Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (18): 3804-3810.doi: 10.12307/2025.664
Previous Articles Next Articles
Autologous scalp repair of wounds in the medium-thickness skin donor area: safety and effectiveness
Cao Dayong, Zheng Junjie, Wang Lei, Yang Yang, Guo Haina, Xing Peipeng, Xia Chengde, Di Haiping
- Department of Burn, The First People’s Hospital of Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou 450004, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2024-05-10Accepted:2024-07-26Online:2025-06-28Published:2024-11-28 -
Contact:Di Haiping, Chief physician, Department of Burn, The First People’s Hospital of Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou 450004, Henan Province, China -
About author:Cao Dayong, MD candidate, Associate chief physician, Department of Burn, The First People’s Hospital of Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou 450004, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Henan Provincial Medical Science and Technology Tackling Program Joint Co-construction Project, No. LHGJ20200698 (to CDY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cao Dayong, Zheng Junjie, Wang Lei, Yang Yang, Guo Haina, Xing Peipeng, Xia Chengde, Di Haiping. Autologous scalp repair of wounds in the medium-thickness skin donor area: safety and effectiveness[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3804-3810.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
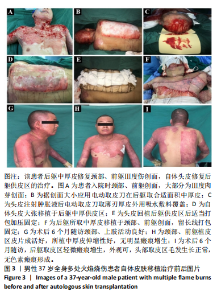
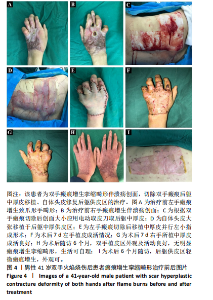
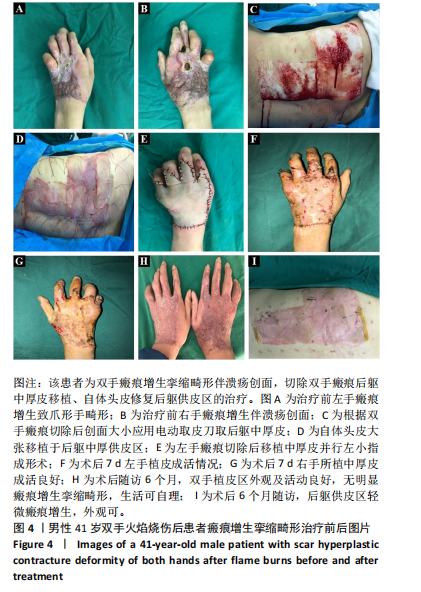
2.7 典型病例 37岁男性患者,全身多处火焰烧伤,烧伤总面积达32%,Ⅲ度伤18%,深Ⅱ度伤14%,外院治疗后转入郑州市第一人民医院,查体:未愈创面主要位于颈部、前躯,面积约8%,Ⅲ度肉芽创面,入院诊断:重度烧伤,火焰烧伤后颈部、前躯肉芽创面。完善术前准备,手术室全麻下行颈部、前躯扩创植皮,后躯、右大腿取中厚皮,头部取皮回植后躯供皮区。术后8 d后躯供皮区创面完全愈合,头部供皮区5 d愈合,不影响毛发生长,植皮区10 d愈合,植皮区及后躯供皮区创面愈合后给予压力衣、功能锻炼等综合康复治疗。术后随访6个月,颈部、前躯植皮区外观、功能良好,无明显瘢痕增生挛缩畸形,后躯头皮移植区皮片接缝处有轻微瘢痕形成,余无明显瘢痕增生,无明显瘙痒等不适症状,头部供皮区毛发生长正常,无色素瘢痕遗留。该患者治疗前后的资料图片,见图3。 41岁男患者,全身多处火焰烧伤后瘢痕增生伴溃疡创面2年余,查体:全身多处烧伤后瘢痕增生,以双手为重,双手背瘢痕增生致屈曲功能受限,呈爪形手,右手背侧可见2个约1 cm×2 cm大小溃疡创面,双手外观及功能受限,生活无法自理。入院诊断:全身多处瘢痕,双手瘢痕增生挛缩畸形伴溃疡创面。完善相关术前准备,手术室全麻下行双手瘢痕及溃疡创面切除松解、后躯取中厚皮,头部取皮回植后躯供皮区。后躯供皮区和双手植皮区打包加压固定,双手植皮区术后7 d拆包换药发现皮片成活良好,后间断换药约15 d植皮区完全愈合。头部供皮区6 d愈合,不影响毛发生长,无色素瘢痕形成,术后7 d后躯供皮区创面完全愈合,双手植皮区小指拔除克氏针后给予压力衣、功能锻炼等综合康复治疗。术后随访6个月,双手植皮区外观及活动良好,无明显瘢痕增生挛缩畸形,生活可自理,后躯中厚取皮区无明显瘢痕增生、瘙痒等不适症状。该患者治疗前后的资料图片,见图4。"
| [1] QI Y, DONG Z, CHU H, et al. Denatured acellular dermal matrix seeded with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for wound healing in mice. Burns. 2019;45(7):1685-1694. [2] 付全有,邢福席,李林,等.人工真皮联合自体瘢痕表皮移植修复大面积烧伤后期关节部位瘢痕畸形[J].中国组织工程研究, 2024,28(10):1533-1539. [3] HENDRIKS T, BOTMAN M, DE HAAS L, et al. Burn scar contracture release surgery effectively improves functional range of motion, disability and quality of life: A pre/post cohort study with longterm follow-up in a Low- and Middle-Income Country. Burns. 2021;47(6): 1285-1294. [4] 高磊,秦新愿,李天博,等.脱细胞同种异体真皮与自体刃厚皮联合移植修复糖尿病足创面[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(14): 2138-2143. [5] CHI Z, LIN D, CHEN Y, et al.Routine closure of the donor site with a second dorsal metacarpal artery flap to avoid the use of a skin graft after harvest of a first dorsal melacarpal artery flap. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2018;71(6):870-875. [6] XIAO H, LIU R, LIU X, et al. Reconstruction of Severe Neck Scar Contracture After Electrical Injury. J Craniofac Surg. 2022;33(1): 203-205. [7] XIA Y, WANG Y, SHAN M, et al. Decoding the molecular landscape of keloids: new insights from single-cell transcriptomics. Burns Trauma. 2023;11:tkad017. [8] LI K, NICOLI F, XI WJ, et al. The 1470 nm diode laser with an intralesional fiber device: a proposed solution for the treatment of inflamed and infected keloids. Burns Trauma. 