Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (22): 4761-4770.doi: 10.12307/2025.445
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bio-3D printed bionic scaffold promotes healing after rotator cuff injury
Xu Jie1, Jiu Jingwei1, Liu Haifeng1, Zhao Bin1, 2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China; 2Shanxi Key Laboratory of Bone and Soft Tissue Repair, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2024-03-23Accepted:2024-05-18Online:2025-08-08Published:2024-12-06 -
Contact:Zhao Bin, MD, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China; Shanxi Key Laboratory of Bone and Soft Tissue Repair, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Xu Jie, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Shanxi Provincial Health Commission Major Science and Technology Research Project, No. 2020XM11 (to ZB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Jie, Jiu Jingwei, Liu Haifeng, Zhao Bin. Bio-3D printed bionic scaffold promotes healing after rotator cuff injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4761-4770.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

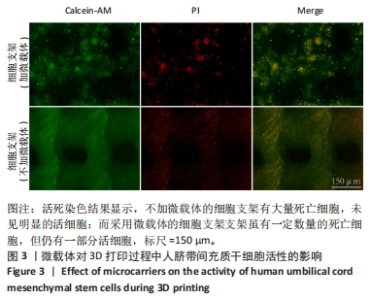
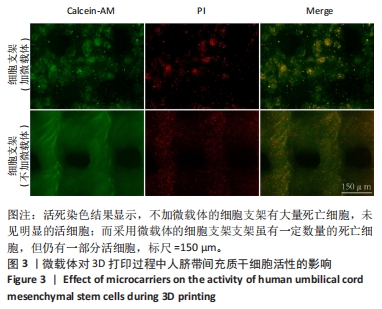
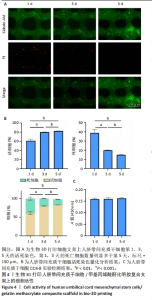
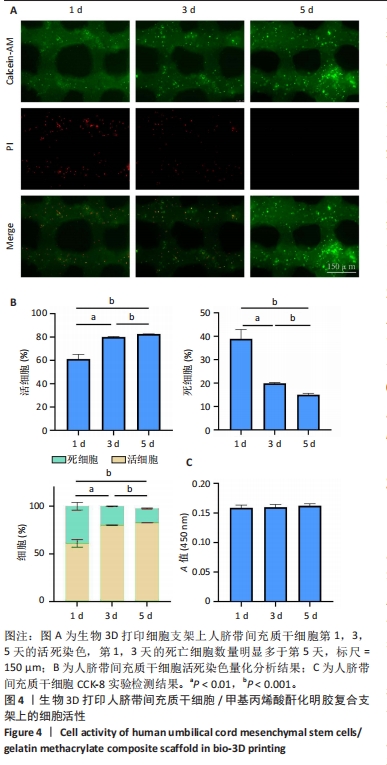
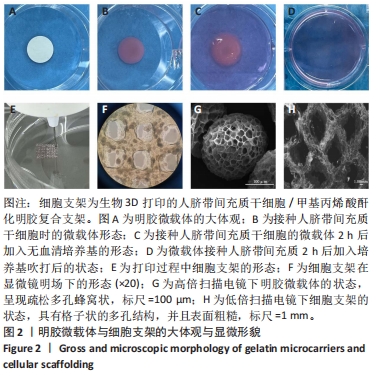
2.1 明胶微载体与3D打印细胞支架的形态特征 多达数万个微载体通过压缩得到实验使用的明胶微载体支架,最终呈多层片状结构(图2A)。将200 μL人脐带间充质干细胞悬液接种于明胶微载体上后,整片微载体膨胀而不散开(图2B),接种2 h后将无血清培养添加至微载体上,微载体颜色变黄但仍呈圆形膨胀状态(图2C),吹打均匀后的微载体均匀分布于培养皿中(图2D)。微载体细胞悬液与甲基丙烯酸酐化明胶打印墨水混匀后上生物3D打印机打印,打印过程中细胞支架状态良好没有松散塌陷(图2E),打印完成后在显微镜明场下观察到微载体均匀地分布在支架上(图2F)。使用扫描电镜分别观察明胶微载体与细胞支架的显微结构,明胶微载体呈现疏松多孔蜂窝状,具有较高的孔隙率(大于90%),这均为细胞的贴壁吸附提供了条件(图2G);细胞支架具有格子状的多孔结构(图2H),为细胞提供了支持并促进营养的扩散,并且孔隙之间的相互连接有利于细胞迁移和营养交换,其次支架的粗糙表面可增强细胞的附着和增殖,建立了稳定的细胞-支架界面。"
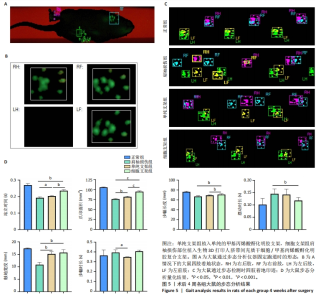
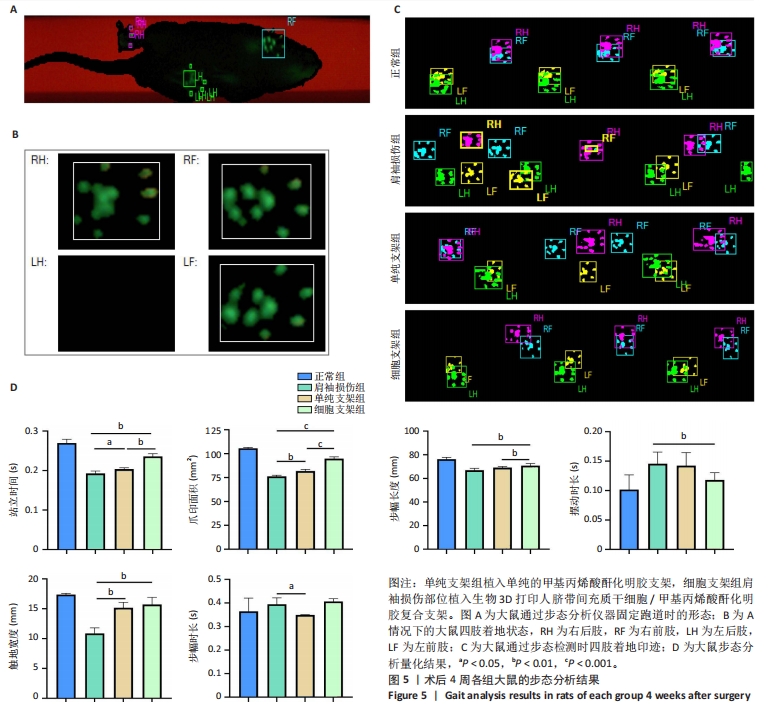
2.4 细胞支架修复大鼠肩袖损伤实验结果 2.4.1 实验动物数量分析 24只SD大鼠全部进入结果分析。 2.4.2 各组大鼠动物行为学测试 术后4周使用CatWalk小动物步态仪对大鼠进行步态分析,大鼠自由通过固定跑道时摄像头能清晰记录四肢印迹(图5A,B)。正常组大鼠通过固定跑道时步态节律整齐;肩袖损伤组大鼠在通过跑道时节律紊乱,右前肢压力不均匀;单纯支架组大鼠步态节律较肩袖损伤组有所改善;相较于单纯支架组,细胞支架组大鼠上肢步态节律更齐(图5C)。 与肩袖损伤组比较,单纯支架组大鼠站立时间、爪印面积、触地宽度均增加(P < 0.05,P < 0.01),步幅时长减少(P < 0.05);细胞支架组大鼠站立时间、爪印面积、步幅长度、触地宽度均增加(P < 0.01,P < 0.001),摆动时长减少(P < 0.05)。与单纯支架组比较,细胞支架组大鼠站立时间、爪印面积与步幅长度均增加(P < 0.01,P < 0.001),见图5D。 "
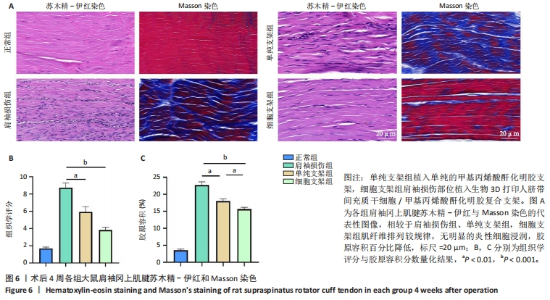
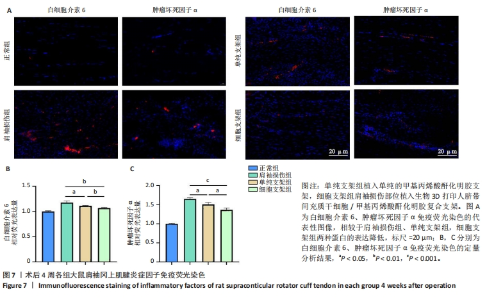
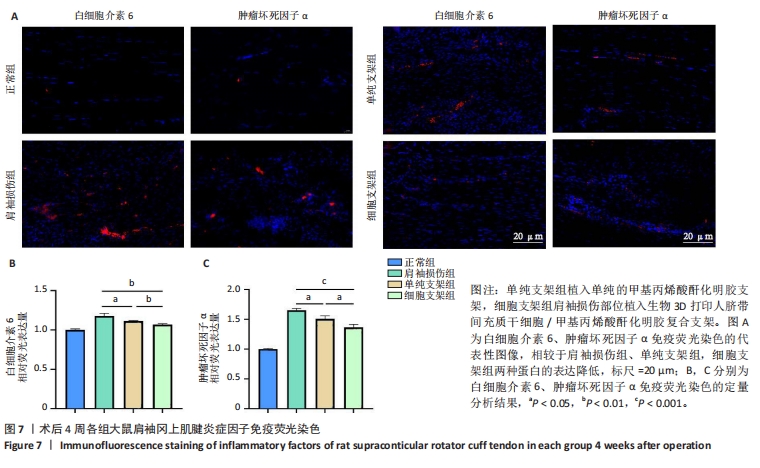
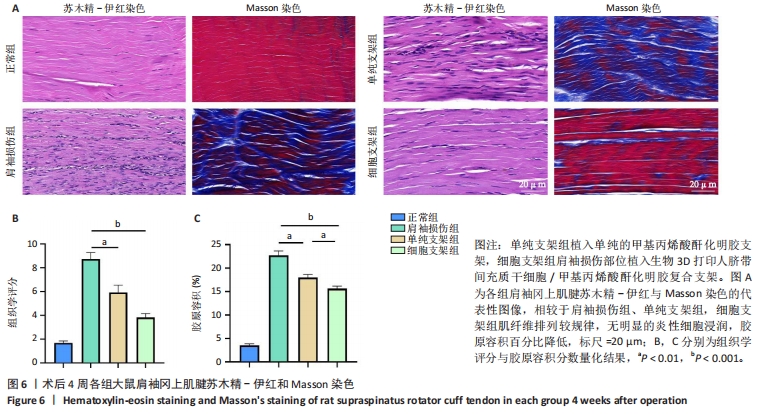
