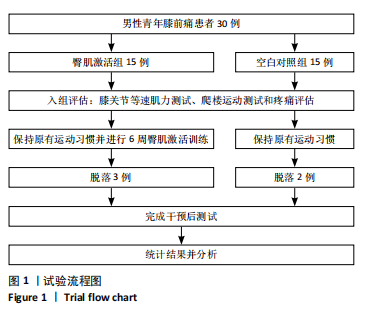
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (18): 3798-3803.doi: 10.12307/2025.656
Previous Articles Next Articles
Gluteal muscle activation exercise therapy improves lower limb muscle strength in young male patients with anterior knee pain
Wu Yue1, 2, Ren Shuang2, Huang Hongshi2, Dai Ruilan1, Ao Yingfang1, 2, Gou Bo3
- 1Tianjin University of Sports, Tianjin 301617, China; 2Institute of Sports Medicine, Peking University Third Hospital; Beijing Key Laboratory of Sports Injuries, Beijing 100191, China; 3Xi’an Physical Education University, Xi’an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2024-06-17Accepted:2024-07-30Online:2025-06-28Published:2024-11-28 -
Contact:Gou Bo, PhD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Xi’an Physical Education University, Xi’an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Wu Yue, Doctoral candidate, Tianjin University of Sports, Tianjin 301617, China Corresponding author: Ao Yingfang, MS, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Tianjin University of Sports, Tianjin 301617, China; Institute of Sports Medicine, Peking University Third Hospital; Beijing Key Laboratory of Sports Injuries, Beijing 100191, China; Xi’an Physical Education University, Xi’an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31900943 (to AYF); the Natural Science Foundation of Beijing, No. 7232354 (to RS); Clinical Key Project of Peking University Third Hospital, No. BYSY2022058 (to RS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Yue, Ren Shuang, Huang Hongshi, Dai Ruilan, Ao Yingfang, Gou Bo. Gluteal muscle activation exercise therapy improves lower limb muscle strength in young male patients with anterior knee pain[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3798-3803.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
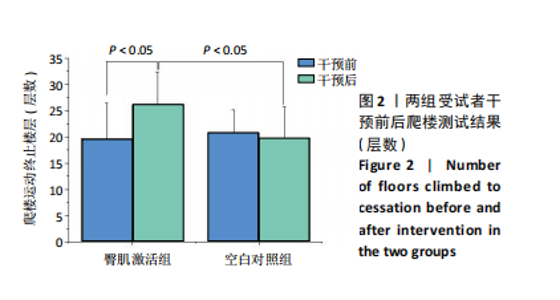
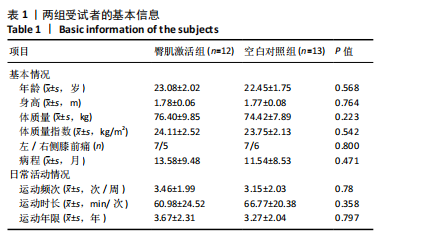
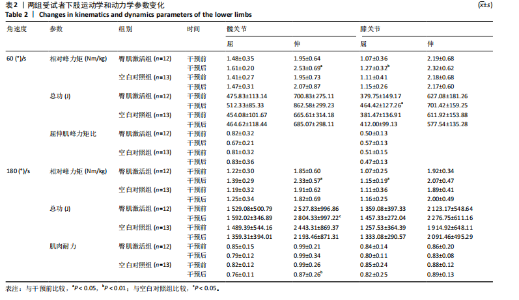
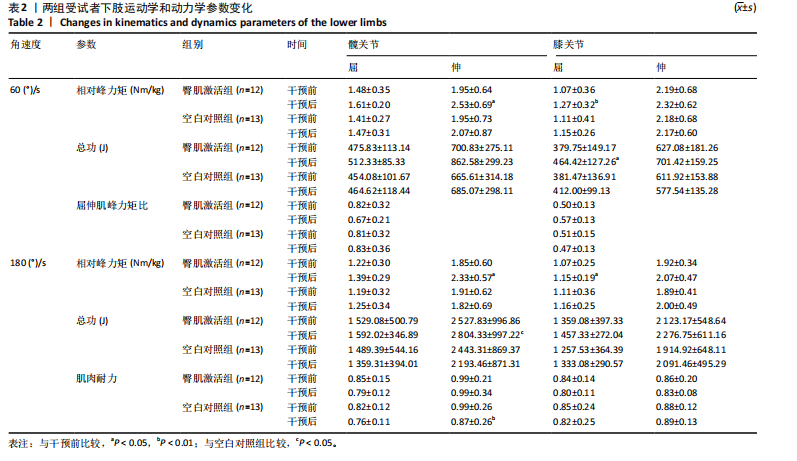
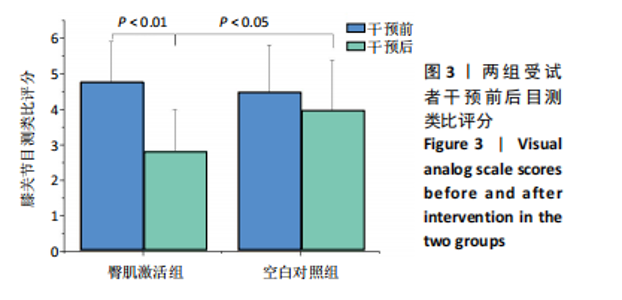
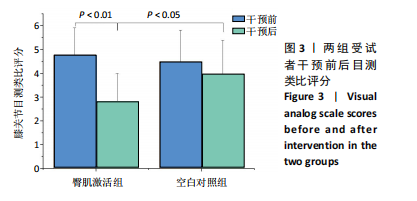
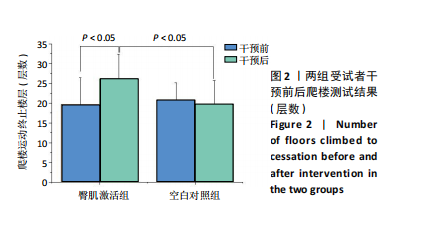
髋后伸肌群总功较空白对照组平均升高(610.87±934.28) J (P=0.024)。 (2)膝关节:①在60 (°)/s角速度时,臀肌激活组膝屈曲肌群的相对峰力矩和总功较干预前分别提高18.69% 和22.29% (P=0.006,P=0.013);②在180 (°)/s角速度时,臀肌激活组膝屈曲肌群相对峰力矩较干预前升高7.47% (P=0.033)。 2.5 干预前后爬楼测试情况 由图2可见,干预前,2组爬楼运动停止时的楼层无显著性差异。干预后,臀肌激活组爬楼层数较空白对照组提高(6.41±6.1)层(P=0.024),臀肌激活组较干预前提高33.11% (P=0.016);空白对照组干预前后无显著性变化(P > 0.05)。"
| [1] CROSSLEY KM, STEFANIK JJ, SELFE J, et al. 2016 Patellofemoral pain consensus statement from the 4th International Patellofemoral Pain Research Retreat, Manchester. Part 1: Terminology, definitions, clinical examination, natural history, patellofemoral osteoarthritis and patient-reported outcome measures. Br J Sports Med. 2016;50(14):839-843. [2] COBURN SL, BARTON CJ, FILBAY SR, et al. Quality of life in individuals with patellofemoral pain: A systematic review including meta-analysis. Phys Ther Sport. 2018;33:96-108. [3] MACLACHLAN LR, COLLINS NJ, HODGES PW, et al. Psychological and pain profiles in persons with patellofemoral pain as the primary symptom. Eur J Pain. 2020;24(6):1182-1196. [4] DUONG V, OO WM, DING C, et al. Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Pain: A Review. JAMA. 2023;330(16):1568-1580. [5] SMITH BE, SELFE J, THACKER D, et al. Incidence and prevalence of patellofemoral pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2018;13(1):e0190892. [6] FERBER R, BOLGLA L, EARL-BOEHM JE, et al. Strengthening of the hip and core versus knee muscles for the treatment of patellofemoral pain: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. J Athl Train. 