the proangiogenic activity of multiple myeloma exosomes via the miR-29b/Akt pathway. J Transl Med. 2020;18(1):298. [44] HO M, CHEN T, LIU J, et al. Targeting histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) in the bone marrow microenvironment inhibits multiple myeloma proliferation by modulating exosomes and IL-6 trans-signaling. Leukemia. 2020;34(1):196-209. [45] VULPIS E, CUOLLO L, BORRELLI C, et al. Doxorubicin-mediated miR-433 expression on exosomes promotes bystander senescence in multiple myeloma cells in a ddr-independent manner. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(7):6862. [46] LEE JY, RYU D, LIM SW, et al. Exosomal miR-1305 in the oncogenic activity of hypoxic multiple myeloma cells: a biomarker for predicting prognosis. J Cancer. 2021;12(10):2825-2834. [47] DENIZ IA, KARBANOVá J, WOBUS M, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell-associated migrasomes: a new source of chemoattractant for cells of hematopoietic origin. Cell Commun Signal. 2023;21(1):36. [48] GARCíA O, RODRíGUEZ G, ENCINAS J, et al. The role of tumor microenvironment in multiple myeloma development and progression. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(2):217. [49] GU J, WANG M, WANG X, et al. Exosomal miR-483-5p in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promotes malignant progression of multiple myeloma by targeting TIMP2. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:862524. [50] PENG Y, SONG X, LAN J, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells derived exosomal miR-10a and miR-16 may be involved in progression of patients with multiple myeloma by regulating EPHA8 or IGF1R/CCND1. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(4):e23447. [51] RAMEZANI A, TAFAZOLI A, SALIMI F, et al. Current knowledge on therapeutic, diagnostic, and prognostics applications of exosomes in multiple myeloma: opportunities and challenges. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2024;756:109994. [52] TIAN X, SUN M, WU H, et al. Exosome-derived miR-let-7c promotes angiogenesis in multiple myeloma by polarizing M2 macrophages in the bone marrow microenvironment. Leuk Res. 2021;105:106566. [53] SUN C, LI W, LI Y, et al. MiR-182-5p mediated by exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell attenuates inflammatory responses by targeting TLR4 in a mouse model of myocardial infraction. Immune Netw. 2022;22(6):e49. [54] ZHAO J, LI X, HU J, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes attenuate myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury through miR-182-regulated macrophage polarization. Cardiovasc Res. 2019;115(7): 1205-1216. [55] LONG S, LONG S, HE H, et al. Exosomal miR-182 derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells drives carfilzomib resistance of multiple myeloma cells by targeting SOX6. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023; 18(1):937. [56] GAO X, ZHOU J, WANG J, et al. Mechanism of exosomal miR-155 derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on stemness maintenance and drug resistance in myeloma cells. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):637. [57] KRISHNAN SR, BEBAWY M. Circulating biosignatures in multiple myeloma and their role in multidrug resistance. Mol Cancer. 2023; 22(1):79. [58] KOCHETKOVA M, SAMUEL MS. Differentiation of the tumor microenvironment: are CAFs the Organizer? Trends Cell Biol. 2022; 32(4):285-294. [59] NIU N, SHEN X, WANG Z, et al. Tumor cell-intrinsic epigenetic dysregulation shapes cancer-associated fibroblasts heterogeneity to metabolically support pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell. 2024;42(5): 869-884.e9. [60] LI Q, YUAN H, ZHAO G, et al. ZNF32 prevents the activation of cancer-associated fibroblasts through negative regulation of TGFB1 transcription in breast cancer. FASEB J. 2023;37(4):e22837. [61] DING Z, SHI R, HU W, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in hematologic malignancies: elucidating roles and spotlighting therapeutic targets. Front Oncol. 2023;13:1193978. [62] SUN M, WANG X, SHOU Y, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived exosome microRNA-21 promotes angiogenesis in multiple myeloma. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):9671. [63] SALTARELLA I, LAMANUZZI A, DESANTIS V, et al. Myeloma cells regulate miRNA transfer from fibroblast-derived exosomes by expression of lncRNAs. J Pathol. 2022;256(4):402-413. [64] ZHANG L, PAN L, XIANG B, et al. Potential role of exosome-associated microRNA panels and in vivo environment to predict drug resistance for patients with multiple myeloma. Oncotarget. 2016;7(21):30876-30891. [65] POURHANIFEH M, MAHJOUBIN T, SHAFIEE A, et al. MicroRNAs and exosomes: Small molecules with big actions in multiple myeloma pathogenesis. IUBMB Life. 2020;72(3):314-333. [66] CARIELLO M, SQUILLA A, PIACENTE M, et al. Drug Resistance: the role of exosomal mirna in the microenvironment of hematopoietic tumors. Molecules. 2022;28(1):116. [67] MANIER S, LIU CJ, AVET-LOISEAU H, et al. Prognostic role of circulating exosomal miRNAs in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2017;129(17): 2429-2436. [68] ZHOU L, LIU XL, LI YW, et al. Clinical study of miRNAs derived from serum exosomes in multiple myeloma. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2022;30(5):1490-1495. [69] ZHANG ZY, LI YC, GENG CY, et al. Potential relationship between clinical significance and serum exosomal miRNAs in patients with multiple myeloma. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:1575468. [70] FANG T, SUN H, SUN X, et al. Exosome miRNAs profiling in serum and prognostic evaluation in patients with multiple myeloma. Blood Sci. 2023;5(3):196-208. [71] ZHANG ZY, LI YC, GENG CY, et al. Serum exosomal microRNAs as novel biomarkers for multiple myeloma. Hematol Oncol. 2019;37(4): 409-417. [72] EL-CHEIKH J, MOUKALLED N, MALARD F, et al. Cardiac toxicities in multiple myeloma: an updated and a deeper look into the effect of different medications and novel therapies. Blood Cancer J. 2023; 13(1):83. [73] YU M, JI L, LI S, et al. Exosomal circ-CACNG2 promotes cardiomyocyte apoptosis in multiple myeloma via modulating miR-197-3p/caspase3 axis. Exp Cell Res. 2022;417(2):113229. [74] SUN R, LIU W, ZHAO Y, et al. Exosomal circRNA as a novel potential therapeutic target for multiple myeloma-related myocardial damage. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21(1):311. [75] YU M, YU J, ZHANG Y, et al. A novel circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network revealed exosomal circ-ATP10A as a biomarker for multiple myeloma angiogenesis. Bioengineered. 2022;13(1):667-683. [76] WU Y, ZHANG Z, WU J, et al. The exosomes containing LINC00461 originated from multiple myeloma inhibit the osteoblast differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells via sponging miR-324-3p. J Healthc Eng. 2022;2022:3282860. [77] TANG JX, CHEN Q, LI Q, et al. Exosomal mRNAs and lncRNAs involved in multiple myeloma resistance to bortezomib. Cell Biol Int. 2021;45(5):965-975. [78] DENG M, YUAN H, LIU S, et al. Exosome-transmitted LINC00461 promotes multiple myeloma cell proliferation and suppresses apoptosis by modulating microRNA/BCL-2 expression. Cytotherapy. 2019;21(1):96-106. [79] YUAN S, LI Q, HE C, et al. Anti-BCMA-engineered exosomes for bortezomib targeted delivery in multiple myeloma. Blood Adv. 2024. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2023012464. [80] RUSSO M, TIRINATO L, SCIONTI F, et al. Raman spectroscopic stratification of multiple myeloma patients based on exosome profiling. ACS Omega. 2020;5(47):30436-30443. [81] DI NOTO G, BUGATTI A, ZENDRINI A, et al. Merging colloidal nanoplasmonics and surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy for enhanced profiling of multiple myeloma-derived exosomes. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;77:518-524. |
| [1] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Xu Hao, Ding Lu, Li Xiao. Investigating the effect of the mechanical wear on abutment screw in Morse taper connection implant implant system by using finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [3] | Han Haihui, Ran Lei, Meng Xiaohui, Xin Pengfei, Xiang Zheng, Bian Yanqin, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 signaling to improve bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1905-1912. |
| [4] | Li Jun, Gong Jingjing, Sun Guobin, Guo Rui, Ding Yang, Qiang Lijuan, Zhang Xiaoli, Fang Zhanhai . miR-27a-3p promotes the proliferation of human hypertrophic scar fibroblasts by regulating mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1609-1617. |
| [5] | Jing Ruyi, Chen Yingxin, Cao Lei . Prognosis of deep lamellar keratoplasty versus penetrating keratoplasty in the treatment of stromal corneal dystrophy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1626-1633. |
| [6] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [7] | Liu Qi, Li Linzhen, Li Yusheng, Jiao Hongzhuo, Yang Cheng, Zhang Juntao. Icariin-containing serum promotes chondrocyte proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells in the co-culture system of three kinds of cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [8] | Aikepaer · Aierken, Chen Xiaotao, Wufanbieke · Baheti. Osteogenesis-induced exosomes derived from human periodontal ligament stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [9] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [10] | Lyu Liting, Yu Xia, Zhang Jinmei, Gao Qiaojing, Liu Renfan, Li Meng, Wang Lu. Bibliometric analysis of research process and current situation of brain aging and exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1457-1465. |
| [11] | Weng Zongqin, Zhao Hailong. Mechanism of exosomal miRNA involved in tumor chemotherapy resistance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1504-1511. |
| [12] | Li Jialin, Zhang Yaodong, Lou Yanru, Yu Yang, Yang Rui. Molecular mechanisms underlying role of mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1512-1522. |
| [13] | Cao Yue, Ye Xinjian, Li Biyao, Zhang Yining, Feng Jianying. Effect of extracellular vesicles for diagnosis and therapy of oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1523-1530. |
| [14] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [15] | Chen Yuning, Jiang Ying, Liao Xiangyu, Chen Qiongjun, Xiong Liang, Liu Yue, Liu Tong. Buqi Huoxue Compounds intervene with the expression of related factors and autophagy related proteins in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1152-1158. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||