Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (14): 2907-2913.doi: 10.12307/2025.603
Previous Articles Next Articles
Periodontal stress distribution of maxillary impacted canine under different working conditions: analysis based on three-dimensional finite element method
Wusimanjiang • Yiming, Zulihumaer • Nuer Aihemaiti, Sedireya • Abulimiti, Nigere • Xiermaimaiti, Wang Ling, Gulibaha • Maimaitili
- Department of Stomatology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-04-29Accepted:2024-07-10Online:2025-05-18Published:2024-09-28 -
Contact:Gulibaha • Maimaitili, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Stomatology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wusimanjiang • Yiming, Master candidate, Department of Stomatology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81860194 (to GM); the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Youth Science Foundation, No. 2022D01C275 (to ZNA)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wusimanjiang • Yiming, Zulihumaer • Nuer Aihemaiti, Sedireya • Abulimiti, Nigere • Xiermaimaiti, Wang Ling, Gulibaha • Maimaitili. Periodontal stress distribution of maxillary impacted canine under different working conditions: analysis based on three-dimensional finite element method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(14): 2907-2913.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
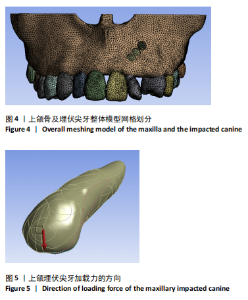
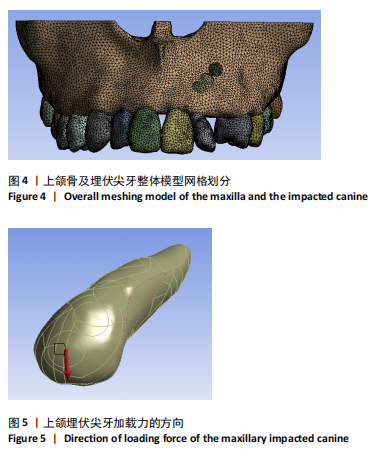
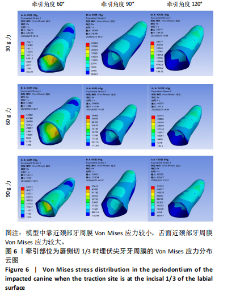
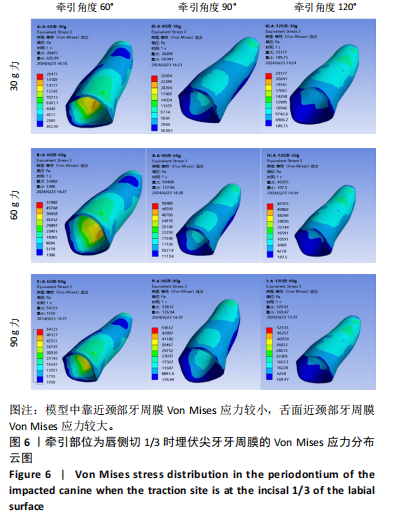
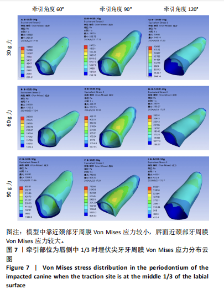
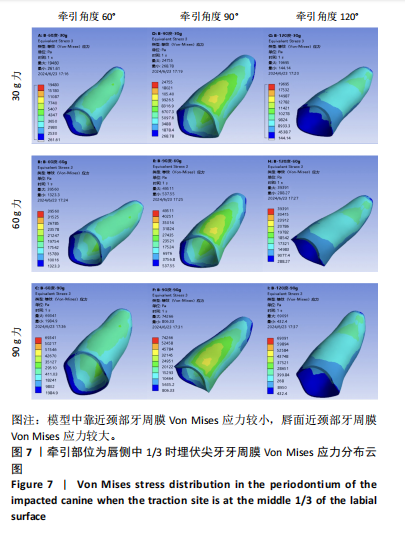
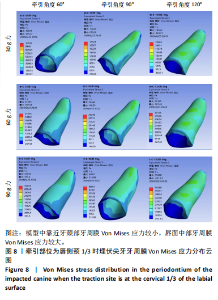
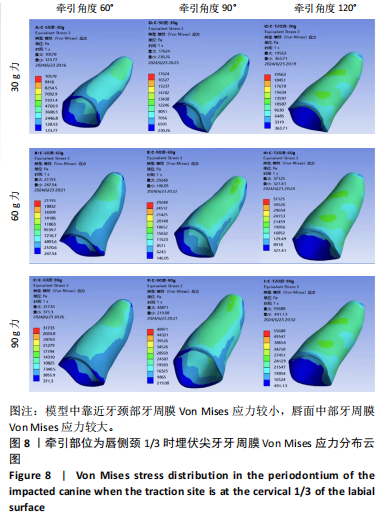
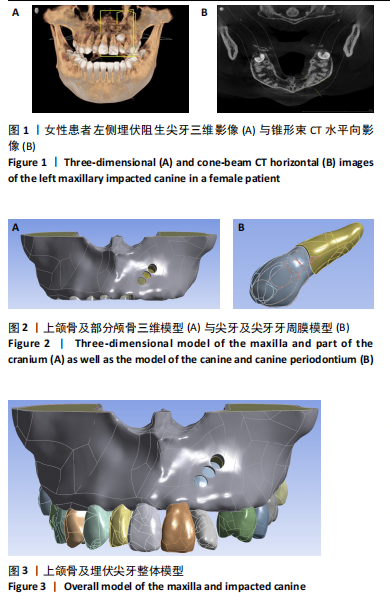
2.1 模型中牙周膜Von Mises应力分布情况 牵引部位为埋伏尖牙唇侧切1/3时,模型中埋伏尖牙牙周膜的Von Mises应力分布云图,见图6。牵引部位为埋伏尖牙唇侧中1/3时,模型中埋伏尖牙牙周膜的Von Mises应力分布云图,见图7。牵引部位为埋伏尖牙唇侧颈1/3时,模型中埋伏尖牙牙周膜Von Mises应力分布云图,见图8。 27种工况下上颌埋伏尖牙牙周膜应力分布特点基本相似,具体表现为:①当在埋伏尖牙切1/3施力时,模型中靠近颈部的区域呈蓝色或淡蓝色,Von Mises应力较小;舌面近颈部区域由黄色逐渐变为红色,说明Von Mises应力值较大。②在埋伏尖牙中1/3施力时,模型中靠近颈部的区域呈蓝色或淡蓝色,说明Von Mises应力较小;唇面近颈部区域由黄色逐渐变为红色,说明Von Mises应力值较大。③在埋伏尖牙颈1/3施力时,模型中靠近牙颈部的区域呈蓝色或淡蓝色,说明Von Mises应力值较小;唇面中部区域颜色逐渐加深,说明Von Mises应力值较大。 2.2 不同工况下上颌埋伏尖牙牙周膜最大和最小Von Mises应力值 见表3。"
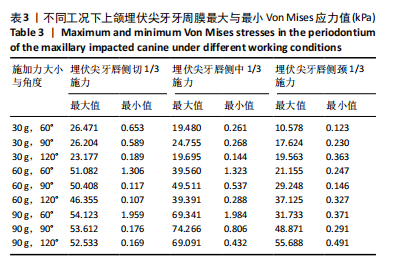
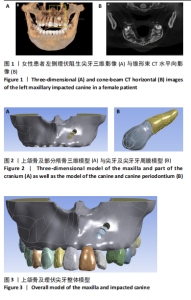
从表3可看出:①当施力部位与施力角度相同时,随着施加力的增大,埋伏尖牙牙周膜最大Von Mises 应力呈不断增加趋势,最小Von Mises应力未呈现明显的递增或递减趋势。②当施加力大小与角度相同时,埋伏尖牙切1/3/、中1/3、颈部1/3的牙周膜最大Von Mises应力呈递减趋势,最小Von Mises应力未呈明显的递增或递减趋势。③在埋伏尖牙切1/3施加相同大小的力时,随着施力角度的增加,牙周膜最大和最小Von Mises应力值均呈减少趋势;在埋伏尖牙中1/3施加相同大小的力时,随着施力角度的增加,牙周膜最大和最小Von Mises应力并未呈逐步增大或逐步减小趋势;在埋伏尖牙颈1/3施加相同大小的力时,随着施力角度的增加,牙周膜最大Von Mises应力呈递增趋势,最小Von Mises应力未呈明显递增或递减趋势。"
