Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (31): 6625-6633.doi: 10.12307/2025.556
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells co-culture combined with ginsenoside Rg1 on heart failure cell model
Ren Shutong1, Hao Miao2, Liu Yue3, Hou Ping1, 4, Quan Juanhua5
- 1Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China; 2Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang Fourth People’s Hospital, Shenyang 110031, Liaoning Province, China; 3Traditional Chinese Medicine Teaching and Research Office of Shenyang Medical University, Shenyang 110031, Liaoning Province, China; 4Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China; 5Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2024-07-18Accepted:2024-09-26Online:2025-11-08Published:2025-02-18 -
Contact:Hou Ping, MS, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China; Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Ren Shutong, Doctoral candidate, Attending physician, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81971389 (to QJH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ren Shutong, Hao Miao, Liu Yue, Hou Ping, Quan Juanhua. Effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells co-culture combined with ginsenoside Rg1 on heart failure cell model[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6625-6633.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
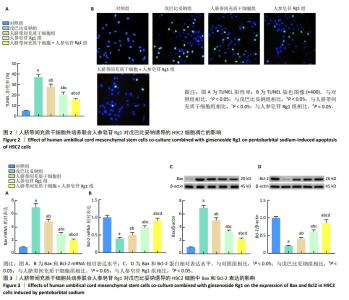
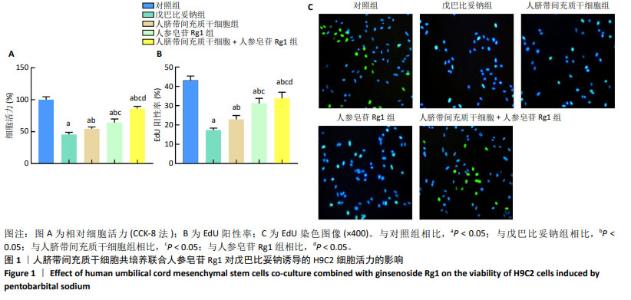
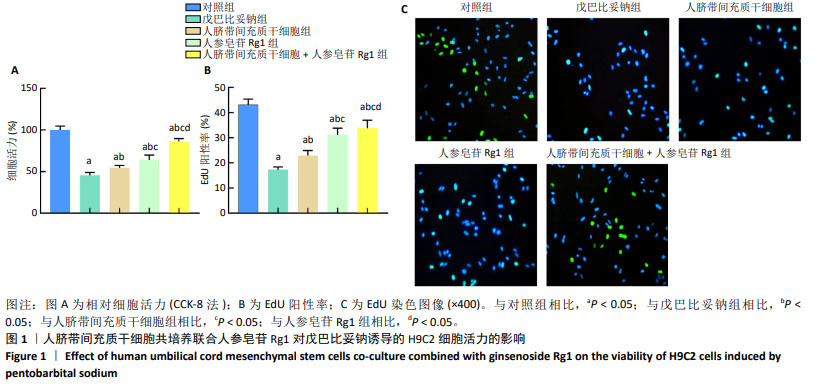
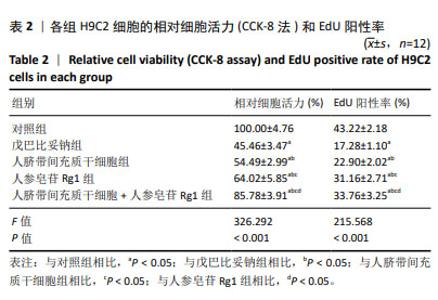
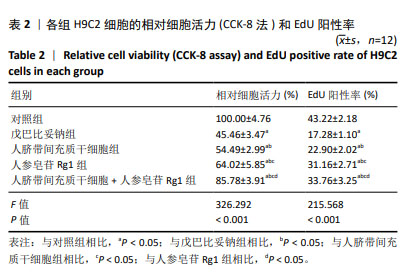
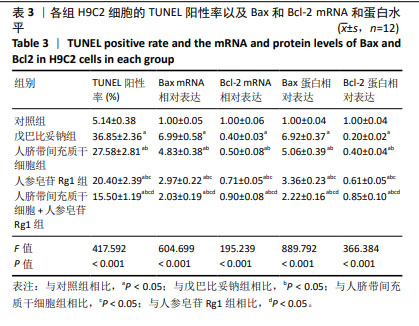
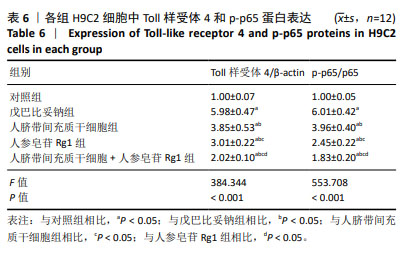
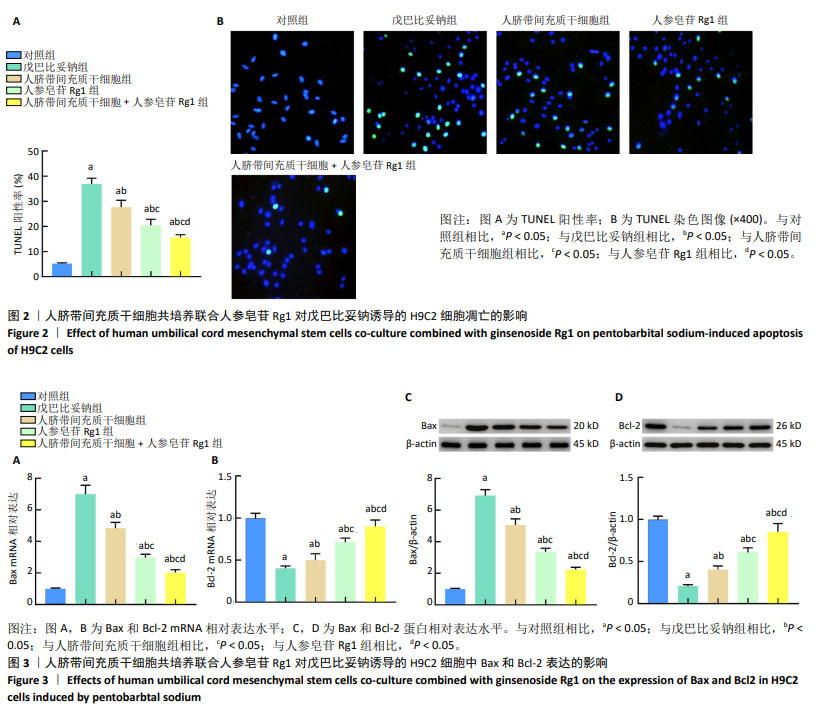
2.2 人脐带间充质干细胞共培养联合人参皂苷Rg1对戊巴比妥钠诱导的H9C2细胞凋亡的影响 与对照组比较,戊巴比妥钠组的TUNEL阳性率以及Bax mRNA和蛋白水平升高,Bcl-2 mRNA和蛋白水平降低(P < 0.05)。与戊巴比妥钠组比较,人脐带间充质干细胞组、人参皂苷Rg1组和人脐带间充质干细胞+人参皂苷Rg1组的TUNEL阳性率以及Bax mRNA和蛋白水平降低,Bcl-2 mRNA和蛋白水平升高(P < 0.05)。与人脐带间充质干细胞组和人参皂苷Rg1组比较,人脐带间充质干细胞+人参皂苷Rg1组的TUNEL阳性率以及Bax mRNA和蛋白水平降低,Bcl-2 mRNA和蛋白水平升高(P < 0.05),见图2,3和表3。"
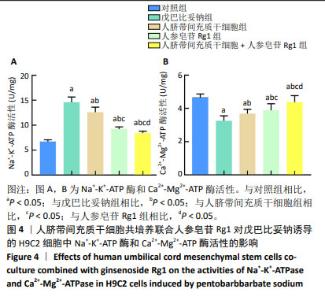
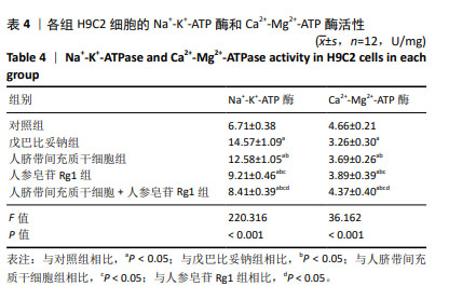
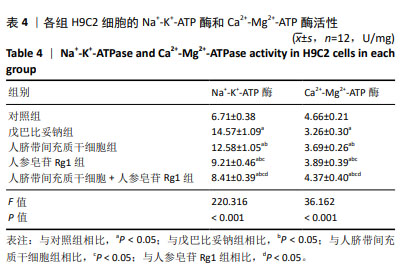
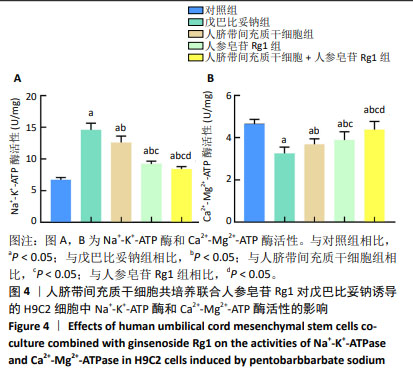
2.3 人脐带间充质干细胞共培养联合人参皂苷Rg1对戊巴比妥钠诱导的H9C2细胞Na+-K+-ATP酶和Ca2+-Mg2+-ATP酶活性的影响 与对照组比较,戊巴比妥钠组的Na+-K+-ATP酶活性升高,Ca2+-Mg2+-ATP酶活性降低(P < 0.05)。与戊巴比妥钠组比较,人脐带间充质干细胞组、人参皂苷Rg1组和人脐带间充质干细胞+人参皂苷Rg1组的Na+-K+-ATP酶活性降低,Ca2+-Mg2+-ATP酶活性升高(P < 0.05)。与人脐带间充质干细胞组和人参皂苷Rg1组比较,人脐带间充质干细胞+人参皂苷Rg1组的Na+-K+-ATP酶活性降低,Ca2+-Mg2+-ATP酶活性升高(P < 0.05),见图4和表4。"
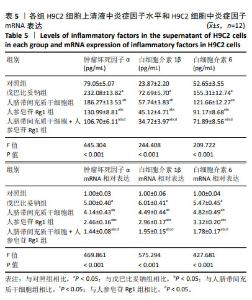
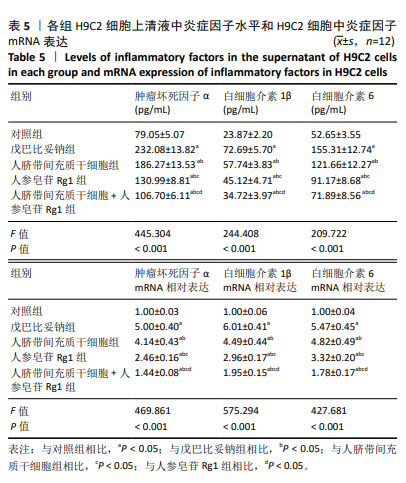