2019;7:5. [9] ASUKU M, YU TC, YAN Q, et al. Split-thickness skin graft donor-site morbidity: a systematic literature review. Burns. 2021;47(7):1525-1546. [10] 中华医学会烧伤外科学分会, 海峡两岸医药卫生交流协会暨烧创伤组织修复专委会. Ⅱ度烧伤创面治疗专家共识(2024版)Ⅱ:手术治疗和感染防治[J].中华烧伤与创面修复杂志,2024,40(2):101-118. [11] SCHULZ A, ROTHERMUND I, LEFERING R, et al. Long-term scar quality after treatment of standardized partial-thick-ness skin graft donor sites. Adv Skin Wound Care.2018;31(3):109-117. [12] DUANE TM, HUSTON JM, COLLOM M, et al. Surgical Infection Society 2020 updated guidelines on the management of complicated skin and soft tissue infections. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2021;22(4):383-399. [13] 刘继松,宋德恒,赵刚宏,等.新型生物敷料Ⅱ型在二度烧伤创面中的应用[J].中华全科医学,2018,16(5):740-743. [14] HALGAS B, BAY C, FOSTER K. A comparison of injury scoring systems in predicting burn mortality. Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2018;31(2):89-93. [15] BARYZA MJ, BARYZA GA. The Vancouver Scar Scale: an administration tool and its interrater reliability. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1995;16(5): 535-538. [16] LV K, LIU H, XU H, et al. Ablative fractional CO2 laser surgery improving sleep quality, pain and pruritus in adult hypertrophic scar patients: a prospective cohort study. Burns Trauma. 2021;9:tkab023. [17] ABAZARI M, GHAFFARI A, RASHIDZADEH H, et al. A systematic review on classification, identification, and healing process of burn wound healing. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2022;21(1):18-30. [18] ZUBAIR M, AHMAD J. Role of growth factors and cytokines in diabetic foot ulcer healing: A detailed review. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2019;20(2):207-217. [19] ABAZARI M, GHAFFARI A, RASHIDZADEH H, et al. A systematic review on classification, identification, and healing process of burn wound healing. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2022;21(1):18-30. [20] HABIBI S, MOHAMMADI T, HMTSHIRAZI R, et al. A bilayer mupirocin/bupivacaine-loaded wound dressing based on chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) nanofibrous mat: preparation, characterization, and controlled drug release. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;240:124399. [21] HENRY S, MAPULA S, GREVIOUS M, et al. Maximizing wound coverage in full-thickness skin defects: a randomized-controlled trial of autologous skin cell suspension and widely meshed autograft versus standard autografting. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2024;96(1):85-93. [22] CHANG LS, KIM YH, KIM SW. Reconstruction of burn scar contracture deformity of the extremities using thin thoracodorsal artery perforator free flaps. ANZ J Surg. 2021;91(9):E578-E583. [23] 高仪轩,周彪,巴特,等.新型敷料在创面修复中的应用与进展[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2022,17(1):68-71. [24] 马少君,栾文康,刘圣洁,等.银离子敷料覆盖联合负压吸引在慢性难愈性创面修复中的应用效果[J].中国美容医学,2022,31(1):23-26. [25] CHAN RK, ROSE LF, WU JC, et al. Autologous graft thickness affects scar contraction and quality in a porcine excisional wound model. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2015;3(7):e468. [26] YANG J, HUANG Z, TAN J, et al. Copper ion/gallic acid MOFs-laden adhesive pomelo peel sponge effectively treats biofilm-infected skin wounds and improves healing quality. Bioact Mater. 2023;32:260-276. [27] 李顺堂,林源,欧斌贤,等.综合治疗医源性库欣综合征患者感染性创面的效果[J].中华烧伤与创面修复杂志,2022,38(6):512-519. [28] YAMMINE K, ASSI C. A meta-analysis of the outcomes of split-thickness skin graft on diabetic leg and foot ulcers. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2019;18(1):23-30. [29] 王振君,潘孙峰,方高丰,等.老年中厚皮供皮区回植自体刃厚皮疗效观察[J].中华全科医学,2022,20(5):773-776. [30] 李智明,黄远发,方云德,等.背部供皮区在大面积烧伤后期整复中的应用[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2012,8(6):336-337. [31] 孟艳斌,雷晋,张海瑞,等.原位保留打孔断层瘢痕基质联合头皮移植与负压封闭引流治疗烧伤后非功能部位增生性瘢痕的临床效果[J].中华烧伤与创面修复杂志,2022,38(3):251-255. [32] KHALID FA, AHMED OA, JIBRAN RABBANI M, et al. An algorithm for reconstruction of electrical injuries of the scalp. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022;150(3):630e-638e. |