| [1] PERALTA-MAMANI M, LÓPEZ-LÓPEZ J, HONÓRIO HM. CBCT vs panoramic radiography in assessment of impacted upper canine and root resorption of the adjacent teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Exp Dent. 2024;16(2):e198. [2] GOH PKT, PULEMOTOV A, NGUYEN H, et al. Treatment duration by morphology and location of impacted maxillary canines: A cone-beam computed tomography investigation. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2024:S0889-5406(24)00148-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2024.04.010. [3] SIMIĆ S, NIKOLIĆ P, STANIŠIĆ ZINDOVIĆ J, et al. Root resorptions on adjacent teeth associated with impacted maxillary canines. Diagnostics. 2022;12(2):380. [4] 钟燕雷,曾祥龙,贾绮林,等.上颌埋伏尖牙阻生的临床分析[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2006,41(8):483-485. [5] ALQERBAN A. Impacted maxillary canine in unilateral cleft lip and palate: A literature review - ScienceDirect. Saudi Dent J. 2019;31(1):84-92. [6] 刘安琪,钱玉芬.上颌尖牙阻生原因及其对周围结构的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2017,26(6):684-688. [7] KUCUKKARACA E. Characteristics of Unilaterally Impacted Maxillary Canines and Effect on Environmental Tissues: A CBCT Study. Children (Basel). 2023;10(10):1694. [8] FEKONJA A. Comparisons of Two Different Treatment Methods for Impacted Maxillary Canines: A Retrospective Study. J Clin Med. 2024; 13(8):2374. [9] 张建航,张晓蓉.上颌尖牙埋伏阻生正畸治疗的研究进展[J].北京口腔医学,2017,25(1):52-54. [10] VIKTORIJA G, DONATA J, KRISTINA K. Diagnostic methods and treatment strategies of impacted maxillary canines: A literature review. Stomatologija. 2019;21(1):3-12. [11] LIU X, CHENG Y, QIN W, et al. Effects of upper-molar distalization using clear aligners in combination with Class II elastics: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1):546. [12] NEVES AM, DO NASCIMENTO MCC, DE ALMEIDA CARDOSO M, et al. Finite element analysis of a newly designed miniplate for orthodontic anchorage in the maxillary anterior region. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2022;162(5):656-667. [13] ELSHAZLY TM, BOURAUEL C, ALDESOKI M, et al. Computer-aided finite element model for biomechanical analysis of orthodontic aligners. Clin Oral Investig. 2023;27(1):115-124. [14] ZHANG Y, HUI S, GUI L, et al. Effects of upper arch expansion using clear aligners on different stride and torque: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. BMC Oral Health. 2023;23(1):891. [15] MAO B, TIAN Y, LI J, et al. Expansion rebound deformation of clear aligners and its biomechanical influence: a three-dimensional morphologic analysis and finite element analysis study. Angle Orthod. 2023;93(5):572-579. [16] 李惠琴,王春娟,王禹,等.无托槽隐形矫治器治疗下颌不同形态扭转牙的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(7):1050-1054. [17] OH S, CHOI YK, KIM YI, et al. The Center of Resistance of an Impacted Maxillary Canine: A Finite Element Analysis. Appl Sci. 2023;13(20): 11256. [18] NG WL, CUNNINGHAM A, PANDIS N, et al. Impacted maxillary canine: Assessment of prevalence, severity and location of root resorption on maxillary incisors: A retrospective CBCT study. Int Orthod. 