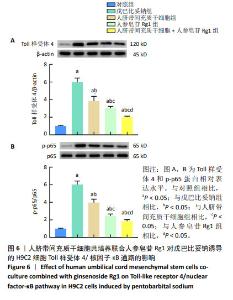
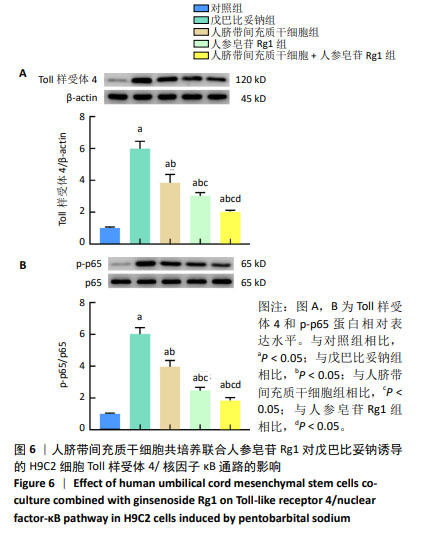
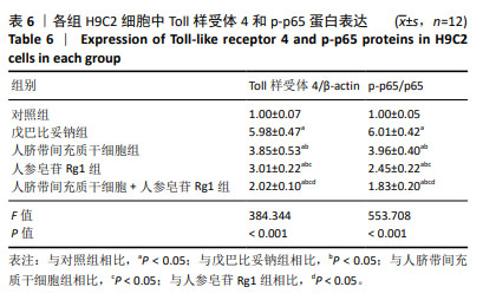
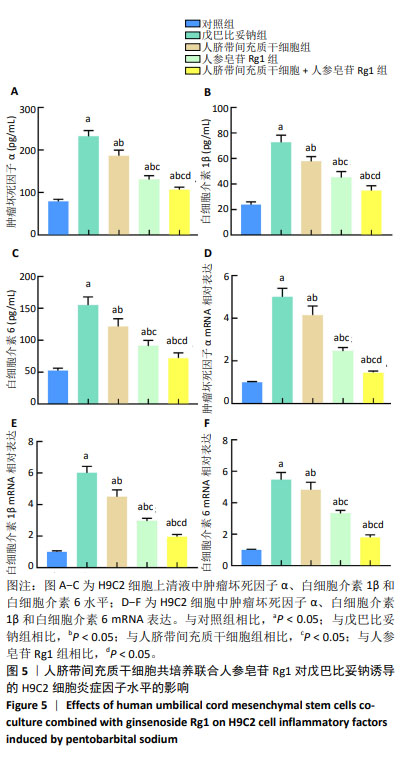
2.4 人脐带间充质干细胞共培养联合人参皂苷Rg1对戊巴比妥钠诱导的H9C2细胞炎症因子水平的影响 与对照组比较,戊巴比妥钠组H9C2细胞上清液中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6水平和H9C2细胞中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6 mRNA表达升高(P < 0.05)。与戊巴比妥钠组比较,人脐带间充质干细胞组、人参皂苷Rg1组和人脐带间充质干细胞+人参皂苷Rg1组H9C2细胞上清液中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6水平和H9C2细胞中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6 mRNA表达降低(P < 0.05)。与人脐带间充质干细胞组和人参皂苷Rg1组比较,人脐带间充质干细胞+人参皂苷Rg1组H9C2细胞上清液中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6水平和H9C2细胞中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6 mRNA表达降低(P < 0.05),见图5和表5。"
| [1] BEAVERS CJ, AMBROSY AP, BUTLER J, et al. Iron Deficiency in Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement from the Heart Failure Society of America. J Card Fail. 2023;29(7):1059-1077. [2] CASTIGLIONE V, AIMO A, VERGARO G, et al. Biomarkers for the diagnosis and management of heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. 2022;27(2): 625-643. [3] GREENE SJ, BAUERSACHS J, BRUGTS JJ, et al. Worsening Heart Failure: Nomenclature, Epidemiology, and Future Directions: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2023;81(4):413-424. [4] KENNELLY P, SAPKOTA R, AZHAR M, et al. Diuretic therapy in congestive heart failure. Acta Cardiol. 2022;77(2):97-104. [5] KUMAR S, PSOTKA MA. Heart failure without a reduced ejection fraction. Am J Manag Care. 2023;29(10 Suppl):S187-S194. [6] MCDONAGH TA, METRA M, ADAMO M, et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: Developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2022;75(6):523. [7] POGLAJEN G, FRLJAK S, ZEMLJIČ G, et al. Stem Cell Therapy for Chronic and Advanced Heart Failure. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2020;17(5):261-270. [8] CASTRO-MANRREZA ME, MONTESINOS JJ. Immunoregulation by mesenchymal stem cells: biological aspects and clinical applications. J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:394917. [9] FAN CG, ZHANG QJ, ZHOU JR. Therapeutic potentials of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human umbilical cord. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2011;7(1):195-207. [10] AREFNEZHAD R, REZAEI-TAZANGI F, ROGHANI-SHAHRAKI H, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: Heralding an effective treatment against esophageal cancer? Cell Biol Int. 2023;47(4): 714-719. [11] CHENG L, WANG S, PENG C, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for psoriasis: a phase 1/2a, single-arm study. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):263. [12] DAI W, YANG H, XU B, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs) alleviate excessive autophagy of ovarian granular cells through VEGFA/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in premature ovarian failure rat model. J Ovarian Res. 2023;16(1):198. [13] FENG H, LIU Q, DENG Z, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate erectile dysfunction in rats with diabetes mellitus through the attenuation of ferroptosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):450. [14] HOANG DM, PHAM PT, BACH TQ, et al. Stem cell-based therapy for human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):272. [15] ABOUZID MR, ALI K, KAMEL I, et al. The Safety and Efficacy of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Patients With Heart Failure and Myocardial Infarction: A Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. Cureus. 2023;15(11):e49645. [16] FAN W, HUANG Y, ZHENG H, et al. Ginsenosides for the treatment of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases: Pharmacology and mechanisms. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;132:110915. [17] SUN Y, LIU Y, CHEN K. Roles and mechanisms of ginsenoside in cardiovascular diseases: progress and perspectives. Sci China Life Sci. 2016;59(3):292-298. [18] CHENG H, LIU J, ZHANG D, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 Alleviates Acute Ulcerative Colitis by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Microbial Tryptophan Metabolism. Front Immunol. 2022;13:817600. [19] GUO J, WANG R, MIN F. Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting ferroptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells. J Leukoc Biol. 2022;112(5):1065-1077. [20] LI J, GAO W, ZHAO Z, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 Reduced Microglial Activation and Mitochondrial Dysfunction to Alleviate Depression-Like Behaviour Via the GAS5/EZH2/SOCS3/NRF2 Axis. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59(5):2855-2873. [21] TIAN G, LI J, ZHOU L. Ginsenoside Rg1 regulates autophagy and endoplasmic reticulum stress via the AMPK/mTOR and PERK/ATF4/CHOP pathways to alleviate alcohol‑induced myocardial injury. Int J Mol Med. 2023;52(1):56. [22] GUAN S, XIN Y, DING Y, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 Protects against Cardiac Remodeling in Heart Failure via SIRT1/PINK1/Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy. Chem Biodivers. 2023;20(2):e202200730. [23] HE F, YU C, LIU T, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 as an Effective Regulator of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Front Pharmacol. 