2.4.3 各组大鼠冈上肌腱苏木精-伊红与Masson染色结果 苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,正常组冈上肌腱结构完整,肌细胞和细胞外基质组织保持良好状态;相比之下,肩袖损伤组冈上肌腱结构不完整,肌纤维排列混乱并伴有大量炎性细胞浸润及新生血管生成;单纯支架组肌纤维排列混乱,炎性细胞浸润较肩袖损伤组稍有所改善;细胞支架组肌纤维排列有序,无明显的炎症细胞浸润,见图6A。Masson染色结果显示,正常组肌纤维与胶原纤维排列整齐,肩袖损伤组肌纤维与胶原纤维排列紊乱,单纯支架组肌纤维与胶原纤维排列紊乱情况轻于肩袖损伤组,细胞支架组肌纤维与胶原纤维排列紊乱情况得到明显改善,见图6A。组织定量分析结果显示,肩袖损伤组组织学评分、胶原容积百分比显著高于正常组(P < 0.001),单纯支架组、细胞支架组组织学评分、胶原容积百分比低于肩袖损伤组(P < 0.01,P < 0.001),细胞支架组胶原容积百分比低于单纯支架组(P < 0.01),见图6B,C。"
| [1] LUI P, ZHANG P, CHAN K, et al. Biology and augmentation of tendon-bone insertion repair. J Orthop Surg Res. 2010;5:59. [2] HERNIGOU J, VERTONGEN P, RASSCHAERT J, et al. Role of Scaffolds, Subchondral, Intra-Articular Injections of Fresh Autologous Bone Marrow Concentrate Regenerative Cells in Treating Human Knee Cartilage Lesions: Different Approaches and Different Results. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(8):3844. [3] LIU Q, HATTA T, QI J, et al. Novel engineered tendon-fibrocartilage-bone composite with cyclic tension for rotator cuff repair. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(7):1690-1701. [4] ZHU Q, MA ZJ, LI HY, et al. Enhancement of rotator cuff tendon-bone healing using combined aligned electrospun fibrous membranes and kartogenin. Rsc Adv. 2019;9(27):15582-15592. [5] AICALE R, BISACCIA RD, OLIVIERO A, et al. Current pharmacological approaches to the treatment of tendinopathy. Expert Opin Pharmaco. 2020;21(12):1467-1477. [6] GOVINDARAJU DT, CHEN CH, SHALUMON KT, et al. Bioactive Nanostructured Scaffold-Based Approach for Tendon and Ligament Tissue Engineering. Nanomaterials. 2023;13(12):35. [7] CHEN J, ZHANG E, ZHANG W, et al. Fos Promotes Early Stage Teno-Lineage Differentiation of Tendon Stem/Progenitor Cells in Tendon. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(11):2009-2019. [8] GE Z, LI W, ZHAO R, et al. Programmable DNA Hydrogel Provides Suitable Microenvironment for Enhancing TSPCS Therapy in Healing of Tendinopathy. Small. 2023;19(32):e2207231. [9] MURCHISON ND, PRICE BA, CONNER DA, et al. Regulation of tendon differentiation by scleraxis distinguishes force-transmitting tendons from muscle-anchoring tendons. Development. 2007;134(14):2697-2708. [10] TSUCHIYA A, TAKEUCHI S, WATANABE T, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapies for liver cirrhosis: MSCs as “conducting cells” for improvement of liver fibrosis and regeneration. Inflamm Regen. 2019;39(1): 6. [11] WANG J, QIN W, ZHONG Y, et al. Injectable collagen hydrogel combines human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to promote endometrial regeneration in rats with thin endometrium. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;254(Pt 1):127591. [12] CAO TT, CHEN H, PANG M, et al. Dose optimization of intrathecal administration of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of subacute incomplete spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(8):1785-1794. [13] WANG S, YAO Z, CHEN L, et al. Preclinical assessment of IL-1β primed human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for tendon functional repair through TGF-β/IL-10 signaling. Heliyon. 2023;9(11):e21411. [14] YUAN Z, YU D, WANG Y, et al. Early delivery of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improves healing in a rat model of Achilles tendinopathy. Regen Med. 2024;19(2):93-102. [15] YEA JH, BAE TS, KIM BJ, et al. Regeneration of the rotator cuff tendon-to-bone interface using umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells and gradient extracellular matrix scaffolds from adipose tissue in a rat model. Acta Biomater. 2020;114:104-116. [16] YAO Z, LI J, XIONG H, et al. MicroRNA engineered umbilical cord stem cell-derived exosomes direct tendon regeneration by mTOR signaling. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):169. [17] ZHANG J, XU W, LI C, et al. Tissue Engineering Microtissue: Construction, Optimization, and Application. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2022;28(2):393-404. [18] ALMEIDA GHD, IGLESIA RP, ARAUJO MS, et al. Uterine Tissue Engineering: Where We Stand and the Challenges Ahead. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2022;28(4):861-890. [19] ZHOU T, YUAN ZN, WENG JY, et al. Challenges and advances in clinical applications of mesenchymal stromal cells. J Hematol Oncol. 2021; 14(1):24. [20] YUAN Z, YUAN X, ZHAO Y, et al. Injectable GelMA Cryogel Microspheres for Modularized Cell Delivery and Potential Vascularized Bone Regeneration. Small. 2021;17(11):e2006596. [21] YAN XR, LI J, NA XM, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Proliferation on Konjac Glucomannan Microcarriers: Effect of Rigidity. Chin J Polym Sci. 2022;40(9):1080-1089. [22] LOUBIÈRE C, SION C, DE ISLA N, et al. Impact of the type of microcarrier and agitation modes on the expansion performances of mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord. Biotechnol Progr. 2019;35(6): 17. [23] YAN X, ZHANG K, YANG Y, et al. Dispersible and Dissolvable Porous Microcarrier Tablets Enable Efficient Large-Scale Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Expansion. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2020;26(5):263-275. [24] GROSS G, HOFFMANN A. Therapeutic strategies for tendon healing based on novel biomaterials, factors and cells. Pathobiology. 2013; 80(4):203-210. [25] FENG Y, ZHU S, MEI D, et al. Application of 3D Printing Technology in Bone Tissue Engineering: A Review. Curr Drug Deliv. 