2015;50(4):366-377. [7] FICK CN, GRANT C, SHEEHAN FT. Patellofemoral Pain in Adolescents: Understanding Patellofemoral Morphology and Its Relationship to Maltracking. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48(2):341-350. [8] BAZETT-JONES DM, NEAL BS, LEGG C, et al. Kinematic and Kinetic Gait Characteristics in People with Patellofemoral Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2023;53(2):519-547. [9] FUKUDA TY, MELO WP, ZAFFALON BM, et al. Hip posterolateral musculature strengthening in sedentary women with patellofemoral pain syndrome: a randomized controlled clinical trial with 1-year follow-up. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2012;42(10):823-830. [10] POWERS CM. The influence of altered lower-extremity kinematics on patellofemoral joint dysfunction: a theoretical perspective. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2003;33(11):639-646. [11] XIE P, ISTVÁN B, LIANG M. The Relationship between Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome and Hip Biomechanics: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Healthcare (Basel). 2022;11(1):99. [12] MARTINELLI N, BERGAMINI AN, BURSSENS A, et al. Does the Foot and Ankle Alignment Impact the Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Clin Med. 2022;11(8):2245. [13] HAMSTRA-WRIGHT KL, AYDEMIR B, EARL-BOEHM J, et al. Lasting Improvement of Patient-Reported Outcomes 6 Months After Patellofemoral Pain Rehabilitation. J Sport Rehabil. 2017;26(4):223-233. [14] 宣磊,吴建贤,潘家武.等速技术在康复医学领域中的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2019,25(7):788-792. [15] COWAN SM, BENNELL KL, CROSSLEY KM, et al. Physical therapy alters recruitment of the vasti in patellofemoral pain syndrome. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2002;34(12):1879-1885. [16] BRITTO P, MUNIZ A, NADAL J. Electromyographic activity of the lower limb in runners with anterior knee pain while running. Res Biomed Eng. 2021; 37(5):135-142. [17] 杨辰,曲峰,刘卉,等.髌股关节痛业余跑者性别特异的下肢生物力学特征[J].医用生物力学,2020,35(6):672-678. [18] BOLGLA LA, MALONE TR, UMBERGER BR, et al. Comparison of hip and knee strength and neuromuscular activity in subjects with and without patellofemoral pain syndrome. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2011;6(4):285-296. [19] MCCLINTON SM, COBIAN DG, HEIDERSCHEIT BC. Physical Therapist Management of Anterior Knee Pain. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2020; 13(6):776-787. [20] 杨雪清,程亮.篮球运动员躯干和下肢等速肌力分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(12):1835-1840. [21] CHENG L, CHANG S, QIAN L, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for isokinetic muscle strength around the knee joint in athletes with patellar tendinopathy. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2019;59(5):822-827. [22] 林长地,程亮,林烯.