2020;10:1565. [24] NEDKOFF L, WEBER C. Heart failure: not just a disease of the elderly. Heart. 2022;108(4):249-250. [25] PINTO YM. Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction - A Metabolic Disease? N Engl J Med. 2023;389(12):1145-1146. [26] SAVARESE G, BECHER PM, LUND LH, et al. Global burden of heart failure: a comprehensive and updated review of epidemiology. Cardiovasc Res. 2023;118(17):3272-3287. [27] SAVARESE G, STOLFO D, SINAGRA G, et al. Heart failure with mid-range or mildly reduced ejection fraction. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2022;19(2):100-116. [28] TERASHVILI M, BOSNJAK ZJ. Stem Cell Therapies in Cardiovascular Disease. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2019;33(1):209-222. [29] CHEN Y, SHEN H, DING Y, et al. The application of umbilical cord-derived MSCs in cardiovascular diseases. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(17): 8103-8114. [30] RAPOSO L, LOURENÇO AP, NASCIMENTO DS, et al. Human umbilical cord tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells as adjuvant therapy for myocardial infarction: a review of current evidence focusing on pre-clinical large animal models and early human trials. Cytotherapy. 2021;23(11):974-979. [31] YAN Y, JIANG W, TAN Y, et al. hucMSC Exosome-Derived GPX1 Is Required for the Recovery of Hepatic Oxidant Injury. Mol Ther. 2017; 25(2):465-479. [32] LI K, YAN G, HUANG H, et al. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of the extracellular vesicles derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on osteoarthritis via M2 macrophages. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):38. [33] SHAIKH MS, SHAHZAD Z, TASH EA, et al. Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Current Literature and Role in Periodontal Regeneration. Cells. 2022;11(7):1168. [34] UMER A, KHAN N, GREENE DL, et al. The Therapeutic Potential of Human Umbilical Cord Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells for the Treatment of Premature Ovarian Failure. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023;19(3): 651-666. [35] ZHANG C, HUANG L, WANG X, et al. Topical and intravenous administration of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in patients with diabetic foot ulcer and peripheral arterial disease: a phase I pilot study with a 3-year follow-up. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):451. [36] ZHU Z, ZHANG Q, LIU L, et al. Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells’ Cultivation and Treatment of Liver Diseases. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;18(3):286-298. [37] KADIVAR M, KHATAMI S, MORTAZAVI Y, et al. In vitro cardiomyogenic potential of human umbilical vein-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;340(2):639-647. [38] WU Y, ZHANG H, WANG S, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived stem cell sheets improve left ventricular function in rat models of ischemic heart failure. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022;925:174994. [39] LONG J, SUN Y, LIU S, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 treats ischemic stroke by regulating CKLF1/CCR5 axis-induced neuronal cell pyroptosis. Phytomedicine. 2024;123:155238. [40] LU M, ZHAO F, RAN C, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates diabetic vascular endothelial dysfunction by inhibiting the calpain-1/ROS/PKC-β axis. Life Sci. 2023;329:121972. [41] TANG BL, LIU Y, ZHANG JL, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension by inhibiting endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition and inflammation by regulating CCN1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;164:114920. [42] WU Z, HUANG J, BAI X, et al. Ginsenoside-Rg1 mitigates cardiac arrest-induced cognitive damage by modulating neuroinflammation and hippocampal plasticity. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023;938:175431. [43] QIN L, FAN S, JIA R, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 protects cardiomyocytes from hypoxia-induced injury through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Pharmazie. 2018;73(6):349-355. [44] LI Q, XIANG Y, CHEN Y, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 Protects Cardiomyocytes Against Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury via Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling and Inhibition of JNK. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(1):21-37. [45] LU ML, WANG J, SUN Y, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates mechanical stress-induced cardiac injury via calcium sensing receptor-related pathway. J Ginseng Res. 2021;45(6):683-694. [46] BUI TQ, BINH NT, PHAM TL, et al. The Efficacy of Transplanting Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Sheets in the Treatment of Myocardial Infarction in Mice. Biomedicines. 2023;11(8):2187. [47] ZHEN J, BAI J, LIU J, et al. Ginsenoside RG1-induced mesenchymal stem cells alleviate diabetic cardiomyopathy through secreting exosomal circNOTCH1 to promote macrophage M2 polarization. Phytother Res. 2024;38(4):1745-1760. [48] 徐菲飞,彭成,王茁伉,等.