2024; 22(3):100890. [19] FIRINCIOGLULARI M, KURT D, KORAL S, et al. Maxillary Canine Impaction: Assessing the Influence of Maxillary Anatomy Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography. Med Sci Monit. 2024;30:e944306. [20] YANG JS, CHA JY, LEE JY, et al. Radiographical characteristics and traction duration of impacted maxillary canine requiring surgical exposure and orthodontic traction: a cross-sectional study. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):19183. [21] 金作林.埋伏阻生牙的正畸综合治疗[J].口腔疾病防治,2023,31(5): 305-311. [22] CHAUHAN D, DATANA S, AGARWAL SS, et al. Development of difficulty index for management of impacted maxillary canine: a CBCT-based study. Med J Armed Forces India. 2022;78(1):61-67. [23] DURGEKAR SG. Evaluation of skeletal and dentoalveolar dimensions in patients with maxillary unilateral impacted canine: A cone beam computed tomographic study. Clin Oral Investig. 2023;27(7):4073-4082. [24] ZENO KG, MUSTAPHA S, AYOUB G, et al. Effect of force direction and tooth angulation during traction of palatally impacted canines: A finite element analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2020;157(3):377-384. [25] JIA L, WANG C, WANG C, et al. Efficacy of various multi-layers of orthodontic clear aligners: a simulated study. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2022;25(15):1710-1721. [26] 吴越琳,刘加荣.三维有限元分析在口腔医学领域的研究进展[J].口腔医学,2021,41(7):659-663. [27] ALHASYIMI AA, AYUB A, FARMASYANTI CA. Effectiveness of the Attachment Design and Thickness of Clear Aligners during Orthodontic Anterior Retraction: Finite Element Analysis. Eur J Dent. 2024;18(1):174-181. [28] 唐倩,欧晓丽,方志欣,等.无托槽隐形矫治器扩展上颌牙弓时附件差异对后牙位移的三维有限元分析[J].中国美容医学,2024, 33(6):117-120. [29] 李慧,张栋梁.两种隐形正畸序列磨牙远移的有限元比较[J].医用生物力学,2024,39(2):326-331. [30] SEO JH, EGHAN-ACQUAH E, KIM MS, et al. Comparative analysis of stress in the periodontal ligament and center of rotation in the tooth after orthodontic treatment depending on clear aligner thickness—Finite element analysis study. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(2):324. [31] HEMANTH M, DEOLI S, RAGHUVEER HP, et al. Stress induced in periodontal ligament under orthodontic loading (Part II): a comparison of linear versus non-linear FEM study. J Int Oral Health. 201;7(9): 114-118. [32] 覃思文,韩雪,徐于婵,等.基于三维有限元分析对无托槽隐形矫治器远中移动上颌尖牙的应力变化趋势初探[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2021,14(5):553-559. [33] ZHAO J, SU M, ZHAO Q, et al. 3D Finite Element Study of the Physiological Anchorage Control Concept on Anchorage Molars in Lingual Orthodontics. J Healthc Eng. 2022;2022:1421586. [34] KıRMALı Ö, TÜRKER N, AKAR T, et al. Finite element analysis of stress distribution in autotransplanted molars. J Dent. 2022;119:104082. [35] 孙志涛,孙阳,宋宇.