全身振动训练对老年女性平衡能力和下肢关节肌力的影响[[J]首都体育学院学报,2015,27(6):572-576. [23] MCCORMACK HM, HORNE DJ, SHEATHER S. Clinical applications of visual analogue scales: a critical review. Psychol Med. 1988;18(4):1007-1019. [24] WANG L, YU G, ZHANG R, et al. Positive effects of neuromuscular exercises on pain and active range of motion in idiopathic frozen shoulder: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):50. [25] GARCÍA-PÉREZ-DE-SEVILLA G, SÁNCHEZ-PINTO PINTO B. Effectiveness of physical exercise and neuromuscular electrical stimulation interventions for preventing and treating intensive care unit-acquired weakness: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Intensive Crit Care Nurs. 2023;74:103333. [26] EMERY CA, OWOEYE OBA, RÄISÄNEN AM, et al. The “SHRed Injuries Basketball” Neuromuscular Training Warm-up Program Reduces Ankle and Knee Injury Rates by 36% in Youth Basketball. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2022;52(1):40-48. [27] FARINA D, GANDEVIA S. The neural control of movement: a century of in vivo motor unit recordings is the legacy of Adrian and Bronk. J Physiol. 2024;602(2):281-295. [28] PENG Y, WANG Z. Differential Cortical and Subcortical Activations during Different Stages of Muscle Control: A Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Brain Sci. 2024;14(4):404. [29] ROSTRON ZP, GREEN RA, KINGSLEY M, et al. Associations Between Measures of Physical Activity and Muscle Size and Strength: A Systematic Review. Arch Rehabil Res Clin Transl. 2021;3(2):100124. [30] DUFFEY MJ, MARTIN DF, CANNON DW, et al. Etiologic factors associated with anterior knee pain in distance runners. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2000; 32(11):1825-1832. [31] HIEMSTRA LA, KERSLAKE S, IRVING C. Anterior knee pain in the athlete. Clin Sports Med. 2014;33(3):437-459. [32] COWAN SM, CROSSLEY KM, BENNELL KL. Altered hip and trunk muscle function in individuals with patellofemoral pain. Br J Sports Med. 2009; 43(8):584-588. [33] POHL MB, PATEL C, WILEY JP, et al. Gait biomechanics and hip muscular strength in patients with patellofemoral osteoarthritis. Gait Posture. 2013; 37(3):440-444. [34] WILLSON JD, PETROWITZ I, BUTLER RJ, et al. Male and female gluteal muscle activity and lower extremity kinematics during running. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2012;27(10):1052-1057. [35] JORGE RT, SOUZA MC, CHIARI A, et al. Progressive resistance exercise in women with osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2015;29(3):234-243. [36] BAKER KR, NELSON ME, FELSON DT, et al. The efficacy of home based progressive strength training in older adults with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. J Rheumatol. 2001;28(7):1655-1665. [37] SLED EA, KHOJA L, DELUZIO KJ, et al. Effect of a home program of hip abductor exercises on knee joint loading, strength, function, and pain in people with knee osteoarthritis: a clinical trial. Phys Ther. 2010;90(6):895-904. [38] JEONG J, CHOI DH, SHIN CS. Core Strength Training Can Alter Neuromuscular and Biomechanical Risk Factors for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury. Am J Sports Med. 2021;49(1):183-192. [39] HOTT A, BROX JI, PRIPP AH, et al. Effectiveness of Isolated Hip Exercise, Knee Exercise, or Free Physical Activity for Patellofemoral Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(6):1312-1322. [40] HOTT A, BROX JI, PRIPP AH, et al. Patellofemoral pain: One year results of a randomized trial comparing hip exercise, knee exercise, or free activity. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2020;30(4):741-753. [41] YUENYONGVIWAT V, DUANGMANEE S, IAMTHANAPORN K, et al. Effect of hip abductor strengthening exercises in knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):284. [42] SIGWARD SM, OTA S, POWERS CM. Predictors of frontal plane knee excursion during a drop land in young female soccer players. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2008;38(11):661-667. |