2021;18(7):847-861. [26] JIANG H, LI X, CHEN T, et al. Bioprinted vascular tissue: Assessing functions from cellular, tissue to organ levels. Mater Today Bio. 2023; 23:100846. [27] MATAI I, KAUR G, SEYEDSALEHI A, et al. Progress in 3D bioprinting technology for tissue/organ regenerative engineering. Biomaterials. 2020;226:119536. [28] BANDYOPADHYAY A, MITRA I, BOSE S. 3D Printing for Bone Regeneration. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020;18(5): 505-514. [29] WANG Z, WANG L, LI T, et al. 3D bioprinting in cardiac tissue engineering. Theranostics. 2021;11(16):7948-7969. [30] ZHANG H, CHEN Y, FAN C, et al. Cell-subpopulation alteration and FGF7 activation regulate the function of tendon stem/progenitor cells in 3D microenvironment revealed by single-cell analysis. Biomaterials. 2022;280:121238. [31] JIAO X, ZHANG Y, LI W, et al. HIF-1α inhibition attenuates severity of Achilles tendinopathy by blocking NF-κB and MAPK pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;106:108543. [32] JIANG L, LIU T, LYU K, et al. Inflammation-related signaling pathways in tendinopathy. Open Life Sci. 2023;18(1):20220729. [33] HUA T, YANG M, SONG H, et al. Huc-MSCs-derived exosomes attenuate inflammatory pain by regulating microglia pyroptosis and autophagy via the miR-146a-5p/TRAF6 axis. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):324. [34] SUN X, HAO H, HAN Q, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate insulin resistance by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammation in type 2 diabetes rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):241. [35] WU LL, PAN XM, CHEN HH, et al. Repairing and Analgesic Effects of Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation in Mice with Spinal Cord Injury. BioMed Res Int. 2020;2020:10. [36] WU J, CHU CC. Block copolymer of poly(ester amide) and polyesters: synthesis, characterization, and in vitro cellular response. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(12):4314-4323. [37] MD FADILAH NI, MOHD ABDUL KADER JAILANI MS, BADRUL HISHAM MAI, et al. Cell secretomes for wound healing and tissue regeneration: Next generation acellular based tissue engineered products. J Tissue Eng. 2022;13:20417314221114273. [38] FOO JB, LOOI QH, CHONG PP, et al. Comparing the Therapeutic Potential of Stem Cells and their Secretory Products in Regenerative Medicine. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:2616807. [39] ASGHAR W, EL ASSAL R, SHAFIEE H, et al. Engineering cancer microenvironments for in vitro 3-D tumor models. Mater Today. 2015;18(10):539-553. [40] JAYARAMAN P, LIM R, NG J, et al. Acceleration of Translational Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapy Through Consistent Quality GMP Manufacturing. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:648472. [41] ACHILLI TM, MEYER J, MORGAN JR. Advances in the formation, use and understanding of multi-cellular spheroids. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12(10):1347-1360. [42] DONG Z, YUAN Q, HUANG K, et al. Gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA)-based biomaterials for bone regeneration. RSC Adv. 2019;9(31): 17737-17744. [43] KURIAN AG, SINGH RK, PATEL KD, et al. Multifunctional GelMA platforms with nanomaterials for advanced tissue therapeutics. Bioact Mater. 2022;8:267-295. [44] JIANG G, LI S, YU K, et al. A 3D-printed PRP-GelMA hydrogel promotes osteochondral regeneration through M2 macrophage polarization in a rabbit model. Acta Biomater. 2021;128:150-162. [45] LV B, LU L, HU L, et al. Recent advances in GelMA hydrogel transplantation for musculoskeletal disorders and related disease treatment. Theranostics. 2023;13(6):2015-2039. [46] YUE K, TRUJILLO-DE SANTIAGO G, ALVAREZ MM, et al. Synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2015;73:254-271. [47] UNAGOLLA JM, JAYASURIYA AC. Hydrogel-based 3D bioprinting: A comprehensive review on cell-laden hydrogels, bioink formulations, and future perspectives. Appl Mater Today. 2020;18:22. [48] JI S, ALMEIDA E, GUVENDIREN M. 3D bioprinting of complex channels within cell-laden hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2019;95:214-224. [49] SAMADI A, MOAMMERI A, POURMADADI M, et al. Cell Encapsulation and 3D Bioprinting for Therapeutic Cell Transplantation. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(4):1862-1890. |
| [1] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [2] | Li Dijun, Jiu Jingwei, Liu Haifeng, Yan Lei, Li Songyan, Wang Bin. Three-dimensional gelatin microspheres loaded human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for chronic tendinopathy repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1356-1362. |
| [3] | Ge Xiao, Zhao Zhuangzhuang, Guo Shuyu, Xu Rongyao. HOXA10 gene-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7701-7708. |
| [4] | Zheng Yitong, Wang Yongxin, Liu Wen, Amujite, Qin Hu. Action mechanism of intrathecal transplantation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for repair of spinal cord injury under neuroendoscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7743-7751. |
| [5] | Wang Kaigang, Hao Dongsheng, Ma Pei, Zhou Shuo, Li Ruimin. Comparison of efficacy of different biological scaffolds for pulp regeneration therapy in immature permanent teeth: a Bayesian network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7447-7460. |
