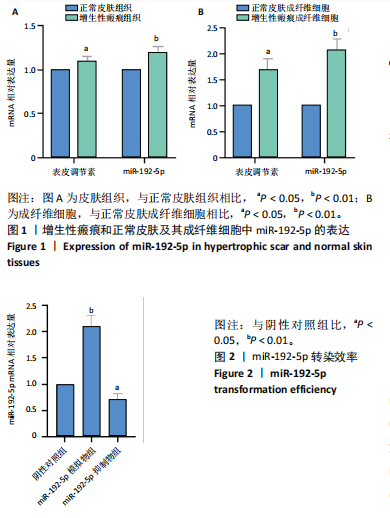
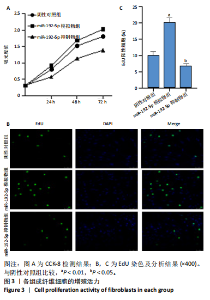
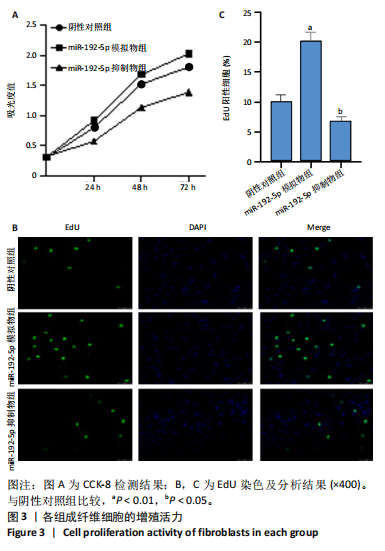
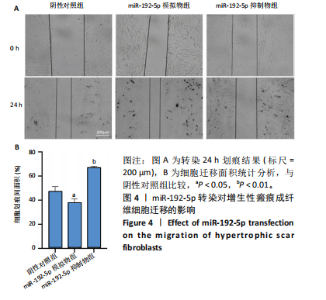
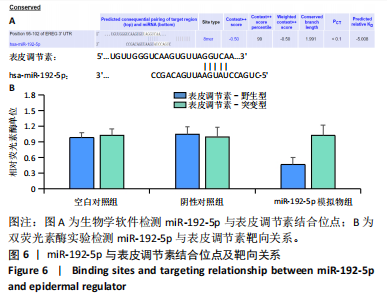
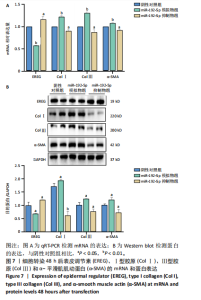
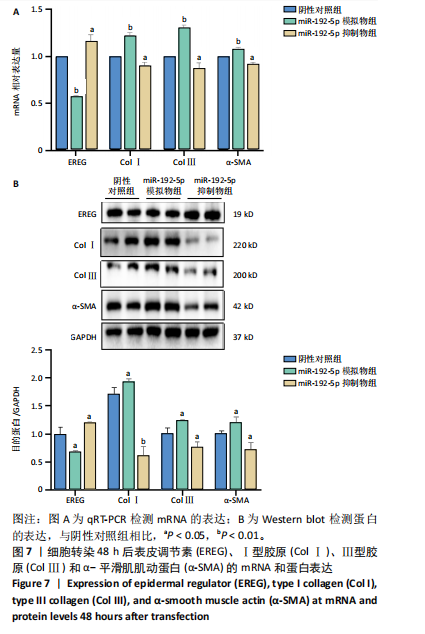
[1] LI Y, ZHANG J, SHI J, et al.Exosomes derived from human adipose mesenchymal stem cells attenuate hypertrophic scar fibrosis by miR-192-5p/IL-17RA/Smad axis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):221.
[2] ZHANG T, WANG XF, WANG ZC, et al.Current potential therapeutic strategies targeting the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway to attenuate keloid and hypertrophic scar formation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020; 129:110287.
[3] MONY MP, HARMON KA, HESS R, et al.An Updated Review of Hypertrophic Scarring.Cells. 2023;12(5):678.
[4] PERRY DM, MCGROUTHER DA, BAYAT A. Current tools for noninvasive objective assessment of skin scars. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;126(3): 912-923.
[5] ZHANG J, LI Y, BAI X, et al.Recent advances in hypertrophic scar. Histol Histopathol. 2018;33(1):27-39.