| [1] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [2] | Sun Xiaojun, Wang Huaming, Zhang Dehong, Song Xuewen, Huang Jin, Zhang Chen, Pei Shengtai. Effect of finite element method in treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1897-1904. |
| [3] | Dong Tingting, Chen Tianxin, Li Yan, Zhang Sheng, Zhang Lei. Causal relationship between modifiable factors and joint sports injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1953-1962. |
| [4] | Liang Haobo, Wang Zeyu, Ma Wenlong, Liu Hao, Liu Youwen. Hot issues in the field of joint revision: infection, rehabilitation nursing, bone defect, and prosthesis loosening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1963-1971. |
| [5] | Wang Juan, Wang Guanglan, Zuo Huiwu. Efficacy of exercise therapy in the treatment of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients: #br# a network meta-analysis #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1714-1726. |
| [6] | Ma Haoyu, Qiao Hongchao, Hao Qianqian, Shi Dongbo. Causal effects of different exercise intensities on the risk of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1305-1311. |
| [7] | Li Jiatong, Jin Yue, Liu Runjia, Song Bowen, Zhu Xiaoqian, Li Nianhu . Association between thyroid function levels and phenotypes associated with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1312-1320. |
| [8] | Wu Guangtao, Qin Gang, He Kaiyi, Fan Yidong, Li Weicai, Zhu Baogang, Cao Ying . Causal relationship between immune cells and knee osteoarthritis: a two-sample bi-directional Mendelian randomization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1081-1090. |
| [9] | Zhu Chuanxi, Qiu Long, Li Lingxu, Ji Guangcheng. Chinese herbal prescription combined with head acupuncture exercise therapy improves limb spasticity in rats with ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7571-7577. |
| [10] | Wang Xuepeng, , He Yong, . Effect of insulin-like growth factor family member levels on inflammatory arthritis: a FinnGen biobank-based analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7656-7662. |
| [11] | Chen Jing, Zhang Nan, Meng Qinghua, Bao Chunyu. Material characterization of finite element computational models of knee joints at different ages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7369-7375. |
| [12] | Yan Feng, Zhang Nan, Meng Qinghua, Bao Chunyu, Ye Lixin, Yu Jia. Finite element modeling of knee joint based on semi-automatic segmentation technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7055-7062. |
| [13] | Wang Rongqiang, Yang Liu, Wu Xiangkun, Shang Lilin. Analysis of factors associated with prognosis of osteoporosis patients after hip arthroplasty and construction of Nomogram prediction model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7137-7142. |
| [14] | Abuduainijiang·Abulimiti, Alimu·Mamuti, Li Simi. Artificial femoral head replacement for femoral neck fracture in the elderly: validation of a risk prediction model for hip dysfunction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7143-7149. |
| [15] | Jiang Tao, Zhang Chuankai, Hao Liang, Liu Yong. MAKO robot- and navigation-assisted knee replacement: comparison of lower limb force alignment and prosthesis position accuracy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7150-7157. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||