| [6] | Hu Chaoran, Cen Chaode, Yang Yang, Zhou Cheng, Huang Huaxian, Yuan Honghao, Luo Qin, Cao Yongfei. 3D printing assisted minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis versus intramedullary nail for treatment of AO12-C middle-proximal humeral fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7116-7122. |
| [7] | Wen Huawei, Zhang Qingsong, Tang Ming, Li Yanan, Tan Hongfei, Fang Yushun. Effects of platelet-derived growth factor-DD on proliferation and multilineage differentiation of human tendon-derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6649-6655. |
| [8] | Ren Shutong, Hao Miao, Liu Yue, Hou Ping, Quan Juanhua. Effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells co-culture combined with ginsenoside Rg1 on heart failure cell model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6625-6633. |
| [9] | Bu Xianmin, Liang Di, Zhang Bin, Xu Yingjie, Ding Hao, Wu Bin, Tian Ronghua. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of osteoporotic femoral fractures in SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6634-6641. |
| [10] | Yuan Xiao, Liang Songlin, Xie Yanan, Guan Dongmei, Fan Longyu, Yin Xiaoxuan. Mesenchymal stem cells from different sources in treatment of inflammatory bowel disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6811-6820. |
| [11] | . Non-surgical influencing factors of rotator cuff retear after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5914-5923. |
| [12] | Wei Luxiao, Huang Bingxue, Du Jing, Shi Shuanxia, Wang Jitian, Wang Ling. Therapeutic effects and mechanism of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells combined with melatonin on premature ovarian insufficiency induced by chemotherapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5281-5288. |
| [13] | Tao Chenyue, Chen Shuai, Wang Liping, Meng Defang, Zhou Dongjie, Zhou Luojing. Expression of Rab27A in ovarian tissue of polycystic ovary syndrome model mice treated with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5289-5295. |
| [14] | Feng Yirui, Gao Tianyun, Wang Yaping, Huang Yahong, Wang Bin. Interleukin-10 engineered human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for superior treatment of inflammatory bowel disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4878-4887. |
| [15] | Li Lingyu, Wei Huafeng, Luo Hao, Wang Hao, He Jiahui, Yao Yawei, Lyu Xinghua. Mechanism of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes against mouse renal ischemia/reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2706-2712. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||