内收力对不同牙槽骨高度后牙影响的三维有限元分析[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2024,38(2):118-122. [36] 林青,邹玉春,许家辉,等.无托槽隐形矫治器用于上颌磨牙组牙扩弓的三维有限元分析[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2022,38(3):353-358. [37] 黄智蕴,李宜宁,李若涵,等.两种加力方式下尖牙远中移动的有限元分析[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2022,38(4):215-218. [38] LEE BW. Relationship between tooth-movement rate and estimated pressure applied. J Dent Res. 1965;44(5):1053. [39] 汤荟文,回记芳,郑文涛,等.不同角度上颌埋伏中切牙牙合向牵引牙周应力分布的分析[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2016,30(1):16-19. [40] 靳淑梅,王媛,任旭升,等.上颌埋伏尖牙及其支持组织三维有限元建模方法的研究[J].上海口腔医学,2010,19(1):95-99. [41] MOUSA MR, HAJEER MY, BURHAN AS, et al. The effectiveness of minimally-invasive corticotomy-assisted orthodontic treatment of palatally impacted canines compared to the traditional traction method in terms of treatment duration, velocity of traction movement and the associated dentoalveolar changes: A randomized controlled trial. F1000Res. 2023;12:699. [42] ALLAREDDY V, CAPLIN J, MARKIEWICZ MR, et al. Orthodontic and surgical considerations for treating impacted teeth. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2020;32(1):15-26. [43] 张建航,张晓蓉.上颌尖牙埋伏阻生正畸治疗的研究进展[J].北京口腔医学,2017,25(1):52-54. [44] CICEK O, GUREL T, DEMIR CICEK B. Investigation of the Relationship of Impacted Maxillary Canines with Orthodontic Malocclusion: A Retrospective Study. Children (Basel). 2023;10(6):950. |
| [1] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [2] | Zhou Zonghao, Luo Siyang, Chen Jiawen, Chen Guangneng, Feng Hongchao. Finite element analysis of bioabsorbable plates versus miniature titanium plates in mandibular fracture fixation in different bone qualities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 818-826. |
| [3] | Chen Yilong, Zhang Xu, Li Hong. Mechanical analysis of fiber post combined with different crown restorations for endodontically treated non-carious cervical lesions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 866-871. |
| [4] | Ye Xiaolong, Zhang Yuxuan, Fu Rongchang, Liu Yun, Yusanjiang·Wuhuer, Escar·Aimer, Ma Yuan. A three-dimensional finite element modal analysis on adolescent idiopathic scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7072-7079. |
| [5] | Zhuang Yan, Wang Xinyu, Cao Yilin, Ding Yuanxin, Wang Jiaqi, Yu Miao, Luan Chunyang, Ding Yuansheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of personalized orthodontic devices for 3D printed maxillary single-rooted rotated tooth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6409-6415. |