参附注射液对戊巴比妥钠致心衰模型心肌细胞膜ATP酶和相关离子的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2013,19(7):196-199. [49] 李硕,苏萍,张广平,等.人参四逆汤及其有效成分对戊巴比妥钠所致心肌细胞损伤模型的保护作用[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2019,25(1):90-95. [50] CHEN P, YUAN M, YAO L, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate liver fibrosis by improving mitochondrial function via Slc25a47-Sirt3 signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;171:116133. [51] SWANSON L, KATKAR GD, TAM J, et al. TLR4 signaling and macrophage inflammatory responses are dampened by GIV/Girdin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(43):26895-26906. [52] ZHAO P, WANG J, HE L, et al. Deficiency in TLR4 signal transduction ameliorates cardiac injury and cardiomyocyte contractile dysfunction during ischemia. J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13(8A):1513-1525. [53] LIU B, DING F, HU D, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium attenuates renal fibrosis by reducing inflammation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):7. [54] LUO M, YAN D, SUN Q, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates cardiomyocyte apoptosis and inflammation via the TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121(4):2994-3004. [55] HUANG Y, YANG H, YANG B, et al. Ginsenoside-Rg1 combined with a conditioned medium from induced neuron-like hUCMSCs alleviated the apoptosis in a cell model of ALS through regulating the NF-κB/Bcl-2 pathway. Chin J Nat Med. 2023;21(7):540-550. |
| [1] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [2] | Li Dijun, Jiu Jingwei, Liu Haifeng, Yan Lei, Li Songyan, Wang Bin. Three-dimensional gelatin microspheres loaded human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for chronic tendinopathy repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1356-1362. |
| [3] | Zheng Yitong, Wang Yongxin, Liu Wen, Amujite, Qin Hu. Action mechanism of intrathecal transplantation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for repair of spinal cord injury under neuroendoscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7743-7751. |
| [4] | Bu Xianmin, Liang Di, Zhang Bin, Xu Yingjie, Ding Hao, Wu Bin, Tian Ronghua. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of osteoporotic femoral fractures in SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6634-6641. |
| [5] | He Changliang, Wang Yan, Luo Ling, Liu Jian. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells thwart pyroptosis of lung tissue cells in septic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6642-6648. |