| [1] | Li Kaiying, Wei Xiaoge, Song Fei, Yang Nan, Zhao Zhenning, Wang Yan, Mu Jing, Ma Huisheng. Mechanism of Lijin manipulation regulating scar formation in skeletal muscle injury repair in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1600-1608. |
| [2] | Li Jun, Gong Jingjing, Sun Guobin, Guo Rui, Ding Yang, Qiang Lijuan, Zhang Xiaoli, Fang Zhanhai . miR-27a-3p promotes the proliferation of human hypertrophic scar fibroblasts by regulating mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1609-1617. |
| [3] | Zhang Debao, Wang Peng, Li Kun, Zhang Shaojie, Li Zhijun, Li Shuwen, Wu Yimin. Epidural fibrous scar formation in rabbits following autologous ligamentum flavum intervention [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1168-1175. |
| [4] | Dong Meilin, Du Haiyu, Liu Yuan. Quercetin-loaded carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel promotes wound healing in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 692-699. |
| [5] | Wu Chen, Jiang Jiahui, Su Dou, Liu Chen, Ci Chao. Decellularized skin matrix/polyurethane blended fibrous scaffolds promote repair of skin defects in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 745-751. |
| [6] | Zhang Fei, Zuo Jun. Inhibition of hypertrophic scar in rats by beta-sitosterol-laden mesoporous silica nanoparticles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7301-7309. |
| [7] | Yan Rui, Wang Yiyu, Liu Xue, Jiang Yourong, Cheng Huanzhi, Ma Zhe. Application of exosome-loaded hydrogel in nerve injury regeneration and wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7439-7446. |
| [8] | Zuo Chaoqi, Zhang Zhiqiang, Cao Nan, Guo Xuan, Xie Kai, Wang Haixia, Zhang Guangliang. Application of concentrated growth factor in treatment of chronic wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6971-6978. |
| [9] | Li Kaiying , Wei Xiaoge, Zhao Zhenning , Song Fei, Yang Nan, Wang Yan, Mu Jing, Ma Huisheng . Lijin manipulation alleviates fibrosis of injured skeletal muscle in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(14): 2914-2921. |
| [10] | Lin Li, Jiao Linxi, Yu Fangning, Ma Yichao, Zhang Bo, Xu Xuying. Preclinical study of platelet-rich plasma combined with adipose stem cell transplantation in accelerating wound healing: a systematic evaluation and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2753-2763. |
| [11] | Long Chenyan, Cheng Biao, Tian Ju. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of platelet-rich plasma in promoting wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2793-2801. |
| [12] | Zhao Jiaojun, Tian Wengrong, Bu Panpan, Qi Yusong, Ma Zhiwei, Li Peipei, Ma Shaolin. Expression and regulation of miR-192-5p in hypertrophic scar tissue and fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2500-2506. |
| [13] | Shen Jiangyong, He Xi, Tang Yuting, Wang Jianjun, Liu Jinyi, Chen Yuanyuan, Wang Xinyi, Liu Tong, Sun Haoyuan. RAS-selective lethal small molecule 3 inhibits the fibrosis of pathological scar fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1168-1173. |
| [14] | Zhang Ya, Mu Qiuju, Wang Zilin, Liu Hongjie, Zhu Lili. Hydrogel loaded with platelet-rich plasma promotes wound healing in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 690-696. |
| [15] | Li Yue, Qiao Hua. miRNA derived from mesenchymal stem cells and its derivatives in treatment of pathological scar [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(31): 5042-5047. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||