[6] 杨斌. 增生性瘢痕和瘢痕疙瘩的发病机制与诊治进展[J]. 皮肤性病诊疗学杂志,2023,30(6):481-488.
[7] 黄仲路,胡鹏,梁彦,等. 增生性瘢痕注射治疗所用药物或生物相关制剂的研究[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2023,34(11):680-682,后插4.
[8] PASQUINELLI AE. MicroRNAs and their targets: recognition, regulation and an emerging reciprocal relationship. Nat Rev Genet. 2012;13(4):271-282.
[9] 郭冰玉,姜栋文,回蔷,等. 微小RNA-205在人增生性瘢痕中的表达及作用[J]. 中华烧伤杂志,2021,37(2):180-186.
[10] BERTOLI G, CAVA C, CASTIGLIONI I. MicroRNAs: New Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis, Therapy Prediction and Therapeutic Tools for Breast Cancer. Theranostics. 2015;5(10):1122-1143.
[11] WANG X, HE Y, MACKOWIAK B, et al. MicroRNAs as regulators, biomarkers and therapeutic targets in liver diseases. Gut. 2021;70(4):784-795.
[12] 田文融,左俊,艾江,等. 微小RNA在增生性瘢痕中的作用及其机制研究进展[J]. 中华烧伤与创面修复杂志,2023,39(2):196-200.
[13] VAN ROOIJ E, KAUPPINEN S. Development of microRNA therapeutics is coming of age. EMBO Mol Med. 2014;6(7):851-864.
[14] 李文涛,徐明鹏,黎雨,等. MiRNA在增生性瘢痕和纤维化疾病中的作用研究进展[J]. 内科,2022,17(6):645-649.
[15] ZHU HY, LI C, BAI WD, et al. MicroRNA-21 regulates hTERT via PTEN in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e97114.
[16] JIN M, XU X. MicroRNA-182-5p Inhibits Hypertrophic Scar Formation by Inhibiting the Proliferation and Migration of Fibroblasts via SMAD4 Pathway. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:565-580.
[17] ZHANG Y, QIU F, YE T, et al. Epiregulin increases stemness-associated genes expression and promotes chemoresistance of non-small cell lung cancer via ERK signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):197.
[18] 刘福源,王旭丹,李霄,等. 表皮调节素的生理功能及其在消化系统肿瘤中的研究进展[J]. 中华普通外科杂志,2023,38(4):312-315.
[19] SHIRAKATA Y, KOMURASAKI T, TOYODA H, et al. Epiregulin, a novel member of the epidermal growth factor family, is an autocrine growth factor in normal human keratinocytes. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(8):5748-5753.
[20] AN L, YIN F.MiR-192-5p suppresses M1 macrophage polarization via epiregulin (EREG) downregulation in gouty arthritis. Tissue Cell. 2021; 73:101669.
[21] 艾江. 肉苁蓉苯乙醇总苷对人增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞的干预及机制研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2021.
[22] YAGMUR C, AKAISHI S, OGAWA R, et al. Mechanical receptor-related mechanisms in scar management: a review and hypothesis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;126(2):426-434.
[23] NERI M, RIEZZO I, PASCALE N, et al. Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury following Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Critical Issue for Clinicians and Forensic Pathologists. Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:7018393.
[24] OOSTERHOFF TCH, BEEKMAN VK, VAN DER LIST JP, et al. Laser treatment of specific scar characteristics in hypertrophic scars and keloid: A systematic review. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2021;74(1):48-64.
[25] 牛梓晗,余扬,艾江,等. 沙棘总黄酮干预兔耳增生性瘢痕组织块的消退[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(2):258-263.
[26] PERRY DM, MCGROUTHER DA, BAYAT A. Current tools for noninvasive objective assessment of skin scars. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;126(3):912-923.
[27] LI Y, ZHANG J, ZHANG W, et al. MicroRNA-192 regulates hypertrophic scar fibrosis by targeting SIP1. J Mol Histol. 2017;48(5-6):357-366.
[28] ODELL ID, STEACH H, GAULD SB, et al. Epiregulin is a dendritic cell-derived EGFR ligand that maintains skin and lung fibrosis. Sci Immunol. 2022;7(78):eabq6691.
[29] MORIN F, KAVIAN N, MARUT W, et al. Inhibition of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase by Erlotinib Prevents Sclerodermatous Graft-Versus-Host Disease in a Mouse Model. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135(10):2385-2393.
[30] O’REILLY S.At the crossroads of inflammation and fibrosis: epiregulin. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023;82(6):740-741. |