| [6] | Zilalai · Julaiti, Mawulanjiang · Abudurenmu, Aikeliya · Ainiwaer, Reyila · Kuerban, Nijiati · Tuersun. Finite element analysis of ultrashort implants applied to the mandibular posterior tooth area under different bone conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4679-4686. |
| [7] | Xia Zhaoxin, Gao Yichen, Deng Yuyao, Wang Xia, Lan Xiaorong, He Yun, Chen Junliang. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of different material implants for replacing single missing anterior tooth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4687-4693. |
| [8] | Fang Wei, Huang Xinghua, Qu Bo, Yang Hongsheng. Effect of differences in vertebral cortical bone reinforcement on biomechanics of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(21): 4430-4438. |
| [9] | Cao Yilin, Wang Xinyu, Zhuang Yan, Wang Yaru Jiang Zhixiu, Liu Danyu, Men Jiuxu, Ding Yuansheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of three-dimensional printed personalized orthodontic appliances for vertical movement of single teeth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3360-3368. |
| [10] | Chen Guangneng, Luo Siyang, Wang Mei, Ye Bin, Chen Jiawen, Liu Yin, Zuo Yuwen, He Xianyu, Shen Jiajin, Ma Minxian. Finite element analysis of various root shield thicknesses in maxillary central incisor socket-shield technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2052-2060. |
| [11] | Ouyang Beiping, Ma Xiangyang, Luo Chunshan, Zou Xiaobao, Lu Tingsheng, Chen Qiling. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new horizontal screw-screw crosslink in posterior atlantoaxial internal fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1320-1324. |
| [12] | Wei Yuanbiao, Lin Zhan, Chen Yanmei, Yang Tenghui, Zhao Xiao, Chen Yangsheng, Zhou Yanhui, Yang Minchao, Huang Feiqi. Finite element analysis of effects of sagittal cervical manipulation on intervertebral disc and facet joints [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 827-832. |
| [13] | Dai Huijuan, Wang Zhaoxin, Baibujiafu·Yelisi, Sun Jiangwei, Gulizainu·Yibulayin, Nijiati·Tuerxun. Biomechanical difference between resin ceramic crown and zirconia all-ceramic crown implant restorations in three occlusal relationships [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 657-663. |
| [14] | Chen Yuanyuan, Wang Wei, Zhao Lu, Annikaer·Aniwaer, Nijati·Turson. Finite element analysis of the influence of scaffold materials on the fixed restoration of edentulous maxillary implants under two designs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 411-418. |
| [15] | Li Xinru, Zhao Wenbo, Ji Yan, Teng Weiwei, Wang Yiming, Zhou Libo. Comparison of initial stability of mandibular first molar repaired with different threaded implants under immediate loading [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(22): 3445-3450. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||