| [6] | Yu Qinghe, Cai Ziming, Wu Jintao, Ma Pengfei, Zhang Xin, Zhou Longqian, Wang Yakun, Lin Xiaoqin, Lin Wenping. Vanillic acid inhibits inflammatory response and extracellular matrix degradation of endplate chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6391-9397. |
| [7] | Chen Yixin, Lu Yan, Zhang Xuan, Chen Xiaoli, Tan Liangyuan, Xu Zhangjie, Chen Wanglong, Su Shaoting, Liang Jiyao, Zhou Honghai. Mechanism by which Tongan Decoction regulates synovial macrophage polarization in rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5621-5631. |
| [8] | Wei Luxiao, Huang Bingxue, Du Jing, Shi Shuanxia, Wang Jitian, Wang Ling. Therapeutic effects and mechanism of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells combined with melatonin on premature ovarian insufficiency induced by chemotherapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5281-5288. |
| [9] | Tao Chenyue, Chen Shuai, Wang Liping, Meng Defang, Zhou Dongjie, Zhou Luojing. Expression of Rab27A in ovarian tissue of polycystic ovary syndrome model mice treated with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5289-5295. |
| [10] | Feng Yirui, Gao Tianyun, Wang Yaping, Huang Yahong, Wang Bin. Interleukin-10 engineered human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for superior treatment of inflammatory bowel disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4878-4887. |
| [11] | Xu Jie, Jiu Jingwei, Liu Haifeng, Zhao Bin. Bio-3D printed bionic scaffold promotes healing after rotator cuff injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4761-4770. |
| [12] |
Fu Changxi, He Ruibo, Ma Gang, Zhu Zheng, Ma Wenchao.
Effect and mechanism of different training modes on skeletal muscle remodeling in rats with heart failure induced by myocardial infarction
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 221-230.
|
| [13] | Shi Peili, Lin Sen, Zhao Wenteng, Peng Yali, Hu Yazhe. Effects of pressor stimulation at different times on rat skeletal muscle morphology and tumor necrosis factor alpha and nuclear factor kappaB [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3588-3595. |
| [14] | Li Lingyu, Wei Huafeng, Luo Hao, Wang Hao, He Jiahui, Yao Yawei, Lyu Xinghua. Mechanism of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes against mouse renal ischemia/reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2706-2712. |
| [15] | Zhang Wenwen , Xu Mengru , Tian Yuan , Zhang Lifei , Shi Shu , Wang Ning , Yuan Yuan , Wang Li , Hao Haihu. Luteolin improves myocardial cell death induced by serum from rats with spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 38-43. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||